Sinus Magnus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
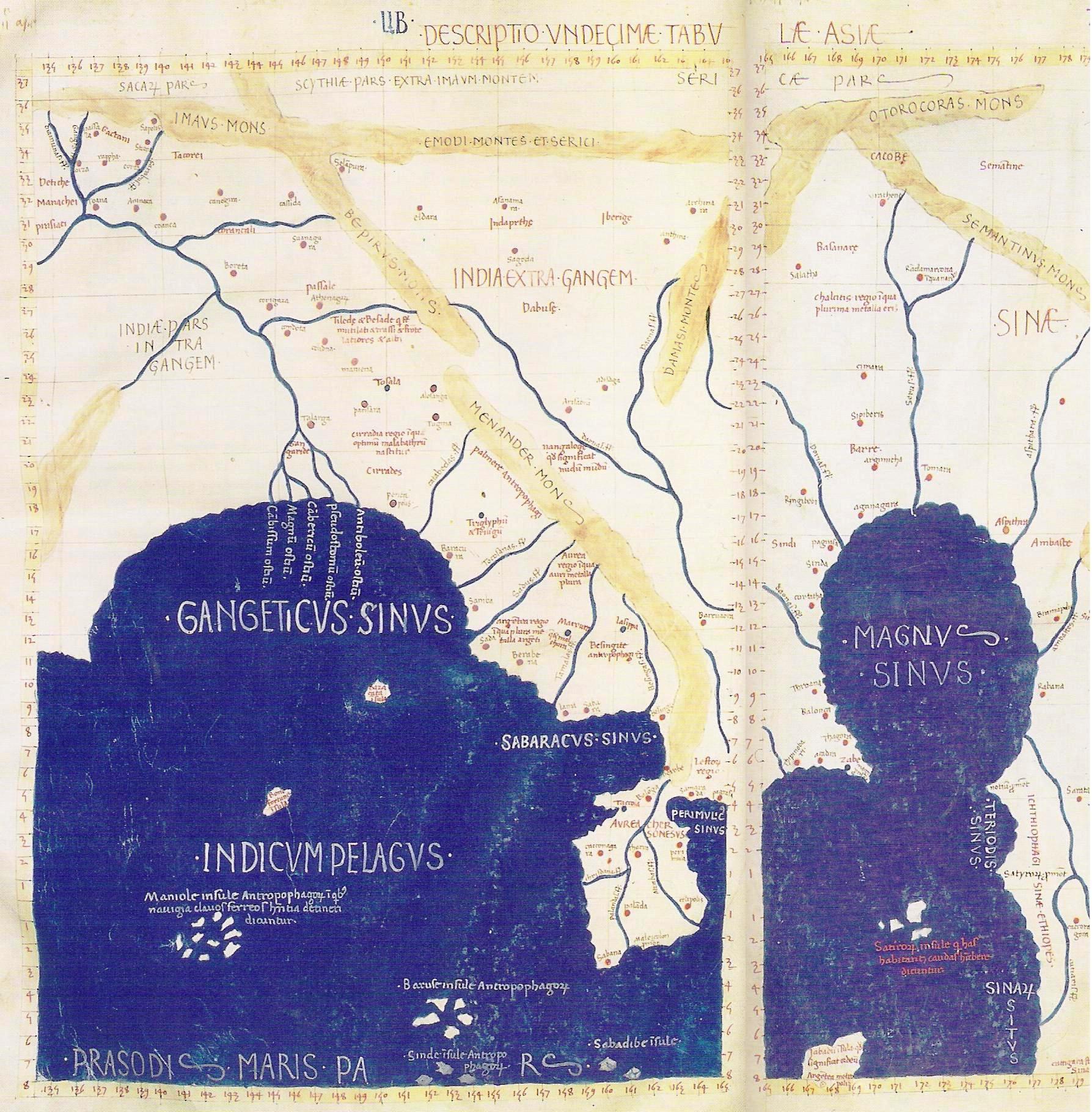 The Magnus Sinus or Sinus Magnus (
The Magnus Sinus or Sinus Magnus (

 The Magnus Sinus or Sinus Magnus (
The Magnus Sinus or Sinus Magnus (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
; , ''o Mégas Kólpos''), also anglicized
Anglicisation or anglicization is a form of cultural assimilation whereby something non-English becomes assimilated into or influenced by the culture of England. It can be sociocultural, in which a non-English place adopts the English language ...
as the was the form of the Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
and South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
known to Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Roman, Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
, Persian, and Renaissance cartographers before the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
. It was then briefly conflated with the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
before disappearing from maps.
History
The gulf and its major port of Cattigara had supposedly been reached by a 1st-centuryGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
trader named Alexander, who returned safely and left a periplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus wa ...
of his voyage. His account that Cattigara was "some days" sail from Zaba was taken by Marinus of Tyre to mean "numberless" days and by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
to mean "a few". Both Alexander and Marinus's works have been lost, but were claimed as authorities by Ptolemy in his ''Geography''. Ptolemy (and presumably Marinus before him) followed Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; , ; BC) was a Ancient Greek astronomy, Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hippar ...
in making the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
a landlocked sea, placing Cattigara on its unknown eastern shoreline. The expanse formed between it and the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
(the " Golden Chersonese"), he called the Great Gulf.
Ptolemy's ''Geography'' was translated into Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
by a team of scholars including al-Khwārizmī in the 9th century during the reign of al-Maʿmūn. By that time, Arab merchants such as Soleiman had begun regular commerce with Tang China
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
and, having passed through the Strait of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, long and from wide, between the Malay Peninsula to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pa ...
''en route'', shown that the Indian Sea communicated with the open ocean. African traders similarly showed that the coastline did not turn sharply east south of Cape Prasum below Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
as Ptolemy held. Al-Khwārizmī's influential ''Book of the Description of the Earth
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mo ...
'', therefore, removed Ptolemy's unknown shores from the Indian Ocean. The robustly-described lands east of the Great Gulf, however, were retained as a phantom peninsula (now generally known as the Dragon's Tail).
Just after 1295, Maximus Planudes
Maximus Planudes (, ''Máximos Planoúdēs''; ) was a Byzantine Greek monk, scholar, anthologist, translator, mathematician, grammarian and theologian at Constantinople. Through his translations from Latin into Greek and from Greek into Latin, ...
restored Ptolemy's Greek text and maps at Chora Monastery
The Chora Church or Kariye Mosque () is a Byzantine church, now converted to a mosque (for the second time), in the Edirnekapı neighborhood of Fatih district, Istanbul, Turkey. It is famous for its outstanding Late Byzantine mosaics and fr ...
in Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
(Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
). This was translated into Latin at Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
by Jacobus Angelus around 1406 and quickly spread the work's information and misinformation throughout Western Europe. The maps initially repeated Ptolemy's enclosed Indian Sea. Following word of Bartholomew Dias's circumnavigation of Africa, maps by Martellus and by Martin of Bohemia replaced this with a new form of the Dragon's Tail peninsula, including details from Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
. As early as 1540, continuing exploration led Sebastian Münster to conflate the Great Gulf with the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
west of the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
, supposing that the 1st-century Alexander had crossed to a port in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
and safely returned. The idea was repeated by Ortelius and others. (Some modern South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
n scholars have returned to the idea as recently as the 1990s, but there remains no substantial evidence to support the idea.) The Great Gulf was finally dispensed with in all its forms as more accurate accounts returned from both the East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
.

Details
The details of the Great Gulf changed somewhat among its various forms, but the ancient and Renaissance Ptolemaic accounts had it bound on the west by the Golden Chersonese and on the north and east by the ports of the Sinae, chief among which was Cattigara. Medieval Islamic cartographers followed al-Khwārizmī in having a strait southeast of the gulf communicating with the Sea of Darkness. Believing thecircumference of the Earth
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the equator, it is . Measured passing through the poles, the circumference is .
Treating the Earth as a sphere, its circumference would be its single most important measuremen ...
to follow Ptolemy's reduced figures or even smaller ones, cartographers during the early phases of the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
expanded the Gulf to form the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
west of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, considered to represent a southeastern peninsula of Asia.
Modern reconstructions agree in naming the Golden Chersonese a form of the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
but differ in their considerations of how much of the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
to include within Ptolemy's reckoning of the Great Gulf. Those following Alexander's route from Zaba on its northern shore to Cattigara to its southeast consider it to be no more than the Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
, with Cattigara located in the Funanese Óc Eo
Óc Eo (Vietnamese language, Vietnamese) is an archaeological site in modern-day Óc Eo communes of Vietnam, commune of Thoại Sơn District in An Giang Province of southern Vietnam. Located in the Mekong Delta, Óc Eo was a busy port of the king ...
ruins at Thoại Sơn. Its Cottiaris River would then be a former course of the Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of wat ...
which once passed the site to enter the Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand (), historically known as the Gulf of Siam (), is a shallow inlet adjacent to the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. ...
. Others ignoring the route as garbled but taking Cattigara to be the major Han entrepôt of Longbian consider the Great Gulf to have been the Gulf of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin ( northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern co ...
, hypothesizing that the Gulf of Thailand (if present) was represented by the smaller inlet on the eastern shore of the Golden Chersonese. Its Cottiaris River would have been Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
's Red River. Panyu (Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about nor ...
) had been the major port of the Kingdom of Nanyue but identifications of Ptolemy's Cattigara with Han-era Nanhai, though common in the past, are credited little more than those placing it in Peru.
Notes
Citations
References
* * * . * * * * * * * * * * {{authority control History of Southeast Asia Ptolemy Ancient Greek geography Historical regions