Signal integrity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an

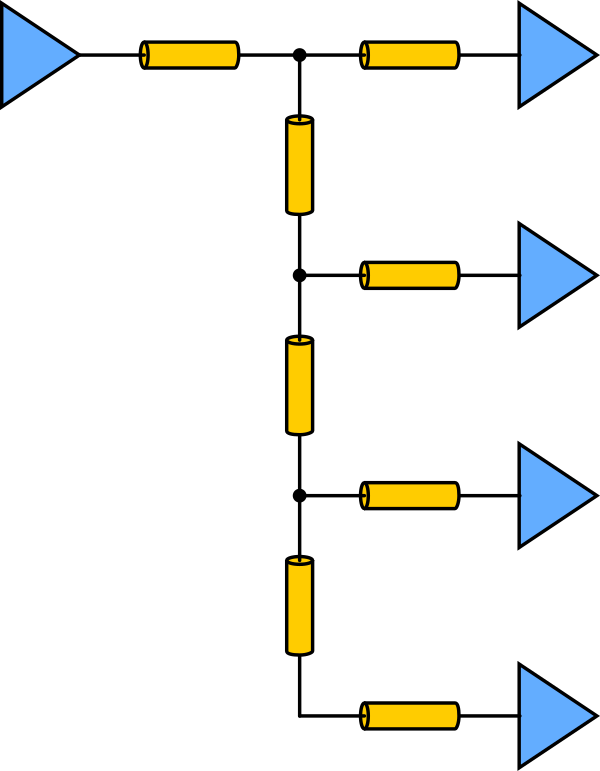 The noise levels on a trace/network is highly dependent on the routing topology selected. In a point-to-point topology, the signal is routed from the transmitter directly to the receiver (this is applied in
The noise levels on a trace/network is highly dependent on the routing topology selected. In a point-to-point topology, the signal is routed from the transmitter directly to the receiver (this is applied in
An Eye is Born
There are special purpose EDA tools that help the engineer perform all these steps on each signal in a design, pointing out problems or verifying the design is ready for manufacture. In selecting which tool is best for a particular task, one must consider characteristics of each such as capacity (how many nodes or elements), performance (simulation speed), accuracy (how good are the models), convergence (how good is the solver), capability (non-linear versus linear, frequency dependent versus frequency independent etc.), and ease of use.
"Using Clock Jitter Analysis to Reduce BER in Serial Data Applications", ''Application Note, literature number 5989-5718EN, Agilent Technologies''
/ref> Each of these fixes may possibly cause other problems. This type of issue must be addressed as part of design flows and
Signal Integrity for PCB Designers
*
Basic Principles of Signal Integrity
Agilent EEsof EDA - Signal Integrity Analysis Resources
"Design tip: Model instruments to improve signal integrity simulation", ''EETimes'', John Olah, 2007-October-25
February 4, 2008 to February 7, 2008
"Understanding Signal Integrity - Signal integrity is becoming a more significant problem as clock frequencies increase"
by Eric Bogatin, GigaTest Labs, Agilent Application Note 5988-5978EN, April 2002, 8 pages, PDF, 0.9 MB
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 1: Single-Port TDR, TDR/TDT, and 2-Port TDR"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5763EN, February 2007, 72 pages, PDF, 5.2 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 2: 4-Port TDR/VNA/PLTS"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5764EN, February 2007, 56 pages, PDF, 3.6 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 3: The ABC's of De-Embedding"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5765EN, July 2007, 48 pages, PDF, 2.5 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis for Automotive Electronics"
(July 2024, 25 pages, PDF, 2.5 MB) Digital electronics Electronic design automation
 Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
. In digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between Binary number, binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical s ...
, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog in nature, and all signals are subject to effects such as noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
, and loss. Over short distances and at low bit rates, a simple conductor can transmit this with sufficient fidelity. At high bit rates and over longer distances or through various mediums, various effects can degrade the electrical signal to the point where errors occur and the system or device fails. Signal integrity engineering is the task of analyzing and mitigating these effects. It is an important activity at all levels of electronics packaging and assembly, from internal connections of an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC), A survey of the field of electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
. Portions of IC section of this article were derived (with permission) from Vol II, Chapter 21, ''Noise Considerations in Digital ICs'', by Vinod Kariat. through the package, the printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
(PCB), the backplane
A backplane or backplane system is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used to connect s ...
, and inter-system connections. While there are some common themes at these various levels, there are also practical considerations, in particular the interconnect flight time versus the bit period, that cause substantial differences in the approach to signal integrity for on-chip connections versus chip-to-chip connections.
Some of the main issues of concern for signal integrity are ringing, crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
, ground bounce
In electronic engineering, ground bounce is a phenomenon associated with transistor switching where the gate voltage can appear to be less than the local ground potential, causing the unstable operation of a logic gate.
Description
Ground bounc ...
, distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
, signal loss, and power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, electric current, current, and frequency to power ...
noise.
History
Signal integrity primarily involves the electrical performance of the wires and other packaging structures used to move signals about within an electronic product. Such performance is a matter of basic physics and as such has remained relatively unchanged since the inception of electronic signaling. The firsttransatlantic telegraph cable
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is a largely obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and dat ...
suffered from severe signal integrity problems, and analysis of the problems yielded many of the mathematical tools still used today to analyze signal integrity problems, such as the telegrapher's equations. Products as old as the Western Electric crossbar telephone exchange (circa 1940), based on the wire-spring relay, suffered almost all the effects seen today - the ringing, crosstalk, ground bounce, and power supply noise that plague modern digital products.
On printed circuit boards, signal integrity became a serious concern when the transition (rise and fall) times of signals started to become comparable to the propagation time across the board. Very roughly speaking, this typically happens when system speeds exceed a few tens of MHz. At first, only a few of the most important, or highest speed, signals needed detailed analysis or design. As speeds increased, a larger and larger fraction of signals needed SI analysis and design practices. In modern (> 100 MHz) circuit designs, essentially all signals must be designed with SI in mind.
For ICs, SI analysis became necessary as an effect of reduced design rules. In the early days of the modern VLSI era, digital chip circuit design and layout were manual processes. The use of abstraction and the application of automatic synthesis techniques have since allowed designers to express their designs using high-level languages and apply an automated design process to create very complex designs, ignoring the electrical characteristics of the underlying circuits to a large degree. However, scaling trends (see Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
) brought electrical effects back to the forefront in recent technology nodes. With scaling of technology below 0.25 μm, the wire delays have become comparable or even greater than the gate delays. As a result, the wire delays needed to be considered to achieve timing closure
The Timing closure in VLSI design and electronics engineering is the process by which a logic design of a clocked synchronous circuit consisting of primitive elements such as combinatorial logic gates ( AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, etc.) and sequ ...
. In nanometer technologies at 0.13 μm and below, unintended interactions between signals (e.g. crosstalk) became an important consideration for digital design. At these technology nodes, the performance and correctness of a design cannot be assured without considering noise effects.
Most of this article is about SI in relation to modern electronic technology - notably the use integrated circuits
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
and printed circuit
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) ...
board technology. Nevertheless, the principles of SI are not exclusive to the signalling technology used. SI existed long before the advent of either technology, and will do so as long as electronic communications persist.
On-chip signal integrity
Signal integrity problems in modern integrated circuits (ICs) can have many drastic consequences for digital designs: * Products can fail to operate at all, or worse yet, become unreliable in the field. * The design may work, but only at speeds slower than planned * Yield may be lowered, sometimes drastically The cost of these failures is very high, and includesphotomask
A photomask (also simply called a mask) is an opaque plate with transparent areas that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. Photomasks are commonly used in photolithography for the production of integrated circuits (ICs or "chips") ...
costs, engineering costs and
opportunity cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone where, given limited resources, a choice needs to be made between several mutually exclusive alternatives. Assuming the best choice is made, ...
due to delayed product introduction. Therefore, electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
(EDA) tools have been developed to analyze, prevent, and correct these problems.
In integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s, or ICs, the main cause of signal integrity problems is crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
.
In CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
technologies, this is primarily due to coupling capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
, but in general it may be caused by mutual inductance, substrate coupling, non-ideal gate operation, and other sources. The fixes normally involve changing the sizes of drivers and/or spacing of wires.
In analog circuits, designers are also concerned with noise that arise from physical sources, such as thermal noise
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
, flicker noise, and shot noise
Shot noise or Poisson noise is a type of noise which can be modeled by a Poisson process.
In electronics shot noise originates from the discrete nature of electric charge. Shot noise also occurs in photon counting in optical devices, where s ...
. These noise sources on the one hand present a lower limit to the smallest signal that can be amplified, and on the other, define an upper limit to the useful amplification.
In digital ICs, noise in a signal of interest arises primarily from coupling effects from switching of other signals. Increasing interconnect density has led to each wire having neighbors that are physically closer together, leading to increased crosstalk between neighboring nets. As circuits have continued to shrink in accordance with Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
, several effects have conspired to make noise problems worse:
* To keep resistance tolerable despite decreased width, modern wire geometries are thicker in proportion to their spacing. This increases the sidewall capacitance at the expense of capacitance to ground, hence increasing the induced noise voltage (expressed as a fraction of supply voltage).
* Technology scaling has led to lower threshold voltage
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important s ...
s for MOS transistors, and has also reduced the difference between threshold and supply voltages, thereby reducing noise margin
In electrical engineering, Noise margin is the maximum voltage amplitude of extraneous signal that can be algebraically added to the noise-free worst-case input level without causing the output voltage to deviate from the allowable logic voltage l ...
s.
* Logic speeds, and clock speeds in particular, have increased significantly, thus leading to faster transition (rise and fall) times. These faster transition times are closely linked to higher capacitive crosstalk. Also, at such high speeds the inductive properties of the wires come into play, especially mutual inductance.
These effects have increased the interactions between signals and decreased the noise immunity of
digital CMOS circuits. This has led to noise being a significant problem for digital ICs that must be considered by every digital chip designer prior to tape-out. There are several concerns that must be mitigated:
* Noise may cause a signal to assume the wrong value. This is particularly critical when the signal is about to be latched (or sampled), for a wrong value could be loaded into a storage element, causing logic failure.
* Noise may delay the settling of the signal to the correct value. This is often called ''noise-on-delay''.
* Noise (e.g. ringing) may cause the input voltage of a gate to drop below ground level, or to exceed the supply voltage. This can reduce the lifetime of the device by stressing components, induce latchup
In electronics, a latch-up is a type of short circuit which can occur in an integrated circuit (IC). More specifically, it is the inadvertent creation of a low-Electrical impedance, impedance path between the power supply rails of a MOSFET circuit ...
, or cause multiple cycling of signals that should only cycle once in a given period.
Finding IC signal integrity problems
Typically, an IC designer would take the following steps for SI verification: * Perform alayout extraction
The electric circuit extraction or simply circuit extraction, also netlist extraction, is the translation of an integrated circuit layout back into the electrical circuit (netlist) it is intended to represent. This extracted circuit is needed for ...
to get the parasitics associated with the layout. Usually worst-case parasitics and best-case parasitics are extracted and used in the simulations. For ICs, unlike PCBs, physical measurement of the parasitics is almost never done, since in-situ measurements with external equipment are extremely difficult. Furthermore, any measurement would occur after the chip has been created, which is too late to fix any problems observed.
* Create a list of expected noise events, including different types of noise, such as coupling and charge sharing.
* Create a model for each noise event. It is critical that the model is as accurate as necessary to model the given noise event.
* For each signal event, decide how to excite the circuit so that the noise event will occur.
* Create a SPICE
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
(or another circuit simulator) netlist
In electronic design, a netlist is a description of the connectivity of an electronic circuit. In its simplest form, a netlist consists of a list of the electronic components in a circuit and a list of the nodes they are connected to. A netwo ...
that represents the desired excitation, to include as many effects (such as parasitic inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
and capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
, and various distortion effects) as necessary.
* Run SPICE simulations. Analyze the simulation results and decide whether any re-design is required. It is common to analyze the results with an eye pattern
In telecommunications, an eye pattern, also known as an eye diagram, is an oscilloscope display in which a digital signal from a receiver is repetitively sampled and applied to the vertical input (''y-axis''), while the data rate is used to tri ...
and by calculating a timing budget.
Modern signal integrity tools for IC design perform all these steps automatically, producing reports that give a design a clean bill of health, or a list of problems that must be fixed. However, such tools generally are not applied across an entire IC, but only selected signals of interest.
Fixing IC signal integrity problems
Once a problem is found, it must be fixed. Typical fixes for IC on-chip problems include: * Removing impedance discontinuities. Finding places where significant shifts in the impedance exist and adjusting the geometry of the path to shift the impedance to better match the rest of the path. * Driver optimization. You can have too much drive, and also not enough. * Buffer insertion. In this approach, instead of upsizing the victim driver, a buffer is inserted at an appropriate point in the victim net. * Aggressor downsizing. This works by increasing the transition time of the attacking net by reducing the strength of its driver. * Add shielding. Add shielding of critical nets or clock nets using GND and VDD shields to reduce the effect of crosstalk (this technique may lead to routing overhead). *Routing
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a Network theory, network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched ...
changes. Routing changes can be very effective in fixing noise problems, mainly by reducing the most troublesome coupling effects via separation.
Each of these fixes may possibly cause other problems. This type of issue must be addressed as part of design flows and design closure
Design Closure is a part of the digital electronic design automation workflow by which an integrated circuit (i.e. VLSI) design is modified from its initial description to meet a growing list of design constraints and objectives.
Every step i ...
. Re-analysis after design changes is a prudent measure.
On-die termination
On-die termination (ODT) or Digitally Controlled Impedance (DCI) is the technology where the termination resistor forimpedance matching
In electrical engineering, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or ...
in transmission lines is located within a semiconductor chip, instead of a separate, discrete device mounted on a circuit board.
The closeness of the termination from the receiver shorten the stub between the two, thus improving the overall signal integrity.
Chip-to-chip signal integrity
For wired connections, it is important to compare the interconnect flight time to the bit period to decide whether an impedance matched or unmatched connection is needed. The channel flight time (delay) of the interconnect is roughly per () ofFR-4
FR-4 (or FR4) is a NEMA grade designation for glass-reinforced epoxy laminate material. FR-4 is a composite material composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder that is flame resistant (''self-extinguishing'').
"FR" stands for ...
stripline
In electronics, stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of planar transmission line.
De ...
(the propagation velocity depends on the dielectric and the geometry). Reflections of previous pulses at impedance mismatches die down after a few bounces up and down the line (i.e. on the order of the flight time). At low bit rates, the echoes die down on their own, and by midpulse, they are not a concern. Impedance matching is neither necessary nor desirable. There are many circuit board types other than FR-4, but usually they are more costly to manufacture.
The gentle trend to higher bit rates accelerated dramatically in 2004, with the introduction by Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
of the PCI-Express standard. Following this lead, the majority of chip-to-chip connection standards underwent an architectural shift from parallel buses to serializer/deserializer ( SERDES) links called "lanes." Such serial links eliminate parallel bus clock skew and reduce the number of traces and resultant coupling effects but these advantages come at the cost of a large increase in bit rate on the lanes, and shorter bit periods.
At multigigabit/s data rates, link designers must consider reflections at impedance changes (e.g. where traces change levels at vias, see Transmission lines
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmis ...
), noise induced by densely packed neighboring connections (crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
), and high-frequency attenuation caused by the skin effect
In electromagnetism, skin effect is the tendency of an alternating current, alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a Conductor (material), conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conduc ...
in the metal trace and dielectric loss tangent. Examples of mitigation techniques for these impairments are a redesign of the via geometry to ensure an impedance match, use of differential signaling
Differential signalling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conduc ...
, and preemphasis filtering, respectively.
At these new multigigabit/s bit rates, the bit period is shorter than the flight time; echoes of previous pulses can arrive at the receiver on top of the main pulse and corrupt it. In communication engineering this is called intersymbol interference (ISI). In signal integrity engineering it is usually called eye closure (a reference to the clutter in the center of a type of oscilloscope trace called an eye diagram). When the bit period is shorter than the flight time, elimination of reflections using classic microwave techniques like matching the electrical impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of Electrical_resistance, resistance and Electrical_reactance, reactance in a electrical circuit, circuit.
Quantitatively, the impedan ...
of the transmitter to the interconnect, the sections of interconnect to each other, and the interconnect to the receiver, is crucial. Termination with a source or load is a synonym for matching at the two ends. The interconnect impedance that can be selected is constrained by the impedance of free space (), a geometric form factor and by the square root of the relative dielectric constant of the stripline filler (typically FR-4, with a relative dielectric constant of ~4). Together, these properties determine the trace's characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a wave travelling in one direction along the line in the absence of reflections in th ...
. is a convenient choice for single-end lines, and for differential.
As a consequence of the low impedance required by matching, PCB signal traces carry much more current than their on-chip counterparts. This larger current induces crosstalk primarily in a magnetic or inductive mode as opposed to a capacitive mode. To combat this crosstalk, digital PCB designers must remain acutely aware of not only the intended signal path for every signal, but also the path of returning signal current for every signal. The signal itself and its returning signal current path are equally capable of generating inductive crosstalk. Differential trace pairs help to reduce these effects.
A third difference between on-chip and chip-to-chip connection involves the cross-sectional size of the signal conductor, namely that PCB conductors are much larger (typically or more in width). Thus, PCB traces have a small series resistance (typically 0.1 Ω/cm) at DC. The high frequency component of the pulse is however attenuated by additional resistance due to the skin effect and dielectric loss tangent associated with the PCB material.
The main challenge often depends on whether the project is a cost-driven consumer application or a performance-driven infrastructure application. They tend to require extensive post-layout verification (using an EM simulator) and pre-layout design optimization (using SPICE
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
and a channel simulator), respectively.
Routing topology

 The noise levels on a trace/network is highly dependent on the routing topology selected. In a point-to-point topology, the signal is routed from the transmitter directly to the receiver (this is applied in
The noise levels on a trace/network is highly dependent on the routing topology selected. In a point-to-point topology, the signal is routed from the transmitter directly to the receiver (this is applied in PCIe
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripher ...
, RapidIO, Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in ...
, DDR2/DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. ...
/ DDR4 DQ/DQS etc.). A point-to-point topology has the least SI-problems since there is no large impedance matches being introduced by line T's (a two-way split of a trace).
For interfaces where multiple packages are receiving from the same line, (for example with a backplane configuration), the line must be split at some point to service all receivers. Some stubs and impedance mismatches are deemed to occur. Multipackage interfaces include B LVDS, DDR2/DDR3/DDR4 C/A bank, RS485 and CAN Bus
A controller area network bus (CAN bus) is a vehicle bus standard designed to enable efficient communication primarily between electronic control units (ECUs). Originally developed to reduce the complexity and cost of electrical wiring in auto ...
. There are two main multipackage topologies: Tree and fly-by.
Finding signal integrity problems
* Perform alayout extraction
The electric circuit extraction or simply circuit extraction, also netlist extraction, is the translation of an integrated circuit layout back into the electrical circuit (netlist) it is intended to represent. This extracted circuit is needed for ...
to get the parasitics associated with the layout. Usually worst-case parasitics and best-case parasitics are extracted and used in the simulations. Because of the distributed nature of many of the impairments, electromagnetic simulation is used for extraction.
* If the PCB or package already exists, the designer can also measure the impairment presented by the connection using high speed instrumentation such as a vector network analyzer. For example, IEEE P802.3ap Task Force uses measured S-parameters
Scattering parameters or S-parameters (the elements of a scattering matrix or S-matrix) describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals.
The parameters are useful ...
as test cases for proposed solutions to the problem of Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
over backplanes.
* Accurate noise modeling is a must. Create a list of expected noise events, including different types of noise, such as coupling and charge sharing. Input Output Buffer Information Specification
Input/output Buffer Information Specification (IBIS) is a specification of a method for integrated circuit vendors to provide information about the Digital buffer, input/output buffers of their product to their prospective customers without revea ...
(IBIS) or circuit models may be used to represent drivers and receivers.
* For each noise event, decide how to excite the circuit so that the noise event will occur.
* Create a SPICE
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
(or another circuit simulator) netlist
In electronic design, a netlist is a description of the connectivity of an electronic circuit. In its simplest form, a netlist consists of a list of the electronic components in a circuit and a list of the nodes they are connected to. A netwo ...
that represents the desired excitation.
* Run SPICE and record the results.
* Analyze the simulation results and decide whether any re-design is required. To analyze the results quite often a data eye is generated and a timing budget is calculated. An example video for generating a data eye can be found on YouTubeAn Eye is Born
There are special purpose EDA tools that help the engineer perform all these steps on each signal in a design, pointing out problems or verifying the design is ready for manufacture. In selecting which tool is best for a particular task, one must consider characteristics of each such as capacity (how many nodes or elements), performance (simulation speed), accuracy (how good are the models), convergence (how good is the solver), capability (non-linear versus linear, frequency dependent versus frequency independent etc.), and ease of use.
Signal Integrity in PCB Design
Signal Integrity (SI) in PCB design refers to the quality of electrical signals as they travel through traces, vias, and components on a printed circuit board. Ensuring good signal integrity is critical for high-speed and high-frequency designs, as poor signal quality can lead to data errors, signal distortion, and system malfunction.Key Factors Affecting Signal Integrity
* Reflection * Crosstalk * Transmission Line Effects * Impedance Mismatch * Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) * Power Integrity (PI) * Rise and Fall TimeFixing signal integrity problems
An IC package or PCB designer removes signal integrity problems through these techniques: * Placing a solidreference plane
In celestial mechanics, the orbital plane of reference (or orbital reference plane) is the plane used to define orbital elements (positions). The two main orbital elements that are measured with respect to the plane of reference are the incli ...
adjacent to the signal traces to control crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
* Controlling the trace width spacing to the reference plane to create consistent trace impedance
* Using terminations to control ringing
* Route traces perpendicular on adjacent layers to reduce crosstalk
* Increasing spacing between traces to reduce crosstalk
* Providing sufficient ground (and power) connections to limit ground bounce
In electronic engineering, ground bounce is a phenomenon associated with transistor switching where the gate voltage can appear to be less than the local ground potential, causing the unstable operation of a logic gate.
Description
Ground bounc ...
(this sub-discipline of signal integrity is sometimes called out separately as power integrity)
* Distributing power with solid plane layers to limit power supply noise
* Adding a pre-emphasis filter to the transmitter driving cell
* Adding an equalizer to the receiving cell
* Improved clock and data recovery (CDR) circuitry with low jitter/phase noise/ref> Each of these fixes may possibly cause other problems. This type of issue must be addressed as part of design flows and
design closure
Design Closure is a part of the digital electronic design automation workflow by which an integrated circuit (i.e. VLSI) design is modified from its initial description to meet a growing list of design constraints and objectives.
Every step i ...
.
See also
* Power integrity * Electromagnetic interference * Electromagnetic compatibilityNotes
References
* Advanced-level reference text for experienced digital designers who want to press their designs to the upper limits of speed and distance. * From the backcover: Draws from author's industrial experience and his work teaching more than five thousand engineers. * * Textbook on the problems of building digital systems, including signal integrity. * This book approaches electrical engineering and signal integrity principles from a basic level, assuming little prior understanding. * * {{cite book , isbn = 978-0-13-615206-4 , author1=Raj , author2=A. Ege Engin. , year = 2008 , publisher = Prentice Hall , location = Upper Saddle River, New Jersey , title = Power integrity modeling and design for semiconductors and systems Using realistic case studies and downloadable software examples, two leading experts demonstrate today's best techniques for designing and modeling interconnects to efficiently distribute power and minimize noise. The authors carefully introduce the core concepts of power distribution design, systematically present and compare leading techniques for modeling noise, and link these techniques to specific applications. Their many examples range from the simplest (using analytical equations to compute power supply noise) through complex system-level applications.Signal Integrity for PCB Designers
*
Basic Principles of Signal Integrity
Agilent EEsof EDA - Signal Integrity Analysis Resources
"Design tip: Model instruments to improve signal integrity simulation", ''EETimes'', John Olah, 2007-October-25
February 4, 2008 to February 7, 2008
"Understanding Signal Integrity - Signal integrity is becoming a more significant problem as clock frequencies increase"
by Eric Bogatin, GigaTest Labs, Agilent Application Note 5988-5978EN, April 2002, 8 pages, PDF, 0.9 MB
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 1: Single-Port TDR, TDR/TDT, and 2-Port TDR"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5763EN, February 2007, 72 pages, PDF, 5.2 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 2: 4-Port TDR/VNA/PLTS"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5764EN, February 2007, 56 pages, PDF, 3.6 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis Series Part 3: The ABC's of De-Embedding"
(Agilent Application Note 5989-5765EN, July 2007, 48 pages, PDF, 2.5 MB)
"Signal Integrity Analysis for Automotive Electronics"
(July 2024, 25 pages, PDF, 2.5 MB) Digital electronics Electronic design automation