sodium phosphate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


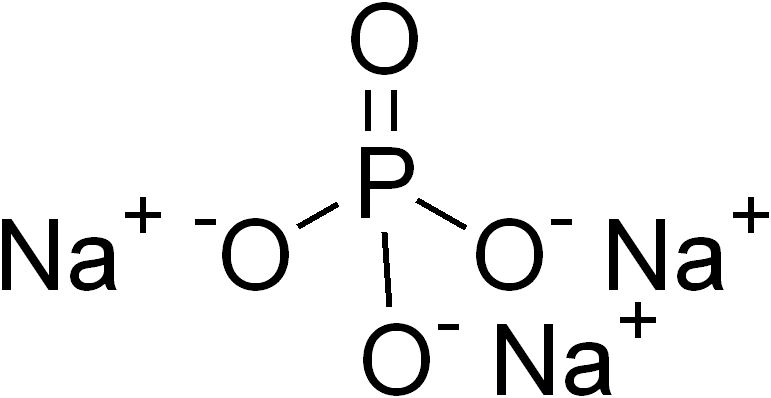 Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms.
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms.


 Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms.
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms.
Uses
Sodium phosphates have many applications in food and for water treatment. For example, sodium phosphates are often used asemulsifier
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Altho ...
s (as in processed cheese), thickening agents, and leavening agents for baked goods. They are also used to control pH of processed foods. They are also used in medicine for constipation and to prepare the bowel for medical procedures. Moreover, they are used in detergents for softening water, and as an efficient anti rust solution.
Adverse effects
Sodium phosphates are popular in commerce in part because they are inexpensive and because they are nontoxic at normal levels of consumption. However, oral sodium phosphates when taken at high doses for bowel preparation forcolonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (''e. ...
may in some individuals carry a risk of kidney injury under the form of phosphate nephropathy
Phosphate nephropathy or nephrocalcinosis is an adverse renal condition that arises with a formation of phosphate crystals within the kidney's tubules. This renal insufficiency is associated with the use of oral sodium phosphate (OSP) such as C.B. ...
. There are several oral phosphate formulations which are prepared extemporaneously. Oral phosphate prep drugs have been withdrawn in the United States, although evidence of causality is equivocal. Since safe and effective replacements for phosphate purgatives are available, several medical authorities have recommended general disuse of oral phosphates.
Monophosphates
Three families of sodium monophosphates are common, those derived from orthophosphate (PO43−), hydrogen phosphate (HPO42−), and dihydrogenphosphate (H2PO4−). Some of the most well known salts are shown in the table.Di- and polyphosphates
In addition to these phosphates, sodium forms a number of useful salts with pyrophosphates (also called diphosphates), triphosphates and high polymers. Of these salts, those of the diphosphates are particularly common commercially. Beyond the diphosphates, sodium salts are known triphosphates, e.g. sodium triphosphate and tetraphosphates. The cyclic polyphosphates, called metaphosphates, include the trimer sodium trimetaphosphate and the tetramer, Na3P3O9 and Na4P4O12, respectively. Polymeric sodium phosphates are formed upon heating mixtures of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4, which induces a condensation reaction. The specific polyphosphate generated depends on the details of the heating and annealing. One derivative is the glassy (i.e., amorphous) Graham's salt. It is a linear polyphosphate the average formula NaO(NaPO3)Na2. Crystalline high molecular weight polyphosphates include Kurrol's salt and Maddrell's salt (CAS#10361-03-2). These species have the formula aPO3sub>n aPO3(OH)sub>2 where n can be as great as 2000. In terms of their structures, these polymers consist of PO3− "monomers", with the chains are terminated by protonated phosphates.References
External links
* * {{Phosphates Phosphates Sodium compounds Edible thickening agents