Sakız on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest


 Chios island is crescent or kidney-shaped, long from north to south, and at its widest, covering an area of . The terrain is mountainous and arid, with a ridge of mountains running the length of the island. The two largest of these mountains, Pelineon () and Epos (), are situated in the north of the island. The center of the island is divided between east and west by a range of smaller peaks, known as Provatas.
Chios island is crescent or kidney-shaped, long from north to south, and at its widest, covering an area of . The terrain is mountainous and arid, with a ridge of mountains running the length of the island. The two largest of these mountains, Pelineon () and Epos (), are situated in the north of the island. The center of the island is divided between east and west by a range of smaller peaks, known as Provatas.
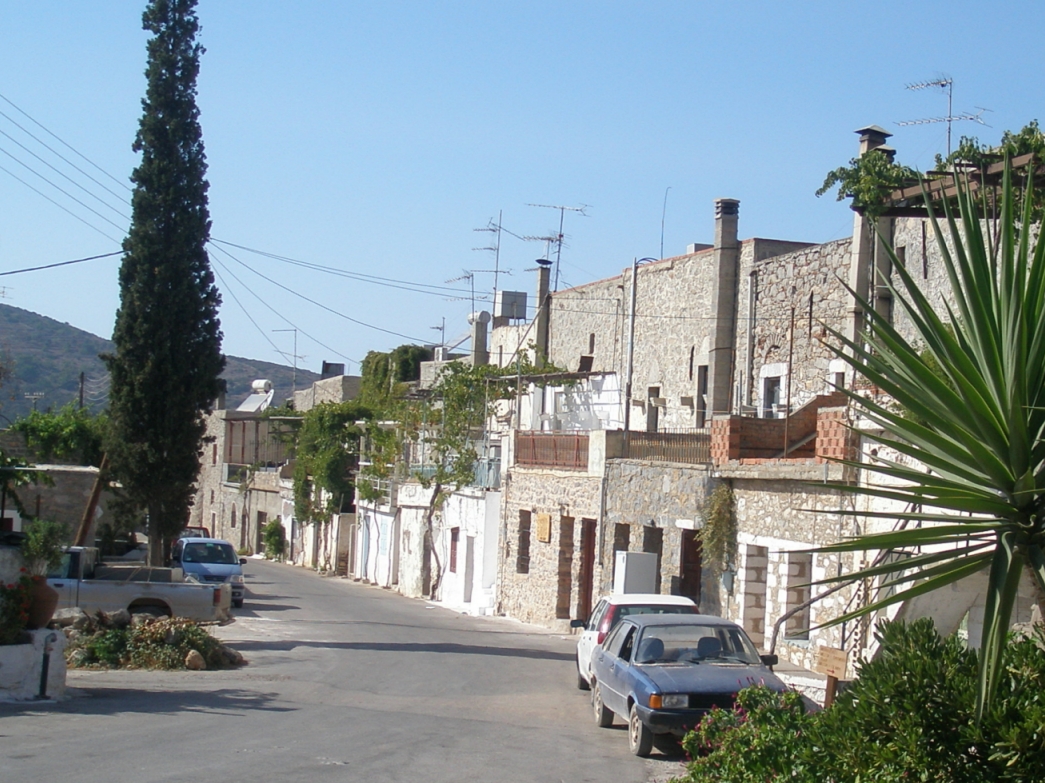
 Midway up the east coast lie the main population centers, the main town of Chios, and the regions of Vrontados and Kambos. Chios Town, with a population of 32,400, is built around the island's main harbour and medieval castle. The current castle, with a perimeter of , was principally constructed during the time of Genoese and Ottoman rule, although remains have been found dating settlements there back to 2000 B.C. The town was substantially damaged by an earthquake in 1881, and only partially retains its original character.
North of Chios Town lies the large suburb of
Midway up the east coast lie the main population centers, the main town of Chios, and the regions of Vrontados and Kambos. Chios Town, with a population of 32,400, is built around the island's main harbour and medieval castle. The current castle, with a perimeter of , was principally constructed during the time of Genoese and Ottoman rule, although remains have been found dating settlements there back to 2000 B.C. The town was substantially damaged by an earthquake in 1881, and only partially retains its original character.
North of Chios Town lies the large suburb of
 Theopompus returned to Chios with the other exiles in 333 BC after
Theopompus returned to Chios with the other exiles in 333 BC after
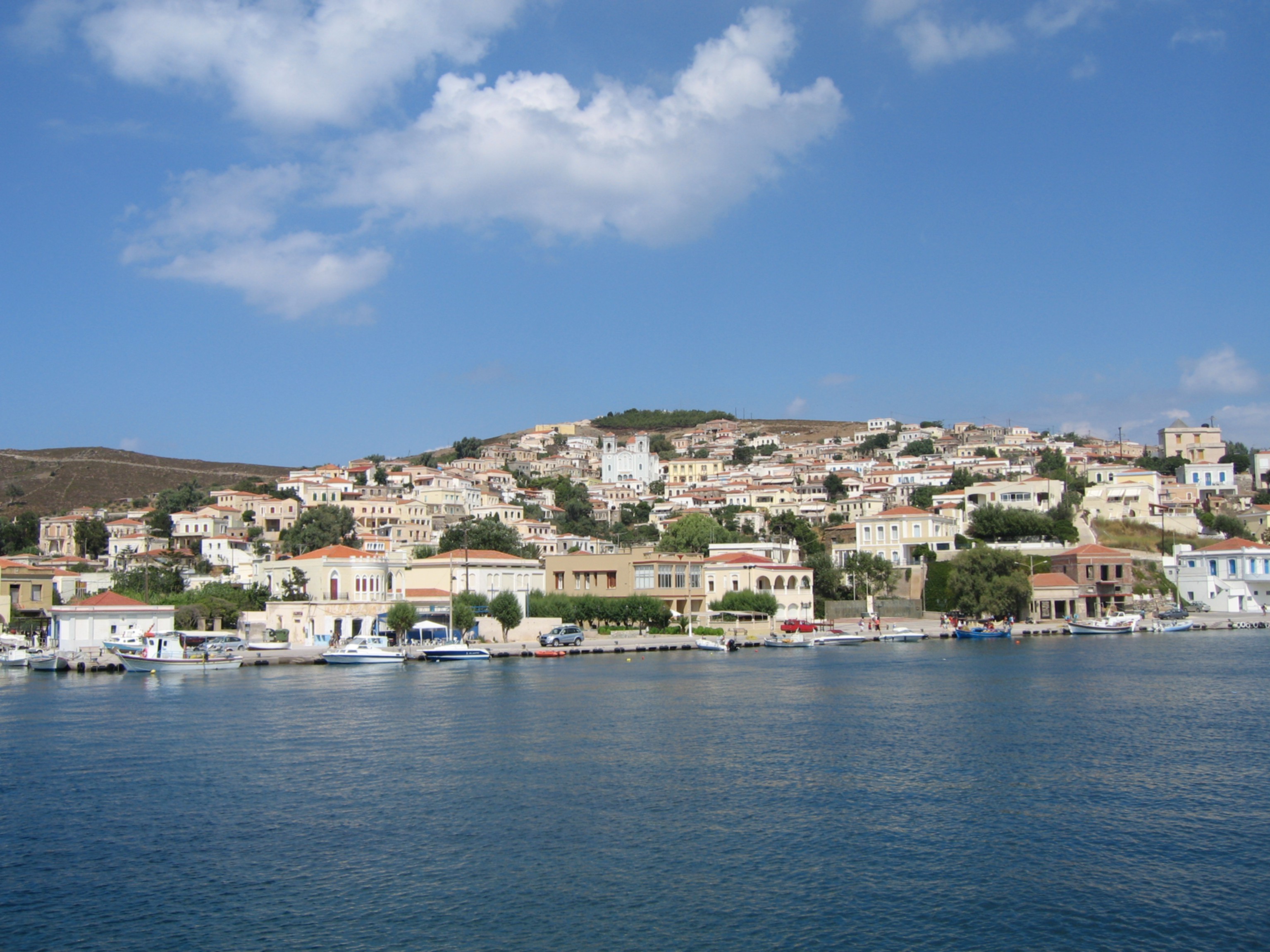 The present municipality Chios was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 8 former municipalities, that became municipal units:
*
The present municipality Chios was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 8 former municipalities, that became municipal units:
*
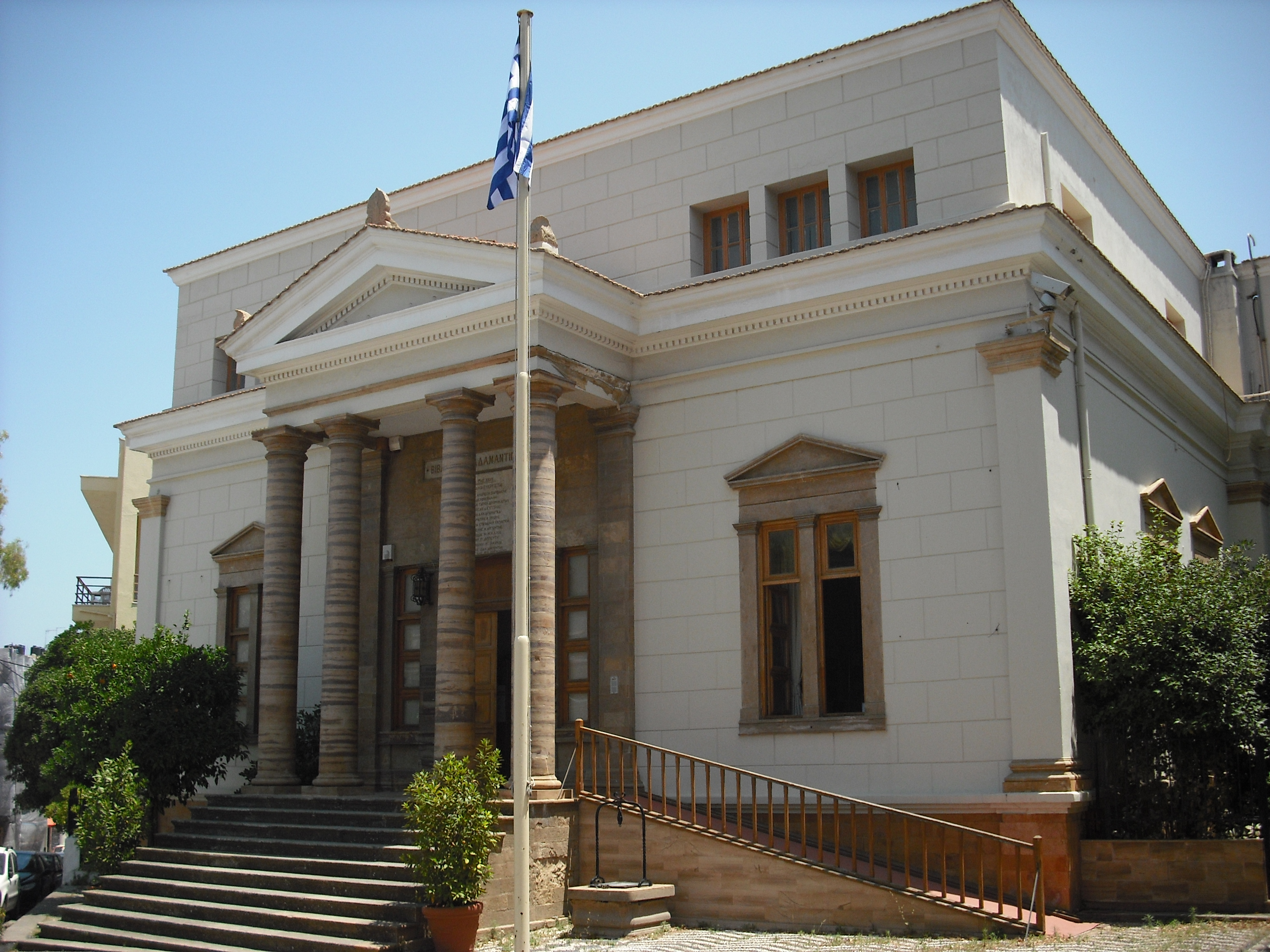
 * Nea Moni is a monastery with fine
* Nea Moni is a monastery with fine
 *
*
 * Saint Markella (14th century), martyr and saint of the Greek Orthodox church
*
* Saint Markella (14th century), martyr and saint of the Greek Orthodox church
*

 * Rodocanachi, noble family
*
* Rodocanachi, noble family
*
(online)
* Arnold C. Smith: ''The Architecture of Chios: Subsidiary Buildings, Implements and Crafts''. Edited by Philip Pandely Argenti. Tison, London 1962. * Michales G. Tsankares, : ''Chios: hekato chronia photographies, 1850–1950.'' (''Chios: One Hundred Years of Photographs, 1850–1950''). Synolo, Athens 1996, . * Eleftherios Yalouris: ''The Archeology and Early History of Chios. (From the Neolithic Period to the End of the Sixth Century B.C.)''. University of Oxford, Merton College, dissertation, 1976.
Official Chios website
��operated by Chios Prefecture (including tourist guide) *
History of Chios
* {{Authority control Ionian League Islands of Greece Islands of the North Aegean Landforms of Chios (regional unit) Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Members of the Delian League Municipalities of the North Aegean Territories of the Republic of Genoa Greek city-states Hellenic Navy bases Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands Populated places in ancient Ionia Populated places in Chios Natura 2000 in Greece
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
, situated in the northern Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
, and the tenth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. The island is separated from Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic gum and its nickname is "the Mastic Island". Tourist attractions include its medieval villages and the 11th-century monastery of Nea Moni, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Chios regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean
The North Aegean Region (, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, and the smallest of the thirteen by population. It comprises the islands of the north-eastern Aegean Sea, called the North Aegean islands, except for Thasos an ...
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
. Locals refer to Chios town as ''Chora'' ( literally means land or country, but usually refers to the capital or a settlement at the highest point of a Greek island).
The island was also the site of the Chios massacre, in which tens of thousands of Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
on the island were massacred, expelled, and enslaved by Ottoman troops during the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
in 1822. Chios remained a part of the Ottoman Empire until 1912.
Geography


 Chios island is crescent or kidney-shaped, long from north to south, and at its widest, covering an area of . The terrain is mountainous and arid, with a ridge of mountains running the length of the island. The two largest of these mountains, Pelineon () and Epos (), are situated in the north of the island. The center of the island is divided between east and west by a range of smaller peaks, known as Provatas.
Chios island is crescent or kidney-shaped, long from north to south, and at its widest, covering an area of . The terrain is mountainous and arid, with a ridge of mountains running the length of the island. The two largest of these mountains, Pelineon () and Epos (), are situated in the north of the island. The center of the island is divided between east and west by a range of smaller peaks, known as Provatas.
Regions
Chios can be divided into five regions.East coast
 Midway up the east coast lie the main population centers, the main town of Chios, and the regions of Vrontados and Kambos. Chios Town, with a population of 32,400, is built around the island's main harbour and medieval castle. The current castle, with a perimeter of , was principally constructed during the time of Genoese and Ottoman rule, although remains have been found dating settlements there back to 2000 B.C. The town was substantially damaged by an earthquake in 1881, and only partially retains its original character.
North of Chios Town lies the large suburb of
Midway up the east coast lie the main population centers, the main town of Chios, and the regions of Vrontados and Kambos. Chios Town, with a population of 32,400, is built around the island's main harbour and medieval castle. The current castle, with a perimeter of , was principally constructed during the time of Genoese and Ottoman rule, although remains have been found dating settlements there back to 2000 B.C. The town was substantially damaged by an earthquake in 1881, and only partially retains its original character.
North of Chios Town lies the large suburb of Vrontados
Vrontados () is a small coastal town located at the eastern part of the island of Chios in Greece. With a population of about 5,300 the town hosts the seat of the municipal unit of Omiroupoli.
Information
The town has a strong tradition in merc ...
(population 4,500), which claims to be the birthplace of Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
. The suburb lies in the Omiroupoli municipality, and its connection to the poet is supported by an archaeological site known traditionally as "Teacher's Rock".
Southern region (Mastichochória)
In the southern region of the island are the (literally 'mastic villages'), the seven villages of Mesta (), Pyrgi (), Olympi (), Kalamoti (), Vessa (), Lithi (), andElata
Elata is a Greek village on the island of Chios. The village is situated on hilly terrain and has a population of several hundred.
Elata
Elata became a village hundreds of years ago when seven tribes came together to protect themselves from Tu ...
(), which together have controlled the production of mastic gum in the area since the Roman period. The villages, built between the 14th and 16th centuries, have a carefully designed layout with fortified gates and narrow streets to protect against the frequent raids by marauding pirates. Between Chios Town and the Mastichochoria lie a large number of historic villages including Armolia (), Myrmighi (), and Kalimassia (). Along the east coast are the fishing villages of Kataraktis () and to the south, Nenita ().
Interior
Directly in the centre of the island, between the villages of Avgonyma to the west and Karyes to the east, is the 11th century monastery of Nea Moni, a UNESCOWorld Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. The monastery was built with funds given by the Byzantine Emperor Constantine IX
Constantine IX Monomachos (; 980/ 1000
– 11 January 1055) reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 1042 to January 1055. Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita chose him as a husband and co-emperor in 1042, although he had been exiled for conspiring again ...
, after three monks, living in caves nearby, had petitioned him while he was in exile on the island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
. The monastery had substantial estates attached, with a thriving community until the massacre of 1822. It was further damaged during the 1881 earthquake. In 1952, due to the shortage of monks, Nea Moni was converted to a convent.
Climate
The island's climate is warm and moderate, categorised as temperate, Mediterranean (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: ''Csa''), with modest variation due to the stabilising effect of the surrounding sea. Average temperatures normally range from a summer high of to a winter low of in January, although temperatures of over or below freezing can sometimes be encountered.
The island normally experiences steady breezes (average ) throughout the year, with wind direction predominantly northerly ("Etesian
The etesians ( or ; ; sometimes found in the Latin form etesiae), meltemia (; pl. of meltemi), or meltem ( Turkish) are the strong, dry north winds of the Aegean Sea, which blow periodically from about mid-May to mid-September. The Etesian winds a ...
" Wind—locally called the "Meltemi") or southwesterly (Sirocco).
Geology
The Chios Basin is a hydrographic sub-unit of the Aegean Sea adjacent to the island of Chios. A kind of white dirt found nearPyrgi
Pyrgi (''Pyrgus'' in Etruscan) was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium, central Italy, to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of th ...
on the southern part of the island. was famed as an astringent
An astringent (sometimes called adstringent) is a chemical that shrinks or constricts body tissues. The word derives from the Latin '' adstringere'', which means "to bind fast". Astringency, the dry, puckering or numbing mouthfeel caused by t ...
and cosmetic since antiquity as Chian earth (; , ''pēlomaiotiko''). Extracted around May
May is the fifth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days.
May is a month of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Therefore, May in the Southern Hemisphere is the ...
each year, it was considered less valuable than the similar medicinal earth produced by Lemnos
Lemnos ( ) or Limnos ( ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos (regional unit), Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean modern regions of Greece ...
given that the Limnian earth was considered protective against venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
s and poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
s but nonetheless reputed to be "the greatest of all cosmetics... giv nga whiteness and smoothness to the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and prevent ngwrinkles
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of bo ...
beyond any of the other substances... for the same purposes."
History

Etymology
The ancient writer Pausanias tells us that the poetIon
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
of Chios believed the island received its name from ''Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
'', the son of Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
by a nymph of the island, who was born amidst snowfall ( 'snow'). Other ancient authors attributed the name to a nymph called Chione. Known as Ophioussa (, 'snake island') and Pityoussa (, 'pine-tree island') in antiquity, during the later Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
the island was ruled by a number of non-Greek powers and was known as ( Genoese), (Italian) and ( in Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish (, ; ) was the standardized register of the Turkish language in the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian. It was written in the Ottoman Turkish alphabet. ...
). The capital during that time was Kastron
Myrina ( , ) is a former municipality on the island of Lemnos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lemnos, of which it is a municipal unit. It covers the west coast of the island, and has a ...
(, 'castle').
Prehistoric period
Archaeological research on Chios has found evidence of habitation dating back at least to theNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
era. The primary sites of research for this period have been cave dwellings at Hagio(n) Galas in the north and a settlement and accompanying necropolis
A necropolis (: necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'' ().
The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distan ...
in modern-day Emporeio (also known as Emporio) at the far south of the island. Scholars lack information on this period. The size and duration of these settlements have therefore not been well-established.
The British School at Athens
The British School at Athens (BSA; ) is an institute for advanced research, one of the eight British International Research Institutes supported by the British Academy, that promotes the study of Greece in all its aspects. Under UK law it is a reg ...
under the direction of Sinclair Hood
Martin Sinclair Frankland Hood, (31 January 1917 – 18 January 2021), generally known as Sinclair Hood, was a British archaeologist and academic. He was Director of the British School at Athens from 1954 to 1962, and led the excavations at Kn ...
excavated the Emporeio site in 1952–1955, and most current information comes from these digs. The Greek Archaeological Service
The Greek Archaeological Service () is a state service, under the auspices of the Greek Ministry of Culture (Greece), Ministry of Culture, responsible for the oversight of all archaeological excavations, museums and the country's archaeologic ...
has also been excavating periodically on Chios since 1970, though much of its work on the island remains unpublished.
The noticeable uniformity in the size of houses at Emporeio leads some scholars to believe that there may have been little social distinction during the Neolithic era on the island. The inhabitants apparently all benefited from agricultural and livestock farming.
It is also widely held by scholars that the island was not occupied by humans during the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
(2300–1600), though researchers have recently suggested that the lack of evidence from this period may only demonstrate the lack of excavations on Chios and the northern Aegean.
By at least the 11th century BC the island was ruled by a monarchy, and the subsequent transition to aristocratic (or possibly tyrannic) rule occurred sometime over the next four centuries. Future excavations may reveal more information about this period. 9th-century Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by ...
n and Cypriote presence on the island is attested by ceramics, while a Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n presence is noted at Erythrae
Erythrae or Erythrai () later Lythri(Λυθρί, turk. Ildırı) was one of the twelve Ionian cities of Asia Minor, situated 22 km north-east of the port of Cyssus (modern name: Çeşme), on a small peninsula stretching into the Bay of ...
, the traditional competitor of Chios on the mainland.
Archaic and Classical periods
Pherecydes, native to the Aegean, wrote that the island was occupied by theLeleges
The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are u ...
, Pre-Greeks who were reported to be subjected to the Minoans on Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
. They were eventually driven out by invading Ionians
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the ...
.
Chios was one of the original twelve member states of the Ionian League
The Ionian League (; , ; or , , in ), also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian Greek city-states (a dodecapolis, of which there were many other ...
. As a result, Chios, at the end of the 7th century BC, was one of the first cities to strike or mint coins, establishing the sphinx
A sphinx ( ; , ; or sphinges ) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
In Culture of Greece, Greek tradition, the sphinx is a treacherous and merciless being with the head of a woman, th ...
as its symbol. It maintained this tradition for almost 900 years.
In the 6th century BC, Chios' government adopted a constitution similar to that developed by Solon
Solon (; ; BC) was an Archaic Greece#Athens, archaic History of Athens, Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy. ...
in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and later developed democratic elements with a voting assembly and people's magistrates called ''damarchoi''.Grant, Michael (1989). The Classical Greeks. Guild Publishing London. p.149
In 546 BC, Chios was subjected to the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
. Chios joined the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris (Asia Minor), Doris, Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Achaemenid Empire, Persian rule, lasting from 499 ...
against the Persians in 499 BC. The naval power of Chios during this period is demonstrated by the fact that the Chians had the largest fleet (100 ships) of all of the Ionians at the Battle of Lade
The Battle of Lade () was a naval battle which occurred during the Ionian Revolt, in 494 BC. It was fought between an alliance of the Ionian cities (joined by the Lesbians) and the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, and resulted in a decisi ...
in 494 BC. At Lade, the Chian fleet doggedly continued to fight the Persian fleet even after the defection of the Samians and others, but the Chians were ultimately forced to retreat and were again subjected to Persian domination.
The defeat of Persia at the Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles (the other being the Battle of Plataea) that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on 27 or 28 August, 479BC on the slopes of Mount Myc ...
in 479 BC meant the liberation of Chios from Persian rule. When the Athenians formed the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
, Chios joined as one of the few members who did not have to pay tribute but who supplied ships to the alliance.
By the fifth to fourth centuries BC, the island had grown to an estimated population of over 120,000 (two to three times the estimated population in 2005), based on the huge necropolis at the main city of Chios. It is thought that the majority of the population lived in that area.
In 412 BC, during the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, Chios revolted against Athens, and the Athenians besieged it. Relief only came the following year when the Spartans were able to raise the siege. In the 4th century BC, Chios was a member of the Second Athenian League
The Second Athenian League was a maritime confederation of Polis, Greek city-states that existed from 378 to 355 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens. The alliance represented a partial revival of the Delian League, which ...
but revolted against Athens during the Social War (357–355 BC)
The Social War, also known as the War of the Allies, was fought from 357 BC to 355 BC between Athens with the Second Athenian League and the allied city-states of Chios, Rhodes, Cos and Byzantion.
Origins
Provoked by Athens' increasingly ...
, and Chios became independent again until the rise of Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
.
Hellenistic period
 Theopompus returned to Chios with the other exiles in 333 BC after
Theopompus returned to Chios with the other exiles in 333 BC after Alexander
Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here ar ...
had invaded Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and decreed their return, as well as the exile or trial of Persian supporters on the island. Theopompus was exiled again sometime after Alexander's death and took refuge in Egypt.
During this period, the island also had become the largest exporter of Greek wine, which was noted for being of relatively high quality (see " Chian wine"). Chian amphoras
An amphora (; ; English ) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storage rooms and packages, tied together with rope and delivered by land ...
, with a characteristic sphinx emblem and bunches of grapes, have been found in nearly every country with whom the ancient Greeks traded. These countries included Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
, Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake N ...
, and Southern Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.
Roman period
During theThird Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman fe ...
, thirty-five vessels allied to Rome, carrying about 1,000 Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here ...
n troops, as well as a number of horses, were sent by Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus I and queen Apollonis, Eumenes was pr ...
to his brother Attalus
Attalus or Attalos may refer to:
People
*Several members of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon
**Attalus I, ruled 241 BC–197 BC
**Attalus II Philadelphus, ruled 160 BC–138 BC
**Attalus III, ruled 138 BC–133 BC
*Attalus, father of Ph ...
. Leaving from Elaea, they were headed to the harbour of Phanae, planning to disembark from there to Macedonia. However, Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
's naval commander Antenor intercepted the fleet between Erythrae
Erythrae or Erythrai () later Lythri(Λυθρί, turk. Ildırı) was one of the twelve Ionian cities of Asia Minor, situated 22 km north-east of the port of Cyssus (modern name: Çeşme), on a small peninsula stretching into the Bay of ...
(on the Western coast of Turkey) and Chios. According to Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
, they were caught completely off-guard by Antenor. Eumenes' officers at first thought the intercepting fleet were friendly Romans, but scattered upon realizing they were facing an attack by their Macedonian enemy, some choosing to abandon ship and swim to Erythrae. Others, crashing their ships into land on Chios, fled toward the city. The Chians however closed their gates, startled at the calamity. And the Macedonians, who had docked closer to the city anyway, cut the rest of the fleet off outside the city gates, and on the road leading to the city. Of the 1,000 men, 800 were killed, 200 taken prisoner.'
After the Roman conquest Chios became part of the province of Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
.
In the spring of 14 BC, King Herod of Judaea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the prese ...
, known for his extensive architectural projects, funded the construction of a stoa
A stoa (; plural, stoas,"stoa", ''Oxford English Dictionary'', 2nd Ed., 1989 stoai, or stoae ), in ancient Greek architecture, is a covered walkway or portico, commonly for public use. Early stoas were open at the entrance with columns, usually ...
on Chios, which had suffered destruction during the Mithridatic War. Additionally, he settled the outstanding taxes owed by the people of Chios to the Romans.
Pliny remarks upon the islanders' use of variegated marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
in their buildings, their appreciation for such stone above murals or other forms of artificial decoration, and the cosmetic properties of the local earth. The marble from Chios, called ''marmor chium'' or "portasanta" today, became one of the most desirable and expensive in the Roman world and later. It has a pinkish coloured background containing yellow-orange, brown and grey spots of variable shape and size, separated by whitish or red veins. The name "portasanta" derives from the door jambs of St. Peter's Basilica, Rome, being made of this marble.
According to the Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
, Luke the Evangelist
Luke the Evangelist was one of the Four Evangelists—the four traditionally ascribed authors of the canonical gospels. The Early Church Fathers ascribed to him authorship of both the Gospel of Luke and the Acts of the Apostles. Prominent figu ...
, Paul the Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first ...
and their companions passed Chios during Paul's third missionary journey, on a passage from Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
to Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
.
Byzantine period
After the permanent division of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in 395 AD, Chios was for seven centuries part of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. This came to an end when the island was briefly held (1090–97) by Tzachas
Chaka Bey (),"Tzachas" is the Hellenized form of a Turkish name which does not appear in any historical documents, but was likely "Chaka", "Chagha", or "Chaqan". The name "Chaka", in the modern Turkish alphabet "Çaka", prevailed especially i ...
, a Turkish bey in the region of Smyrna during the first expansion of the Turks to the Aegean coast. However, the Turks were driven back from the Aegean coast by the Byzantines aided by the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
, and the island was restored to Byzantine rule by admiral Constantine Dalassenos.
This relative stability was ended by the sacking of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
(1204) and during the turmoil of the 13th century the island's ownership was constantly affected by the regional power struggles. After the Fourth Crusade, the Byzantine empire was divided up by the Latin emperors of Constantinople, with Chios nominally becoming a possession of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
. However, defeats for the Latin empire resulted in the island reverting to Byzantine rule in 1225.
Genoese period (1304–1566)
The Byzantine rulers had little influence and through the Treaty of Nymphaeum, authority was ceded to theRepublic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
(1261). At this time the island was frequently attacked by pirates, and by 1302–1303 was a target for the renewed Turkish fleets. To prevent Turkish expansion, the island was reconquered and kept as a renewable concession, at the behest of the Byzantine emperor Andronicus II Palaeologus
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored empire's final decline. ...
, by the Genovese Benedetto I Zaccaria
Benedetto I Zaccaria (c. 1235 – 1307) was an Italian admiral of the Republic of Genoa. He was the Lord of Phocaea (from 1288) and first Lord of Chios (from 1304), and the founder of Zaccaria fortunes in Byzantine and Latin Greece. He was, at d ...
(1304), then admiral to Philip of France. Zaccaria installed himself as ruler of the island, founding the short-lived Lordship of Chios. His rule was benign and effective control remained in the hands of the local Greek landowners. Benedetto Zacharia was followed by his son Paleologo and then his grandsons or nephews Benedetto II and Martino. They attempted to turn the island towards the Latin and Papal powers, and away from the predominant Byzantine influence. The locals, still loyal to the Byzantine Empire, responded to a letter from the emperor and, despite a standing army of a thousand infantrymen, a hundred cavalrymen and two galleys, expelled the Zacharia family from the island (1329) and dissolved the fiefdom.
Local rule was brief. In 1346, a chartered company or ''Maona
A maona ( ''ma‘ūnah''; ; ''mu‘āwanah''; ) also as mahona (pl. mahone) or societas comperarum was a medieval Italian association of investors formed to manage the purchased shares (''loca'' or ''partes'') of the revenue due to the relevant ...
'' (the "'' Maona di Chio e di Focea''") was set up in Genoa to reconquer and exploit Chios and the neighbouring town of Phocaea
Phocaea or Phokaia (Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: Φώκαια, ''Phókaia''; modern-day Foça in Turkey) was an ancient Ionian Ancient Greece, Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Colonies in antiquity, Greek colonists from Phoc ...
in Asia Minor. Although the islanders firmly rejected an initial offer of protection, the island was invaded by a Genoese fleet, led by Simone Vignoso, and the castle besieged. Again rule was transferred peacefully, as on 12 September the castle was surrendered and a treaty signed with no loss of privileges to the local landowners as long as the new authority was accepted. The Maona was controlled by the Giustiniani
The House of Giustinian or Giustiniani was a prominent Italian family which originally belonged to Venice, but also established itself in Genoa, and at various times had representatives in Naples, Canary Islands, Corsica and in the islands of the ...
family.
The Genoese, being interested in profit rather than conquest, controlled the trade-posts and warehouses, in particular the trade of mastic, alum, salt and pitch. Other trades such as grain, wine oil and cloth and most professions were run jointly with the locals. After a failed uprising in 1347, and being heavily outnumbered (less than 10% of the population in 1395), the Latins maintained light control over the local population, remaining largely in the town and allowing full religious freedom. In this way the island remained under Genoese control for two centuries. A notable Genoese inhabitant from this period was Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
who lived in Chios in the 1470s before his voyages to the Americas. In 1566, when Genoa lost Chios to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, there were 12,000 Greeks and 2,500 Genoese (or 17% of the total population) in the island.
Ottoman period: economic prosperity and the Great Destruction
In April 1566, the island of Chios was captured by theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
after the surrender to Piyale Pasha
Piali Pasha (; ) (–1578) was an Ottoman Grand Admiral (Kapudan Pasha) between 1553 and 1567, and a Vizier (minister) after 1568. He is also known as Piale Pasha in English.
Early life
His exact place of birth is unknown, though he was probab ...
. Subsequently, the Genoans were sent to the capital and after some time upon the request of the French ambassador they were allowed to return with a firman.
During Ottoman rule, the government and tax gathering again remained in the hands of Greeks and the Turkish garrison was small and inconspicuous.
As well as the Latin and Turkish influx, documents record a small Jewish population from at least 1049 AD. The original Greek ( Romaniote) Jews, thought to have been brought over by the Romans, were later joined by Sephardic Jews welcomed by the Ottomans during the Iberian expulsions of the late 15th century.
The mainstay of the island's famous wealth was the mastic crop. Chios was able to make a substantial contribution to the imperial treasury while at the same time maintaining only a light level of taxation. The Ottoman government regarded it as one of the most valuable provinces of the Empire.
When the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
broke out, the island's leaders were reluctant to join the revolutionaries, fearing the loss of their security and prosperity. However, in March 1822, several hundred armed Greeks from the neighbouring island of Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
landed in Chios. They proclaimed the revolution and launched attacks against the Turks, at which point islanders decided to join the struggle.
Ottomans landed a large force on the island consequently and put down the rebellion. The Ottoman massacre of Chios expelled, killed or enslaved thousands of the inhabitants of the island. It wiped out whole villages and affected the Mastichochoria
Mastichochoria (, , lit. "the mastic villages" in English) is a former municipality on the island of Chios (Χίος), North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal u ...
area, the mastic growing villages in the south of the island. It triggered also negative public reaction in Western Europe, as portrayed by Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( ; ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French people, French Romanticism, Romantic artist who was regarded as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: ...
, and in the writing of Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
and Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romanticism, Romantic author, poet, essayist, playwright, journalist, human rights activist and politician.
His most famous works are the novels ''The Hunchbac ...
. In 1825, Thomas Barker of Bath painted a fresco depicting the Chios Massacre on the walls of Doric House, Bath, Somerset
Bath (Received Pronunciation, RP: , ) is a city in Somerset, England, known for and named after its Roman Baths (Bath), Roman-built baths. At the 2021 census, the population was 94,092. Bath is in the valley of the River Avon, Bristol, River A ...
. Finally, Chios was not included in the modern Greek state
The history of modern Greece covers the history of Greece from the recognition by the Great Powers — United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the United Kingdom, Kingdom of France, France and Russian Empire, Russia — of its Greek War of ...
and remained under Ottoman rule.
The 1881 Chios earthquake
The 1881 Chios earthquake occurred at 13:40 local time (11:30 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC) on 3 April. It caused severe damage on the island of Chios and also affected Çeşme and Alaçatı on the coast of Turkey. The earthquake had an estima ...
, estimated as 6.5 on the moment magnitude scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mwg, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. was defined in a 1979 paper ...
, damaged a large portion of the island's buildings and resulted in great loss of life. Reports of the time spoke of 5,500–10,000 fatalities.
Remarkably, despite the terrible devastation, in the later 19th century Chios emerged as the motherland of the modern Greek shipping industry. Indicatively, while in 1764, Chios had 6 vessels with 90 sailors on record, in 1875 there were 104 ships with over 60,000 registered tonnes, and in 1889 were recorded 440 sailing ships of various types with 3,050 sailors. The dynamic development of Chian shipping in the 19th century is further attested by the various shipping related services that were present in the island during this time, such as the creation of the shipping insurance companies ''Chiaki Thalassoploia'' (Χιακή Θαλασσοπλοΐα), ''Dyo Adelfai'' (Δυο Αδελφαί), ''Omonoia'' (Ομόνοια) and the shipping bank ''Archangelos'' (Αρχάγγελος) (1863). The boom of Chian shipping took place with the successful transition from sailing vessels to steam. To this end, Chian ship owners were supported by the strong ''diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of birth, place of origin. The word is used in reference to people who identify with a specific geographic location, but currently resi ...
'' presence of Chian merchants and bankers, and the connections they had developed with the financing centers of the time (Istanbul, London), the establishment in London of shipping businessmen, the creation of shipping academies in Chios and the expertise of Chian personnel on board.
In independent Greece
Chios joined the rest of independent Greece after theFirst Balkan War
The First Balkan War lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and involved actions of the Balkan League (the Kingdoms of Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Greece, Greece and Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro) agai ...
(1912). The Greek Navy landed at Chios in November 1912 and took control of the island after a series of clashes that lasted for over a month. The Ottoman Empire recognized Greece's annexation of Chios and the other Aegean islands by signing the Treaty of London (1913)
The Treaty of London (1913) was signed on 30 May following the London Conference of 1912–1913. It dealt with the territorial adjustments arising out of the conclusion of the First Balkan War. The London Conference had ended on 23 January 1913 ...
.
Although Greece was officially neutral, the island was occupied by the British during World War I, on 17 February 1916. This may have been due to the island's proximity to the Ottoman Empire and the city of İzmir in particular.
It was affected also by the population exchange after the Greco–Turkish War of 1919–1922, with the incoming Greek refugees settling in Kastro (previously a Turkish neighborhood) and in new settlements hurriedly built south of Chios town.
The island saw some local violence during the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
setting neighbour against neighbour. This ended when the final band of communist fighters was trapped and killed in the orchards of Kampos and their bodies driven through the main town on the back of a truck. In March 1948, the island was used as an internment camp for female political detainees (communists or relatives of guerillas) and their children, who were housed in military barracks near the town of Chios. Up to 1300 women and 50 children were housed in cramped and degrading conditions, until March 1949 when the camp was closed and the inhabitants moved to Trikeri.
The production of mastic was threatened by the Chios forest fire that swept the southern half of the island in August 2012 and destroyed some mastic groves.
By 2015, Chios had become a transit point for refugees and asylum seekers entering the EU from Turkey. A reception and identification centre was formed at VIAL near the village of Chalkeio, however, in 2021 the Greek government announced a new closed reception centre will be built in a more isolated location at Akra Pachy near the village of Pantoukios.
Demographics
Government
Agios Minas
Agios Minas () is a former municipality on the island of Chios, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal unit. It is located on the central east coast of the isla ...
* Amani
* Chios (town)
Chios () is the main town and a former municipality on the island of Chios, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 22. ...
* Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
* Kampochora
* Kardamyla
Kardamyla () is a village and a former municipality on the island of Chios, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal unit.
It is located in the northeastern corne ...
* Mastichochoria
Mastichochoria (, , lit. "the mastic villages" in English) is a former municipality on the island of Chios (Χίος), North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal u ...
* Omiroupoli
Economy

Commerce
The local merchantshipping
Freight transport, also referred to as freight forwarding, is the physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it has been ...
community transports several locally grown products including mastic, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
s, fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and i ...
s, wine, mandarins, and cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The name ...
.
Cuisine
Local specialities of the island include: * ''Kordelia'', pasta * ''Malathropita'' * ''Neratzopita'' * ''Mastello'' (cheese) * ''Valanes'', type of pasta * '' Sfougato'', type of omelette * ''Mamoulia'' (dessert) * ''Masourakia'' (dessert) * '' Mastiha (drink)'' * '' Souma (drink)''Antimony mines
Sporadically for some time during the early 19th century to 1950s there was mining activity on the island at Keramos Antimony Mines.Culture
 * Nea Moni is a monastery with fine
* Nea Moni is a monastery with fine mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
s from Constantine IX
Constantine IX Monomachos (; 980/ 1000
– 11 January 1055) reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 1042 to January 1055. Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita chose him as a husband and co-emperor in 1042, although he had been exiled for conspiring again ...
's reign and a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
* An ancient inscription (at Chios Archaeological Museum) from a fifth-century funerary monument for Heropythos the son of Philaios, traced his family back over fourteen generations to Kyprios at the tenth century BC, before there were any written records in Greece.
;Forts
* Castle of Chios, a Byzantine fort built in the 10th century
** St. George's church
;Museums
* Chios Byzantine Museum
* The Chios Mastic Museum
* Archaeological Museum of Chios
The Archaeological Museum of Chios is a museum located on Michalon Street in Chios town, Chios, Greece. Designed by the Greek architects Souzána Antonakáki and Dimitris Antonakakis & Eleni Gousi-Desylla in 1965, it has been widely regarded as ...
* Chios Maritime Museum
;Traditions
* The town of Vrontados
Vrontados () is a small coastal town located at the eastern part of the island of Chios in Greece. With a population of about 5,300 the town hosts the seat of the municipal unit of Omiroupoli.
Information
The town has a strong tradition in merc ...
is home to a unique Easter celebration, where competing teams of locals gather at the town's two (rival) churches to fire tens of thousands of homemade rockets at the other church's bell tower while the Easter service is going on inside the churches, in what has become known as '' rouketopolemos''.
;Sports
* F.C. Lailapas (Chios town)
* NC Chios, water polo
* Panchiakos GS
;Media
* Alithia TV
* '' Chiakos Laos'', newspaper
* '' Politis'', newspaper
* ''Dimokratiki'', newspaper
Twin town, sister cities
Chios is twinned with: *Brezno
Brezno (; 1927–1948: ; or ; ) is a town in central Slovakia with a population of around 21,000.
Etymology
The name is derived from the Slovak word "breza" for birch.
Geography
Brezno is located within the Geomorphological division of Slovak ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
* Çeşme
Çeşme, officially the Çeşme Municipality, is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of İzmir Province, Turkey. Its area is 285 km2, and its population is 48,924 (2022). It sits at Turkey's westernmost end, on a promontory on t ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
* Ermoupoli
Ermoupoli (), also known by the formal older name Ermoupolis or Hermoupolis ( < "Town of Hermes"), is a town and former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality on the island of Syros, in the Cyclades, Greece. Since the 2011 loca ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
* Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
''(since 1985)''
* Guiyang
Guiyang; Mandarin pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, alternatively as Kweiyang is the capital of Guizhou, Guizhou province in China. It is centrally located within the province, on the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, eastern part of the Yun ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
* Ortona
Ortona ( Abruzzese: '; ) is a coastal town and municipality of the Province of Chieti in the Italian region of Abruzzo, with some 23,000 inhabitants.
In 1943 Ortona was the site of the bloody Battle of Ortona, known as "Western Stalingrad". ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Polykastro
Polykastro (, before 1928 , ''Karasoúli''; ''Pandektis: Name Changes of Settlements in Greece'', compiled by the/ref>) is a town and a former municipality in Kilkis (regional unit), Kilkis regional unit of Central Macedonia, Greece. Since the 20 ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
Notable natives and inhabitants
A native of Chios is known in English as a Chian.Ancient
 *
* Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
(8th century BC), poet. See History of the Pelopennesian War by Thucydides, section 3.104.5, wherein Thucydides quotes Homer's self-reference: "A blind old man of Scio's rocky isle."
* Glaucus of Chios (c. 700 BC), Greek sculptor in metal
* Oenopides
Oenopides of Chios (; born c. 490 BCE) was an ancient Greece, Greek geometer, astronomer and mathematician, who lived around 450 Common Era, BCE.
Biography
Only limited information is known about the early life of Oenopides, other than that h ...
(c. 490 – c. 420 BC), mathematician and geometer
* Ion of Chios
Ion of Chios (; ; c. 490/480 – c. 420 BC) was a Greek writer, dramatist, lyric poet and philosopher. He was a contemporary of Aeschylus, Euripides and Sophocles. Of his many plays and poems only a few titles and fragments have survived. He also ...
(484-421 BC), tragedy writer
* Hippocrates of Chios
Hippocrates of Chios (; c. 470 – c. 421 BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician, geometer, and astronomer.
He was born on the isle of Chios, where he was originally a merchant. After some misadventures (he was robbed by either pirates or ...
(c. 470 – c. 410 BC), notable mathematician, geometer and astronomer
* Likymnios of Chios (5th century – 4th century BC), Greek sophist
A sophist () was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught ''arete'', "virtue" or "excellen ...
and dithyrambic poet
* Metrodorus of Chios
Metrodorus of Chios (; fl. 4th century BC) was a Greek philosopher, belonging to the school of Democritus, and an important forerunner of Epicurus.
Metrodorus was a pupil of Nessos of Chios, or, as some accounts prefer, of Democritus himself.Dio ...
(4th century BC), Greek philosopher
* Theopompus
Theopompus (, ''Theópompos''; 380 BC 315 BC) was an ancient Greek historian and rhetorician who was a student of Isocrates.
Biography
Early life and education
Theopompus was born on the Aegean island of Chios in 378 or 377 BCE. In his ear ...
of Chios (378 – c. 320 BC), rhetorical historian
* Erasistratus
Erasistratus (; ; c. 304 – c. 250 BC) was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where they carried out anatomical research ...
of Chios (304–250 BC), pioneering anatomist, royal physician and founder of the ancient medical school of Alexandria, who discovered the linking between organs through the systems of veins, arteries and nerves
* Aristo of Chios
Aristo of Chios ( ''Ariston ho Chios''; fl. c. 260 BC), also spelled Ariston, was a Greek Stoic philosopher and colleague of Zeno of Citium. He outlined a system of Stoic philosophy that was, in many ways, closer to earlier Cynic philosophy. He ...
(c. 260 BC), Stoic philosopher
* Claudia Metrodora (c. 54–68 AD), public benefactor
Medieval
 * Saint Markella (14th century), martyr and saint of the Greek Orthodox church
*
* Saint Markella (14th century), martyr and saint of the Greek Orthodox church
* Leo Kalothetos
Leo Kalothetos (, ) was a provincial governor of the Byzantine Empire.
Kalothetos was a native of Chios, where he is mentioned for the first time in 1315.PLP 10617 At the time, the island was a possession of the Genoese Zaccaria family, who hel ...
(1315–1363), provincial governor of the Byzantine empire
* Leonard of Chios
Leonard of Chios (; ), also called Leonardo Giustiniani, was a Greek scholar of the Dominican Order and Latin Bishop of Mytilene, best known for his eye-witness account of the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, which is one of the main sources for the ...
(15th century), Greek Dominican scholar
* Giovanni Giustiniani (1418-1453), died during the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
and buried in Chios
* Matrona of Chios
Saint Matrona of Chios (also called "Saint Matrona Chiopolitis") was born during the 15th century in the village of Volissos on the island of Chios, Greece. This is the same village in which St. Markella was martyred in 1462. The Church celebrates ...
(* 15th century, † before 1455), saint of the Greek Orthodox church
* Andreas Argenti (saint) († 1465 n. Chr.), neomartyr of the Orthodox Church
* Andrea Bianco (15th century), Genoese cartographer resided on Chios
* In 1982, Ruth Durlacher hypothesised that Chios was Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
's birthplace. Columbus himself said he was from the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
, which included the island of Chios at the time. Columbus was friendly with a number of Chian Genoese families, referenced Chios in his writings and used the Greek language for some of his notes. 'Columbus' remains a common surname on Chios. Other common Greek spellings are: Kouloumbis and Couloumbis.
* Vincenzo Giustiniani (Dominican) (1516–1582), cardinal
* Vincenzo Giustiniani (1564–1637), Italian banker and art collector
* (16th century), pilot of Magellan expedition, the first circumnavigation of the Earth
* Leo Allatius
Leo Allatius ( Greek: Λέων Αλλάτιος, ''Leon Allatios'', Λιωνής Αλάτζης, ''Lionis Allatzis''; Italian: ''Leone Allacci, Allacio''; Latin: ''Leo Allatius, Allacius''; 1586 – January 1669) was a Greek scholar, theologi ...
(Leone Allacci) (c. 1586–1669), Greek Catholic scholar and theologian
* Constantine Rodocanachi
Constantine Rodocanachi, also Rhodocanaces or Rhodocanakis (; 1635–1687) was an Ottoman Greek physician to Charles II of England, chemist, lexicographer and academic. Rodocanachi was born on the island of Chios on 5 December 1635 and lived much o ...
(1635–1687), Ottoman Greek academic, chemist, lexicographer, and physician to Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651 and King of England, Scotland, and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest su ...
Modern

Scylitzes
John Skylitzes, commonly Latinized as Ioannes Scylitzes (, ; , ; early 1040s – after 1101), was a Byzantine historian of the late 11th century.
Life
Very little is known about his life. The title of his work records him as a '' kouropalat ...
, noble family of Byzantine descent
* Mavrokordatos, noble, then princely family in Eastern Europe
* Negroponte, noble family
* Damalas
The House of Zaccaria de Damalà—now Damalas— (', ') is a formerly ruling family of Republic of Genoa, Genoese origin, established in the 14th century on the Greek island of Chios, due to the marriage of Admiral Benedetto I Zaccaria with a s ...
, princely family, former rulers during the Frankokratia
The Frankish Occupation (; anglicized as ), also known as the Latin Occupation () and, for the Venetian domains, Venetian Occupation (), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French ...
* Rallis
The Rallis family, also spelled Ralli, Ralles or Rallet in Romanian language, Romanian is the name of an old Greek Phanariots, Phanariote family, whose members played important political role in the history of modern Kingdom of Greece, Greece, Dan ...
, noble family of which the famous Ralli Brothers
The five Ralli brothers, Zannis a.k.a. John (1785–1859), Augustus (1792–1878),
Pandia a.k.a. Zeus (1793–1865),
Toumazis (1799–1858), and
Eustratios (1800–84), founded Ralli Brothers, perhaps the most successful expatriate Greek merchant ...
/Ralli baronets
The Ralli Baronetcy, of Park Street in the City of Westminster, is a title in the Baronetage of the United Kingdom. It was created on 8 February 1912 for Lucas Ralli, head of the firm of Ralli Brothers, financiers, shippers, cotton and grain mer ...
descend from
* Athanasios Parios (1722–1813), Greek hieromonk and notable theologian, philosopher, educator, and hymnographer of his time
* Macarius of Corinth
Macarius of Corinth (also Makarios; born Michael Notaras, Μιχαὴλ Νοταρᾶς; ; 1731–1805) was Metropolitan bishop of Corinth, was a mystic and spiritual writer who worked to revive and mostly sustain the Eastern Orthodox Church und ...
(1731–1805), metropolitan bishop of Corinth, mystic and spiritual theological writer
* Nikephoros of Chios (ca. 1750–1821), abbot of Nea Moni monastery, theological writer and orthodox saint
* (1685–1762), theological writer and medical doctor
* Eustratios Argenti (national hero) (1767‒1798), executed with Rigas Velestinlis
* Alexandros Kontostavlos
Alexandros Kontostavlos (; c. 1789, Chios – 1865, Athens) was a Greek banker, magnate and politician.
Biography
Konstavlos was born on the island of Chios in about 1789 and descended from a noble family that traced its origins to the Byzantine ...
(1789–1865), politician
* Christophorus Plato Castanis (1814–1866), Ottoman Greek academic, author and classicist, as well as former slave, orphan and refugee to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
* Alexandros Georgios Paspatis (1814–1891), linguist, historian and physician, researcher of the Romani language
Romani ( ; also Romanes , Romany, Roma; ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani people. The largest of these are Vlax Romani language, Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Roma ...
and of the history and culture of the Roma people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, ...
* George Colvocoresses (1816–1872), military officer
* Mustapha Khaznadar (1817–1878), was Prime Minister of the Beylik of Tunis
* Michel Emmanuel Rodocanachi (1821–1901), trader and banker of London
* Andreas Syggros (1830–1899), banker, descended from Chios
* George Glarakis (1789-1855), politician, Minister of Education (1838)
* Patriarch Constantine V of Constantinople (1833–1914)
* Ibrahim Edhem Pasha (1819–1893), Ottoman Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
* Namık Kemal
Namık Kemal (, ; ; 21 December 1840 – 2 December 1888) was an Ottoman writer, poet, democrat, intellectual, reformer, journalist, playwright, and political activist who was influential in the formation of the Young Ottomans and their stru ...
(1840–1888), one of the principal founders of modern Turkish literature, served as a sub-prefect (exiled in practical terms) of Chios from 1886 to his death on the island in 1888
* Osman Hamdi Bey
Osman Hamdi Bey (30 December 1842 – 24 February 1910) was an Ottoman Turkish administrator, intellectual, art expert and also a prominent and pioneering painter. He was the Ottoman Empire's first modern archaeologist, and is regarded as the ...
(1842–1910), Ottoman painter, archaeologist
* Ioannis Psycharis
Ioannis (Yiannis) Psycharis ( Greek: Ιωάννης (Γιάννης) Ψυχάρης; French: ''Jean Psychari''; 1854–1929) was a Russian-born philologist who was much of his life a national of France. He was of Greek descent. He was also a w ...
(1854–1929), philologist, descended from Chios
* Ambrosios Skaramagas, merchant
* Konstantinos Amantos (1874–1960), Byzantine scholar, professor at the University of Athens, member of the Athens Academy
* Stylianos Miliadis (1881-1965), painter
* Kostia Vlastos (1883–1967), banker, of the old Vlastos
The Vlastos family, also spelled Vlasto is the name of an old Greek Phanariote family of Byzantine origin, whose members played important political role in the history of Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Sout ...
family
* John D. Chandris (1890–1942), Greek shipowner
* Stavros Livanos (1891–1963), shipping magnate
* Ioannis Despotopoulos (1903–1992), architect
* Kostas Perrikos (1905–1943), Greek Resistance figure, leader of PEAN
* Yiannis Carras
John Constantine Carras (; 1907–1989) was a Greek shipping magnate, grandson of captain and sailing-ship owner Ioannis I. Carras from Kardamyla of Chios.
Early life
John Carras studied economics in Lausanne and subsequently became a princip ...
(1907–1989), shipowner
* Adamantios Lemos
Adamantios Lemos (; 13 January 1916 – 12 June 2006) was a Greek actor. He was one of the most influential figures in modern Greek theatre. During his 60-year career, he worked as a theatrical producer, actor, manager, theatrical teacher, dir ...
(1916–2006), actor
* Andreas Papandreou
Andreas Georgiou Papandreou (, ; 5 February 1919 – 23 June 1996) was a Greek academic and economist who founded the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK) and served three terms as Prime minister of Greece, prime minister of Third Hellenic Repu ...
(1919–1996), politician, Prime Minister of Greece
* Mikis Theodorakis
Michail "Mikis" Theodorakis ( ; 29 July 1925 – 2 September 2021) was a Greek composer and lyricist credited with over 1,000 works.
He scored for the films '' Zorba the Greek'' (1964), '' Z'' (1969), and '' Serpico'' (1973). He was a three-ti ...
(1925-2021), composer, born on the island
* Jani Christou
Jani Christou (, ''Giánnīs Chrī́stou''; 8 or 9 January 1926 – 8 January 1970) was a Greek composer.
Biography
There is some disagreement about Christou's birth, the date of which is given by some authorities as 8 January; while others stat ...
(1926–1970), composer
* George P. Livanos (1926–1997), Greek shipowner
* Petros Molyviatis (1928), politician
* Stamatios Krimigis
Stamatios (Tom) Mike Krimizis (; born September 10, 1938) is a Greek-American scientist in space exploration. He has contributed to many of the United States' unmanned space exploration programs of the Solar System and beyond. He has contributed ...
(1938), NASA space scientist
* Takis Fotopoulos
Takis Fotopoulos (; born 14 October 1940) is a Greek people, Greek political philosophy, political philosopher, economist and writer who founded the Inclusive Democracy movement, aiming at a Thesis, antithesis, synthesis, synthesis of classical d ...
(1940), political philosopher
* Adamantios Vassilakis
Adamantios Vassilakis (; June 13, 194230 June 2021), was a distinguished Greek diplomat and negotiator.
Adamantios Vassilakis was a graduate of the Commercial High School of Chios, Greece, and held a Licence in Political and Diplomatic Sciences fr ...
(1942), diplomat
* Dimitris Varos (1949), author, poet, journalist
* Mark Palios
Markos Palios (born 9 November 1952) is an English chartered accountant, football administrator and former professional footballer. In August 2014, it was announced that he and his wife Nicola were taking ownership of Tranmere Rovers F.C., wher ...
(1952, of Chian descent), former professional footballer and former chief executive of the English Football Association
* Matthew Mirones (1956), New York politician
* Nikos Pateras
Nikolas D. Pateras is a seventh-generation Greek shipowner and founder of Contships Management Inc. He was born on August 26, 1963, in Athens, Greece, and is originally from the island of Oinousses. He has 3 children, Anastasia, Diamantis and Joh ...
(1963), shipowner
* Angeliki Frangou (1965), shipowner
* John Sitaras (1972), fitness professional
* Ioannis Fountoulis
Ioannis Fountoulis (also Giannis, ; born 25 May 1988) is a Greek professional water polo player. He is currently the captain of Greece men's national water polo team, with whom he won a bronze medal at the 2015 World Championships, a bronze meda ...
(1988), water polo player
See also
* Chian wine * Chian diasporaReferences
Further reading
* Fanny Aneroussi, Leonidas Mylonadis: ''The Kampos of Chios in its Heyday: Houses and Surroundings''. Translated from the Greek by Antonis Scotiniotis. (Aipos Series, no 12). Akritas Publications, Nea Smyrni 1992, . * Charalambos Th. Bouras: ''Chios''. (Guides to Greece, no 4). National Bank of Greece, Athens 1974. * Charalambos Th. Bouras: ''Greek Traditional Architecture: Chios''. Melissa, Athens 1984. * Athena Zacharou-Loutrari, Vaso Penna, Tasoula Mandala: ''Chios: History and Art.'' Translated from the Greek by Athena Dallas-Damis ... (The Monuments of Chios). The Chios Prefecture, Chios 1989. . *Hubert Pernot
Hubert Octave Pernot (7 August 1870, in Froideconche – 27 June 1946, Paris) was a French linguist, specializing in Modern Greek studies.
He studied at the École des langues orientales in Paris as a pupil of Émile Legrand and Jean Psich ...
: ''En Pays Turc: L’île de Chios''. (Dijon, Imprimerie Darantière, Rue Chabot-Charny, 65). Avec 17 mélodies populaires et 118 simili-gravures. J. Maisonneuve, Libraire-Éditeur, Paris 1903(online)
* Arnold C. Smith: ''The Architecture of Chios: Subsidiary Buildings, Implements and Crafts''. Edited by Philip Pandely Argenti. Tison, London 1962. * Michales G. Tsankares, : ''Chios: hekato chronia photographies, 1850–1950.'' (''Chios: One Hundred Years of Photographs, 1850–1950''). Synolo, Athens 1996, . * Eleftherios Yalouris: ''The Archeology and Early History of Chios. (From the Neolithic Period to the End of the Sixth Century B.C.)''. University of Oxford, Merton College, dissertation, 1976.
External links
Official Chios website
��operated by Chios Prefecture (including tourist guide) *
History of Chios
* {{Authority control Ionian League Islands of Greece Islands of the North Aegean Landforms of Chios (regional unit) Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece Members of the Delian League Municipalities of the North Aegean Territories of the Republic of Genoa Greek city-states Hellenic Navy bases Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands Populated places in ancient Ionia Populated places in Chios Natura 2000 in Greece