sidereal zodiac on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In astrology, '' sidereal'' and ''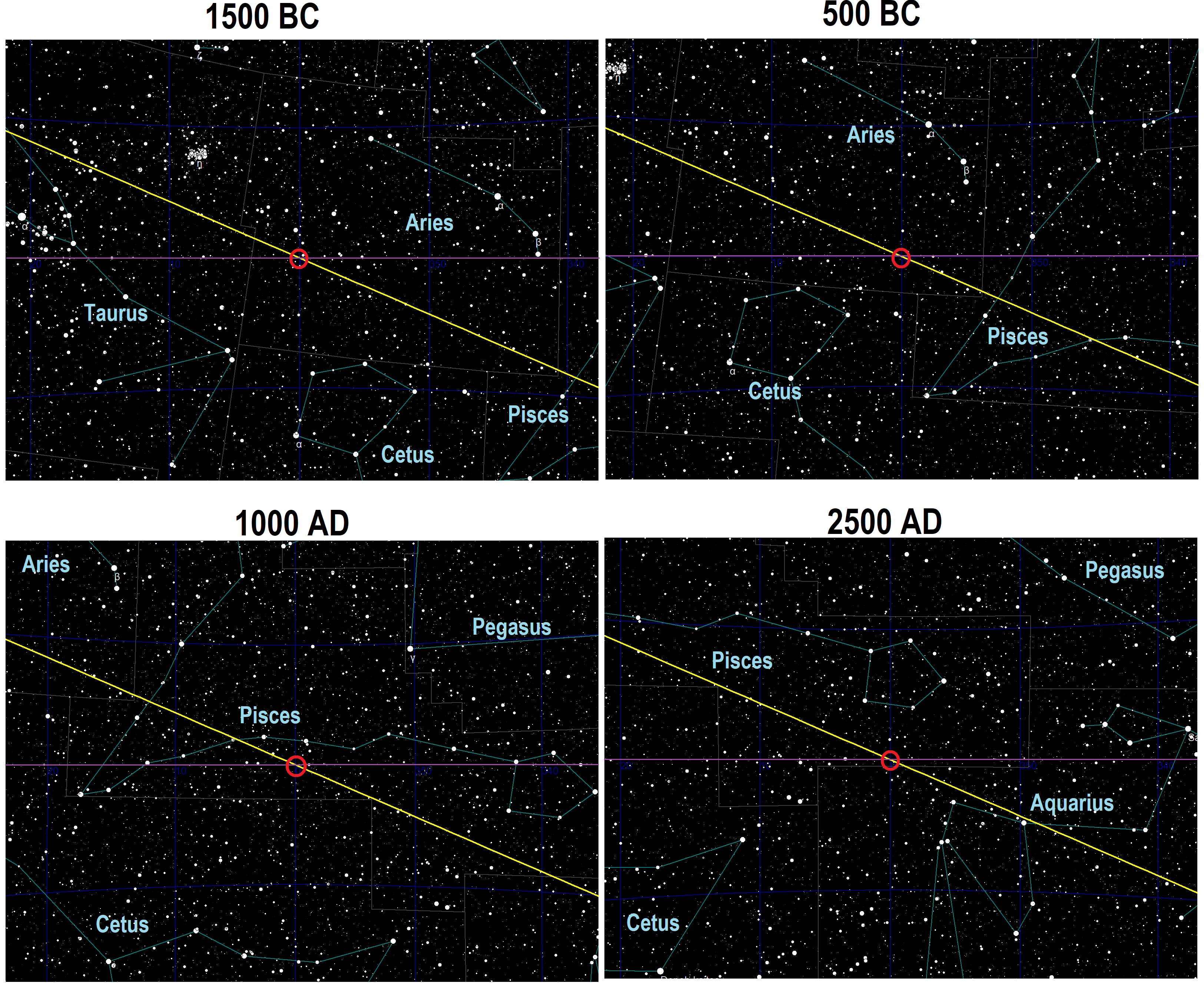
Vedic astrology -- critically examined
by Dieter Koch, with an extended discussion of sidereal and tropical astrology. {{DEFAULTSORT:Sidereal Astrology Astrology by type Hindu astrology History of astrology Spring equinox
tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
'' are terms that refer to two different systems of ecliptic coordinates
In astronomy, the ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system commonly used for representing the apparent positions, orbits, and pole orientations of Solar System objects. Because most planets (except Mercury) and many small So ...
used to divide the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
into twelve "signs". Each sign is divided into 30 degrees, making a total of 360 degrees. The terms sidereal and tropical may also refer to two different definitions of a year, applied in sidereal solar calendars or tropical solar calendar
A solar calendar is a calendar whose dates indicates the season or almost equivalently the apparent position of the Sun relative to the stars. The Gregorian calendar, widely accepted as a standard in the world, is an example of a solar calendar.
...
s.
While sidereal systems of astrology calculate twelve zodiac signs based on the observable sky and thus account for the apparent backwards movement of fixed stars of about 1 degree every 72 years from the perspective of the Earth due to the Earth's axial precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In parti ...
, tropical systems consider 0 degrees of Aries as always coinciding with the March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the ver ...
(known as the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere) and define twelve zodiac signs from this starting point, basing their definitions upon the seasons and not upon the observable sky wherein the March equinox currently falls in Pisces due to the Earth's axial precession. These differences have caused sidereal and tropical zodiac systems, which were aligned around 2,000 years ago when the March equinox coincided with Aries in the observable sky, to drift apart over the centuries.
Sidereal astrology accounts for the Earth's axial precession and maintains the alignment between signs and constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
s via corrective systems known as ayanamsas (Sanskrit: ''Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
as the sign that coincides with the spring equinox instead of Aries.
Ayanamsa systems used in Hindu astrology (also known as Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
astrology) include the Lahiri ayanamsa and the Raman ayanamsa, of which the Lahiri ayanamsa is the most widely used. The Fagan-Bradley ayanamsa is an example of an ayanamsa system used in Western sidereal astrology. As of 2020, sun signs calculated using the Sri Yukteswar ayanamsa were around 23 degrees behind tropical sun signs. Per these calculations, persons born between March 12 – April 12, for instance, would have the sun sign of Pisces. Per tropical calculations, in contrast, persons born between March 21 – April 19 would have the sun sign of Aries.
Astronomic zodiac
A small number of sidereal astrologers do not take the astrological signs as an equal division of the ecliptic but define their signs based on the actual width of the individual constellations. They also include constellations that are disregarded by the traditional zodiac but are still in contact with the ecliptic. For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by theInternational Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU ''boundary'' of Aries on April 19 at the lower right corner, a position that is still rather closer to the "body" of Pisces, as the first sign rather than of Aries. The IAU defined the constellation boundaries without consideration of astrological purposes.
The dates the Sun passes through the 12 astronomical constellations of the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
are listed below, accurate to the year 2011. The dates will progress by an increment of one day every 70.5 years. The corresponding tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and sidereal dates are given as well.
See also
*Great year
The term Great Year has multiple meanings. In scientific astronomy, it refers to the time required for the equinoxes to complete one full cycle around the ecliptic, a period of approximately 25,800 years. According to Ptolemy, his teacher Hipparc ...
* Astrology and science
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems that hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events or descriptions of personality in the human world. Astrology has been rejected by the scientific community as havin ...
* Synoptical astrology
References
* * * * *External links
Vedic astrology -- critically examined
by Dieter Koch, with an extended discussion of sidereal and tropical astrology. {{DEFAULTSORT:Sidereal Astrology Astrology by type Hindu astrology History of astrology Spring equinox