septate junctions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
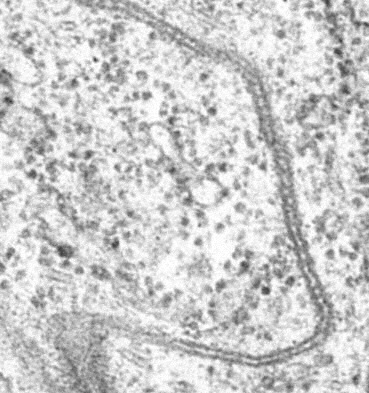 Septate junctions are intercellular junctions found in invertebrate epithelial cells, appearing as ladder-like structures under
Septate junctions are intercellular junctions found in invertebrate epithelial cells, appearing as ladder-like structures under
 Septate junctions are intercellular junctions found in invertebrate epithelial cells, appearing as ladder-like structures under
Septate junctions are intercellular junctions found in invertebrate epithelial cells, appearing as ladder-like structures under electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a ...
. They are thought to provide structural strength and a barrier to solute diffusion through the intercellular space. They are considered somewhat analogous to the (vertebrate) tight junction
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
s; however, tight and septate junctions are different in many ways. Known insect homologues of tight junction components are components of conserved signalling pathways that localize to either adherens junction
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or "belt desmosome") are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. ...
s, the subapical complex, or the marginal zone
Zone or The Zone may refer to:
Places Climate and altitude zones
* Death zone (originally the lethal zone), altitudes above a certain point where the amount of oxygen is insufficient to sustain human life for an extended time span
* Frigid zone, ...
. Recent studies show that septate junctions are also identified in the myelinated nerve fibers of the vertebrates.
Structure
The main trait of septate junctions structure is that cross-bridges or septa are in the ladder-like shape and cover the 15–20 nm intermembrane space of cell–cell contacts. Septate junctions are in a tight arrangement which is parallel to each other. For the septate junctions, several components are related to the function or the morphology of septate junctions, like Band 4.1-Coracle, Discs-large, fasciclin III, Neurexin IV (NRX) and so on. Band 4.1-Coracle is necessary for the interaction of the cell. Discs-large, a key component of septate junctions, is needed for the growth control. Fasciclin III acts as an adhesion protein. Neurexin IV (NRX) is a required transmembrane protein for the formation of septate junctions. For example, the glial–glial septate junctions that lack NRX will cause the blood barriers to break down. Gliotactin (Gli), is also a necessary a transmembrane protein for the formation of pleated septate junctions. Tsp2A and Undicht are newly identified components that are needed for the formation of smooth septate junctions and septate junctions. There are three knownclaudin
Claudins are a family of proteins which, along with occludin, are the most important components of the tight junctions ( zonulae occludentes). Tight junctions establish the paracellular barrier that controls the flow of molecules in the intercel ...
s contained in the septate junctions, Megatrachea (Mega), Sinuous (Sinu) and Kune-kune (Kune). Among these three claudin
Claudins are a family of proteins which, along with occludin, are the most important components of the tight junctions ( zonulae occludentes). Tight junctions establish the paracellular barrier that controls the flow of molecules in the intercel ...
s, Kune-kune (Kune) plays a more central role in septate junctions organization and function.
Function
There are several functions of septate junctions. * Pleated SJs(pSJs) play roles in development and cell signaling. * Form the mechanical link between cells which can densely pack the epithelial sheaths. * Intermediate the adjacent cells interaction. * Prevent the freediffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
of water and solutes among adjacent epithelial cells.
* Preserve the epithelial polarity and cell adhesion.
*Have a function in the morphogenesis like tracheal morphology that regulate the cell size and the cell length.
*Regulate cell proliferation.
*Characterize the properties of the paracellular pathway in insect Malpighian tubules (MTs).
*Some unusual septate junctions have the function in ''the Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many s ...
'' testis
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster ...
like keeping premature sperm staying inside.
For the septate junctions in the vertebrates, they play some roles of tight junctions.
Na+/K+ ATPase works for the function of septate junctions.
Classification
In ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or " pomace fly". Starting with ...
'', there are two types of septate junctions, smooth SJs (sSJs) and pleated SJs(pSJs). sSJs and pSJs are distributed in different tissues. sSJs are in gut endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
and Malpighian tubules
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids and tardigrades.
The system consists of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water ...
, while pSJs are in the ectodermally derived epithelia. sSJs and pSJs vary in shape but have the same function.
See also
*Tight junction
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
s
* Adherens junction
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or "belt desmosome") are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. ...
s
* Desmosome
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adh ...
s
*Hemidesmosomes
Hemidesmosomes are very small stud-like structures found in keratinocytes of the epidermis of skin that attach to the extracellular matrix. They are similar in form to desmosomes when visualized by electron microscopy, however, desmosomes attach to ...
* Gap junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regula ...
s
References
{{Reflist Cell anatomy Cell biology