Saprolite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of
Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of
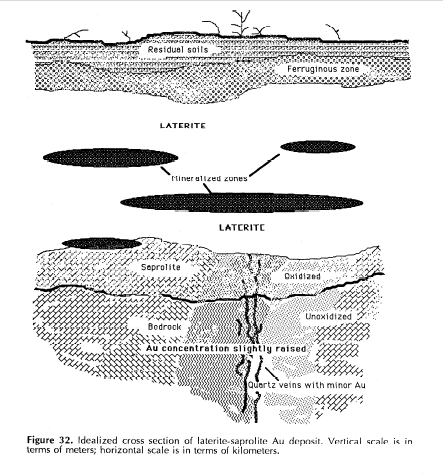 Saprolite (from Greek σαπρος (sapros) = putrid + λιθος (lithos) = rock) is a chemically weathered rock (literally, it means "rotten rock"). More intense weathering results in a continuous transition from saprolite to
Saprolite (from Greek σαπρος (sapros) = putrid + λιθος (lithos) = rock) is a chemically weathered rock (literally, it means "rotten rock"). More intense weathering results in a continuous transition from saprolite to
 Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of
Saprolite is a chemically weathered rock. Saprolites form in the lower zones of soil profile
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. ...
s and represent deep weathering of the bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of bed ...
surface. In most outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth and other terrestrial planets.
Features
Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most p ...
s, its color comes from ferric
In chemistry, iron(III) or ''ferric'' refers to the chemical element, element iron in its +3 oxidation number, oxidation state. ''Ferric chloride'' is an alternative name for iron(III) chloride (). The adjective ''ferrous'' is used instead for i ...
compounds. Deeply weathered profiles are widespread on the continental landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land that is in one piece and not noticeably broken up by oceans. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the fiel ...
es between latitudes 35°N and 35°S.
Conditions for the formation of deeply weathered regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestria ...
include a topographically moderate relief flat enough to prevent erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
and to allow leaching of the products of chemical weathering. A second condition is long periods of tectonic stability; tectonic activity and climate change can cause erosion. The third condition is humid tropical to temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ra ...
.
Poorly weathered saprolite grit aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s are capable of producing groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
, often suitable for livestock. Deep weathering causes the formation of many secondary and supergene ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically including metals, concentrated above background levels, and that is economically viable to mine and process. The grade of ore refers to the concentration ...
s: bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
, iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
s, saprolitic gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, supergene copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
, and heavy minerals in residual accumulations.
Definition, description and locations
laterite
Laterite is a soil type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolo ...
.
Saprolites form in the lower zones of soil horizons
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. ...
and represent deep weathering of the bedrock surface. In lateritic regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestria ...
s – regoliths are the loose layer of rocks that rest on the bedrock – saprolite may be overlain by upper horizons of residual laterite; most of the original profile is preserved by residual soils or transported overburden. Weathering formed thin kaolinitic l2Si2O5(OH)4saprolites 1,000 to 500 million years ago; thick kaolinitic saprolites 200 to 66 million years ago; and medium-thick immature saprolites 5 million years ago in Sweden. The general structure of kaolinite has silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
i2O5sheets bonded to aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
hydroxide l2(OH)4layers.
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
compounds are the primary coloring agents in saprolites. At most outcrops the color comes from ferric compounds; the color relates to the mineralogy and particle size. Submicron-sized goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the α- polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
eO(OH)is yellow; coarse goethite is brown. Sub-micron-sized hematite e2O3is red; coarse hematite is gray to black.
Regoliths vary from a few meters to over thick, depending on the age of the land surface, tectonic activity, climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
, climate history and the composition of the bedrock. Although these deeply weathered terrain
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientati ...
s now occur in a wide variety of climates ranging from warm humid to arid, tropical to temperate, they were formed under similar conditions in the past. In parts of Africa, India, South America, Australia and southeast Asia, regolith has been forming continuously for over 100 million years. Deeply weathered regoliths are widespread in the inter-tropical belt, particularly on the continental landmasses between latitudes 35°N and 35°S. Similar weathered regoliths exist at much higher latitudes – 35–42°S in southeast Australia (Victoria and Tasmania), 40–45°N in the United States (Oregon and Wisconsin) and 55°N in Europe (Northern Ireland, Germany) – although these are not regionally extensive. In some localities it is possible to relatively date saprolite by considering that the saprolite must be younger than the parent material and older than any thick cover unit such a lava or sedimentary rock. This principle is useful in some contexts but in others, like certain parts of Sweden where grus is formed from Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
rocks and overlain by Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
deposits, it is of little value.
Formation
The regolith of a region is the product of its long weathering history; leaching and dispersion are dominant during the initial phase of weathering under humid conditions. Saprolites form in high rainfall regions which result in chemical weathering and are characterised by distinct decomposition of the parent rock's mineralogy. Conditions for the formation of deeply weathered regolith include a topographically moderate relief flat enough to allow leaching of the products of chemical weathering. A second condition is long periods of tectonic stability; tectonic activity and climate change partially erode the regolith. Weathering rates of per million years suggest that deep regoliths require several million years to develop. The third condition is a humid tropical to temperate climate; higher temperatures enable reactions to occur more rapidly. Deep weathering can occur in cooler climates but over longer periods.Sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
s are some of the most unstable minerals in humid, oxidizing environments; many cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
sulfides are easily leached to deep in the profile. Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
s are highly soluble, especially in acidic environments; the elements hosted by them – calcium, magnesium, manganese and strontium – are strongly leached. Serpentinite
Serpentinite is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of serpentine group minerals formed by serpentinization of mafic or ultramafic rocks. The ancient origin of the name is uncertain; it may be from the similarity of its texture or color ...
– oxidized and hydrolized low-silicon, iron- and magnesium-rich oxide igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
s – are progressively weathered through this zone. Ferromagnesian minerals are the principal hosts for nickel, cobalt, copper, and zinc in sulfide-poor mafic and ultramafic rocks and are retained higher in the profile than sulfide-hosted metals. They are leached from the upper horizons and reprecipitate with secondary iron-manganese oxides in the mid- to lower saprolite.
Uses
Aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
are of saprolite grit. Poorly weathered saprolite grit aquifers are capable of producing groundwater, often suitable for livestock. Yields depend on the texture of the materials and their depth from which the aquifer is derived.
The distributions of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
or calcium magnesium carbonates are closely correlated and documented in the southern Yilgarn craton, Western Australia, in the top of the soil profile and locally as deep as . The gold-carbonate association is also apparent in the Gawler craton
The Gawler Craton covers approximately 440,000 square kilometres of central South Australia. Its Precambrian crystalline basement crustal block was cratonised ca. 1550–1450 Ma. Prior to 1550 Ma the craton comprised a number of active Protero ...
, South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
. Supergene enrichment occurs near the surface and involves water circulation with its resulting oxidation and chemical weathering. Deep weathering causes the formation of many secondary and supergene ores – bauxite, iron ores, saprolitic gold, supergene copper, uranium and heavy minerals in residual accumulations.
See also
* * ResiduumReferences
{{Authority control Soil science Sedimentology Weathering Ore deposits Pedology Regolith