Snake skull on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A
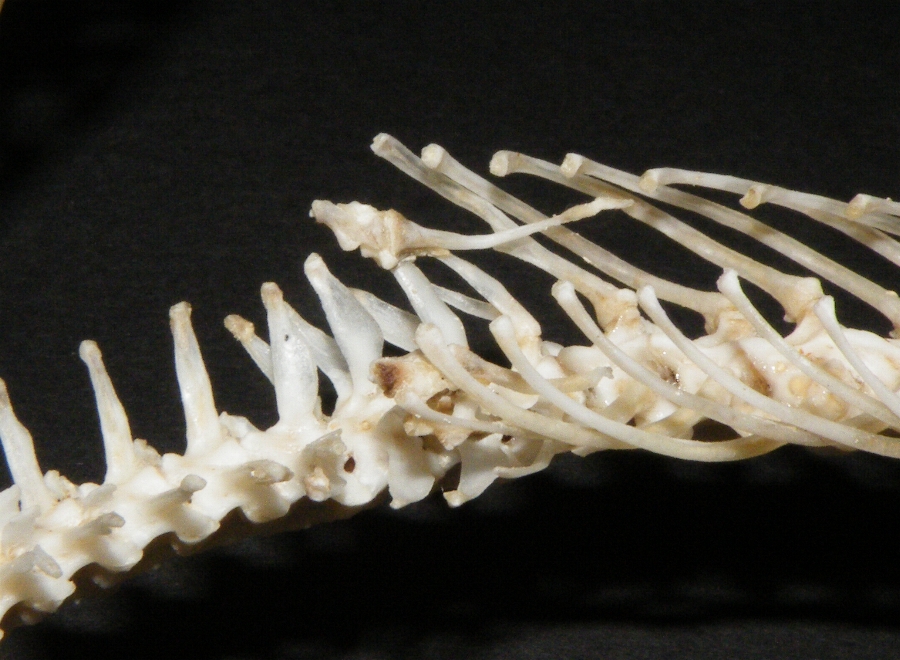 No living snake shows any remains of the pectoral arch, but remains of the
No living snake shows any remains of the pectoral arch, but remains of the
Snake Anatomy
External and Internal snake anatomy with postmortem images. Snake anatomy Skeletons
snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
consists primarily of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, vertebrae
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
, and rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s, with only vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
remnants of the limbs.
Skull
Theskull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
of a snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
is a very complex structure, with numerous joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s to allow the snake to swallow prey far larger than its head.
The typical snake skull has a solidly ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calv ...
, with the separate frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
s and the united parietal bone
The parietal bones ( ) are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint known as a cranial suture, form the sides and roof of the neurocranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four bord ...
s extending downward to the basisphenoid, which is large and extends forward into a rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
** podium
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ...
extending to the ethmoidal region. The nose is less ossified, and the paired nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.
Eac ...
s are often attached only at their base. The occipital condyle
The occipital condyles are undersurface protuberances of the occipital bone in vertebrates, which function in articulation with the superior facets of the Atlas (anatomy), atlas vertebra.
The condyles are oval or reniform (kidney-shaped) in shape ...
is either trilobate and formed by the basioccipital and the exoccipitals, or a simple knob formed by the basioccipital; the supraoccipital is excluded from the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
. The basioccipital may bear a
curved ventral process or hypapophysis in the vipers.
The prefrontal bone
The prefrontal bone is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls. It first evolved in the sarcopterygian clade Rhipidistia, which includes lungfish and the Tetrapodomorpha. The prefrontal is found in most modern and ...
is situated, on each side, between the frontal bone and the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
, and may or may not be in contact with the nasal bone.
The postfrontal bone, usually present, borders the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
behind, rarely also above, and in the pythons a supraorbital bone is intercalated between it and the prefrontal bone.
The premaxillary bone is single and small and as a rule, connected with the maxillary only by ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
.
The paired vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms ...
is narrow.
The palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones (; derived from the Latin ''palatum'') are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.
Stru ...
and pterygoid Pterygoid, from the Greek for 'winglike', may refer to:
* Pterygoid bone, a bone of the palate of many vertebrates
* Pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone
** Lateral pterygoid plate
** Medial pterygoid plate
* Lateral pterygoid muscle
* Medial ...
are long and parallel to the axis of the skull, the latter diverging behind and extending to the quadrate or to the articular extremity of the mandible; the pterygoid is connected with the maxillary by the ectopterygoid or transverse bone, which may be very long, and the maxillary often emits a process towards the palatine, the latter bone being usually produced inwards and upwards towards the anterior extremity of the basisphenoid.
The quadrate is usually large and elongate, and attached to the cranium through the supratemporal (often regarded as the squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestra ...
).
In rare cases, ('' Polemon'') the transverse bone is forked and articulates with the two branches of the maxilla.
The quadrate and maxillary and palatopterygoid arches are more or less movable to allow for the distension required by the passage of prey, often much exceeding the size of the mouth. For the same reason, the rami of the lower jaw, which consist of dentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone ...
, splenial
The splenial is a small bone in the lower jaw of reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology ...
, angular, and articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two o ...
elements, with the addition of a coronoid in the boas and a few other small families, are connected at the symphysis
A symphysis (, : symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint.
# A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint.
# A growing together o ...
by a very extensible elastic ligament.
The hyoid apparatus is reduced to a pair of cartilaginous filaments situated below the trachea, and united in front.
There are various modifications according to the genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
. A large hole may be present between the frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
s and the basisphenoid (''Psammophis
''Psammophis'' is a genus of snakes in the family Psammophiidae. The genus comprises 33 species, which are found in Africa and Asia.. www.reptile-database.org. ''Psammophis'' are diurnal and prey on lizards and rodents which they actively hunt. ...
'', '' Coelopeltis''); the maxillary may be much abbreviated and movable vertically, as in the Viperidae
Vipers are snakes in the family Viperidae, found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, New Zealand, Ireland, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous snake, venomous and have long (relat ...
; the pterygoids may taper and converge posteriorly, without any connection with the quadrate, as in the Amblycephalidae; the supratemporal may be much reduced, and wedged in between the adjacent bones of the cranium
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
; the quadrate may be short or extremely large; the prefrontals may join in a median suture in front of the frontals; the dentary may be freely movable, and detached from the articular posteriorly.
The deviation from the normal type is much greater still when we consider the degraded wormlike members of the families Typhlopidae
The Typhlopidae are a family of blind snakes. They are found mostly in the tropical regions of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and all mainland Australia and various islands. The rostral scale overhangs the mouth to form a shovel-like burrowing str ...
and Glauconiidae, in which the skull is very compact and the maxillary much reduced. In the former this bone is loosely attached to the lower aspect of the cranium; in the latter, it borders the mouth and is suturally joined to the premaxillary and the prefrontal. Both the transverse bone and the supratemporal are absent, but the coronoid element is present in the mandible.
Joints of the snake skull
*Red A: thejoint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
between the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
and quadrate. It is analogous
Analogy is a comparison or correspondence between two things (or two groups of things) because of a third element that they are considered to share.
In logic, it is an inference or an argument from one particular to another particular, as oppose ...
to the joint in mammalian jaws.
*Red B: the joint between the quadrate and the supratemporal The supratemporal bone is a paired Skull, cranial bone present in many Tetrapod, tetrapods and Tetrapodomorpha, tetrapodomorph fish. It is part of the temporal region (the portion of the skull roof behind the eyes), usually lying medial (inwards) re ...
. It is highly mobile in most directions, allowing a wider gape (i.e., the snake can open its mouth wider) and greater jaw flexibility.
*Red C: the joint between the prefrontal and maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
. It allows the maxilla to pivot in the plane of the photograph, and while it does not increase gape, it does facilitate the complex action by which the snake draws prey into its mouth.
*Green A: the joint between the frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
and nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.
Eac ...
. It allows the nose
A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the ...
to upturn slightly, increasing gape and assisting in swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mou ...
.
*Green B: allows the lower jaws to bow outwards, further increasing the gape.
*Blue: the joint between the supratemporal and parietal. Immobile, except for '' Dasypeltis''.
Snake dentition
In mostsnake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s, teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
are located on the dentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone ...
of the lower jaw
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
, the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
, the palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones (; derived from the Latin ''palatum'') are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.
Stru ...
and the lateral pterygoid plate
The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid (from Greek ''pteryx'', ''pterygos'', "wing"), one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.
Each process consists of a me ...
. The latter form an "inner row" of teeth that can move separately from the rest of the jaws and are used to help "walk" the jaws over prey. Several snake lineages have evolved venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
which is typically delivered by specialized teeth called fang
A fang is a long, pointed tooth. In mammals, a fang is a modified maxillary tooth, used for biting and tearing flesh. In snakes, it is a specialized tooth that is associated with a venom gland (see snake venom). Spiders also have external fangs, ...
s located on the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
.
Most snakes can be placed into one of four groups, based on their teeth, which correlate strongly with venom and lineage.
Aglyph
Aglyphous snakes (''lacking grooves'') have no specialized teeth; each tooth is similar in shape and often size. When teeth vary in size, as in some bird eaters, they do not vary in shape. Most aglyphous snakes are non-venomous; some, like '' Thamnophis'', are considered mildly venomous. The feature is not asynapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel Phenotypic trait, character or character state that has evolution, evolved from its ancestral form (or Plesiomorphy and symplesiomorphy, plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy sh ...
.
Opisthoglyph
Opisthoglyphous ("rearward grooves") snakes possess venom injected by a pair of enlarged teeth at the back of the maxillae, which normally angle backward and are grooved to channel venom into the puncture. Since these fangs are not located at the front of the mouth, this arrangement is vernacularly called "rear-fanged". In order to envenomate prey, an opisthoglyphous snake must move the prey into the rear of its mouth and then penetrate it with its fangs, presenting difficulties with large prey although they can quickly move smaller prey into position. The opisthoglyphous dentition appears at least two times in the history of snakes. The venom of some opisthoglyphous snakes is strong enough to harm humans; notably,herpetologist
Herpetology (from Ancient Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is a branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, salamanders, and caecilians (Gymnophiona)) and reptiles (in ...
s Karl Schmidt and Robert Mertens
Robert Friedrich Wilhelm Mertens (1 December 1894 – 23 August 1975) was a German herpetologist. Several taxa of reptiles are named after him.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore ...
were killed by a boomslang and a twig snake, respectively, after each underestimated the effects of the bite and failed to seek medical help. Opisthoglyphous snakes are found mostly in the families Colubridae
Colubridae (, commonly known as colubrids , from , 'snake') is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest fossil species of the family date back to the Late Eocene epoch, with earlier origins suspected. C ...
and Homalopsidae
The Homalopsidae are a family of snakes which contains about 30 genus, genera and more than 50 species. They are commonly known as Indo-Australian water snakes, mudsnakes, or bockadams. They are also known as (lit. "water snake") in Indonesian. ...
.
Proteroglyph
Proteroglyphous snakes (''forward grooved'') have shortened maxillae bearing few teeth except for a substantially enlarged fang pointing downwards and completely folded around the venom channel, forming a hollow needle. Because the fangs are only a fraction of an inch long in even the largest species, these snakes must hang on, at least momentarily, as they inject their venom. Somespitting cobra
A "spitting" cobra is any of several species of cobra that can intentionally, defensively shoot their snake venom, venom directly from their fangs. This substance has two functions, with the first being as venom that can be absorbed via the vict ...
s have modified fang tips allowing them to spray venom at an attacker's eyes. This form of dentition is unique to elapids.
Solenoglyph
Solenoglyphous snakes (''pipe grooved'') have the most advanced venom delivery method of any snake. Each maxilla is reduced to a nub supporting a single hollow fang tooth. The fangs, which can be as long as half the length of the head, are folded against the roof of the mouth, pointing posteriorly. The skull has a series of interacting elements that ensure that the fangs rotate into biting position when the jaws open. Solenoglyphous snakes open their mouths almost 180 degrees, and the fangs swing into a position to allow them to penetrate deep into the prey. While solenoglyph venom is typically less toxic than that of proteroglyphs, this system allows them to deeply inject large quantities of venom. This form of dentition is unique toviper
Vipers are snakes in the family Viperidae, found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, New Zealand, Ireland, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipe ...
s.
Exceptions
A few snakes do not conform to these categories. '' Atractaspis'' is solenoglyphous but the fangs swing out sideways, allowing it to strike without opening its mouth, perhaps allowing it to hunt in small tunnels. Scolecophidia (blind burrowing snakes) typically have few teeth, often only in the upper or lower jaw.Informal or popular terminology
Common names for the various types of snake dentition originate largely from older literature, but still are encountered in informal publications. Aglyphous snakes are commonly called fangless; opisthoglyphous snakes rear-fanged or back-fanged; and both proteroglyphous and solenoglyphous snakes are referred to as front-fanged.Rose, Walter; The reptiles and amphibians of southern Africa; Pub: Maskew Miller, 1950Engelmann, Wolf-Eberhard. Snakes (No. 05352). Publisher Bookthrift 1982.Taxonomic key of skull modifications
Modifications of the skull in the European genera: *I. Quadrate articulating with the cranium, supratemporal absent; mandible much shorter than the skull, with coronoid bone; maxillary small, on lower aspect of cranium; pterygoids not extending to quadrate; nasals forming long sutures with the premaxillary, prefrontals, and frontal: '' Typhlops''. *II. Quadrate suspended from the supratemporal; mandible at least as long as the skull; pterygoids extending to quadrate or mandible. :*A. Mandible with coronoid bone; nasals in sutural contact with frontals and prefrontals; transverse bone short, not projecting much beyond cranium; maxillary not half as long as mandible, which is not longer than skull (to occiput): '' Eryx''. :*B. No coronoid bone; nasals isolated. ::*1. Maxillary elongate, not movable vertically. :::*a. Maxillary half as long as mandible. ::::*Supratemporal half as long as skull, projecting far beyond cranium; mandible much longer than skull: '' Tropidonotus''. ::::*Supratemporal not half as long as skull, projecting far beyond cranium; mandible much longer than skull: '' Zamenis''. ::::*Supratemporal not half as long as skull, projecting but slightly beyond cranium; mandible much longer than skull: '' Coluber''. ::::*Supratemporal not half as long as skull, not projecting beyond cranium; mandible not longer than skull: '' Coronella, Contia''. :::*b. Maxillary not half as long as mandible, which is longer than skull; supratemporal not half as long as skull, projecting beyond cranium. ::::*Quadrate longer than supratemporal; maxillary much longer than quadrate, nearly straight in front of prefrontal; a large vacuity between the frontal bones and the basisphenoid: '' Coelopeltis''. ::::*Quadrate not longer than supratemporal; maxillary little longer than quadrate, strongly curved in front of prefrontal:'' Macroprotodon'' ::::*Quadrate longer than supratemporal; maxillary little longer than quadrate, nearly straight in front of prefrontal: '' Tarbophis'' ::*2. Maxillary much abbreviated and erectile; supratemporal not half as long as skull; mandible much longer than skull; basioccipital with a strong process. :::*Maxillary bone solid: ''Vipera
''Vipera'' (; commonly known as the palaearctic vipers Spawls S, Branch B (1995). ''The Dangerous Snakes of Africa: Natural History, Species Directory, Venoms and Snakebite''. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books / Dubai: Oriental Press. ...
''.
:::*Maxillary bone hollow: '' Ancistrodon''.
:::*The vertebrae number 130 to 500 - in the European forms 147 ('' Vipera ursinii'') to 330 ('' Coluber leopardinus'').
Vertebrae and ribs
A snake has from 175 to more than 400 vertebrae in its backbone. The means by which vertebrae are secured are twofold: either a ball and socket joint, or zygopophyses, which stick out from each vertebra to poke rear-pointing projections from the vertebrae ahead of it. This results in a spine well-adapted to the snake's method of movement. Thevertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
consists of an atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
(composed of two vertebrae) without rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s; numerous precaudal vertebrae, all of which, except the first or first three, bear long, movable, curved ribs with a small posterior tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
at the base, the last of these ribs sometimes forked; two to ten so-called lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
without ribs, but with bifurcate transverse processes
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
(lymphapophyses) enclosing the lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
s; and a number of ribless caudal vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx.
In many reptiles, some of the caud ...
with simple transverse processes. When bifid, the ribs or transverse processes have the branches regularly superposed.
The centra
Centra is a convenience shop chain that operates throughout Ireland. The chain operates as a symbol group owned by Musgrave Group, the food wholesaler, meaning the individual shops are all owned by individual franchisees.
The chain has three ...
have the usual ball and socket joint
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of ...
, with the nearly hemispherical or transversely elliptic condyle
A condyle (;Entry "condyle"
in
at the back ( procoelous vertebrae), while the in
neural arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
is provided with additional articular surfaces in the form of pre- and post- zygapophyses, broad, flattened, and overlapping, and of a pair of anterior wedge-shaped processes called zygosphene, fitting into a pair of corresponding concavities, zygantrum, just below the base of the neural spine. Thus the vertebrae of snakes articulate with each other by eight joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s in addition to the cup-and-ball on the centrum, and interlock by parts reciprocally receiving and entering one another, like the mortise and tenon
A mortise and tenon (occasionally mortice and tenon) is a Woodworking joints, joint that connects two pieces of wood or other material. Woodworking, Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly ...
joints. The precaudal vertebrae have a more or less high neural spine which, as a rare exception (Xenopholis
''Xenopholis'' is a genus of rear-fanged snakes of the family Colubridae.
Geographic range
The genus ''Xenopholis'' is endemic to South America.
Description
The genus ''Xenopholis'' is characterized by distinctive vertebrae. The spinous proce ...
), may be expanded and plate-like above, and short or moderately long transverse processes to which the ribs are attached by a single facet. The centra of the anterior vertebrae emit more or less developed descending processes, or haemapophyses, which are sometimes continued throughout, as in '' Tropidonotus'', ''Vipera
''Vipera'' (; commonly known as the palaearctic vipers Spawls S, Branch B (1995). ''The Dangerous Snakes of Africa: Natural History, Species Directory, Venoms and Snakebite''. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books / Dubai: Oriental Press. ...
'', and '' Ancistrodon'', among Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an genera.
In the caudal region, elongate transverse processes take the place of ribs, and the haemapophyses are paired, one on each side of the haemal canal. In the rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genus, genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting sm ...
s the seven or eight last vertebrae are enlarged and fused into one.
Vestigial limbs
 No living snake shows any remains of the pectoral arch, but remains of the
No living snake shows any remains of the pectoral arch, but remains of the pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
are found in:
* Boas and Pythons: a long ilium, attached to the lower branch of the first bifurcate transverse process of the lumbar vertebrae, bearing three short bones, the longest of which, regarded as the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
, terminates in a claw-like pelvic spur
Pelvic spurs (also known as vestigial legs) are external protrusions found around the cloaca in certain superfamilies of snakes belonging to the greater infraorder ''Alethinophidia''.Pough, F. H. (Ed.). (2004). ''Herpetology'' (3rd ed). Prentice ...
which usually appears externally on each side of the cloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilagin ...
.
*Leptotyphlopidae
The Leptotyphlopidae (commonly called slender blind snakes or thread snakes) are a family of small snakes found in North America, South America, Africa and Asia. All are fossorial and adapted to burrowing, feeding on ants and termites. Two subfa ...
: ilium, pubis, and ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
, and rudimentary femur, the ischium forming a ventral symphysis
A symphysis (, : symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint.
# A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint.
# A growing together o ...
.
*Aniliidae
The Aniliidae are a monotypic family created for the monotypic genus ''Anilius'' that contains the single species ''Anilius scytale''. Common names include the American pipe snake and false coral snake. It is found in South America. This snake po ...
*Typhlopidae
The Typhlopidae are a family of blind snakes. They are found mostly in the tropical regions of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and all mainland Australia and various islands. The rostral scale overhangs the mouth to form a shovel-like burrowing str ...
: a single bone on each side.
References
*George Albert Boulenger
George Albert Boulenger (19 October 1858 – 23 November 1937) was a Belgian-British zoologist who described and gave scientific names to over 2,000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles, and amphibians. Boulenger was also an active botani ...
. '' The Snakes Of Europe'', 2nd edition. London: Methuen & Co., Ltd., 1913.
{{Reflist
External links
Snake Anatomy
External and Internal snake anatomy with postmortem images. Snake anatomy Skeletons