Seifert Matrix on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The standard
The standard
 In
In mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, a Seifert surface (named after German mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
Herbert Seifert
Herbert Karl Johannes Seifert (; 27 May 1907, Bernstadt – 1 October 1996, Heidelberg) was a German mathematician known for his work in topology.
Biography
Seifert was born in Bernstadt auf dem Eigen, but soon moved to Bautzen, where he atte ...
) is an orientable surface
A surface, as the term is most generally used, is the outermost or uppermost layer of a physical object or space. It is the portion or region of the object that can first be perceived by an observer using the senses of sight and touch, and is ...
whose boundary is a given knot
A knot is an intentional complication in Rope, cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including List of hitch knots, hitches, List of bend knots, bends, List of loop knots, loop knots, ...
or link.
Such surfaces can be used to study the properties of the associated knot or link. For example, many knot invariants
In the mathematical field of knot theory, a knot invariant is a quantity (in a broad sense) defined for each knot which is the same for equivalent knots. The equivalence is often given by ambient isotopy but can be given by homeomorphism. Some ...
are most easily calculated using a Seifert surface. Seifert surfaces are also interesting in their own right, and the subject of considerable research.
Specifically, let ''L'' be a tame oriented knot or link in Euclidean 3-space (or in the 3-sphere
In mathematics, a hypersphere or 3-sphere is a 4-dimensional analogue of a sphere, and is the 3-dimensional n-sphere, ''n''-sphere. In 4-dimensional Euclidean space, it is the set of points equidistant from a fixed central point. The interior o ...
). A Seifert surface is a compact
Compact as used in politics may refer broadly to a pact or treaty; in more specific cases it may refer to:
* Interstate compact, a type of agreement used by U.S. states
* Blood compact, an ancient ritual of the Philippines
* Compact government, a t ...
, connected, oriented surface
A surface, as the term is most generally used, is the outermost or uppermost layer of a physical object or space. It is the portion or region of the object that can first be perceived by an observer using the senses of sight and touch, and is ...
''S'' embedded in 3-space whose boundary is ''L'' such that the orientation on ''L'' is just the induced orientation from ''S''.
Note that any compact, connected, oriented surface with nonempty boundary in Euclidean 3-space is the Seifert surface associated to its boundary link. A single knot or link can have many different inequivalent Seifert surfaces. A Seifert surface must be oriented. It is possible to associate surfaces to knots which are not oriented nor orientable, as well.
Examples
 The standard
The standard Möbius strip
In mathematics, a Möbius strip, Möbius band, or Möbius loop is a Surface (topology), surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist. As a mathematical object, it was discovered by Johann Bened ...
has the unknot
In the knot theory, mathematical theory of knots, the unknot, not knot, or trivial knot, is the least knotted of all knots. Intuitively, the unknot is a closed loop of rope without a Knot (mathematics), knot tied into it, unknotted. To a knot ...
for a boundary but is not a Seifert surface for the unknot because it is not orientable.
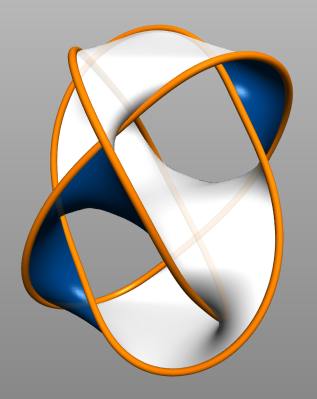
The "checkerboard" coloring of the usual minimal crossing projection of the trefoil knot
In knot theory, a branch of mathematics, the trefoil knot is the simplest example of a nontrivial knot (mathematics), knot. The trefoil can be obtained by joining the two loose ends of a common overhand knot, resulting in a knotted loop (topology ...
gives a Mobius strip with three half twists. As with the previous example, this is not a Seifert surface as it is not orientable. Applying Seifert's algorithm to this diagram, as expected, does produce a Seifert surface; in this case, it is a punctured torus of genus ''g'' = 1, and the Seifert matrix is
:
Existence and Seifert matrix
It is atheorem
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement (logic), statement that has been Mathematical proof, proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to esta ...
that any link always has an associated Seifert surface. This theorem was first published by Frankl and Pontryagin in 1930. A different proof was published in 1934 by Herbert Seifert
Herbert Karl Johannes Seifert (; 27 May 1907, Bernstadt – 1 October 1996, Heidelberg) was a German mathematician known for his work in topology.
Biography
Seifert was born in Bernstadt auf dem Eigen, but soon moved to Bautzen, where he atte ...
and relies on what is now called the Seifert algorithm. The algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
produces a Seifert surface , given a projection of the knot or link in question.
Suppose that link has ''m'' components ( for a knot), the diagram has ''d'' crossing points, and resolving the crossings (preserving the orientation of the knot) yields ''f'' circles. Then the surface is constructed from ''f'' disjoint disks by attaching ''d'' bands. The homology group
In mathematics, the term homology, originally introduced in algebraic topology, has three primary, closely-related usages. The most direct usage of the term is to take the ''homology of a chain complex'', resulting in a sequence of abelian grou ...
is free abelian on 2''g'' generators, where
:
is the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of . The intersection form ''Q'' on is skew-symmetric, and there is a basis of 2''g'' cycles with
equal to a direct sum of the ''g'' copies of the matrix
:
The 2''g'' × 2''g'' integer Seifert matrix
:
has the linking number
In mathematics, the linking number is a numerical invariant that describes the linking of two closed curves in three-dimensional space. Intuitively, the linking number represents the number of times that each curve winds around the other. In E ...
in Euclidean 3-space (or in the 3-sphere
In mathematics, a hypersphere or 3-sphere is a 4-dimensional analogue of a sphere, and is the 3-dimensional n-sphere, ''n''-sphere. In 4-dimensional Euclidean space, it is the set of points equidistant from a fixed central point. The interior o ...
) of ''a''''i'' and the "pushoff" of ''a''''j'' in the positive direction of . More precisely, recalling that Seifert surfaces are bicollared, meaning that we can extend the embedding of to an embedding of