Smart label on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
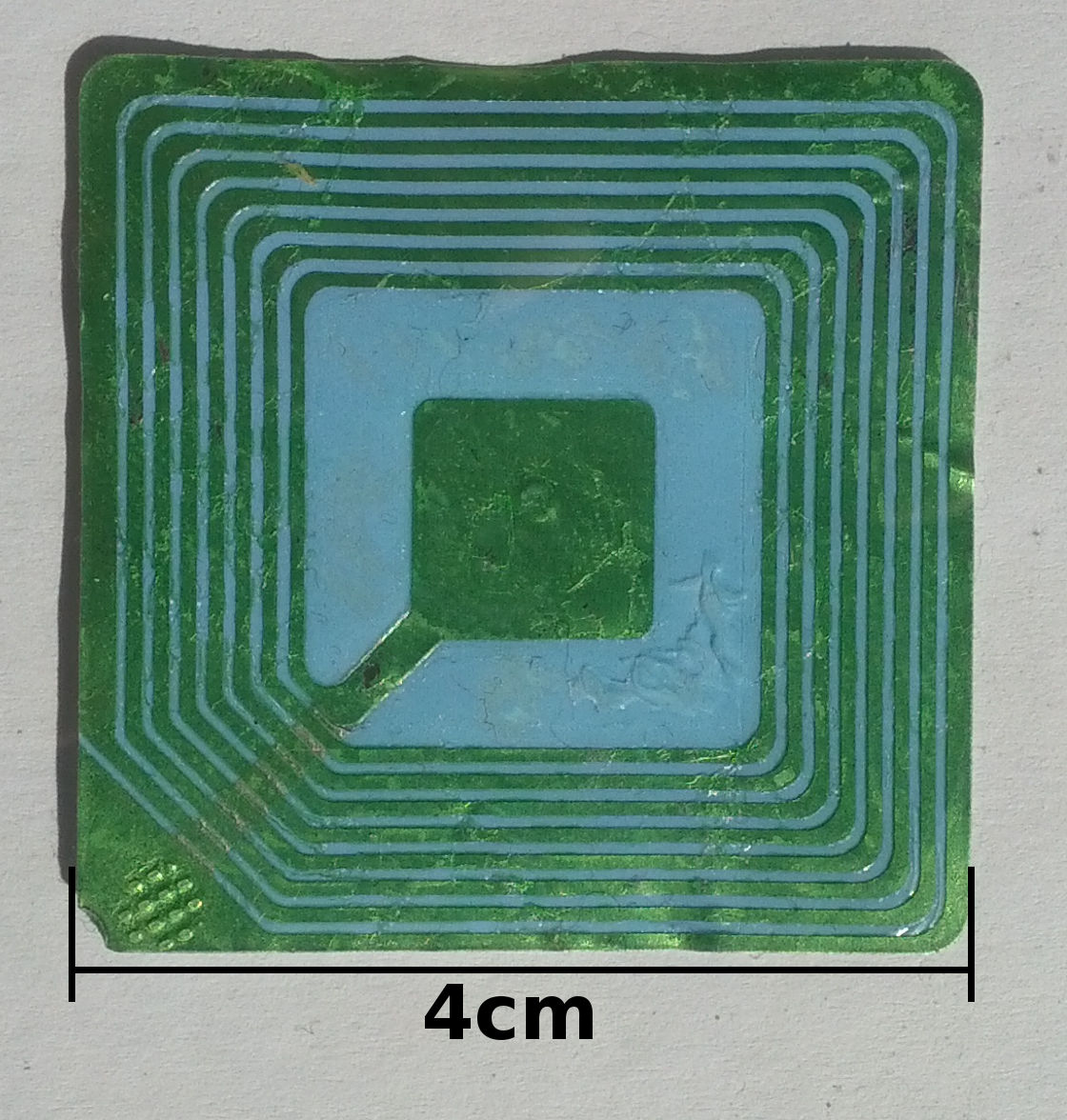
A smart label, also called a smart tag, is an extremely flat configured
transponder
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
under a conventional print-coded label
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product. Labels are most often affixed to packaging and containers using an adhesive, or sewing when affix ...
, which includes chip, antenna and bonding wires as a so-called inlay. The labels, made of paper, fabric or plastics, are prepared as a paper roll with the inlays laminate
Simulated flight (using image stack created by μCT scanning) through the length of a knitting needle that consists of laminated wooden layers: the layers can be differentiated by the change of direction of the wood's vessels
Shattered windshi ...
d between the rolled carrier and the label media for use in specially designed printer units.
In many processes in logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
and transportation
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
, the barcode, or the 2D-barcode, is well established as the key means for identification in short distance. Whereas the automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
of such optical coding is limited in appropriate distance for reading success and usually requires manual operation for finding the code or scanner gates that scan all the surface of a coded object, the RFID-inlay allows for better tolerance in fully automated reading from a certain specified distance. However, the mechanical vulnerability of the RFID-inlay is higher than the ordinary label, which has its weaknesses in its resistance to scratch.
Thus, the smartness of the smart label is earned in compensation of typical weaknesses with the combination of the technologies of plain text, optical character recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronics, electronic or machine, mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo ...
and radio code.
Processing
The processing of these labels is basically as with ordinary labels in all stages of production and application, except the inlay is inserted in an automated processing step to ensure identical positioning for each label and careful processing to prevent any damage to the bonding. The printing is processed in two steps, including * normal ink-jet printing, except the space with the bonded chip, with clearly intelligible text and * eitherbarcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, Machine-readable data, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly ref ...
or 2D barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, Machine-readable data, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly ref ...
for later semi-automatic reading with handheld readers or fix-mount scanners
* writing coherently concatenated information to the RFID-chip
* reading the written information on the RFID-chip subsequently in the printer for control purpose (read after write)
Classification

Chip labels
Customisation of smart labels is available with chip cards. Also combinations of magnetic stripes with RFID chips are used, especially for credit cards.Printable labels
Replacing silicon processors, smart tags that are printed collect information themselves and process it. The result of decades of research and development by ThinFilm Electronics are “printed transistors, the multilayer tags combine a year’s worth of battery power, sensors and a small display, and will initially be used to show a temperature record of perishable food and medications. Roughly 3 x 1.5 inches in size and consisting of five layers sandwiched in a roll-to-roll production process, the ThinFilm labels use the company’s own ferroelectric polymer technology for storing information. Chains of non-toxic polymers can be flipped between two orientations – representing binary “0″ and “1″ – to store non-volatile data.”Electronic labels
While price increases when labels are electronic, the very small percentage of labels that are electric is increasing. Electronic labels have features that supersede non-electronic labels. Electronic versions can signal what is happening in real-time and most can store a digital record.Application
Smart labels are applied directly to packages or topallet
A pallet (also called a skid) is a flat transport structure, which supports goods in a stable fashion while being lifted by a forklift, a pallet jack, a Loader (equipment), front loader, a Jack (mechanical), jacking device, or an erect cra ...
s or other shipping container
A shipping container is a container with strength suitable to withstand shipment, storage, and handling. Shipping containers range from large reusable steel boxes used for intermodal shipments to the ubiquitous corrugated box design, corrugated b ...
s. The application directly to the product is still of neglectible importance
* due to the cost of the labels, which may be justified easier for agglomerations of more than one product
* because all metallic, liquid or otherwise electrically not transparent products reflect or reduce the radio waves
* due to the handling, which normally addresses the package and lesser the unpacked product.
Use
The technologies with the smart labels are all mature and well standardised. After the first wave of technology hype with RFID, current consolidation in the market shows hard competitiveDarwinism
''Darwinism'' is a term used to describe a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others. The theory states that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural sel ...
. With increasing sales quantities, the inlays are still annually redesigned and appear in releases with new extensions to performance. However, the integration of RFID to handling processes requires sound engineering to ensure the balance of benefit and effort.
In 2008, ThinFilm and Polyera announced their partnership to produce high volumes of smart labels. The collaboration brings printed integrated systems, such as smart sensor tags, closer to commercial availability.
See also
*Barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, Machine-readable data, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly ref ...
* Barcode#2D barcodes
* Radio Frequency Identification
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically Automatic identification system, identify and Tracking system, track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, ...
* Track and trace
In the distribution and logistics of many types of products, track and trace or tracking and tracing concerns a process of determining the current and past locations (and other information) of a unique item or property. Mass serialization is t ...
References
{{labeling Labels Smart devices Automatic identification and data capture Radio-frequency identification Packaging materials