skull base on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
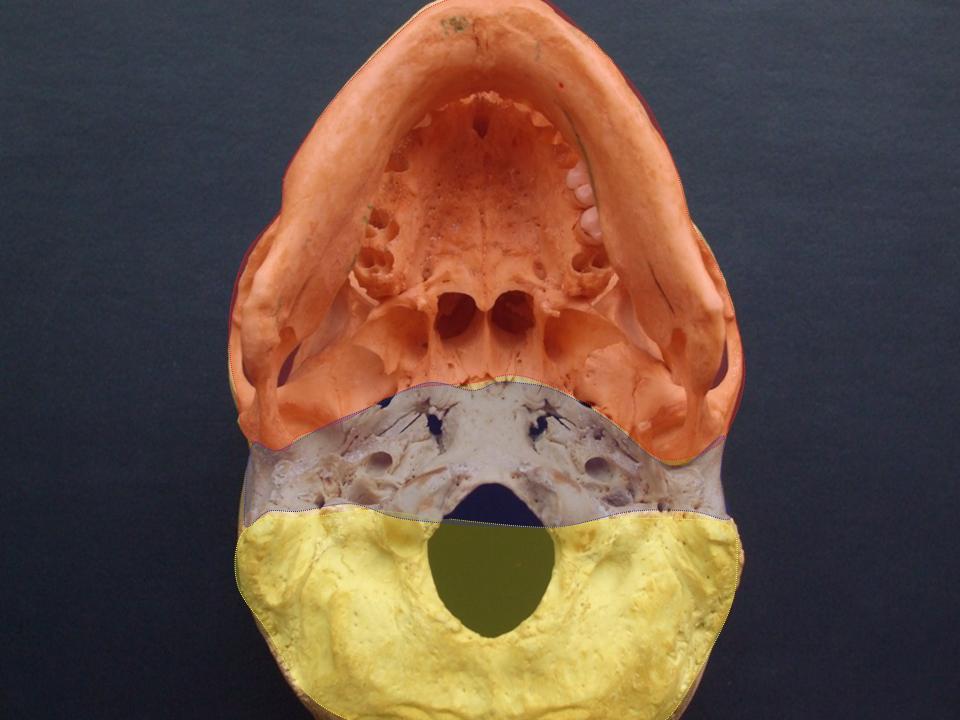
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the
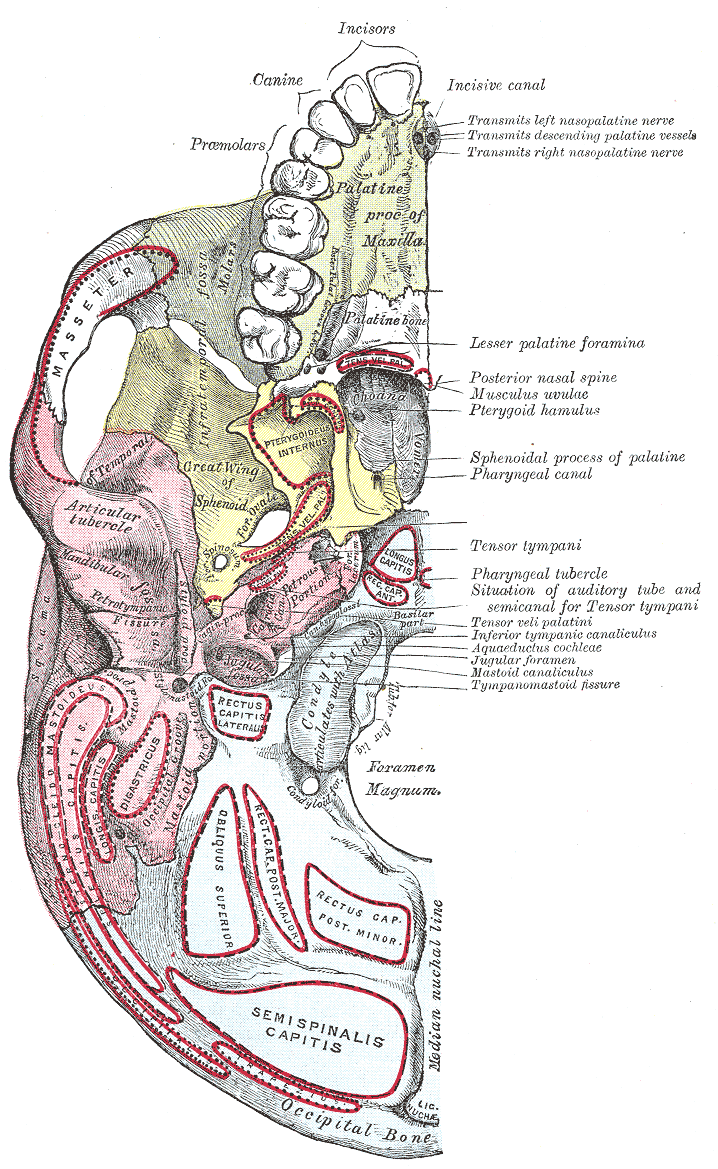 Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:


 * Sphenoidal lingula
* Subarcuate fossa
* Dorsum sellae
*
* Sphenoidal lingula
* Subarcuate fossa
* Dorsum sellae
*
File:Gray193.png , Base of the skull. Upper surface
File:Schädelbasis1.jpg, Base of skull
File:Base of skull 3.jpg, Base of skull - crista galli, cribriform plate and foramen cecum
File:Base of skull 11.jpg, Base of skull - sella turcica
File:Base of skull 24.jpg, The anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa in different colors
{{Authority control
Skull
Human head and neck
Bones of the head and neck
Otorhinolaryngology
Neurosurgery
skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. It is composed of the endocranium
The endocranium in comparative anatomy is a part of the skull base in vertebrates and it represents the basal, inner part of the cranium. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the dura mater in human anatomy.
Structure
Structurally, t ...
and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
 Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Structures found at the base of the skull are for example:
Bones
There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone (; from ) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical (cube-shaped) bone is lightweight due to a spongy constructi ...
*Sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
*Occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
*Frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
*Temporal bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ...

Sinuses
*Occipital sinus
The occipital sinus is the smallest of the dural venous sinuses. It is usually unpaired, and is sometimes altogether absent. It is situated in the attached margin of the falx cerebelli. It commences near the foramen magnum, and ends by draining in ...
*Superior sagittal sinus
The superior sagittal sinus (also known as the superior longitudinal sinus), within the human head, is an unpaired dural venous sinus lying along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of the a ...
*Superior petrosal sinus
The superior petrosal sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses located beneath the brain. It receives blood from the cavernous sinus and passes backward and laterally to drain into the transverse sinus. The sinus receives superior petrosal veins, ...
Foramina of the skull
* Foramen cecum *Optic foramen
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is ...
*Foramen lacerum
The foramen lacerum () is a triangular hole in the base of the skull. It is located between the sphenoid bone, the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and the basilar part of the occipital bone.
Structure
The foramen lacerum () is a ...
*Foramen rotundum
The foramen rotundum is a circular hole in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Structure
T ...
*Foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
* Foramen ovale
*Jugular foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the ...
*Internal auditory meatus
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa ...
*Mastoid foramen
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery t ...
*Sphenoidal emissary foramen
In the base of the skull, in the great wings of the sphenoid bone, medial to the foramen ovale, a small aperture, the sphenoidal emissary foramen, may occasionally be seen (it is often absent) opposite the root of the pterygoid process. When pres ...
*Foramen spinosum
The foramen spinosum is a Foramen, small open hole in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone that gives passage to the middle meningeal artery and vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (sometimes it passes through the Foramen ova ...


Sutures
*Frontoethmoidal suture
The frontoethmoidal suture is the Sutures of skull, suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone.
It is located in the anterior cranial fossa.
References
External links
*
Bones of the head and neck
Cranial sutures
Human head ...
*Sphenofrontal suture
The sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the v ...
*Sphenopetrosal suture
The sphenopetrosal fissure (or sphenopetrosal suture) is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
It is in the middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and t ...
*Sphenoethmoidal suture
The sphenoethmoidal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
It is located in the anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting ...
*Petrosquamous suture
The petrosquamous suture is a cranial suture between the petrous portion and the squama of the temporal bone. It forms the Koerner's septum. The petrous portion forms the medial component of the osseous margin, while the squama forms the latera ...
*Sphenosquamosal suture
The sphenosquamosal suture is a cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the squama of the temporal bone.
Additional images
File:Sphenosquamosal suture - animation4.gif, Animation of sphenosquamosal suture
File:Sphenosquamosal suture - ...
Other
Jugular process
The jugular process is a quadrilateral or triangular bony plate projecting lateralward from the posterior half of the occipital condyle; it is a part of the lateral part of the occipital bone.
The jugular process is excavated in front by the jugu ...
* Petro-occipital fissure
* Condylar canal
* Jugular tubercle
* Tuberculum sellae
*Carotid groove
The carotid groove is an anatomical groove in the sphenoid bone located above the attachment of each great wing of the sphenoid bone. The groove is curved like the italic letter f, and lodges the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid ar ...
* Fossa hypophyseos
*Posterior clinoid processes
The posterior clinoid processes are the tubercles of the sphenoid bone situated at the superior angles of the dorsum sellae (one on each angle) which represents the posterior boundary of the sella turcica. They vary considerably in size and form. ...
*Sigmoid sulcus
The inner surface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus
The transverse sinuses (left and right lateral sinuses), within the human head, are two ...
* Internal occipital protuberance
* Internal occipital crest
* Ethmoidal spine
*Vestibular aqueduct
At the posterior lateral wall of the temporal bone is the vestibular aqueduct, which extends to the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. The vestibular aqueduct parallels the petrous apex, in contrast to the cochlear ...
* Chiasmatic groove
*Middle clinoid process
The middle clinoid process is a small, bilaterally paired elevation on either side of the tuberculum sellae, at the anterior boundary of the sella turcica. A (larger) anterior clinoid process is situated lateral to each middle clinoid process. ...
*Groove for sigmoid sinus
Groove for Sigmoid Sinus is a groove in the posterior cranial fossa. It starts at lateral parts of occipital bone, curves around jugular process, and ends at posterior inferior angle of parietal bone
The parietal bones ( ) are two bones in th ...
*Trigeminal ganglion
The trigeminal ganglion (also known as: Gasserian ganglion, semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion of each trigeminal nerve (CN V). The trigeminal ganglion is located within the trigeminal cave (Meckel's cave), a cav ...
*Middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull ...
*Anterior cranial fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and ...
*Middle meningeal artery
The middle meningeal artery (') is typically the third branch of the maxillary artery#First portion, first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum t ...
*Cribriform plate
In mammalian anatomy, the cribriform plate (Latin for lit. '' sieve-shaped''), horizontal lamina or lamina cribrosa is part of the ethmoid bone. It is received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. It s ...
*Posterior cranial fossa
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brai ...
*Nasociliary nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal ner ...
* Hypoglossal canal
Additional images