Simsapa Tree on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
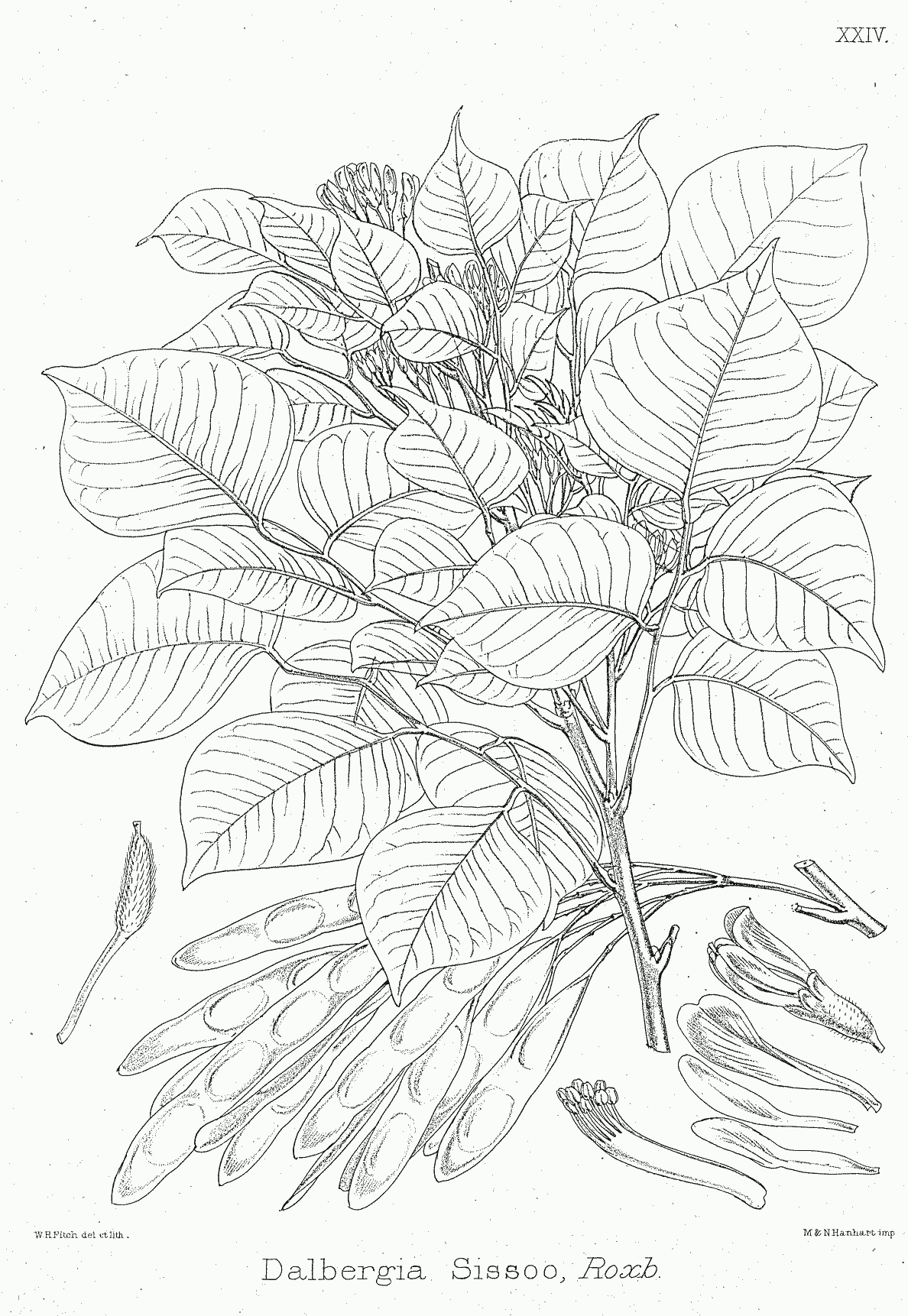 The Simsapa tree (
The Simsapa tree (
 The Simsapa tree (
The Simsapa tree (Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist '' Pāli Canon'' or '' Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of '' Theravāda'' Bud ...
: ) is mentioned in ancient Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
discourses traditionally believed to have been delivered 2,500 years ago. The tree has been identified as either ''Dalbergia sissoo
''Dalbergia sissoo'', known commonly as North Indian rosewood or ''shisham'', is a fast-growing, hardy, deciduous rosewood tree native to the Indian subcontinent and southern Iran. ''D. sissoo'' is a large, crooked tree with long, leathery lea ...
'', a rosewood tree common to India and southeast Asia, or ''Amherstia nobilis
''Amherstia nobilis'' ( my, သော်ကကြီး ; the Pride of Burma, in the family Fabaceae) is a tropical tree with large, showy flowers. It is the only member of the genus ''Amherstia''. It is widely cultivated for ornament in the hu ...
'', another South Asian tree, of the family Caesalpiniaceae
Caesalpinioideae is a botanical name at the rank of subfamily, placed in the large family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. Its name is formed from the generic name '' Caesalpinia''. It is known also as the peacock flower subfamily. The Caesalpinioideae ...
.
Buddhist scriptural references
In Buddhism'sPali Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school.
During ...
, there is a discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. ...
entitled, "The Simsapa Grove" ( Samyutta Nikaya 56.31). This discourse is described as having been delivered by the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in ...
to monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s while dwelling beneath a simsapa grove in the city of Kosambi
Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi (Sanskrit) was an important city in ancient India. It was the capital of the Vatsa kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was located on the Yamuna River about southwest of its confluence with the Gange ...
. In this discourse, the Buddha compares a few simsapa leaves in his hand with the number of simsapa leaves overhead in the grove to illustrate what he teaches (in particular, the Four Noble Truths
In Buddhism, the Four Noble Truths (Sanskrit: ; pi, cattāri ariyasaccāni; "The four Arya satyas") are "the truths of the Noble Ones", the truths or realities for the "spiritually worthy ones".[aFour Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encycl ...
) and what he does not teach (things unrelated to the holy life).
Elsewhere in the Pali Canon, simsapa groves are mentioned in the "Payasi Sutta" (Digha Nikaya
Digha is a seaside resort town in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies in Purba Medinipur district and at the northern end of the Bay of Bengal. It has a low gradient with a shallow sand beach. It is a popular sea resort in West Bengal.
...
23) and in the "Hatthaka Discourse" (Anguttara Nikaya 3.34).For both canonical and atthakatha, post-canonical references, see Rhys Davids & Stede (1921-25), p. 708, entry for "Siŋsapā" (retrieved 17 Nov 2008 from "U. Chicago" at http://dsal.uchicago.edu/cgi-bin/philologic/getobject.pl?c.4:1:104.pali).
See also
*Ashoka tree Ashoka tree is a common name for two plants which are frequently confused with each other:
*'' Saraca asoca'', native to South Asia and western Myanmar
*'' Saraca indica'', native to eastern Myanmar and Southeast Asia
*'' Monoon longifolium'' i ...
Notes
Sources
* Bodhi, Bhikkhu (trans., ed.) (2000). ''The Connected Discourses of the Buddha: A Translation of the Samyutta Nikaya''. Boston: Wisdom Publications. . * Rhys Davids, T.W. & William Stede (eds.) (1921-5). ''The Pali Text Society’s Pali–English Dictionary''. Chipstead:Pali Text Society
The Pali Text Society is a text publication society founded in 1881 by Thomas William Rhys Davids "to foster and promote the study of Pāli texts".
Pāli is the language in which the texts of the Theravada school of Buddhism are preserved. The ...
. A general on-line search engine for the PED is available at http://dsal.uchicago.edu/dictionaries/pali/.
* Thanissaro Bhikkhu (trans.) (1997). ''Simsapa Sutta: The Simsapa Leaves'' ( SN 56.31). Retrieved 16 Nov 2008 from "Access to Insight" at http://www.accesstoinsight.org/tipitaka/sn/sn56/sn56.031.than.html.
* Thanissaro Bhikkhu (trans.) (1999). ''Hatthaka Sutta: To Hatthaka (on Sleeping Well in the Cold Forest) (excerpt)'' ( AN 3.34). Retrieved 16 Nov 2008 from "Access to Insight" at http://www.accesstoinsight.org/tipitaka/an/an03/an03.034.than.html.
* Walshe, Maurice O'C. (trans.) (1985). ''Samyutta Nikaya: An Anthology (Part III)'' (Wheel Nos. 318-321). Kandy: Buddhist Publication Society
The Buddhist Publication Society (BPS) is a publishing house with charitable status whose objective is to disseminate the teaching of Gautama Buddha. It was founded in Kandy, Sri Lanka in 1958 by two Sri Lankan lay Buddhists, A.S. Karunaratna an ...
. Retrieved 16 Nov 2008 from "Access to Insight" (2007) at http://www.accesstoinsight.org/lib/authors/walshe/wheel318.html.
* Walshe, Maurice (1987/1995). ''The Long Discourses of the Buddha: A Translation of the Digha Nikaya
Digha is a seaside resort town in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies in Purba Medinipur district and at the northern end of the Bay of Bengal. It has a low gradient with a shallow sand beach. It is a popular sea resort in West Bengal.
...
''. Boston: Wisdom Publications. {{ISBN, 0-86171-103-3.
Trees in Buddhism
Plant common names