Semna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The region of Semna is 15 miles south of
The region of Semna is 15 miles south of
 The fort had several advanced features – the mudbrick walls were reinforced with logs, there were doubly fortified gates, there was a fortified corridor down to the Nile allowing ready access to water supplies. The logs increased the vulnerability to fire, and traces of fires can be seen on the walls.
The fort had several advanced features – the mudbrick walls were reinforced with logs, there were doubly fortified gates, there was a fortified corridor down to the Nile allowing ready access to water supplies. The logs increased the vulnerability to fire, and traces of fires can be seen on the walls.
 They found little evidence of Middle Kingdom occupation, but did discover ruins of a Christian settlement at Semna South. The Christian settlement was not fully excavated by the Sudan Antiquities Service expedition, but they did note that the houses had been reconstructed by the Christian inhabitants and that they had built a new stone girdle wall around the west side of the fort. They concluded that the Christian settlement had been inhabited by a fairly poor community.
They found little evidence of Middle Kingdom occupation, but did discover ruins of a Christian settlement at Semna South. The Christian settlement was not fully excavated by the Sudan Antiquities Service expedition, but they did note that the houses had been reconstructed by the Christian inhabitants and that they had built a new stone girdle wall around the west side of the fort. They concluded that the Christian settlement had been inhabited by a fairly poor community.
 The Oriental Institute Expedition also excavated the large cemetery to the north of the fort. This cemetery contained approximately 560 graves—representing over 800 individuals—of which about 494 were from the Meroitic period (4th century BC – 4th century AD), 50 from the
The Oriental Institute Expedition also excavated the large cemetery to the north of the fort. This cemetery contained approximately 560 graves—representing over 800 individuals—of which about 494 were from the Meroitic period (4th century BC – 4th century AD), 50 from the
 Excavated between 1956–57 and 1966–68, Semna South is a 12th Dynasty fort located in
Excavated between 1956–57 and 1966–68, Semna South is a 12th Dynasty fort located in
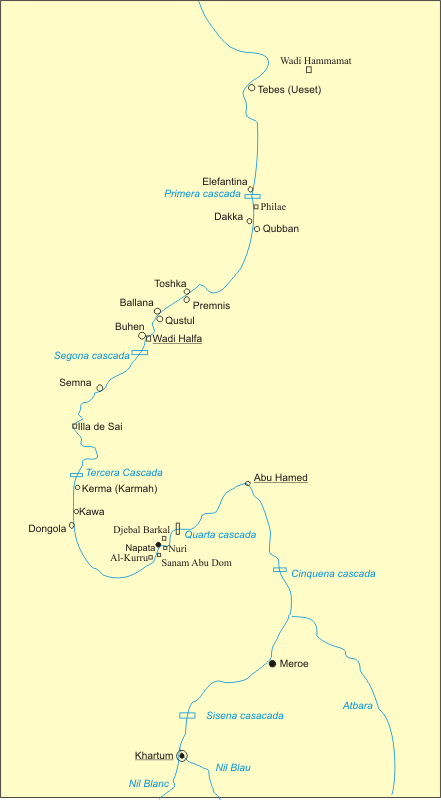
 The region of Semna is 15 miles south of
The region of Semna is 15 miles south of Wadi Halfa
(, , ":wikt:esparto, Esparto Valley") is a city in the Northern (state), Northern state of Sudan on the shores of Lake Nasser, Lake Nubia near the Egypt–Sudan border, border with Egypt. It is the terminus of a rail transport in Sudan, rail lin ...
and is situated where rocks cross the Nile narrowing its flow—the Semna Cataract.
Semna was a fortified area established in the reign of Senusret I
Senusret I (Egyptian language, Middle Egyptian: wikt:z-n-wsrt, z-n-wsrt; /suʀ nij ˈwas.ɾiʔ/) also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 ...
(1965–1920 BC) on the west bank of the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
at the southern end of a series of Middle Kingdom fortresses founded during the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is a series of rulers reigning from 1991–1802 BC (190 years), at what is often considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom (Dynasties XI–XIV). The dynasty period ...
(1985–1795 BC) in the Second-Cataract area of Lower Nubia
Lower Nubia (also called Wawat) is the northernmost part of Nubia, roughly contiguous with the modern Lake Nasser, which submerged the historical region in the 1960s with the construction of the Aswan High Dam. Many ancient Lower Nubian monuments, ...
. There are three forts at Semna: Semna West (Semna Gharb), Semna East (Semna Sherq, also called Kummeh or Kumma), and Semna South (Semna Gubli). The forts to the east and west of the Semna Cataract are Semna East and West, respectively; Semna South is approximately one kilometer south of Semna West on the west bank of the Nile.
The Semna gorge, at the southern edge of ancient Egypt, was the narrowest part of the Nile valley. It was here, at this strategic location, that the 12th Dynasty pharaohs built a cluster of four mud-brick fortresses: Semna, Kumma, Semna South and Uronarti
Uronarti is an island and archaeological site in the Nile just south of the Cataracts of the Nile, Second Cataract in the north of Sudan. The site features a massive ancient fortress that still stands on its northern end. This fortress is one of ...
— all covered by the waters of Lake Nasser
Lake Nasser ( ', ) is a large reservoir (water), reservoir in southern Egypt and northern Sudan. It was created by the construction of the Aswan Dam, Aswan High Dam and is one of the List of reservoirs by volume, largest man-made lakes in the wo ...
since the completion of the Aswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, surpassing the Chatuge D ...
in 1971. Many of its monuments were relocated as part of the International Campaign to Save the Monuments of Nubia
The International Campaign to Save the Monuments of Nubia was the effort to relocate 22 monuments in Lower Nubia, in Southern Egypt and northern Sudan, between 1960 and 1980. This was done in order to make way for the building of the Aswan Dam, a ...
.
Archaeology of Semna
The rectangular Kumma fortress, the L-shaped Semna fortress (on the opposite bank) and the smaller square fortress of Semna South were each investigated by the American archaeologist George Reisner in 1924 and 1928. Semna and Kumma also included the remains of temples, houses and cemeteries dating to the New Kingdom (1550–1069 BC), which would have been roughly contemporary with such lower Nubian towns as Amara West and Sesebisudla, when the second cataract region had become part of an Egyptian 'empire', rather than simply a frontier zone. The fort had several advanced features – the mudbrick walls were reinforced with logs, there were doubly fortified gates, there was a fortified corridor down to the Nile allowing ready access to water supplies. The logs increased the vulnerability to fire, and traces of fires can be seen on the walls.
The fort had several advanced features – the mudbrick walls were reinforced with logs, there were doubly fortified gates, there was a fortified corridor down to the Nile allowing ready access to water supplies. The logs increased the vulnerability to fire, and traces of fires can be seen on the walls.
Semna South Fort
As a 12th Dynasty fort, Semna South is one of 17 Middle Kingdom Egyptian forts in Nubia built for the purpose of controlling trade traffic along the Nile. The Egyptian state placed great importance on control of Nubia and its goods. As Reisner (1929) notes, “the southern products, the ebony, the ivory, the pelts, the incense and resin, the ostrich feathers, the black slaves, were as much desired by the kings of the Middle Kingdom as by their forebears”. Thus, forts were built along the Nile to protect the waterway from nomadic tribes and to facilitate the flow of Nubian goods into Egypt. Forts surrounding Semna South were excavated by the Joint Egyptian Expedition ofHarvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and the Boston Museum of Fine Arts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
in the 1920s, but Semna South was not formally excavated until the late 1950s. The initial excavation of the fort was directed by Jean Vercoutter and Sayed Thabit Hassan Thabit with the Sudan Antiquities Service in 1956–1957. Further excavations of the fort and an adjacent cemetery were conducted by the Oriental Institute Expedition to Sudanese Nubia, under the direction of Dr. Louis Vico Žabkar, in 1966–1968. Today, the human remains from Semna South are curated at Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public university, public research university in Tempe, Arizona, United States. Founded in 1885 as Territorial Normal School by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, the university is o ...
and the archaeological artifacts are curated at the University of Chicago Oriental Institute
The Institute for the Study of Ancient Cultures, West Asia & North Africa (ISAC), formerly known as the Oriental Institute, is the University of Chicago's interdisciplinary research center for ancient Near Eastern studies and archaeology museum. ...
.(H. McDonald, personal communication, October 22, 2012).
Site geology and geography
Semna South is located in the Batn-El-Hajar (“Belly of the Rock”) region of Nubia between the second and third cataracts. As its name implies, the Batn-El-Hajar is “characterized by ‘baregranite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
ridges and gullies’, a narrowed Nile run, and heavy deposits of wind-blown sand". Semna is situated above a geological formation known as the Basement Complex; this complex is a deposit of Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
and later igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
. There is only a thin layer of fertile alluvial soil
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
overlying this complex which results in poor agricultural potential.
Archaeological excavations of Semna South
While the fort at Semna South was described by Reisner (1929), it was not formally excavated until 1956–1957 by the Sudan Antiquities Service under the direction of Jean Vercoutter and Sayed Thabit Hassan Thabit. This excavation explored the majority (four-fifths) of the fort and “made a limited trial digging” in the adjacent Meroitic cemetery. Vercoutter (1966) notes that their work was preliminary and by no means complete. He encouraged further investigation of the site: “it seems of the utmost importance for the history of the site that new excavations are undertaken at Semna South before its flooding under the waters of the new Aswan Dam”. Beginning in 1966 the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago continued excavating where Vercoutter and colleagues had ended. Between 1966 and 1968 the University of Chicago Oriental Institute Expedition to Sudanese Nubia excavated the remainder of the Semna South fort and the adjacent cemetery. Detailed excavations were conducted of the fort walls, a church, a dump site, and the cemetery. To the author's knowledge, this was the final archaeological excavation conducted at Semna South.Results and significance of the excavations
Results from the 1950s
During the 1956–1957 field season, Vercoutter and colleagues were able to interpret the building plan of the fort. The building is composed of the following features: aglacis
A glacis (, ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glaci ...
, outer girdle wall, an inner ditch, a main wall, and an open inner space. They concluded that the fort was never inhabited permanently; rather, it was occupied for limited periods of time by men of the garrison coming from the fort at Semna West.  They found little evidence of Middle Kingdom occupation, but did discover ruins of a Christian settlement at Semna South. The Christian settlement was not fully excavated by the Sudan Antiquities Service expedition, but they did note that the houses had been reconstructed by the Christian inhabitants and that they had built a new stone girdle wall around the west side of the fort. They concluded that the Christian settlement had been inhabited by a fairly poor community.
They found little evidence of Middle Kingdom occupation, but did discover ruins of a Christian settlement at Semna South. The Christian settlement was not fully excavated by the Sudan Antiquities Service expedition, but they did note that the houses had been reconstructed by the Christian inhabitants and that they had built a new stone girdle wall around the west side of the fort. They concluded that the Christian settlement had been inhabited by a fairly poor community.
Results from the 1960s
=Architectural findings
= The 1966–1968 excavations at Semna South determined, contrary to Vercoutter, that the fort was permanently occupied from the reign of Senusret I to the first few years of reign ofAmenemhat III
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.''
Amenemhat III (Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet III, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the sixth king of the Twelfth Dyn ...
of the 12th Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is a series of rulers reigning from 1991–1802 BC (190 years), at what is often considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom (Dynasties XI–XIV). The dynasty periodically expanded its terr ...
. Excavations of the church, sometimes called the “Sheik’s tomb,” revealed that only a portion of the original structure still remained. As of 1982 when Žabkar and Žabkar published their report, they were not able to date the church due to the paucity of pottery within the church or nearby. However, they did provide a hypothetical estimate: “the church in its final, that is apsidal, form would date to the classic Christian period in Nubia, somewhere between the ninth and the first part of the eleventh century A.D.".
This expedition unearthed a great wall which connected the forts at Semna South and Semna West. This wall strengthened the view that the military fortifications in the Semna region were built by the Egyptians in response to the “strong pressures and infiltration attempts on the part of southerners during the 12th Dynasty, allusions to which are found in the well-known Semna Stela and Semna Dispatches”. Žabkar and Žabkar (1982) speculate that perhaps there was a complex of fortifications which embraced Semna South and West, and perhaps other forts in the region, but there is no definitive evidence for such a complex.
=Artefactual findings
= An area located on the fort's north-west side previously called a ‘graveyard,’ ‘occupation site,’ or an ‘encampment,’ and covered in pot sherds was also excavated during the 1966–1968 field seasons. Upon excavation, it was revealed to be a 12th Dynasty dump site, and was “the most significantind
Ind or IND may refer to:
General
* Independent (politician), a politician not affiliated to any political party
* Independent station, used within television program listings and the television industry for a station that is not affiliated with ...
for the study of the history of the Semna South fort, particularly for the study of its communications with the other forts of the first and second cataract regions”. The dump site was a series of holes which were initially clay quarries and later utilized as a dumping place for discarded fort objects. Some of the holes were deep and some were shallow; the two deepest were K-1 and K-4. Within these holes, the discarded objects and pottery sherds were mixed into a loose mass of debris with no discernible stratigraphic layers.
The finds within these holes are of great significance. The first is a well-preserved 12th Dynasty axe, which according to Žabkar and Žabkar (1982), is a rare occurrence in Sudanese and Egyptian Nubia. Second, pottery sherds of the C-Group
The C-Group culture is an archaeological culture found in Nubia, Lower Nubia, which dates from 2400 BCE to 1550 BCE. It was named by George A. Reisner. With no central site and no written evidence about what these people called themselves, Re ...
type (indigenous Nubian inhabitants from ca. 2000 – 1500 BC) were found which suggests a peaceful coexistence between the C-Group individuals and the Egyptians. Third, and most importantly, were seal impressions on numerous pieces of pottery. The most significant seals are those which bore the name of the fort, which until this discovery was only partially known.
Prior to this seal being found, the Egyptian name of the fort at Semna South was written in hieratic as “Repressing the…” on a fragmentary piece of papyrus discovered in 1896 by James Quibell
James Edward Quibell (11 November 1867 – 5 June 1935) was a British Egyptologist.
Life
Quibell was born in Newport, Shropshire. He married the Scottish artist and archaeologist Annie Abernethie Pirie in 1900.Bierbrier, M. L. 2012. ''Who Was W ...
near the Ramesseum
The Ramesseum is the Temples of a Million years, memorial temple (or mortuary temple) of Pharaoh Ramesses II ("Ramesses the Great", also spelled "Ramses" and "Rameses"). It is located in the Theban Necropolis in Upper Egypt, on the west of the Ni ...
. After studying these seals, Dr. Žabkar translated the hieroglyphics as “Subduer of the Setiu-Nubians” or “Subduer of the Seti-land”. This find is important because it officially confirms the Egyptian name of the fort at Semna South and clarifies the fragmentary name written on the Ramesseum papyrus. Additionally it signifies the role of Egypt in Nubia: ruler.
=Bioarchaeological findings
= The Oriental Institute Expedition also excavated the large cemetery to the north of the fort. This cemetery contained approximately 560 graves—representing over 800 individuals—of which about 494 were from the Meroitic period (4th century BC – 4th century AD), 50 from the
The Oriental Institute Expedition also excavated the large cemetery to the north of the fort. This cemetery contained approximately 560 graves—representing over 800 individuals—of which about 494 were from the Meroitic period (4th century BC – 4th century AD), 50 from the X-Group
The X-Group Culture (ca. 300- 600 AD) was an ancient Nubian civilization that existed in Lower Nubia. Cemetery excavations revealed that the civilization stretched from the Dodekaschoinos in the north to Delgo in the south.
Excavations
George ...
period (4th – 6th century AD), and 16 from the Christian period (550 – 1500 AD). The Meroitic period through the Christian period is a span of approximately 2,000 years, which indicates that the fort was used for an extended period of time during Egyptian and Nubian history.
The Meroitic graves were oriented east to west and were of several styles: rectangular pit graves with superstructures resembling mastaba
A mastaba ( , or ), also mastabah or mastabat) is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks or limestone. These edifices marked the burial sites ...
s, oblong pits without superstructures, and rectangular pits with mud-brick burial vaults. For those remains found in situ, the heads were oriented to the west and the bodies were extended on their backs with hands over the pelvis. Numerous artifacts were found within the Meroitic graves: black and brown wear pottery; copper and bronze bowls; a finely carved wooden bowl; a glass ointment jar; bronze mirrors; copper, iron, and bronze jewelry; beads and pendants; hunting equipment; leather; and fragments of shrouds.
The graves of the X-Group were oriented north to south and most were deep pits with a lateral chamber. Most of the graves, according to Žabkar and Žabkar (1982), “had a shelf, composed of earth, mud-brick, or stones, running alongside the chamber, which supported the blocking material”. For the remains found in situ, the bodies were in a flexed position on their sides with the heads facing towards the north, northwest, or south. In most cases a burial shroud was present, although it was often fragmentary. Objects recovered from these graves are as follows: red ware pottery; jewelry; personal grooming tools; hunting equipment; leather sandals; and clothing.
The Christian period graves were oriented east to west and most were deep, narrow, oblong shaft tombs. Only one grave had a superstructure. Of the remains in situ, the bodies were usually extended and supine with the hands over the pelvis with the heads oriented towards the west. One body was found on its side in a flexed position facing north. Most of the bodies were wrapped in a linen or wool shroud which had been secured by a chord.
Additional analysis of Semna South material
The human remains recovered from Semna South have been studied by numerous anthropologists and other specialists. Hrdy (1978) analyzed hair samples from Semna South mummies. He concluded that the hair color of these individuals was lighter than previously thought in ancient Nubia and the hair of the X-Group males was curlier than the Meroitic males. In 1993, Arriaza, Merbs, and Rothschild published a study evaluating the prevalence of a pathological condition known asdiffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition characterized by abnormal calcification/bone formation (hyperostosis) of the soft tissues surrounding the joints of the spine, and also of the peripheral or appendicular skeleton. In ...
(DISH). They found that approximately 13% of the individuals from the Meroitic cemetery were afflicted with this condition and that it was more common among males. Alvrus (1999) assessed the skeletal fracture patterns for almost 600 individuals from the Semna South site. She analyzed healed fractures of the skull and appendicular skeleton
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the vertebrate endoskeleton consisting of the bones, cartilages and ligaments that support the paired appendages ( fins, flippers or limbs). In most terrestrial vertebrates (except snakes, legless li ...
and found that almost 21% of adults had at least one healed fracture and that the skull was the most frequently injured region of the body. She attributes much of the trauma to the rocky physical environment, but also notes that craniofacial trauma may be the result of interpersonal violence.
Dissertations and theses which used the Semna South remains are numerous. They include topics such as the sexual dimorphism of dental pathology, the presence of schistosomiasis in ancient Nubia, non-metric biological distance analysis, and a craniometric analysis.
Conclusions
 Excavated between 1956–57 and 1966–68, Semna South is a 12th Dynasty fort located in
Excavated between 1956–57 and 1966–68, Semna South is a 12th Dynasty fort located in Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
—the present Republic of Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
—on the west bank of the Nile. These excavations revealed the building plan of the fort, a church, a cemetery, and numerous other settlement-related features. Some of the most important discoveries were found within dumps near the fort. In particular, Žabkar recovered pottery seals which provided the Egyptian name of the fort (“Subduer of the Setiu-Nubians” or “Subduer of the Seti-land”) which was unknown until the 1966-1968 field seasons.
The artifacts recovered from these excavations, including pottery sherds, textiles, jewelry, an axe, and additional seals, indicate that the fort at Semna South was utilized during the Middle Kingdom. The adjacent cemetery with burials from the Meroitic, X-Group, and Christian periods suggests a much longer habitation of the region: from the Middle Kingdom until the Middle Ages.
Archaeological excavations of Semna South have contributed to the overall understanding of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period of Egypt, First Intermediate Period. The Middl ...
fort system. These forts established military control over Upper and Lower Nubia
Lower Nubia (also called Wawat) is the northernmost part of Nubia, roughly contiguous with the modern Lake Nasser, which submerged the historical region in the 1960s with the construction of the Aswan High Dam. Many ancient Lower Nubian monuments, ...
and the Nile river transport of commodities, and were integral parts of the Egyptian empire.
The temples of Dedwen
Dedun (or Dedwen) was a Kushite or Nehasi (C-Group culture) god worshipped during ancient times in ancient Egypt and Sudan and attested as early as 2400 BC. There is much uncertainty about their original nature, especially since he was depicted as ...
and Sesostris III were moved to the National Museum of Sudan in Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital city of Sudan as well as Khartoum State. With an estimated population of 7.1 million people, Greater Khartoum is the largest urban area in Sudan.
Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile – flo ...
prior to the flooding of Lake Nasser
Lake Nasser ( ', ) is a large reservoir (water), reservoir in southern Egypt and northern Sudan. It was created by the construction of the Aswan Dam, Aswan High Dam and is one of the List of reservoirs by volume, largest man-made lakes in the wo ...
.
References
Bibliography
* * Retrieved from ProQuest. (3210094) * * * * Retrieved from ProQuest. (8216427) * * * * (unpublished). * * * (unpublished). * * * * * * * {{Coord, 21.500, N, 30.967, E, display=title, source:dewiki History of Nubia Archaeological sites in Sudan Former populated places in Egypt