sciatic nerve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large
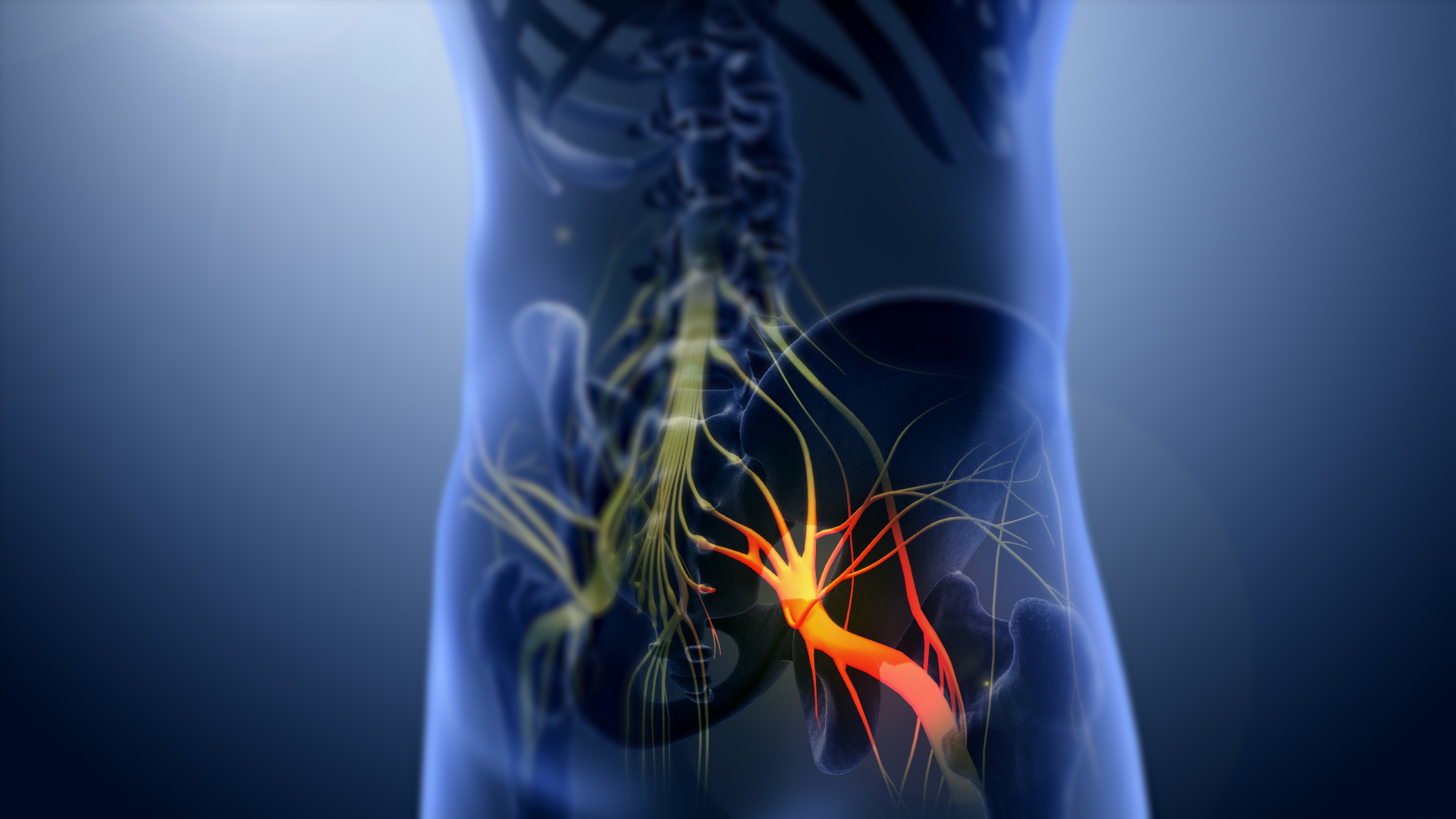

File:Sciatic nerve1.jpg, Sciatic nerve.
File:Gray344.png, Structures surrounding left hip-joint.
File:Gray832.png, Nerves of the right lower extremity. Posterior view.
File:Slide4i.JPG, Sciatic nerve.
File:Slide8z.JPG, Sciatic nerve.
File:Slide4hh.JPG, Sciatic nerve.
Sciatica and the Sciatic Nerve
{{Authority control Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso
nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verteb ...
and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (album), ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
{{Disambiguation ...
. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, org ...
, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into ...
L4 to S3. It contains fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.
Structure
In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of thespinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
. The lumbosacral trunk from the L4 and L5 roots descends between the sacral promontory and ala, and the S1 to S3 roots emerge from the ventral sacral foramina. These nerve roots unite to form a single nerve in front of the piriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the buttock, gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.
The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, ...
. The nerve passes beneath the piriformis and through the greater sciatic foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies ...
, exiting the pelvis. From here, it travels down the posterior thigh to the popliteal fossa
The popliteal fossa (also referred to as hough or kneepit in analogy to the cubital fossa) is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces ...
. The nerve travels in the posterior compartment of the thigh behind (superficial to) the adductor magnus muscle and is itself in front of (deep to) the long head of the biceps femoris muscle
The biceps femoris () is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this ...
. At the popliteal fossa, the nerve divides into its two branches:
* The tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
, which travels down the posterior compartment of the leg into the foot
* The common fibular nerve (also called the common peroneal nerve
The common fibular nerve (also known as the common peroneal nerve, external popliteal nerve, or lateral popliteal nerve) is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides a ...
), which travels down the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and lateral compartments of the leg into the foot
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body.


Development
Function
The sciatic nerve supplies sensation to theskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
of the foot
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up o ...
, as well as the entire lower leg (except for its inner side). Sensation to skin to the sole of the foot is provided by the tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
, and the lower leg and upper surface of the foot via the common fibular nerve.
The sciatic nerve also innervates muscles. In particular:
* Via the tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg and sole of the foot (plantar aspect).
* Via the common fibular nerve, the muscles in the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and lateral compartments of the leg.
Clinical significance
Sciatica
Pain caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve by a problem in the lower back is calledsciatica
Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities such as heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often desc ...
. Common causes of sciatica include the following lower back and hip conditions: spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
, degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the vertebral column, spine. DDD can take ...
, lumbar spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is when one spinal vertebra slips out of place compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (o ...
, and piriformis syndrome
Piriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from nerve compression at the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. It is a specific case of deep gluteal syndrome.
The largest and most bulky nerve in the human body is the s ...
. Other acute causes of sciatica include cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing, muscular hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, and sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
.
Injury
A sciatic nerve injury occurs between 0.5% and 2.0% of the time during a hip replacement. Sciatic nerve palsy is a complication of total hip arthroplasty with an incidence of 0.2% to 2.8% of the time, or with an incidence of 1.7% to 7.6% following revision. Following the procedure, in rare cases, a screw, broken piece of trochanteric wire, fragment ofmethyl methacrylate
Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula . This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
History
MMA ...
bone cement, or Burch-Schneider antiprofusio cage can impinge on the nerve; this can cause sciatic nerve palsy, which may resolve after the fragment is removed and the nerve is freed. The nerve can be surrounded by oxidised, regenerated cellulose to prevent further scarring. Sciatic nerve palsy can also result from severe spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in ...
following the procedure, which can be addressed by spinal decompression
Spinal decompression is the relief of pressure on the spinal cord or on one or more compressed nerve roots passing through or exiting the spinal column. Decompression of the spinal neural elements is a key component in treating spinal radiculopat ...
surgery. It is unclear if inversion therapy is able to decompress the sacral vertebrae; it may only work on the lumbar aspects of the sciatic nerves.
A sciatic nerve injury may also occur from improperly performed injections into the buttock, and may result in sensory loss.
Other disease
Bernese periacetabularosteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It i ...
resulted in major nerve deficits in the sciatic or femoral nerves in 2.1% of 1760 patients, of whom approximately half experienced complete recovery within a mean of 5.5 months.
Sciatic nerve exploration can be done by endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
in a minimally invasive procedure to assess lesions of the nerve. Endoscopic treatment for sciatic nerve entrapment has been investigated in deep gluteal syndrome. Patients were treated with sciatic nerve decompression by resection of fibrovascular scar bands, piriformis tendon release, obturator internus
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis (bone), pubis.
It exits the pelvis, pelvic cavity through the lesser sc ...
, or quadratus femoris, or by hamstring
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.
Etymology
The word " ham" is derived from the Old ...
tendon scarring.
Anaesthetic
Signals from the sciatic nerve and its branches can be blocked, in order to interrupt the transmission of pain signals from the innervation area, by performing a regional nerve blockade called a sciatic nerve block.Society and culture
According toJewish law
''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is based on biblical commandments ('' mit ...
, the sciatic nerve (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: Gid hanasheh) may not be eaten by Jews to commemorate Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
's injury in his struggle with an angel
An angel is a spiritual (without a physical body), heavenly, or supernatural being, usually humanoid with bird-like wings, often depicted as a messenger or intermediary between God (the transcendent) and humanity (the profane) in variou ...
.
Additional images
See also
* Lesser sciatic notch * Greater sciatic notch * Lumbosacral plexus *Sacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verteb ...
* Tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
* Common peroneal nerve
The common fibular nerve (also known as the common peroneal nerve, external popliteal nerve, or lateral popliteal nerve) is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides a ...
* Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside t ...
* Sciatica
Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities such as heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often desc ...
* Spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
* Piriformis syndrome
Piriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from nerve compression at the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. It is a specific case of deep gluteal syndrome.
The largest and most bulky nerve in the human body is the s ...
* Deep gluteal syndrome
Notes
References
External links
* * * () * ()Sciatica and the Sciatic Nerve
{{Authority control Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso