sidewheel steamer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A paddle steamer is a
A paddle steamer is a 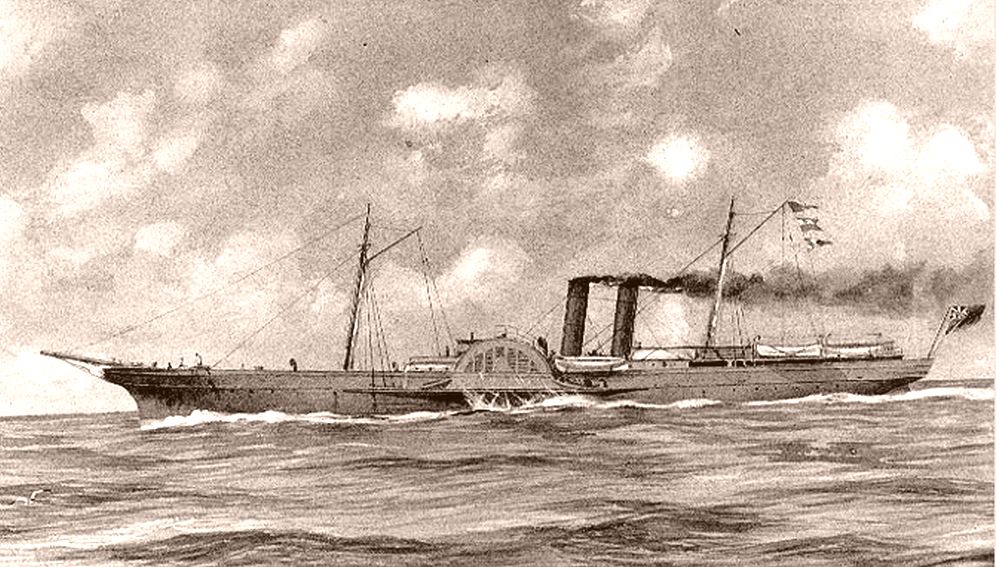 In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the
In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the
 The three types of paddle wheel steamer are sidewheeler, with one paddlewheel on each side; sternwheeler, with a single paddlewheel at the
The three types of paddle wheel steamer are sidewheeler, with one paddlewheel on each side; sternwheeler, with a single paddlewheel at the
 One of the drawings of the Anonymous Author of the
One of the drawings of the Anonymous Author of the  The next successful attempt at a paddle-driven steam ship was by Scottish engineer
The next successful attempt at a paddle-driven steam ship was by Scottish engineer
 The first mention of a paddle-wheel ship from China is in the ''
The first mention of a paddle-wheel ship from China is in the ''
 The first seagoing trip of a paddle steamer was by the ''Albany'' in 1808. It steamed from the
The first seagoing trip of a paddle steamer was by the ''Albany'' in 1808. It steamed from the
 At the start of the
At the start of the
University of Wisconsin–La Crosse Historic Steamboat Photographs
* Dumpleton, Bernard, "The Story of the Paddle Steamer", Melksham, 2002. *
links to videos on paddle wheelers
links to photos of a modern design on paddle wheelers
Australian paddle steamers
A brief history
Paddle Steamer Preservation Society (PSPS)
{{Authority control 1774 introductions Vehicles introduced in the 18th century Marine steam propulsion Ship types
 A paddle steamer is a
A paddle steamer is a steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
or steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. The term ''steamboat'' is used to refer to small steam-powered vessels worki ...
powered by a steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
driving paddle wheel
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened end (the ''blade'') used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered watercraft by p ...
s to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, whereby the first uses were wheelers driven by animals or humans.
 In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the
In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the screw propeller
A propeller (often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working flu ...
and other marine propulsion
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electri ...
systems that have a higher efficiency, especially in rough or open water. Paddle wheels continue to be used by small, pedal-powered paddle boats and by some ships that operate tourist voyages. The latter are often powered by diesel engines.
Paddle wheels
The paddle wheel is a large steel framework wheel. The outer edge of the wheel is fitted with numerous, regularly spaced paddle blades (called floats or buckets). The bottom quarter or so of the wheel travels under water. An engine rotates the paddle wheel in the water to producethrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that ...
, forward or backward as required. More advanced paddle-wheel designs feature "feathering" methods that keep each paddle blade closer to vertical while in the water to increase efficiency. The upper part of a paddle wheel is normally enclosed in a paddlebox to minimise splashing.
Types of paddle steamers
 The three types of paddle wheel steamer are sidewheeler, with one paddlewheel on each side; sternwheeler, with a single paddlewheel at the
The three types of paddle wheel steamer are sidewheeler, with one paddlewheel on each side; sternwheeler, with a single paddlewheel at the stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
; and (rarely) inboard, with the paddlewheel mounted in a recess amidships.
Sidewheeler
The earliest s were sidewheelers, and the type was by far the dominant mode of marine steam propulsion, both for steamships and steamboats, until the increasing adoption of screw propulsion from the 1850s. Though the side wheels and enclosingsponson
Sponsons are projections extending from the sides of land vehicles, aircraft or watercraft to provide protection, Instantaneous stability, stability, storage locations, mounting points for weapons or other devices, or equipment housing.
Watercra ...
s make them wider than sternwheelers, they may be more maneuverable, since they can sometimes move the paddles at different speeds, and even in opposite directions. This extra maneuverability makes side-wheelers popular on the narrower, winding rivers of the Murray–Darling system in Australia, where a number still operate.
European sidewheelers, such as , connect the wheels with solid drive shafts that limit maneuverability and give the craft a wide turning radius. Some were built with paddle clutches that disengage one or both paddles so they can turn independently. However, wisdom gained from early experience with sidewheelers deemed that they be operated with clutches out, or as solid-shaft vessels. Crews noticed that as ships approached the dock, passengers moved to the side of the ship ready to disembark. The shift in weight, added to independent movements of the paddles, could lead to imbalance and potential capsizing
Capsizing or keeling over occurs when a boat or ship is rolled on its side or further by wave action, instability or wind force beyond the angle of positive static stability or it is upside down in the water. The act of recovering a vessel fr ...
. Paddle tugs were frequently operated with clutches in, as the lack of passengers aboard meant that independent paddle movement could be used safely and the added maneuverability exploited to the full.
Most sidewheelers used two wheels, but some ships had multiple wheels behind each other. The SS Bessemer was a noteworthy example.
Sternwheeler
Although the first sternwheelers were invented in Europe, they saw the most service in North America, especially on the Mississippi River. was built atBrownsville, Pennsylvania
Brownsville is a borough in Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States, first settled in 1785 as the site of a trading post a few years after the defeat of the Iroquois enabled a resumption of westward migration after the American Revolutionary ...
, in 1814 as an improvement over the less efficient side-wheelers. The second stern-wheeler built, ''Washington'' of 1816, had two decks and served as the prototype for all subsequent steamboats of the Mississippi, including those made famous in Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by the pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, and essayist. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has produced," with William Fau ...
's book ''Life on the Mississippi
''Life on the Mississippi'' is a memoir by Mark Twain of his days as a steamboat pilot on the Mississippi River before the American Civil War published in 1883. It is also a travel book, recounting his trips on the Mississippi River, from St. L ...
''.
Inboard paddlewheeler
Recessed or inboard paddlewheel boats were designed to ply narrow and snag-infested backwaters. By recessing the wheel within the hull it was protected somewhat from damage. It was enclosed and could be spun at a high speed to provide acute maneuverability. Most were built with inclined steam cylinders mounted on both sides of the paddleshaft and timed 90 degrees apart like a locomotive, making them instantly reversing.Feathering paddle wheel
In a simple paddle wheel, where the paddles are fixed around the periphery, power is lost due to churning of the water as the paddles enter and leave the water surface. Ideally, the paddles should remain vertical while under water. This ideal can be approximated by use of levers and linkages connected to a fixed eccentric. The eccentric is fixed slightly forward of the main wheel centre. It is coupled to each paddle by a rod and lever. The geometry is designed such that the paddles are kept almost vertical for the short duration that they are in the water.History
Western world
The use of a paddle wheel in navigation appears for the first time in the mechanical treatise of theRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
engineer Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
(''De architectura'', X 9.5–7), where he describes multigeared paddle wheels working as a ship odometer
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two (electromechanical). The noun derives from ancient Gr ...
. The first mention of paddle wheels as a means of propulsion comes from the fourth– or fifth-century military treatise (chapter XVII), where the anonymous Roman author describes an ox-driven paddle-wheel warship:
Italian physician Guido da Vigevano (''circa'' 1280–1349), planning for a new crusade, made illustrations for a paddle boat that was propelled by manually turned compound cranks.
 One of the drawings of the Anonymous Author of the
One of the drawings of the Anonymous Author of the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, a ...
shows a boat with a pair of paddlewheels at each end turned by men operating compound cranks. The concept was improved by the Italian Roberto Valturio in 1463, who devised a boat with five sets, where the parallel cranks are all joined to a single power source by one connecting rod, an idea adopted by his compatriot Francesco di Giorgio
Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439–1501) was an Italian architect, engineer, painter, sculptor, and writer. As a painter, he belonged to the Sienese School. He was considered a visionary architectural theorist—in Nikolaus Pevsner's terms ...
.
In 1539, Spanish engineer Blasco de Garay received the support of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
to build ships equipped with manually-powered side paddle wheels. From 1539 to 1543, Garay built and launched five ships, the most famous being the modified Portuguese carrack
A carrack (; ; ) is a three- or four- masted ocean-going sailing ship that was developed in the 14th to 15th centuries in Europe, most notably in Portugal and Spain. Evolving from the single-masted cog, the carrack was first used for Europea ...
''La Trinidad'', which surpassed a nearby galley
A galley is a type of ship optimised for propulsion by oars. Galleys were historically used for naval warfare, warfare, Maritime transport, trade, and piracy mostly in the seas surrounding Europe. It developed in the Mediterranean world during ...
in speed and maneuverability on June 17, 1543, in the harbor of Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
. The project, however, was discontinued. 19th century writer Tomás González claimed to have found proof that at least some of these vessels were steam-powered, but this theory was discredited by the Spanish authorities. It has been proposed that González mistook a steam-powered desalinator created by Garay for a steam boiler.
In 1705, Papin constructed a ship powered by hand-cranked paddles. An apocryphal story originating in 1851 by Louis Figuire held that this ship was steam-powered rather than hand-powered and that it was therefore the first steam-powered vehicle of any kind. The myth was refuted as early as 1880 by , though still it finds credulous expression in some contemporary scholarly work.
In 1787, Patrick Miller of Dalswinton invented a double-hulled boat that was propelled on the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate ...
by men working a capstan that drove paddles on each side.
One of the first functioning steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
s, '' Palmipède'', which was also the first paddle steamer, was built in France in 1774 by Marquis Claude de Jouffroy and his colleagues. The steamer with rotating paddles sailed on the Doubs River
The Doubs ( ; ; ; ) is a river in far eastern France which strays into western Switzerland. It is a left-bank tributary of the Saône. It rises near Mouthe in the western Jura mountains, at and its mouth is at Verdun-sur-le-Doubs, a village a ...
in June and July 1776. In 1783, a new paddle steamer by de Jouffroy, , successfully steamed up the river Saône
The Saône ( , ; ; ) is a river in eastern France (modern Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté). It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges (department), Vosges Departments of France, department an ...
for 15 minutes before the engine failed. Bureaucracy and the French Revolution thwarted further progress by de Jouffroy.
 The next successful attempt at a paddle-driven steam ship was by Scottish engineer
The next successful attempt at a paddle-driven steam ship was by Scottish engineer William Symington
William Symington (1764–1831) was a Scottish engineer and inventor during the Georgian era. He is most well known as the builder of the first practical steamboat, the Charlotte Dundas. The engine has been described as ''"without doubt the mo ...
, who suggested steam power to Patrick Miller of Dalswinton. Experimental boats built in 1788 and 1789 worked successfully on Lochmaben
Lochmaben () is a small town and civil parish in Scotland, and site of a castle. It lies west of Lockerbie, in Dumfries and Galloway. By the 12th century the Bruce family had become the local landowners and, in the 14th century, Edward I of Engl ...
Loch. In 1802, Symington built a barge
A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The firs ...
-hauler, , for the Forth and Clyde Canal Company. It successfully hauled two 70-ton barges almost in 6 hours against a strong headwind on test in 1802. Enthusiasm was high, but some directors of the company were concerned about the banks of the canal being damaged by the wash from a powered vessel, and no more were ordered.
While ''Charlotte Dundas'' was the first commercial paddle steamer and steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. The term ''steamboat'' is used to refer to small steam-powered vessels worki ...
, the first commercial success was possibly Robert Fulton
Robert Fulton (November 14, 1765 – February 24, 1815) was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the (also known as ''Clermont''). In 1807, that steamboat ...
's '' Clermont'' in New York, which went into commercial service in 1807 between New York City and Albany. Many other paddle-equipped river boats followed all around the world; the first in Europe being designed by Henry Bell which started a scheduled passenger service on the River Clyde
The River Clyde (, ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde, in the west of Scotland. It is the eighth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the second longest in Scotland after the River Tay. It runs through the city of Glasgow. Th ...
in 1812.
In 1812, the first U.S. Mississippi River paddle steamer began operating out of New Orleans. By 1814, Captain Henry Shreve had developed a "steamboat" suitable for local conditions. Landings in New Orleans went from 21 in 1814 to 191 in 1819, and over 1,200 in 1833.
The first stern-wheeler was designed by Gerhard Moritz Roentgen
Gerhard Moritz Roentgen (1795–1852) was a Dutch Navy officer, machine building engineer and ship builder. As of 1823 he was involved in founding the Nederlandsche Stoomboot Maatschappij (NSM). At first he was one of NSM two chief executives. La ...
from Rotterdam, and used between Antwerp and Ghent in 1827.
Team boats, paddle boats driven by horses, were used for ferries
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus.
...
the United States from the 1820s–1850s, as they were economical and did not incur licensing costs imposed by the steam navigation monopoly. In the 1850s, they were replaced by steamboats.
After the American Civil War, as the expanding railroads took many passengers, the traffic became primarily bulk cargoes. The largest, and one of the last, paddle steamers on the Mississippi was the sternwheeler ''Sprague''. Built in 1901, she pushed coal and petroleum until 1948.
In Europe from the 1820s, paddle steamers were used to take tourists from the rapidly expanding industrial cities on river cruises, or to the newly established seaside resort
A seaside resort is a city, resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of an official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requi ...
s, where pleasure piers were built to allow passengers to disembark regardless of the state of the tide. Later, these paddle steamers were fitted with luxurious saloons in an effort to compete with the facilities available on the railways. Notable examples are the Thames steamers which took passengers from London to Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in south-eastern Essex, England. It lies on the nor ...
and Margate
Margate is a seaside resort, seaside town in the Thanet District of Kent, England. It is located on the north coast of Kent and covers an area of long, north-east of Canterbury and includes Cliftonville, Garlinge, Palm Bay, UK, Palm Bay and W ...
, Clyde steamer
The Clyde steamer is the collective term for several passenger services that existed on the River Clyde in Scotland, running from Glasgow downstream to Rothesay and other towns, a journey known as going ''doon the watter''.
The era of the Cl ...
s that connected Glasgow with the resort of Rothsay and the Köln-Düsseldorfer cruise steamers on the River Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Const ...
. Paddle steamer services continued into the mid-20th century, when ownership of motor cars finally made them obsolete except for a few heritage examples.
China
 The first mention of a paddle-wheel ship from China is in the ''
The first mention of a paddle-wheel ship from China is in the ''History of the Southern Dynasties
The ''History of the Southern Dynasties'' is one of the official Chinese historical works in the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' canon. It contain 80 volumes and covers the period from 420 to 589, the histories of the Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang, ...
'', compiled in the 7th century but describing the naval ships of the Liu Song dynasty
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern dynasties (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties peri ...
(420–479) used by admiral Wang Zhen'e in his campaign against the Qiang in 418 AD. The ancient Chinese mathematician and astronomer Zu Chongzhi
Zu Chongzhi (; 429 – 500), courtesy name Wenyuan (), was a Chinese astronomer, inventor, mathematician, politician, and writer during the Liu Song and Southern Qi dynasties. He was most notable for calculating pi as between 3.1415926 and 3.1415 ...
(429–500) had a paddle-wheel ship built on the Xinting River (south of Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
) known as the " thousand league boat". Needham, Joseph (1965). ''Science and Civilization in China, Vol. IV: Physics and Physical Technology'', p.416. . When campaigning against Hou Jing
Hou Jing (; died 26 May 552), courtesy name Wanjing (萬景), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician. He was a general of Northern Wei, Eastern Wei, and Liang, and briefly, after controlling the Liang imperial regime for severa ...
in 552, the Liang dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () or Xiao Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was pre ...
(502–557) admiral Xu Shipu employed paddle-wheel boats called "water-wheel boats". At the siege of Liyang in 573, the admiral Huang Faqiu employed foot-treadle powered paddle-wheel boats. A successful paddle-wheel warship design was made in China by Prince Li Gao in 784 AD, during an imperial examination of the provinces by the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(618–907) emperor. The Chinese Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
(960–1279) issued the construction of many paddle-wheel ships for its standing navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
, and according to the British biochemist, historian, and sinologist Joseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, initia ...
:
"...between 1132 and 1183 (AD) a great number of treadmill-operated paddle-wheel craft, large and small, were built, including sternwheelers and ships with as many as 11 paddle-wheels a side,".Needham, 476The standard Chinese term "wheel ship" was used by the Song period, whereas a litany of colorful terms were used to describe it beforehand. In the 12th century, the Song government used paddle-wheel ships ''en masse'' to defeat opposing armies of pirates armed with their own paddle-wheel ships. At the
Battle of Caishi
The Battle of Caishi () was a major naval engagement of the Jin–Song Wars of China that took place on November 26–27, 1161. It ended with a decisive Song victory, aided by their use of gunpowder weapons.
Soldiers under the command of Wan ...
in 1161, paddle-wheelers were also used with great success against the Jin dynasty
Jin may refer to:
States Jìn 晉
* Jin (Chinese state) (晉國), major state of the Zhou dynasty, existing from the 11th century BC to 376 BC
* Jin dynasty (266–420) (晉朝), also known as Liang Jin and Sima Jin
* Jin (Later Tang precursor) ...
(1115–1234) navy. The Chinese used the paddle-wheel ship even during the First Opium War
The First Opium War ( zh, t=第一次鴉片戰爭, p=Dìyīcì yāpiàn zhànzhēng), also known as the Anglo-Chinese War, was a series of military engagements fought between the British Empire and the Chinese Qing dynasty between 1839 and 1 ...
(1839–1842) and for transport around the Pearl River
The Pearl River (, or ) is an extensive river system in southern China. "Pearl River" is often also used as a catch-all for the watersheds of the Pearl tributaries within Guangdong, specifically the Xi ('west'), Bei ('north'), and Dong ( ...
during the early 20th century.
Seagoing paddle steamers
 The first seagoing trip of a paddle steamer was by the ''Albany'' in 1808. It steamed from the
The first seagoing trip of a paddle steamer was by the ''Albany'' in 1808. It steamed from the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
along the coast to the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
. This was purely for the purpose of moving a river-boat to a new market, but paddle-steamers began regular short coastal trips soon after. In 1816 Pierre Andriel, a French businessman, bought in London the paddle steamer ''Margery'' (later renamed ''Elise'') and made an eventful London-Le Havre
Le Havre is a major port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the Seine, river Seine on the English Channel, Channe ...
-Paris crossing, encountering heavy weather on the way. He later operated his ship as a river packet on the Seine, between Paris and Le Havre.
In 1822 Charles Napier's , the world's first iron ship, made the first direct steam crossing from London to Paris and the first seagoing voyage by an iron ship. The first paddle-steamer to make a long ocean voyage crossing the Atlantic Ocean was , built in 1819 expressly for this service. ''Savannah'' set out from the port of Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Brita ...
for Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
on May 24, 1819, sighting Ireland after 23 days at sea. This was the first powered crossing of the Atlantic, although ''Savannah'' was built as a sailing ship with a steam auxiliary; she also carried a full rig of sail for when winds were favorable, being unable to complete the voyage under power alone.
In 1838, , a fairly small steam packet built for the Cork
"Cork" or "CORK" may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Stopper (plug), or "cork", a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
*** Wine cork an item to seal or reseal wine
Places Ireland
* ...
to London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
route, became the first vessel to cross the Atlantic under sustained steam power, beating Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel ( ; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engi ...
's much larger by a day. ''Great Western'', however, was actually built for the transatlantic trade, and so had sufficient coal for the passage; ''Sirius'' had to burn furniture and other items after running out of coal. ''Great Western''s more successful crossing began the regular sailing of powered vessels across the Atlantic. was the first coastal steamship to operate in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
of North America. Paddle steamers helped open Japan to the Western World in the mid-19th century.
The largest paddle-steamer ever built was Brunel's , but it also had screw propulsion and sail rigging. It was long and weighed 32,000 tons, its paddlewheels being in diameter.
In oceangoing service, paddle steamers became much less useful after the invention of the screw propeller, but they remained in use in coastal service and as river tugboats
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, such ...
, thanks to their shallow draught and good maneuverability.
The last crossing of the Atlantic by paddle steamer began on September 18, 1969, the first leg of a journey to conclude six months and nine days later. The steam paddle tug was never intended for oceangoing service, but nevertheless was steamed from Newcastle to San Francisco. As the voyage was intended to be completed under power, the tug was rigged as steam propelled with a sail auxiliary. The transatlantic stage of the voyage was completed exactly 150 years after the voyage of ''Savannah''.
As of 2022, the PS Waverley is the last seagoing passenger-carrying paddle steamer in the world.
Paddle-driven steam warships
Paddle frigates
Beginning in the 1820s, the BritishRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
began building paddle-driven steam frigate
Steam frigates (including screw frigates) and the smaller steam corvettes, steam sloops, steam gunboats and steam schooners, were steam-powered warships that were not meant to stand in the line of battle. The first such ships were paddle stea ...
s and steam sloops. By 1850 these had become obsolete due to the development of the propeller
A propeller (often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working flu ...
– which was more efficient and less vulnerable to cannon fire. One of the first screw-driven warships, , demonstrated her superiority over paddle steamers during numerous trials, including one in 1845 where she pulled a paddle-driven sister ship backwards in a tug of war
Tug of war (also known as tug o' war, tug war, rope war, rope pulling, or tugging war) is a sport in which two teams compete by pulling on opposite ends of a rope, with the goal of bringing the rope a certain distance in one direction against ...
. However, paddle warships were used extensively by the Russian Navy
The Russian Navy is the Navy, naval arm of the Russian Armed Forces. It has existed in various forms since 1696. Its present iteration was formed in January 1992 when it succeeded the Navy of the Commonwealth of Independent States (which had i ...
during the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
of 1853–1856, and by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
during the Mexican War of 1846–1848 and the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
of 1861–1865. With the arrival of ironclad battleships from the late 1850s, the last remaining paddle frigates were decommissioned and sold into merchant-navy service by the 1870s. These included , which became one of the first Boston steamers in 1867. Other paddle frigates were converted to auxiliary roles, a notable example is , a troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable to land troops directly on shore, typic ...
which was wrecked in 1852.
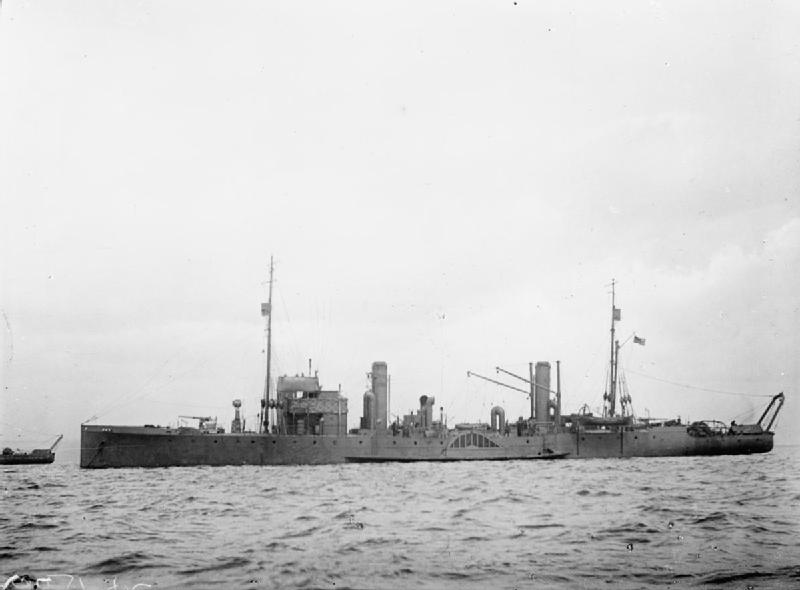
Paddle minesweepers
 At the start of the
At the start of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Royal Navy requisitioned more than fifty pleasure paddle steamers for use as auxiliary minesweeper
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
s.Plummer 1995, p. 3 The large spaces on their decks intended for promenading passengers proved to be ideal for handling the minesweeping booms and cables, and the paddles allowed them to operate in coastal shallows and estuaries. These were so successful that a new class of paddle ships, the Racecourse-class minesweeper
The Racecourse-class minesweepers were 32 ships delivered to the Royal Navy during the First World War. They were built to two related designs as paddlewheel coastal Minesweeper (ship), minesweeping sloop of war, sloops under the Emergency Wa ...
s, were ordered and 32 of them were built before the end of the war.
In the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, some thirty pleasure paddle steamers were again requisitioned; an added advantage was that their wooden hulls did not activate the new magnetic mines. The paddle ships formed six minesweeping flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' ( fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same cla ...
s, based at ports around the British coast. Other paddle steamers were converted to anti-aircraft ships. More than twenty paddle steamers were used as emergency troop transports during the Dunkirk Evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the ...
in 1940, where they were able to get close inshore to embark directly from the beach. One example was , which saved an estimated 7,000 men over the nine days of the evacuation, and claimed to have shot down three German aircraft. Another paddle minesweeper, , was deliberately beached twice to allow soldiers to cross to other vessels using her as a jetty. The paddle steamers between them were estimated to have rescued 26,000 Allied troops during the operation, for the loss of six of them. A number of paddle steamers participated in various roles in the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
in 1944 and supported the Allied advance along the coast of the Belgium and Holland.Plummer 1995, pp. 25-27
See also
* * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Bibliography
* Clark, John and Wardle, David (2003). ''PS Enterprise''. Canberra:National Museum of Australia
The National Museum of Australia (NMA), in the national capital Canberra, preserves and interprets Australia's social history, exploring the key issues, people and events that have shaped the nation. It was formally established by the ''Nation ...
.
University of Wisconsin–La Crosse Historic Steamboat Photographs
* Dumpleton, Bernard, "The Story of the Paddle Steamer", Melksham, 2002. *
External links
links to videos on paddle wheelers
links to photos of a modern design on paddle wheelers
Australian paddle steamers
A brief history
Paddle Steamer Preservation Society (PSPS)
{{Authority control 1774 introductions Vehicles introduced in the 18th century Marine steam propulsion Ship types