Sherlock Holmes () is a
fictional detective created by British author
Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Hol ...
. Referring to himself as a "
consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction,
forensic science
Forensic science combines principles of law and science to investigate criminal activity. Through crime scene investigations and laboratory analysis, forensic scientists are able to link suspects to evidence. An example is determining the time and ...
and
logical reasoning
Logical reasoning is a mind, mental Action (philosophy), activity that aims to arrive at a Logical consequence, conclusion in a Rigour, rigorous way. It happens in the form of inferences or arguments by starting from a set of premises and reason ...
that borders on the fantastic, which he employs when investigating cases for a wide variety of clients, including
Scotland Yard.
The character Sherlock Holmes first appeared in print in 1887's ''
A Study in Scarlet''. His popularity became widespread with the first series of short stories in ''
The Strand Magazine'', beginning with "
A Scandal in Bohemia" in 1891; additional tales appeared from then until 1927, eventually totalling
four novels and 56 short stories. All but one are set in the
Victorian or
Edwardian eras between 1880 and 1914. Most are narrated by the character of Holmes's friend and biographer,
Dr. John H. Watson, who usually accompanies Holmes during his investigations and often shares quarters with him at the address of
221B Baker Street, London, where many of the stories begin.
Though not the first fictional detective, Sherlock Holmes is arguably the best-known.
By the 1990s, over 25,000 stage adaptations, films, television productions, and publications had featured the detective,
and ''
Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, list ...
'' lists him as the most portrayed human literary character in film and television history.
Holmes's popularity and fame are such that many have believed him to be not a fictional character but an actual individual;
numerous literary and fan societies have been founded on
this pretence. Avid readers of the Holmes stories helped create the modern practice of
fandom, with the
Sherlock Holmes fandom being one of the first cohesive fan communities in the world.
The character and stories have had a profound and lasting effect on
mystery writing and
popular culture
Popular culture (also called pop culture or mass culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of cultural practice, practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as popular art f. pop art
F is the sixth letter of the Latin alphabet.
F may also refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* F or f, the number 15 (number), 15 in hexadecimal and higher positional systems
* ''p'F'q'', the hypergeometric function
* F-distributi ...
or mass art, sometimes contraste ...
as a whole, with the original tales, as well as thousands
written by authors other than Conan Doyle, being
adapted into stage and radio plays, television, films, video games, and other media for over one hundred years.
Inspiration for the character
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely re ...
's
C. Auguste Dupin is generally acknowledged as the forerunner of the modern detective story in English fiction and served as the prototype for many later characters, including Holmes. Conan Doyle once wrote, "Each
f Poe's detective storiesis a root from which a whole literature has developed ... Where was the detective story until Poe breathed the breath of life into it?" Similarly, the stories of
Émile Gaboriau's
Monsieur Lecoq were extremely popular at the time Conan Doyle began writing Holmes, and Holmes's speech and behaviour sometimes follow those of Lecoq. Doyle has his main characters discuss these literary antecedents near the beginning of ''A Study in Scarlet'', which is set soon after Watson is first introduced to Holmes. Watson attempts to compliment Holmes by comparing him to Dupin, to which Holmes replies that he found Dupin to be "a very inferior fellow" and Lecoq to be "a miserable bungler".
Conan Doyle repeatedly said that Holmes was inspired by the real-life figure of
Joseph Bell, a surgeon at the
Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, whom Conan Doyle met in 1877 and had worked for as a clerk. Like Holmes, Bell was noted for drawing broad conclusions from minute observations. However, he later wrote to Conan Doyle: "You are yourself Sherlock Holmes and well you know it". Sir
Henry Littlejohn, Chair of
Medical Jurisprudence at the
University of Edinburgh Medical School, is also cited as an inspiration for Holmes. Littlejohn, who was also Police Surgeon and Medical Officer of Health in Edinburgh, provided Conan Doyle with a link between medical investigation and the detection of crime.
Other possible inspirations have been proposed, though never acknowledged by Doyle, such as ''Maximilien Heller'', by French author Henry Cauvain. In this 1871 novel (sixteen years before the first appearance of Sherlock Holmes), Henry Cauvain imagined a depressed, anti-social, opium-smoking
polymath
A polymath or polyhistor is an individual whose knowledge spans many different subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific problems. Polymaths often prefer a specific context in which to explain their knowledge, ...
detective, operating in Paris. It is not known if Conan Doyle read the novel, but he was fluent in French.
Biography
Family and early life
Details of Sherlock Holmes' life in Conan Doyle's stories are scarce and often vague. Nevertheless, mentions of his early life and extended family paint a loose biographical picture of the detective.
A statement of Holmes' age in "
His Last Bow" places his year of birth at 1854; the story, set in August 1914, describes him as sixty years of age. His parents are not mentioned, although Holmes mentions that his "ancestors" were "
country squires". In "
The Adventure of the Greek Interpreter", he claims that his grandmother was sister to the French artist Vernet, without clarifying whether this was
Claude Joseph,
Carle
Carle or Carlé is a surname. Notable people with the name include:
*Andrea Cosima Carle, whose stage name is Maggie Mae (1960–2021), German singer
* Barbara Carle (born 1958), French-American poet, critic, translator and Italianist
* David Ca ...
, or
Horace Vernet. Holmes' brother
Mycroft, seven years his senior, is a government official. Mycroft has a unique
civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil service personnel hired rather than elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leadership. A civil service offic ...
position as a kind of human database for all aspects of government policy. Sherlock describes his brother as the more intelligent of the two, but notes that Mycroft lacks any interest in physical investigation, preferring to spend his time at the
Diogenes Club.
Holmes says that he first developed his methods of deduction as an undergraduate; his earliest cases, which he pursued as an amateur, came from his fellow university students. A meeting with a classmate's father led him to adopt detection as a profession.
Life with Watson

In the first tale of Sherlock Holmes, ''A Study in Scarlet'', financial difficulties lead Holmes and
Dr. Watson to share rooms together at
221B Baker Street, London. Their residence is maintained by their landlady,
Mrs. Hudson. Holmes works as a detective for twenty-three years, with Watson assisting him for seventeen of those years. Most of the stories are
frame narratives written from Watson's point of view, as summaries of the detective's most interesting cases. Holmes frequently calls Watson's records of Holmes's cases sensational and populist, suggesting that they fail to accurately and objectively report the "science" of his craft:
Nevertheless, when Holmes recorded a case himself, he was forced to concede that he could more easily understand the need to write it in a manner that would appeal to the public rather than his intention to focus on his own technical skill.
Holmes's friendship with Watson is his most significant relationship. When Watson is injured by a bullet, although the wound turns out to be "quite superficial", Watson is moved by Holmes's reaction:
After confirming Watson's assessment of the wound, Holmes makes it clear to their opponent that the man would not have left the room alive if he genuinely had killed Watson.
Practice
Holmes' clients vary from the most powerful monarchs and governments of Europe, to wealthy
aristocrats and
industrialists, to impoverished
pawnbrokers and
governesses. He is known only in select professional circles at the beginning of the first story, but is already collaborating with
Scotland Yard. However, his continued work and the publication of Watson's stories raise Holmes's profile, and he rapidly becomes well known as a detective; so many clients ask for his help instead of (or in addition to) that of the police that, Watson writes, by 1887 "Europe was ringing with his name" and by 1895 Holmes has "an immense practice". Police outside London ask Holmes for assistance if he is nearby. A
British prime minister and the
King of Bohemia[Klinger I, pp. 15-16—"A Scandal in Bohemia"] visit 221B Baker Street in person to request Holmes's assistance; the
President of France
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country, the po ...
awards him the
Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
for capturing an assassin; the King of Scandinavia is a client; and he aids the
Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Geography
* Vatican City, an independent city-state surrounded by Rome, Italy
* Vatican Hill, in Rome, namesake of Vatican City
* Ager Vaticanus, an alluvial plain in Rome
* Vatican, an unincorporated community in the ...
at least twice. The detective acts on behalf of the British government in matters of national security several times and declines a
knighthood "for services which may perhaps some day be described". However, he does not actively seek fame and is usually content to let the police take public credit for his work.
The Great Hiatus
The first set of Holmes stories was published between 1887 and 1893. Conan Doyle killed off Holmes in a final battle with the criminal mastermind
Professor James Moriarty in "
The Final Problem" (published 1893, but set in 1891), as Conan Doyle felt that "my literary energies should not be directed too much into one channel". However, the reaction of the public surprised him very much. Distressed readers wrote anguished letters to ''
The Strand Magazine'', which suffered a terrible blow when 20,000 people cancelled their subscriptions to the magazine in protest.
Conan Doyle himself received many protest letters, and one lady even began her letter with "You brute".
Legend has it that Londoners were so distraught upon hearing the news of Holmes's death that they wore black armbands in mourning, though there is no known contemporaneous source for this; the earliest known reference to such events comes from 1949. However, the recorded public reaction to Holmes's death was unlike anything previously seen for fictional events.
After resisting public pressure for eight years, Conan Doyle wrote ''
The Hound of the Baskervilles'' (serialised in 1901–02, with an implicit setting before Holmes's death). In 1903, Conan Doyle wrote "
The Adventure of the Empty House"; set in 1894, Holmes reappears, explaining to a stunned Watson that he had faked his death to fool his enemies. Following "The Adventure of the Empty House", Conan Doyle would sporadically write new Holmes stories until 1927.
Holmes aficionados refer to the period from 1891 to 1894—between his disappearance and presumed death in "The Final Problem" and his reappearance in "The Adventure of the Empty House"—as the Great Hiatus. The earliest known use of this expression dates to 1946.
Retirement
In ''His Last Bow'', the reader is told that Holmes has retired to a small farm on the
Sussex Downs and taken up
beekeeping
Beekeeping (or apiculture, from ) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in artificial beehives. Honey bees in the genus '' Apis'' are the most commonly kept species but other honey producing bees such as '' Melipona'' stingless bees are ...
as his primary occupation. The move is not dated precisely, but can be presumed to be no later than 1904 (since it is referred to retrospectively in "
The Adventure of the Second Stain", first published that year). The story features Holmes and Watson coming out of retirement to aid the British
war effort. Only one other adventure, "
The Adventure of the Lion's Mane", takes place during the detective's retirement.
Personality and habits

Watson describes Holmes as "
bohemian" in his habits and lifestyle. Said to have a "cat-like" love of personal cleanliness, at the same time Holmes is an
eccentric with no regard for contemporary standards of tidiness or good order. Watson describes him as
While Holmes is characterised as dispassionate and cold, he can be animated and excitable during an investigation. He has a flair for showmanship, often keeping his methods and evidence hidden until the last possible moment so as to impress observers. Holmes is willing to break the law as a means for righting a wrong, contending that "there are certain crimes which the law cannot touch, and which therefore, to some extent, justify private revenge." His companion condones the detective's willingness to do this on behalf of a client—lying to the police, concealing evidence or breaking into houses—when he also feels it morally justifiable.
Except for that of Watson, Holmes avoids casual company. In
"The ''Gloria Scott''", he tells the doctor that during two years at college he made only one friend: "I was never a very sociable fellow, Watson ... I never mixed much with the men of my year."
[Klinger I, p. 502—"The ''Gloria Scott''"] The detective goes without food at times of intense intellectual activity, believing that "the faculties become refined when you starve them". At times, Holmes relaxes with music, either playing the violin or enjoying the works of composers such as
Wagner and
Pablo de Sarasate.
Drug use
Holmes occasionally uses addictive drugs, especially in the absence of stimulating cases. He sometimes uses
morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
and sometimes
cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, the latter of which he injects in a seven-percent solution; both drugs
were legal in 19th-century England. As a physician, Watson strongly disapproves of his friend's cocaine habit, describing it as the detective's only vice, and concerned about its effect on Holmes's
mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
and intellect. In "
The Adventure of the Missing Three-Quarter", Watson says that although he has "weaned" Holmes from drugs, the detective remains an addict whose habit is "not dead, but merely sleeping".
Watson and Holmes both use tobacco, smoking cigarettes, cigars, and
pipes
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circu ...
. Although his chronicler does not consider Holmes's smoking a vice ''per se'', Watson—a physician—does criticise the detective for creating a "poisonous atmosphere" in their confined quarters.
Finances
Holmes is known to charge clients for his expenses and claim any reward offered for a problem's solution, such as in "
The Adventure of the Speckled Band", "
The Red-Headed League", and "
The Adventure of the Beryl Coronet". The detective states at one point that "My professional charges are upon a fixed scale. I do not vary them, save when I remit them altogether." In this context, a client is offering to double his fee, and it is implied that wealthy clients habitually pay Holmes more than his standard rate. In "
The Adventure of the Priory School", Holmes earns a £6,000 fee (at a time where annual expenses for a rising young professional were in the area of £500). However, Watson notes that Holmes would refuse to help even the wealthy and powerful if their cases did not interest him.
Attitudes towards women
As Conan Doyle wrote to Joseph Bell, "Holmes is as inhuman as a
Babbage's Calculating Machine and just about as likely to fall in love." Holmes says of himself that he is "not a whole-souled admirer of womankind", and that he finds "the motives of women ... inscrutable. ... How can you build on such quicksand? Their most trivial actions may mean volumes". In ''
The Sign of Four'', he says, "Women are never to be entirely trusted—not the best of them", a feeling Watson notes as an "atrocious sentiment". In "The Adventure of the Lion's Mane", Holmes writes, "Women have seldom been an attraction to me, for my brain has always governed my heart." At the end of ''The Sign of Four'', Holmes states that "love is an emotional thing, and whatever is emotional is opposed to that true, cold reason which I place above all things. I should never marry myself, lest I bias my judgement." Ultimately, Holmes claims outright that "I have never loved."
But while Watson says that the detective has an "aversion to women", he also notes Holmes as having "a peculiarly ingratiating way with
hem
A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the ga ...
. Watson notes that their housekeeper Mrs. Hudson is fond of Holmes because of his "remarkable gentleness and courtesy in his dealings with women. He disliked and distrusted the sex, but he was always a chivalrous opponent." In "
The Adventure of Charles Augustus Milverton", the detective becomes
engaged under false pretenses in order to obtain information about a case, abandoning the woman once he has the information he requires.
Irene Adler
Irene Adler is a retired American opera singer and actress who appears in "
A Scandal in Bohemia". Although this is her only appearance, she is one of only a handful of people who bests Holmes in a battle of wits, and the only woman. For this reason, Adler is the frequent subject of
pastiche writing. The beginning of the story describes the high regard in which Holmes holds her:
Five years before the story's events, Adler had a brief liaison with Crown Prince of
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
Wilhelm von Ormstein. As the story opens, the Prince is engaged to another. Fearful that the marriage would be called off if his fiancée's family learns of this past impropriety, Ormstein hires Holmes to regain a photograph of Adler and himself. Adler slips away before Holmes can succeed. Her memory is kept alive by the photograph of Adler that Holmes received for his part in the case.
Knowledge and skills
Shortly after meeting Holmes in the first story, ''A Study in Scarlet'' (generally assumed to be 1881, though the exact date is not given), Watson assesses the detective's abilities:
In ''A Study in Scarlet'', Holmes claims to be unaware that the Earth revolves around the Sun since such information is irrelevant to his work; after hearing that fact from Watson, he says he will immediately try to forget it. The detective believes that the mind has a finite capacity for information storage, and learning useless things reduces one's ability to learn useful things. The later stories move away from this notion: in ''
The Valley of Fear'', he says, "All knowledge comes useful to the detective", and in "The Adventure of the Lion's Mane", the detective calls himself "an omnivorous reader with a strangely retentive memory for trifles". Looking back on the development of the character in 1912, Conan Doyle wrote that "In the first one, the ''Study in Scarlet'',
olmeswas a mere calculating machine, but I had to make him more of an educated human being as I went on with him."
Despite Holmes's supposed ignorance of politics, in "A Scandal in Bohemia" he immediately recognises the true identity of the disguised "Count von Kramm".
At the end of ''A Study in Scarlet'', Holmes demonstrates a knowledge of
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. The detective cites
Hafez,
Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Polit ...
, as well as
a letter from
Gustave Flaubert to
George Sand
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil (; 1 July 1804 – 8 June 1876), best known by her pen name George Sand (), was a French novelist, memoirist and journalist. Being more renowned than either Victor Hugo or Honoré de Balz ...
in the original French. In ''The Hound of the Baskervilles'', the detective recognises works by
Godfrey Kneller
Sir Godfrey Kneller, 1st Baronet (born Gottfried Kniller; 8 August 1646 – 19 October 1723) was a German-born British painter. The leading Portrait painting, portraitist in England during the late Stuart period, Stuart and early Georgian eras ...
and
Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter who specialised in portraits. The art critic John Russell (art critic), John Russell called him one of the major European painters of the 18th century, while Lucy P ...
: "Watson won't allow that I know anything of art, but that is mere jealousy since our views upon the subject differ." In "
The Adventure of the Bruce-Partington Plans", Watson says that "Holmes lost himself in a monograph which he had undertaken upon the Polyphonic
Motets of
Lassus", considered "the last word" on the subject — which must have been the result of an intensive and very specialized musicological study with no obvious application to the solution of criminal mysteries.
Holmes is a
cryptanalyst, telling Watson that "I am fairly familiar with all forms of secret writing, and am myself the author of a trifling monograph upon the subject, in which I analyse one hundred and sixty separate ciphers." Holmes also demonstrates a knowledge of psychology in "A Scandal in Bohemia", luring Irene Adler into betraying where she hid a photograph based on the premise that a woman will rush to save her most valued possession from a fire. Another example is in "
The Adventure of the Blue Carbuncle", where Holmes obtains information from a salesman with a wager: "When you see a man with whiskers of that cut and
the 'Pink 'un' protruding out of his pocket, you can always draw him by a bet ... I daresay that if I had put 100 pounds down in front of him, that man would not have given me such complete information as was drawn from him by the idea that he was doing me on a wager."
Maria Konnikova points out in an interview with
D. J. Grothe that Holmes practises what is now called mindfulness, concentrating on one thing at a time, and almost never "multitasks". She adds that in this he predates the science showing how helpful this is to the brain.
Holmesian deduction
Holmes observes the dress and attitude of his clients and suspects, noting skin marks (such as tattoos), contamination (such as ink stains or clay on boots), emotional state, and physical condition in order to deduce their origins and recent history. The style and state of wear of a person's clothes and personal items are also commonly relied on; in the stories, Holmes is seen applying his method to items such as walking sticks, pipes, and hats. For example, in "A Scandal in Bohemia", Holmes infers that Watson had got wet lately and had "a most clumsy and careless servant girl". When Watson asks how Holmes knows this, the detective answers:
In the first Holmes story, ''A Study in Scarlet'', Dr. Watson compares Holmes to
C. Auguste Dupin, Edgar Allan Poe's fictional detective, who employed a similar methodology. Alluding to an episode in "
The Murders in the Rue Morgue", where Dupin determines what his friend is thinking despite their having walked together in silence for a quarter of an hour, Holmes remarks: "That trick of his breaking in on his friend's thoughts with an apropos remark ... is really very showy and superficial." Nevertheless, Holmes later performs the same 'trick' on Watson in "
The Cardboard Box" and "
The Adventure of the Dancing Men".
Though the stories always refer to Holmes's intellectual detection method as "
deduction", Holmes primarily relies on
abduction:
inferring an explanation for observed details.
"From a drop of water," he writes, "a logician could infer the possibility of an
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
or a
Niagara without having seen or heard of one or the other." However, Holmes does employ deductive reasoning as well. The detective's guiding principle, as he says in ''The Sign of Four'', is: "When you have eliminated the impossible, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the truth."
Holmes follows
Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathe ...
's rule of ''"hypotheses non fingo"'', for instance commenting in "
A Scandal in Bohemia": "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts."
Despite Holmes's remarkable reasoning abilities, Conan Doyle still paints him as fallible in this regard (this being a central theme of "
The Yellow Face").
Forensic science

Though Holmes is famed for his reasoning capabilities, his investigative technique relies heavily on the acquisition of hard evidence. Many of the techniques he employs in the stories were at the time in their infancy.
The detective is particularly skilled in the analysis of
trace evidence and other physical evidence, including latent prints (such as footprints, hoof prints, and shoe and tire impressions) to identify actions at a crime scene, using tobacco ashes and cigarette butts to identify criminals, utilizing
handwriting analysis and
graphology
Graphology is the analysis of handwriting in an attempt to determine the writer's personality traits. Its methods and conclusions are not supported by scientific evidence, and as such it is considered to be a pseudoscience.
Graphology has been ...
, comparing
typewritten letters to expose a fraud, using gunpowder residue to expose two murderers, and analyzing small pieces of human remains to expose two murders.
Because of the small scale of much of his evidence, the detective often uses a magnifying glass at the scene and an
optical microscope at his Baker Street lodgings. He uses
analytical chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute t ...
for
blood residue analysis and
toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating ex ...
to detect poisons; Holmes's home chemistry laboratory is mentioned in "
The Naval Treaty".
Ballistics feature in "The Adventure of the Empty House" when spent bullets are recovered to be matched with a suspected murder weapon, a practice which became regular police procedure only some fifteen years after the story was published.
Laura J. Snyder has examined Holmes's methods in the context of mid- to late-19th-century criminology, demonstrating that, while sometimes in advance of what official investigative departments were formally using at the time, they were based upon existing methods and techniques. For example, fingerprints were proposed to be distinct in Conan Doyle's day, and while Holmes used a thumbprint to solve a crime in "
The Adventure of the Norwood Builder" (generally held to be set in 1895), the story was published in 1903, two years after
Scotland Yard's fingerprint bureau opened.
Though the effect of the Holmes stories on the development of forensic science has thus often been overstated, Holmes inspired future generations of forensic scientists to think scientifically and analytically.
Disguises
Holmes displays a strong aptitude for acting and disguise. In several stories ("
The Sign of Four", "
The Adventure of Charles Augustus Milverton", "
The Man with the Twisted Lip", "
The Adventure of the Empty House" and "
A Scandal in Bohemia"), to gather evidence undercover, he uses disguises so convincing that Watson fails to recognise him. In others ("
The Adventure of the Dying Detective" and "
A Scandal in Bohemia"), Holmes feigns injury or illness to incriminate the guilty. In the latter story, Watson says, "The stage lost a fine actor ... when
olmesbecame a specialist in crime."
Guy Mankowski has said of Holmes that his ability to change his appearance to blend into any situation "helped him personify the idea of the English eccentric chameleon, in a way that prefigured the likes of
David Bowie
David Robert Jones (8 January 194710 January 2016), known as David Bowie ( ), was an English singer, songwriter and actor. Regarded as one of the most influential musicians of the 20th century, Bowie was acclaimed by critics and musicians, pa ...
".
Agents
Until Watson's arrival at Baker Street, Holmes largely worked alone, only occasionally employing agents from the city's underclass. These agents included a variety of
informants
An informant (also called an informer or, as a slang term, a "snitch", "rat", "canary", "stool pigeon", "stoolie", "tout" or "grass", among other terms) is a person who provides privileged information, or (usually damaging) information inten ...
, such as Langdale Pike, a "human book of reference upon all matters of social scandal", and Shinwell Johnson, who acted as Holmes's "agent in the huge criminal underworld of London". The best known of Holmes's agents are a group of street children he called "the
Baker Street Irregulars
The Baker Street Irregulars are fictional characters who appear in three Sherlock Holmes stories, specifically two novels and one short story, by Arthur Conan Doyle. They are street boys who are employed by Holmes as intelligence agents. The na ...
".
Combat

Pistols
Holmes and Watson often carry pistols with them to confront criminals—in Watson's case, his old service weapon (probably a Mark III
Adams revolver, issued to British troops during the 1870s).
Holmes and Watson shoot the eponymous hound in ''The Hound of the Baskervilles'', and in "The Adventure of the Empty House", Watson
pistol-whips Colonel
Sebastian Moran. In "
The Problem of Thor Bridge", Holmes uses Watson's revolver to solve the case through an experiment.
Other weapons
As a gentleman, Holmes often carries a stick or cane. He is described by Watson as an expert at
singlestick,
and uses his cane thrice as a weapon. In ''A Study in Scarlet'', Watson describes Holmes as an expert swordsman,
and in "The ''Gloria Scott''", the detective says he practised
fencing
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: Foil (fencing), foil, épée, and Sabre (fencing), sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fe ...
while at university.
In several stories ("
A Case of Identity", "The Red-Headed League", "
The Adventure of the Six Napoleons"), Holmes wields a
riding crop, described in the latter story as his "favourite weapon".
Personal combat

The detective is described (or demonstrated) as possessing above-average physical strength. In "
The Yellow Face", Holmes's chronicler says, "Few men were capable of greater muscular effort." In "
The Adventure of the Speckled Band", Dr. Roylott demonstrates his strength by bending a fire poker in half. Watson describes Holmes as laughing and saying, If he had remained I might have shown him that my grip was not much more feeble than his own.' As he spoke he picked up the steel poker and, with a sudden effort, straightened it out again."
Holmes is an adept
bare-knuckle fighter; "
The ''Gloria Scott''" mentions that Holmes boxed while at university.
In
''The Sign of Four'', he introduces himself to McMurdo, a
prize fighter, as "the
amateur
An amateur () is generally considered a person who pursues an avocation independent from their source of income. Amateurs and their pursuits are also described as popular, informal, autodidacticism, self-taught, user-generated, do it yourself, DI ...
who fought three rounds with you at Alison's rooms on the night of your benefit four years back". McMurdo remembers: "Ah, you're one that has wasted your gifts, you have! You might have aimed high if you had joined the fancy." In "The Yellow Face", Watson says: "He was undoubtedly one of the finest boxers of his weight that I have ever seen." In "The Solitary Cyclist", Holmes visits a country
pub to make enquiries regarding a certain Mr Woodley which results in violence. Mr Woodley, Holmes tells Watson,
[Klinger II, p. 915—"The Solitary Cyclist"]
Another character subsequently refers to Mr Woodley as looking "much disfigured" as a result of his encounter with Holmes.
In "
The Adventure of the Empty House", Holmes tells Watson that he used a
Japanese martial art
Japanese martial arts refers to the variety of martial arts native to the country of Japan. At least three Japanese terms (''budō'', ''bujutsu'', and ''bugei'') are used interchangeably with the English phrase Japanese martial arts.
The usage ...
known as
baritsu to fling Moriarty to his death in the
Reichenbach Falls. "Baritsu" is Conan Doyle's version of
bartitsu, which combines
jujitsu with boxing and
cane fencing.
Reception
Popularity
The first two Sherlock Holmes stories, the novels ''
A Study in Scarlet'' (1887) and ''
The Sign of the Four'' (1890), were moderately well received, but Holmes first became very popular early in 1891 when the first six short stories featuring the character were published in ''
The Strand Magazine''. Holmes became widely known in Britain and America.
The character was so well known that in 1893 when Arthur Conan Doyle killed Holmes in the short story "
The Final Problem", the strongly negative response from readers was unlike any previous public reaction to a fictional event. The ''Strand'' reportedly lost more than 20,000 subscribers as a result of Holmes's death. Public pressure eventually contributed to Conan Doyle writing another Holmes story in 1901 and resurrecting the character in a story published in 1903.
In Japan, Sherlock Holmes (and
Alice from ''
Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (also known as ''Alice in Wonderland'') is an 1865 English Children's literature, children's novel by Lewis Carroll, a mathematics university don, don at the University of Oxford. It details the story of a ...
'') became immensely popular in the country in the 1890s as it was opening up to the West, and they are cited as two British fictional Victorians who left an enormous creative and cultural legacy there.
Many fans of Sherlock Holmes have written letters to Holmes's address,
221B Baker Street. Though the address 221B Baker Street did not exist when the stories were first published, letters began arriving to the large
Abbey National building which first encompassed that address almost as soon as it was built in 1932. Fans continue to send letters to Sherlock Holmes; these letters are now delivered to the
Sherlock Holmes Museum. Some of the people who have sent letters to 221B Baker Street believe Holmes is real.
Members of the general public have also believed Holmes actually existed. In a 2008 survey of British teenagers, 58 per cent of respondents believed that Sherlock Holmes was a real individual.
Some scholarly discussion of Holmes has occasionally been written (usually facetiously) from the perspective of Holmes and Dr. Watson having existed; an example of this are the five critical essays, "Studies in Sherlock Holmes", by the author and essayist
Dorothy L. Sayers in her 1946 non-fiction collection, ''Unpopular Opinions'', including an article examining Watson's ''signature'' which was allegedly visible in some original ''Strand'' illustrations.
The Sherlock Holmes stories continue to be widely read.
Holmes's continuing popularity has led to many reimaginings of the character in adaptations.
''Guinness World Records'', which awarded Sherlock Holmes the title for "most portrayed literary human character in film & TV" in 2012, released a statement saying that the title "reflects his enduring appeal and demonstrates that his detective talents are as compelling today as they were 125 years ago".
Honours


The London
Metropolitan Railway
The Metropolitan Railway (also known as the Met) was a passenger and goods railway that served London from 1863 to 1933, its main line heading north-west from the capital's financial heart in the City to what were to become the Middlesex su ...
named one of its twenty
electric locomotives deployed in the 1920s for Sherlock Holmes. He was the only fictional character so honoured, along with eminent Britons such as
Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
,
Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman, Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a ...
, and
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during th ...
.
A number of London streets are associated with Holmes. York Mews South, off Crawford Street, was renamed Sherlock Mews, and Watson's Mews is near Crawford Place.
The Sherlock Holmes is a
public house
A pub (short for public house) is in several countries a drinking establishment licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption Licensing laws of the United Kingdom#On-licence, on the premises. The term first appeared in England in the ...
in Northumberland Street in London which contains a large collection of memorabilia related to Holmes, the original collection having been put together for display in
Baker Street during the
Festival of Britain in 1951.
In 2002, the
Royal Society of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the ...
bestowed an honorary fellowship on Holmes for his use of forensic science and analytical chemistry in popular literature, making him (as of 2024) the only fictional character thus honoured. Holmes has been commemorated numerous times on UK postage stamps issued by the
Royal Mail, most recently in their
August 2020 series to celebrate the ''Sherlock'' television series.
There are multiple statues of Sherlock Holmes around the world. The first, sculpted by
John Doubleday, was unveiled in
Meiringen, Switzerland, in September 1988. The second was unveiled in October 1988 in
Karuizawa, Japan, and was sculpted by Yoshinori Satoh. The third was installed in Edinburgh, Scotland, in 1989, and was sculpted by
Gerald Laing.
In 1999, a
statue of Sherlock Holmes in London, also by John Doubleday, was unveiled near the fictional detective's address, 221B Baker Street. In 2001, a sculpture of Holmes and Arthur Conan Doyle by
Irena Sedlecká was unveiled in a statue collection in Warwickshire, England. A sculpture depicting both Holmes and Watson was unveiled in 2007 in Moscow, Russia, based partially on
Sidney Paget's illustrations and partially on the actors in ''
The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson''. In 2015, a sculpture of Holmes by
Jane DeDecker was installed in the police headquarters of
Edmond, Oklahoma, United States. In 2019, a statue of Holmes was unveiled in
Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
, Illinois, United States, as part of a series of statues honouring cartoonist
E. C. Segar and his characters. The statue is titled "Sherlock & Segar", and the face of the statue was modelled on Segar.
Societies
In 1934, the Sherlock Holmes Society (in London) and the
Baker Street Irregulars
The Baker Street Irregulars are fictional characters who appear in three Sherlock Holmes stories, specifically two novels and one short story, by Arthur Conan Doyle. They are street boys who are employed by Holmes as intelligence agents. The na ...
(in New York) were founded. The latter is still active. The Sherlock Holmes Society was dissolved later in the 1930s, but was succeeded by a society with a slightly different name, the Sherlock Holmes Society of London, which was founded in 1951 and remains active. These societies were followed by many more, first in the US (where they are known as "scion societies"—offshoots—of the Baker Street Irregulars) and then in England and Denmark. There are at least 250 societies worldwide, including Australia, Canada (such as
The Bootmakers of Toronto), India, and Japan. Fans tend to be called "Holmesians" in the UK and "Sherlockians" in the US, though recently "Sherlockian" has also come to refer to fans of the
Benedict Cumberbatch-led BBC series regardless of location.
Legacy
The detective story
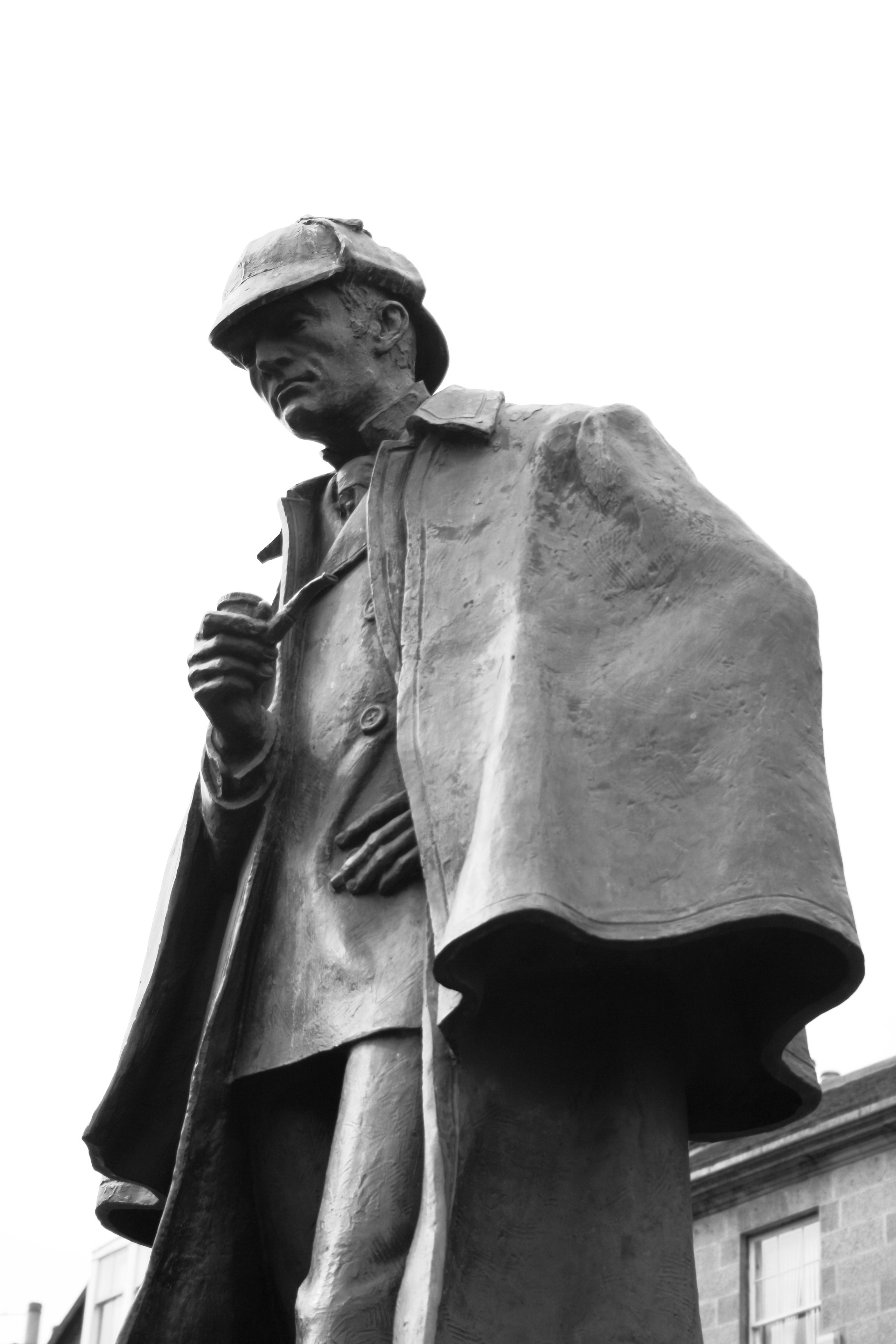

Although Holmes is not the original fictional detective, his name has become synonymous with the role. Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories introduced multiple literary devices that have become major conventions in detective fiction, such as the companion character who is not as clever as the detective and has solutions explained to him (thus informing the reader as well), as with
Dr. Watson in the Holmes stories. Other conventions introduced by Doyle include the arch-criminal who is too clever for the official police to defeat, like Holmes's adversary
Professor Moriarty, and the use of forensic science to solve cases.
The Sherlock Holmes stories established crime fiction as a respectable genre popular with readers of all backgrounds, and Doyle's success inspired many contemporary detective stories.
[ Holmes influenced the creation of other "eccentric gentleman detective" characters, like ]Agatha Christie
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English people, English author known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving ...
's fictional detective Hercule Poirot, introduced in 1920. Holmes also inspired a number of anti-hero characters "almost as an antidote to the masterful detective", such as the gentleman thief characters A. J. Raffles (created by E. W. Hornung in 1898) and Arsène Lupin
Arsène Lupin () is a fictional gentleman thief and master of disguise created in 1905 by French writer Maurice Leblanc. The character was first introduced in a series of short stories serialized in the magazine '' Je sais tout''. The first ...
(created by Maurice Leblanc in 1905).
"Elementary, my dear Watson"
The phrase "Elementary, my dear Watson" has become one of the most quoted and iconic aspects of the character. However, although Holmes often observes that his conclusions are "elementary", and occasionally calls Watson "my dear Watson", the phrase "Elementary, my dear Watson" is never uttered in any of the sixty stories by Conan Doyle.Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
''. However, the script was revised numerous times over the course of some three decades of revivals and publications, and the phrase is present in some versions of the script, but not others.
The Great Game
 Conan Doyle's 56 short stories and four novels are known as the " canon" by Holmes aficionados. The Great Game (also known as the Holmesian Game, the Sherlockian Game, or simply the Game, also the Higher Criticism) applies the methods of literary and especially Biblical criticism to the canon, operating on the pretense that Holmes and Watson were real people and that Conan Doyle was not the author of the stories but Watson's literary agent. From this basis, it attempts to resolve or explain away contradictions in the canon—such as the location of Watson's war wound, described as being in his shoulder in ''A Study in Scarlet'' and in his leg in ''The Sign of Four''—and clarify details about Holmes, Watson and their world, such as the exact dates of events in the stories, combining historical research with references from the stories to construct scholarly analyses.
Conan Doyle's 56 short stories and four novels are known as the " canon" by Holmes aficionados. The Great Game (also known as the Holmesian Game, the Sherlockian Game, or simply the Game, also the Higher Criticism) applies the methods of literary and especially Biblical criticism to the canon, operating on the pretense that Holmes and Watson were real people and that Conan Doyle was not the author of the stories but Watson's literary agent. From this basis, it attempts to resolve or explain away contradictions in the canon—such as the location of Watson's war wound, described as being in his shoulder in ''A Study in Scarlet'' and in his leg in ''The Sign of Four''—and clarify details about Holmes, Watson and their world, such as the exact dates of events in the stories, combining historical research with references from the stories to construct scholarly analyses.
Museums and special collections
For the 1951 Festival of Britain, Holmes's living room was reconstructed as part of a Sherlock Holmes exhibition, with a collection of original material. After the festival, items were transferred to The Sherlock Holmes (a London pub) and the Conan Doyle collection housed in Lucens, Switzerland, by the author's son, Adrian
Adrian is a form of the Latin given name Adrianus or Hadrianus. Its ultimate origin is most likely via the former river Adria from the Venetic and Illyrian word ''adur'', meaning "sea" or "water".
The Adria was until the 8th century BC the ma ...
. Both exhibitions, each with a Baker Street sitting-room reconstruction, are open to the public.University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota Twin Cities (historically known as University of Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint ...
founded a collection that is now "the world's largest gathering of material related to Sherlock Holmes and his creator". Access is closed to the general public, but is occasionally open to tours.
In 1990, the Sherlock Holmes Museum opened on Baker Street in London, followed the next year by a museum in Meiringen (near the Reichenbach Falls) dedicated to the detective.
Postcolonial criticism
The Sherlock Holmes stories have been scrutinized by a few academics for themes of empire and colonialism.
Susan Cannon Harris claims that themes of contagion and containment are common in the Holmes series, including the metaphors of Eastern foreigners as the root cause of "infection" within and around Europe.Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
n cannibals (also known as Batak) who throw poisonous darts, and in "The Speckled Band", a "long residence in the tropics" was a negative influence on one antagonist's bad temper.[Raheja, Lauren. "Anxieties of Empire in Doyle's Tales of Sherlock Holmes". ''Nature, Society, and Thought'', vol. 19, no. 4, 2006, p. 417, ProQuest Central.] Yumna Siddiqi argues that Doyle depicted returned colonials as "marginal, physically ravaged characters that threaten the peace", while putting non-colonials in a much more positive light.
Adaptations and derived works
The popularity of Sherlock Holmes has meant that many writers other than Arthur Conan Doyle have created tales of the detective in a wide variety of different media, with varying degrees of fidelity to the original characters, stories, and setting. The first known pastiche dates from 1891. Titled "My Evening with Sherlock Holmes", it was written by Conan Doyle's close friend J. M. Barrie.H. P. Lovecraft
Howard Phillips Lovecraft (, ; August 20, 1890 – March 15, 1937) was an American writer of Weird fiction, weird, Science fiction, science, fantasy, and horror fiction. He is best known for his creation of the Cthulhu Mythos.
Born in Provi ...
's Cthulhu Mythos The Cthulhu Mythos is a mythopoeia and a shared fictional universe, originating in the works of American Horror fiction, horror writer H. P. Lovecraft. The term was coined by August Derleth, a contemporary correspondent and protégé of Lovecraft, t ...
in Neil Gaiman
Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman (; born Neil Richard Gaiman; 10 November 1960) is an English author of short fiction, novels, comic books, audio theatre, and screenplays. His works include the comic series ''The Sandman (comic book), The Sandma ...
's " A Study in Emerald" (which won the 2004 Hugo Award
The Hugo Award is an annual literary award for the best science fiction or fantasy works and achievements of the previous year, given at the World Science Fiction Convention (Worldcon) and chosen by its members. The award is administered by th ...
for Best Short Story). An especially influential pastiche was Nicholas Meyer's '' The Seven-Per-Cent Solution'', a 1974 ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' bestselling novel (made into the 1976 film of the same name) in which Holmes's cocaine addiction has progressed to the point of endangering his career. It served to popularize the trend of incorporating clearly identified and contemporaneous historical figures (such as Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
, Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley ( ; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, novelist, mountaineer, and painter. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the pr ...
, Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies seen as originating fro ...
, or Jack the Ripper) into Holmesian pastiches, something Conan Doyle himself never did. Another common pastiche approach is to create a new story fully detailing an otherwise-passing canonical reference (such as an aside by Conan Doyle mentioning the " giant rat of Sumatra, a story for which the world is not yet prepared" in " The Adventure of the Sussex Vampire").
The first translation of a Sherlock Holmes story into a Chinese variety was done by ''Chinese Progress'' in 1896. That publication rendered the name as 呵爾唔斯, which would be 呵尔唔斯 in Simplified Chinese
Simplification, Simplify, or Simplified may refer to:
Mathematics
Simplification is the process of replacing a mathematical expression by an equivalent one that is simpler (usually shorter), according to a well-founded ordering. Examples include: ...
and Hē'ěrwúsī in Modern Standard Mandarin. Shanghai Civilization Books later issued versions rendering Holmes's name differently, as 福爾摩斯 in Traditional Chinese
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examp ...
, which would be 福尔摩斯 in Simplified Chinese and Fú'ěrmósī in Modern Standard Mandarin; this version became the common way of rendering "Holmes" in Chinese languages.
Original Chinese version: - Original title: "福尔摩斯为何姓“福”?不是因为分不清f和h的福建人,而是因为上海人!"
Original text here
/ref>
Related and derivative writings
In addition to the Holmes canon, Conan Doyle wrote other material featuring Holmes, especially plays: 1899's ''Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
'' (with William Gillette), 1910's '' The Speckled Band'', and 1921's ''The Crown Diamond'' (the basis for " The Adventure of the Mazarin Stone"). These and other Holmes-related but non-canonical works have been collected in several works released since Conan Doyle's death.Agatha Christie
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English people, English author known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving ...
, Anthony Burgess, Neil Gaiman
Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman (; born Neil Richard Gaiman; 10 November 1960) is an English author of short fiction, novels, comic books, audio theatre, and screenplays. His works include the comic series ''The Sandman (comic book), The Sandma ...
, Dorothy B. Hughes, Stephen King
Stephen Edwin King (born September 21, 1947) is an American author. Dubbed the "King of Horror", he is widely known for his horror novels and has also explored other genres, among them Thriller (genre), suspense, crime fiction, crime, scienc ...
, Tanith Lee, A. A. Milne, and P. G. Wodehouse have all written Sherlock Holmes pastiches. Contemporary with Conan Doyle, Maurice Leblanc directly featured Holmes in his popular series about the gentleman thief, Arsène Lupin
Arsène Lupin () is a fictional gentleman thief and master of disguise created in 1905 by French writer Maurice Leblanc. The character was first introduced in a series of short stories serialized in the magazine '' Je sais tout''. The first ...
, though legal objections from Conan Doyle forced Leblanc to modify the name to "Herlock Sholmes" in reprints and later stories. Mystery writer John Dickson Carr collaborated with Arthur Conan Doyle's son, Adrian Conan Doyle, on '' The Exploits of Sherlock Holmes'', a pastiche collection from 1954. In 2011, Anthony Horowitz published a Sherlock Holmes novel, '' The House of Silk'', presented as a continuation of Conan Doyle's work and with the approval of the Conan Doyle estate; a follow-up, '' Moriarty'', appeared in 2014. The "MX Book of New Sherlock Holmes Stories" series of pastiches, edited by David Marcum and published by MX Publishing, contains fifty-two volumes and features hundreds of stories echoing the original canon which were compiled for the restoration of Undershaw and the support of Stepping Stones School, now housed in it.
In 1980's '' The Name of the Rose'', Italian author Umberto Eco creates a Sherlock Holmes of the 1320s in the form of a Franciscan friar and main protagonist named Brother William of Baskerville, his name a clear reference to Holmes per '' The Hound of the Baskervilles''.beekeeping
Beekeeping (or apiculture, from ) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in artificial beehives. Honey bees in the genus '' Apis'' are the most commonly kept species but other honey producing bees such as '' Melipona'' stingless bees are ...
who tackles the case of a missing parrot belonging to a Jewish refugee boy. Mitch Cullin's novel '' A Slight Trick of the Mind'' (2005) takes place two years after the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and explores an old and frail Sherlock Holmes (now 93) as he comes to terms with a life spent in emotionless logic; this was also adapted into a film, 2015's '' Mr. Holmes''.
Minor characters
Some authors have written tales centred on characters from the canon other than Holmes. Anthologies edited by Michael Kurland and George Mann are entirely devoted to stories told from the perspective of characters other than Holmes and Watson. John Gardner, Michael Kurland, and Kim Newman, amongst many others, have all written tales in which Holmes's nemesis Professor Moriarty is the main character. Mycroft Holmes has been the subject of several efforts: ''Enter the Lion'' by Michael P. Hodel and Sean M. Wright (1979), a four-book series by Quinn Fawcett, and 2015's '' Mycroft Holmes'', by Kareem Abdul-Jabbar and Anna Waterhouse. M. J. Trow has written a series of seventeen books using Inspector Lestrade as the central character, beginning with ''The Adventures of Inspector Lestrade'' in 1985. Carole Nelson Douglas' Irene Adler series is based on "the woman" from "A Scandal in Bohemia", with the first book (1990's ''Good Night, Mr. Holmes'') retelling that story from Adler's point of view. Martin Davies has written three novels where Baker Street housekeeper Mrs. Hudson is the protagonist.
Parodies
A popular form of Holmesian pastiche is the parody
A parody is a creative work designed to imitate, comment on, and/or mock its subject by means of satire, satirical or irony, ironic imitation. Often its subject is an Originality, original work or some aspect of it (theme/content, author, style, e ...
. "My Evening with Sherlock Holmes", by J. M. Barrie, was released in 1891, four years after Holmes first appearance in print and four months after “A Scandal in Bohemia” appeared in ''The Strand''; it is generally considered a parody.Ellery Queen
Ellery Queen is a pseudonym created in 1928 by the American detective fiction writers Frederic Dannay (1905–1982) and Manfred Bennington Lee (1905–1971). It is also the name of their main fictional detective, a mystery writer in New York City ...
) published '' The Misadventures of Sherlock Holmes'', a collection of thirty-three pastiches written by various well-known authors, featuring numerous parodies.
Scholarly works
There have been many scholarly works dealing with Sherlock Holmes, some working within the bounds of the Great Game, and some written from the perspective that Holmes is a fictional character. In particular, there have been three major annotated editions of the complete series. The first was William Baring-Gould's 1967 ''The Annotated Sherlock Holmes''. This two-volume set was ordered to fit Baring-Gould's preferred chronology, and was written from a Great Game perspective. The second was 1993's ''The Oxford Sherlock Holmes'' (general editor: Owen Dudley Edwards), a nine-volume set written in a straight scholarly manner. The most recent is Leslie Klinger's '' The New Annotated Sherlock Holmes'' (2004–05), a three-volume set that returns to a Great Game perspective.
Adaptations in other media
In 2012, ''Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, list ...
'' listed Holmes as the most portrayed literary human character in film and television history, with more than 75 actors playing the part in over 250 productions.Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
'', by Conan Doyle and William Gillette, was a synthesis of several Conan Doyle stories. In addition to its popularity, the play is significant because it, rather than the original stories, introduced one of the key visual qualities commonly associated with Holmes today: his calabash pipe; the play also formed the basis for Gillette's 1916 film, ''Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
''. Gillette performed as Holmes some 1,300 times. In the early 1900s, H. A. Saintsbury
Harry Arthur Saintsbury, usually called H. A. Saintsbury (18 December 1869 – 19 June 1939), was an English people, English actor and playwright. A leading man, he became well known for his stage interpretation of Sherlock Holmes, was an early ...
took over the role from Gillette for a tour of the play. Between this play and Conan Doyle's own stage adaptation of " The Adventure of the Speckled Band", Saintsbury portrayed Holmes over 1,000 times.
Holmes's first screen appearance was in the 1900 Mutoscope film, '' Sherlock Holmes Baffled''.20th Century Fox
20th Century Studios, Inc., formerly 20th Century Fox, is an American film studio, film production and Film distributor, distribution company owned by the Walt Disney Studios (division), Walt Disney Studios, the film studios division of the ...
and a dozen for Universal Pictures
Universal City Studios LLC, doing business as Universal Pictures (also known as Universal Studios or simply Universal), is an American filmmaking, film production and film distribution, distribution company headquartered at the 10 Universal Ci ...
) and in '' The New Adventures of Sherlock Holmes'' radio show. While the Fox films were period pieces, the Universal films abandoned Victorian Britain and moved to a then-contemporary setting in which Holmes occasionally battled Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
.
The character has also enjoyed numerous radio adaptations, beginning with Edith Meiser's '' The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes'', which ran from 1930 to 1936. Basil Rathbone and Nigel Bruce continued with their roles for most of the run of '' The New Adventures of Sherlock Holmes'', airing from 1939 to 1950. Bert Coules, having dramatised the entire Holmes canon for BBC Radio Four from 1989 to 1998,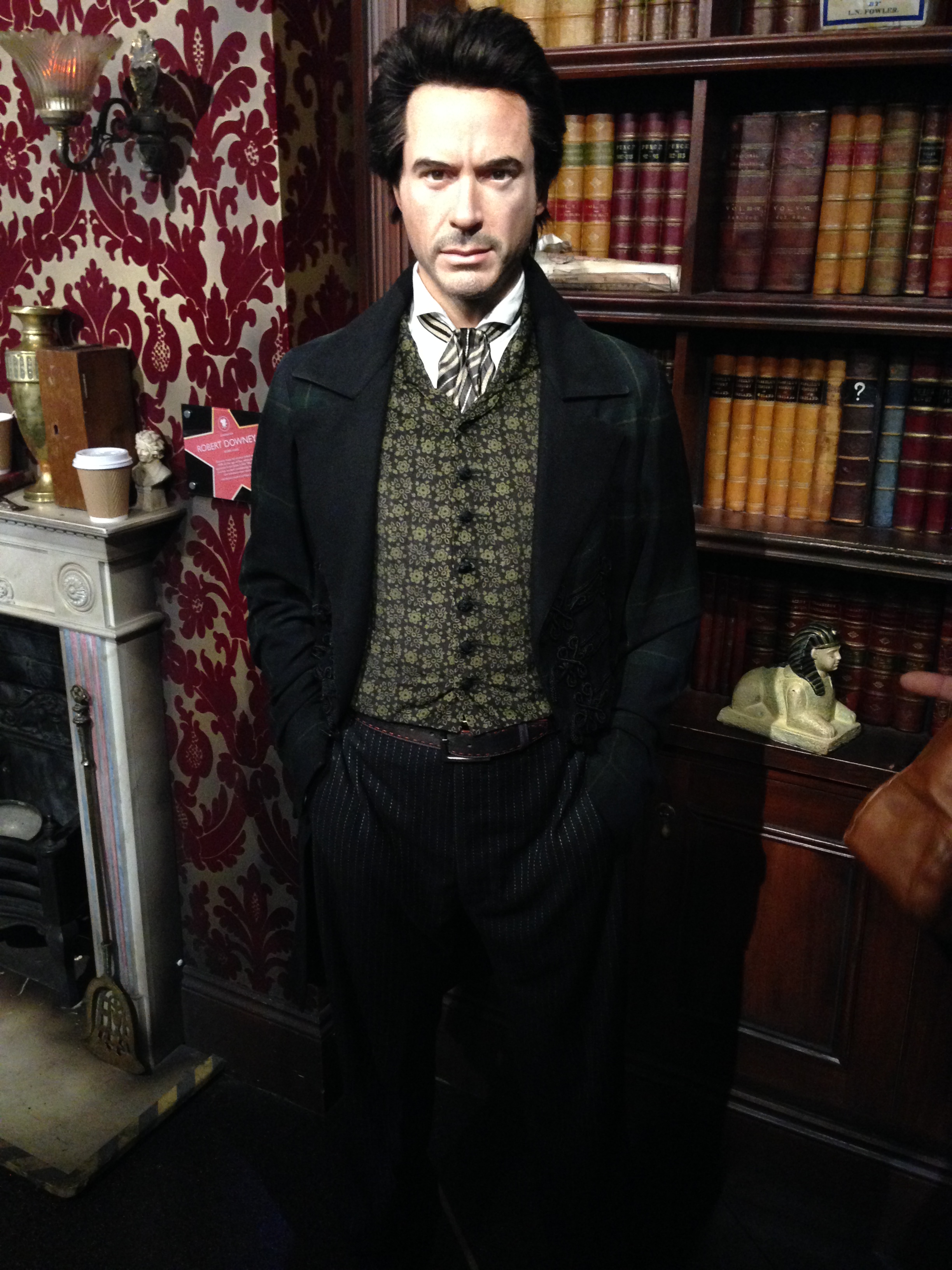 The 1984–85 Italian/Japanese
The 1984–85 Italian/Japanese anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
series '' Sherlock Hound'' adapted the Holmes stories for children, with its characters being anthropomorphic dogs. The series was co-directed by Hayao Miyazaki
is a Japanese animator, filmmaker, and manga artist. He co-founded Studio Ghibli and serves as honorary chairman. Throughout his career, Miyazaki has attained international acclaim as a masterful storyteller and creator of Anime, Japanese ani ...
. Between 1979 and 1986, the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
studio Lenfilm produced a series of five television films, '' The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson''. The series were split into eleven episodes and starred Vasily Livanov as Holmes and Vitaly Solomin as Watson. For his performance, in 2006 Livanov was appointed an Honorary Member of the Order of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding valuable service in a wide range of useful activities. It comprises five classes of awards across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two o ...
.
Jeremy Brett
Peter Jeremy William Huggins (3 November 1933 – 12 September 1995), known professionally as Jeremy Brett, was an English actor. He is best known for his portrayal of Sherlock Holmes from 1984 to 1994 in 41 episodes of a Sherlock Holmes (1984 TV ...
played the detective in ''Sherlock Holmes'' for Granada Television from 1984 to 1994. Watson was played by David Burke (in the first two series) and Edward Hardwicke (in the remainder). Brett and Hardwicke also appeared on stage in 1988–89 in ''The Secret of Sherlock Holmes'', directed by Patrick Garland.
In the 2004–2012 Fox's show ''House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air c ...
'', the titular character Gregory House is an adaptation of Sherlock Holmes in a medical drama setting. The two characters share many parallels and House's name is a play on Holmes' one.Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
'' earned Robert Downey Jr. a Golden Globe Award
The Golden Globe Awards are awards presented for excellence in both international film and television. It is an annual award ceremony held since 1944 to honor artists and professionals and their work. The ceremony is normally held every Janua ...
for his portrayal of Holmes and co-starred Jude Law as Watson. Downey and Law returned for a 2011 sequel, '' Sherlock Holmes: A Game of Shadows''.
Benedict Cumberbatch
Benedict Timothy Carlton Cumberbatch (born 19 July 1976) is an English actor. He has received List of awards and nominations received by Benedict Cumberbatch, various accolades, including a BAFTA TV Award, a Primetime Emmy Award and a Laurenc ...
plays a modern version of the detective and Martin Freeman as a modern version of John Watson in the BBC One
BBC One is a British free-to-air public broadcast television channel owned and operated by the BBC. It is the corporation's oldest and flagship channel, and is known for broadcasting mainstream programming, which includes BBC News television b ...
TV series '' Sherlock'', which premiered in 2010. In the series, created by Mark Gatiss
Mark Gatiss (; born 17 October 1966) is an English actor, comedian, screenwriter, director, producer and novelist. Best known for his acting work on stage and screen as well as for co-creating television shows with Steven Moffat, he has received ...
and Steven Moffat, the stories' original Victorian setting is replaced by present-day London, with Watson a veteran of the modern War in Afghanistan. Similarly, '' Elementary'' premiered on CBS in 2012 and ran for seven seasons until 2019. Set in contemporary New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, the series stars Jonny Lee Miller as Sherlock Holmes and Lucy Liu as a female Dr. Joan Watson. The series was filmed primarily in New York City, and, by the end of season two, Miller became the actor who had portrayed Sherlock Holmes the most in television and/or film.
The 2015 film '' Mr. Holmes'' starred Ian McKellen as a retired Sherlock Holmes living in Sussex, in 1947, who grapples with an unsolved case involving a beautiful woman. The film is based on Mitch Cullin's 2005 novel '' A Slight Trick of the Mind''.
The 2018 television adaptation, '' Miss Sherlock'', was a Japanese-language production and the first adaptation with a woman (portrayed by Yūko Takeuchi) in the signature role. The episodes were based in modern-day Tokyo, with many references to Conan Doyle's stories.
Holmes has also appeared in video games, including the ''Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
'' series of eight main titles. According to the publisher, Frogwares, by 2017 the series sold over seven million copies.
Copyright issues
The copyright for Conan Doyle's works expired in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia at the end of 1980, fifty years after Conan Doyle's death.public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
in those countries.
Works
Novels
* '' A Study in Scarlet'' (published November 1887 in '' Beeton's Christmas Annual'')
* '' The Sign of the Four'' (published February 1890 in ''Lippincott's Monthly Magazine
''Lippincott's Monthly Magazine'' was a 19th-century literary magazine published in Philadelphia from 1868 to 1915, when it relocated to New York to become ''Robert M. McBride, McBride's Magazine''. It merged with ''Scribner's Magazine'' in 1916. ...
'')
* '' The Hound of the Baskervilles'' (serialised 1901–1902 in ''The Strand'')
* '' The Valley of Fear'' (serialised 1914–1915 in ''The Strand'')
Short story collections
The short stories, originally published in magazines, were later collected in five anthologies:
* '' The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes'' (stories published 1891–1892 in ''The Strand'')
* '' The Memoirs of Sherlock Holmes'' (stories published 1892–1893 in ''The Strand'')
* '' The Return of Sherlock Holmes'' (stories published 1903–1904 in ''The Strand'')
* '' His Last Bow: Some Later Reminiscences of Sherlock Holmes'' (stories published 1908–1917)
* '' The Case-Book of Sherlock Holmes'' (stories published 1921–1927)
See also
* List of Holmesian studies
* Popular culture references to Sherlock Holmes
* Sherlock Holmes fandom
* Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Hol ...
* Professor Moriarty
* Jack the Ripper
Notes
Sherlock Holmes story references
* Klinger, Leslie (ed.). ''The New Annotated Sherlock Holmes, Volume I'' (New York: W. W. Norton, 2005). ("Klinger I")
* Klinger, Leslie (ed.). ''The New Annotated Sherlock Holmes, Volume II'' (New York: W. W. Norton, 2005). ("Klinger II")
* Klinger, Leslie (ed.). ''The New Annotated Sherlock Holmes, Volume III'' (New York: W. W. Norton, 2006). ("Klinger III")
Citations
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Fenoli Marc, Qui a tué Sherlock Holmes ? ho shot Sherlock Holmes ? Review L'Alpe 45, Glénat-Musée Dauphinois, Grenoble-France, 2009.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Lieboe, Eli. ''Doctor Joe Bell: Model for Sherlock Holmes''. Bowling Green, Ohio: Bowling Green University Popular Press, 1982; Madison, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin Press
The University of Wisconsin Press (sometimes abbreviated as UW Press) is a Non-profit organization, non-profit university press publishing Peer review, peer-reviewed books and journals. It publishes work by scholars from the global academic comm ...
, 2007.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Previously published as chapter 2, pp. 17–52 of
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
The Sherlock Holmes Museum
221b Baker Street London NW1 6XE England.
*
Sherlock Holmes plaques
on openplaques.org
at Stanford University
essay by Edward Winter
"The Burden of Holmes"
– 23.12.09 article in ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' (''WSJ''), also referred to simply as the ''Journal,'' is an American newspaper based in New York City. The newspaper provides extensive coverage of news, especially business and finance. It operates on a subscriptio ...
''
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle audio books
by Lit2Go from the University of South Florida
The University of South Florida (USF) is a Public university, public research university with its main campus located in Tampa, Florida, Tampa, Florida, United States, and other campuses in St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg and Sarasota, ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Holmes, Sherlock
English male characters in television
Crime film characters
Culture of the United Kingdom
Edwardian era
Fictional beekeepers
Fictional British detectives
Fictional chemists
Fictional cocaine users
Fictional criminologists
Fictional opioid users
Fictional English people
Fictional gentleman detectives
Fictional private investigators
Fictional spies
Fictional violinists
Literary characters introduced in 1887
Male characters in film
Male characters in literature
Male characters in television
Martial artist characters in literature
Sherlock Holmes characters
Thriller film characters
Victorian culture
Fictional characters with eidetic memory
Fictional characters from the 19th century
Fictional characters incorrectly presumed dead
 In the first tale of Sherlock Holmes, ''A Study in Scarlet'', financial difficulties lead Holmes and Dr. Watson to share rooms together at 221B Baker Street, London. Their residence is maintained by their landlady, Mrs. Hudson. Holmes works as a detective for twenty-three years, with Watson assisting him for seventeen of those years. Most of the stories are frame narratives written from Watson's point of view, as summaries of the detective's most interesting cases. Holmes frequently calls Watson's records of Holmes's cases sensational and populist, suggesting that they fail to accurately and objectively report the "science" of his craft:
Nevertheless, when Holmes recorded a case himself, he was forced to concede that he could more easily understand the need to write it in a manner that would appeal to the public rather than his intention to focus on his own technical skill.
Holmes's friendship with Watson is his most significant relationship. When Watson is injured by a bullet, although the wound turns out to be "quite superficial", Watson is moved by Holmes's reaction:
After confirming Watson's assessment of the wound, Holmes makes it clear to their opponent that the man would not have left the room alive if he genuinely had killed Watson.
In the first tale of Sherlock Holmes, ''A Study in Scarlet'', financial difficulties lead Holmes and Dr. Watson to share rooms together at 221B Baker Street, London. Their residence is maintained by their landlady, Mrs. Hudson. Holmes works as a detective for twenty-three years, with Watson assisting him for seventeen of those years. Most of the stories are frame narratives written from Watson's point of view, as summaries of the detective's most interesting cases. Holmes frequently calls Watson's records of Holmes's cases sensational and populist, suggesting that they fail to accurately and objectively report the "science" of his craft:
Nevertheless, when Holmes recorded a case himself, he was forced to concede that he could more easily understand the need to write it in a manner that would appeal to the public rather than his intention to focus on his own technical skill.
Holmes's friendship with Watson is his most significant relationship. When Watson is injured by a bullet, although the wound turns out to be "quite superficial", Watson is moved by Holmes's reaction:
After confirming Watson's assessment of the wound, Holmes makes it clear to their opponent that the man would not have left the room alive if he genuinely had killed Watson.
 Watson describes Holmes as " bohemian" in his habits and lifestyle. Said to have a "cat-like" love of personal cleanliness, at the same time Holmes is an eccentric with no regard for contemporary standards of tidiness or good order. Watson describes him as
While Holmes is characterised as dispassionate and cold, he can be animated and excitable during an investigation. He has a flair for showmanship, often keeping his methods and evidence hidden until the last possible moment so as to impress observers. Holmes is willing to break the law as a means for righting a wrong, contending that "there are certain crimes which the law cannot touch, and which therefore, to some extent, justify private revenge." His companion condones the detective's willingness to do this on behalf of a client—lying to the police, concealing evidence or breaking into houses—when he also feels it morally justifiable.
Except for that of Watson, Holmes avoids casual company. In "The ''Gloria Scott''", he tells the doctor that during two years at college he made only one friend: "I was never a very sociable fellow, Watson ... I never mixed much with the men of my year."Klinger I, p. 502—"The ''Gloria Scott''" The detective goes without food at times of intense intellectual activity, believing that "the faculties become refined when you starve them". At times, Holmes relaxes with music, either playing the violin or enjoying the works of composers such as Wagner and Pablo de Sarasate.
Watson describes Holmes as " bohemian" in his habits and lifestyle. Said to have a "cat-like" love of personal cleanliness, at the same time Holmes is an eccentric with no regard for contemporary standards of tidiness or good order. Watson describes him as
While Holmes is characterised as dispassionate and cold, he can be animated and excitable during an investigation. He has a flair for showmanship, often keeping his methods and evidence hidden until the last possible moment so as to impress observers. Holmes is willing to break the law as a means for righting a wrong, contending that "there are certain crimes which the law cannot touch, and which therefore, to some extent, justify private revenge." His companion condones the detective's willingness to do this on behalf of a client—lying to the police, concealing evidence or breaking into houses—when he also feels it morally justifiable.
Except for that of Watson, Holmes avoids casual company. In "The ''Gloria Scott''", he tells the doctor that during two years at college he made only one friend: "I was never a very sociable fellow, Watson ... I never mixed much with the men of my year."Klinger I, p. 502—"The ''Gloria Scott''" The detective goes without food at times of intense intellectual activity, believing that "the faculties become refined when you starve them". At times, Holmes relaxes with music, either playing the violin or enjoying the works of composers such as Wagner and Pablo de Sarasate.
 Though Holmes is famed for his reasoning capabilities, his investigative technique relies heavily on the acquisition of hard evidence. Many of the techniques he employs in the stories were at the time in their infancy.
The detective is particularly skilled in the analysis of trace evidence and other physical evidence, including latent prints (such as footprints, hoof prints, and shoe and tire impressions) to identify actions at a crime scene, using tobacco ashes and cigarette butts to identify criminals, utilizing handwriting analysis and
Though Holmes is famed for his reasoning capabilities, his investigative technique relies heavily on the acquisition of hard evidence. Many of the techniques he employs in the stories were at the time in their infancy.
The detective is particularly skilled in the analysis of trace evidence and other physical evidence, including latent prints (such as footprints, hoof prints, and shoe and tire impressions) to identify actions at a crime scene, using tobacco ashes and cigarette butts to identify criminals, utilizing handwriting analysis and  The detective is described (or demonstrated) as possessing above-average physical strength. In " The Yellow Face", Holmes's chronicler says, "Few men were capable of greater muscular effort." In " The Adventure of the Speckled Band", Dr. Roylott demonstrates his strength by bending a fire poker in half. Watson describes Holmes as laughing and saying, If he had remained I might have shown him that my grip was not much more feeble than his own.' As he spoke he picked up the steel poker and, with a sudden effort, straightened it out again."
Holmes is an adept bare-knuckle fighter; " The ''Gloria Scott''" mentions that Holmes boxed while at university. In ''The Sign of Four'', he introduces himself to McMurdo, a prize fighter, as "the
The detective is described (or demonstrated) as possessing above-average physical strength. In " The Yellow Face", Holmes's chronicler says, "Few men were capable of greater muscular effort." In " The Adventure of the Speckled Band", Dr. Roylott demonstrates his strength by bending a fire poker in half. Watson describes Holmes as laughing and saying, If he had remained I might have shown him that my grip was not much more feeble than his own.' As he spoke he picked up the steel poker and, with a sudden effort, straightened it out again."
Holmes is an adept bare-knuckle fighter; " The ''Gloria Scott''" mentions that Holmes boxed while at university. In ''The Sign of Four'', he introduces himself to McMurdo, a prize fighter, as "the 
 The London
The London  Although Holmes is not the original fictional detective, his name has become synonymous with the role. Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories introduced multiple literary devices that have become major conventions in detective fiction, such as the companion character who is not as clever as the detective and has solutions explained to him (thus informing the reader as well), as with Dr. Watson in the Holmes stories. Other conventions introduced by Doyle include the arch-criminal who is too clever for the official police to defeat, like Holmes's adversary Professor Moriarty, and the use of forensic science to solve cases.
The Sherlock Holmes stories established crime fiction as a respectable genre popular with readers of all backgrounds, and Doyle's success inspired many contemporary detective stories. Holmes influenced the creation of other "eccentric gentleman detective" characters, like
Although Holmes is not the original fictional detective, his name has become synonymous with the role. Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories introduced multiple literary devices that have become major conventions in detective fiction, such as the companion character who is not as clever as the detective and has solutions explained to him (thus informing the reader as well), as with Dr. Watson in the Holmes stories. Other conventions introduced by Doyle include the arch-criminal who is too clever for the official police to defeat, like Holmes's adversary Professor Moriarty, and the use of forensic science to solve cases.
The Sherlock Holmes stories established crime fiction as a respectable genre popular with readers of all backgrounds, and Doyle's success inspired many contemporary detective stories. Holmes influenced the creation of other "eccentric gentleman detective" characters, like  The 1984–85 Italian/Japanese
The 1984–85 Italian/Japanese