Sakhalin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in
 Humans lived on Sakhalin in the
Humans lived on Sakhalin in the 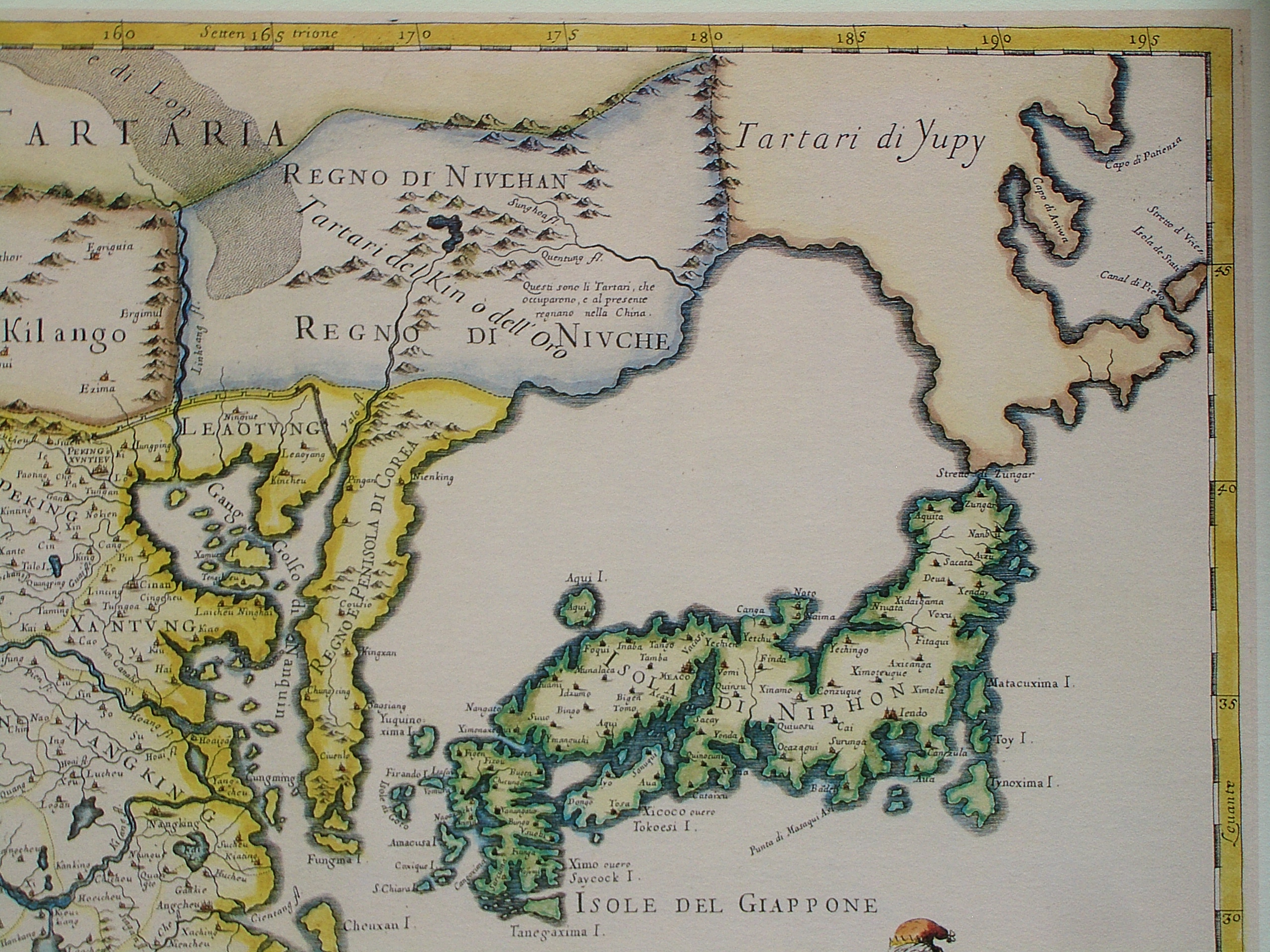
 The first European known to visit Sakhalin was Martin Gerritz de Vries, who mapped Cape Patience and Cape Aniva on the island's east coast in 1643. The Dutch captain, however, was unaware that it was an island, and 17th-century maps usually showed these points (and often Hokkaido as well) as part of the mainland. As part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program,
The first European known to visit Sakhalin was Martin Gerritz de Vries, who mapped Cape Patience and Cape Aniva on the island's east coast in 1643. The Dutch captain, however, was unaware that it was an island, and 17th-century maps usually showed these points (and often Hokkaido as well) as part of the mainland. As part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program,
 On the basis of its belief that it was an extension of Hokkaido, both geographically and culturally, Japan again proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island (as well as the
On the basis of its belief that it was an extension of Hokkaido, both geographically and culturally, Japan again proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island (as well as the
 Japanese forces invaded and occupied Sakhalin in the closing stages of the
Japanese forces invaded and occupied Sakhalin in the closing stages of the
 On 1 September 1983, Korean Air Flight 007, a South Korean civilian airliner, flew over Sakhalin and was shot down by the Soviet Union, just west of Sakhalin Island, near the smaller Moneron Island. The Soviet Union claimed it was a spy plane; however, commanders on the ground realized it was a commercial aircraft. All 269 passengers and crew died, including a U.S. Congressman, Larry McDonald.
On 27 May 1995, the 7.0 Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former Russian settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt.
On 1 September 1983, Korean Air Flight 007, a South Korean civilian airliner, flew over Sakhalin and was shot down by the Soviet Union, just west of Sakhalin Island, near the smaller Moneron Island. The Soviet Union claimed it was a spy plane; however, commanders on the ground realized it was a commercial aircraft. All 269 passengers and crew died, including a U.S. Congressman, Larry McDonald.
On 27 May 1995, the 7.0 Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former Russian settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt.
– an article in the ''
File:Sakhalin and her surroundings English ver.png, Sakhalin and its surroundings
File:Кекуры Мыса Великан 3.jpg, Velikan Cape, Sakhalin
File:Хребет Жданко и бухта Тихая.jpg, Zhdanko Mountain Ridge
 According to the 1897 census, Sakhalin had a population of 28,113, of which 56.2% were Russians, 8.4%
According to the 1897 census, Sakhalin had a population of 28,113, of which 56.2% were Russians, 8.4%

 The whole of the island is covered with dense
The whole of the island is covered with dense
File:Sakhalin Train.jpg, A passenger train in Nogliki
File:Japanese SL D51-22.jpg, A Japanese D51 steam locomotive outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Railway Station
 The economy of Sakhalin relies primarily on oil and gas exports,
The economy of Sakhalin relies primarily on oil and gas exports,
Map of the Sakhalin Hydrocarbon Region
– at Blackbourn Geoconsulting
TransGlobal Highway
– Proposed Sakhalin–Hokkaidō Friendship Tunnel
Maps of Ezo, Sakhalin and Kuril Islands
from 1854 {{Chinese historical placenames in Outer Manchuria Ainu geography Geography of Northeast Asia Islands of Sakhalin Oblast Islands of the Pacific Ocean Islands of the Russian Far East Islands of the Sea of Okhotsk Pacific Coast of Russia Physiographic provinces Former Japanese colonies
Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia or Northeastern Asia is a geographical Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia. Its northeastern landmass and islands are bounded by the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean.
The term Northeast Asia was popularized during the 1930s by Ame ...
. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai
Khabarovsk Krai (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is located in the Russian Far East and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative centre of the krai is the types of ...
in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
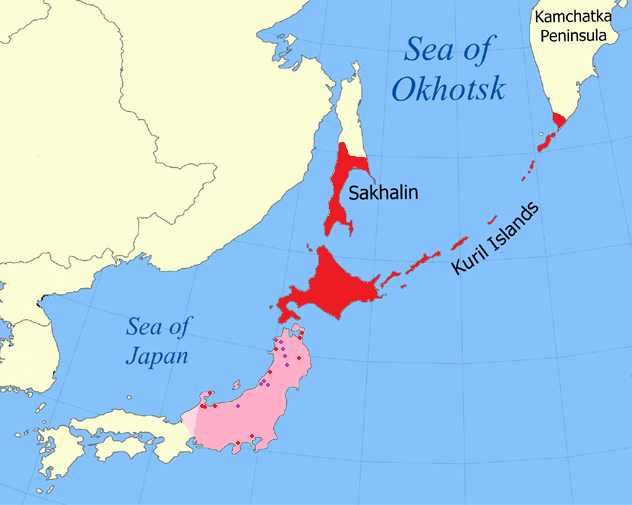
. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it ...
to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
. The indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers.
The island's name is derived from the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
was loose for the most part.
The ownership of the island has been contested during the past millienium, with China, Russia, and Japan all making claims on the territory at different times. Over the course of the 19th and 20th centuries it was Russia and Japan, and the disputes sometimes involved military conflicts and divisions of the island between the two powers. In 1875, Japan ceded its claims to Russia in exchange for the northern Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands are a volcanic archipelago administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. The islands stretch approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, separating the ...
. In 1897 more than half of the population were Russians and other European and Asian minorities. In 1905, following the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
, the island was divided, with Southern Sakhalin going to Japan. After the Siberian intervention, Japan invaded the northern parts of Sakhalin, and ruled the entire island from 1918 to 1925. Russia has held all of the island since seizing the Japanese portion in the final days of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in 1945, as well as all of the Kurils. Japan no longer claims any of Sakhalin, although it does still claim the southern Kuril Islands. Most Ainu on Sakhalin moved to Hokkaido, to the south across the La Pérouse Strait
La Pérouse Strait (), or , is a strait dividing the southern part of the Russian island of Sakhalin from the northern part of the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, and connecting the Sea of Japan on the west with the Sea of Okhotsk on the east.
...
, when Japanese civilians were displaced from the island in 1949.
Etymology
Sakhalin has several names including ( ), ( zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島), ( mnc, ), (), ( Nivkh: ). TheManchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) an ...
called it . , the word that has been borrowed in the form of "Sakhalin", means "black" in Manchu, means "river" and is the proper Manchu name of the Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is ...
.
The island was also called "Kuye Fiyaka". The word "Kuye" used by the Qing is "most probably related to ''kuyi'', the name given to the Sakhalin Ainu by their Nivkh and Nanai neighbors." When the Ainu migrated onto the mainland, the Chinese described a "strong Kui (or Kuwei, Kuwu, Kuye, Kugi, ''i.e.'' Ainu) presence in the area otherwise dominated by the Gilemi or Jilimi (Nivkh and other Amur peoples)." Related names were in widespread use in the region, for example the Kuril Ainu called themselves .
The origins of the traditional Japanese name, (), are unclear and multiple competing explanations have been proposed. These include:
* A borrowing of Mongolian ''karahoton'', meaning "distant fortress".
* A modification of ''Karahito'', meaning "Chinese person", from the presence of Chinese traders on the island.
* A derivation from dialect words meaning "prawns" or "many herring".
* An aphetic form of (''kamuy kar put ya mosir'') "The island created by God at the estuary".
The Japanese form 樺太 equates to ''Hwangt'ae'', an earlier name for the island now superseded by the transcription 사할린 ''Sahallin''.
The island was also historically referred to as "Tschoka" by European travelers in the late 18th century, such as Lapérouse and Langsdorff. This name is believed to derive from an obsolete endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
used by Sakhalin Ainu, possibly based on the word ' (, "we") in Sakhalin Ainu language
Sakhalin Ainu is an extinct Ainu language, or perhaps several Ainu languages, that was or were spoken on the island of Sakhalin, now part of Russia.
History and present situation
The Ainu of Sakhalin appear to have been present on Sakhalin ...
.
History
Early history
 Humans lived on Sakhalin in the
Humans lived on Sakhalin in the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
Stone Age. Flint implements such as those found in Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
have been found at Dui and Kusunai in great numbers, as well as polished stone hatchets similar to European examples, primitive pottery with decorations like those of the Olonets, and stone weights used with fishing nets. A later population familiar with bronze left traces in earthen walls and kitchen-midden
A midden is an old dump for domestic waste. It may consist of animal bones, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human oc ...
s on Aniva Bay.

Indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
of Sakhalin include the Ainu in the southern half, the Oroks in the central region, and the Nivkhs in the north.
Yuan and Ming tributaries
After theMongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
conquered the Jin dynasty (1234), they suffered raids by the Nivkh and Udege peoples. In response, the Mongols established an administration post at Nurgan (present-day Tyr, Russia) at the junction of the Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
and Amgun rivers in 1263, and forced the submission of the two peoples.
From the Nivkh perspective, their surrender to the Mongols essentially established a military alliance against the Ainu who had invaded their lands. According to the '' History of Yuan'', a group of people known as the ''Guwei'' ( zh, labels=no, t=骨嵬, p=Gǔwéi, the Nivkh name for Ainu) from Sakhalin invaded and fought with the Jilimi (Nivkh people) every year. On 30 November 1264, the Mongols attacked the Ainu. The Ainu resisted the Mongol invasions but by 1308 had been subdued. They paid tribute to the Mongol Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
at posts in Wuliehe, Nanghar, and Boluohe.
The Chinese Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
(1368–1644) placed Sakhalin under its "system for subjugated peoples" (''ximin tizhi''). From 1409 to 1411 the Ming established an outpost called the Nurgan Regional Military Commission near the ruins of Tyr on the Siberian mainland, which continued operating until the mid-1430s. There is some evidence that the Ming eunuch Admiral Yishiha reached Sakhalin in 1413 during one of his expeditions to the lower Amur, and granted Ming titles to a local chieftain. Link is to partial text.
The Ming recruited headmen from Sakhalin for administrative posts such as commander ( zh, labels=no, p=zhǐhuīshǐ, c=指揮使), assistant commander ( zh, labels=no, p=zhǐhuī qiānshì, t=指揮僉事), and "official charged with subjugation" ( zh, labels=no, p=wèizhènfǔ, t=衛鎮撫). In 1431, one such assistant commander, Alige, brought marten pelts as tribute to the Wuliehe post. In 1437, four other assistant commanders (Zhaluha, Sanchiha, Tuolingha, and Alingge) also presented tribute. According to the '' Ming Veritable Records'', these posts, like the position of headman, were hereditary and passed down the patrilineal line. During these tributary missions, the headmen would bring their sons, who later inherited their titles. In return for tribute, the Ming awarded them with silk uniforms.
Nivkh women in Sakhalin married Han Chinese Ming officials when the Ming took tribute from Sakhalin and the Amur river region.
Qing tributary
The ManchuQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, which came to power in China in 1644, called Sakhalin "Kuyedao" () or "Kuye Fiyaka" ( ). The Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) an ...
called it "Sagaliyan ula angga hada" (Island at the Mouth of the Black River). The Qing first asserted influence over Sakhalin after the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk, which defined the Stanovoy Mountains as the border between the Qing and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
s. In the following year the Qing sent forces to the Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
estuary and demanded that the residents, including the Sakhalin Ainu, pay tribute. This was followed by several further visits to the island as part of the Qing effort to map the area. To enforce its influence, the Qing sent soldiers and mandarins across Sakhalin, reaching most parts of the island except the southern tip. The Qing imposed a fur-tribute system on the region's inhabitants.
The Qing dynasty established an office in Ningguta, situated midway along the Mudan River, to handle fur from the lower Amur and Sakhalin. Tribute was supposed to be brought to regional offices, but the lower Amur and Sakhalin were considered too remote, so the Qing sent officials directly to these regions every year to collect tribute and to present awards. By the 1730s, the Qing had appointed senior figures among the indigenous communities as "clan chief" (''hala-i-da'') or "village chief" (''gasan-da'' or ''mokun-da''). In 1732, 6 ''hala'', 18 ''gasban'', and 148 households were registered as tribute bearers in Sakhalin. Manchu officials gave tribute missions rice, salt, other necessities, and gifts during the duration of their mission. Tribute missions occurred during the summer months. During the reign of the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, personal name Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China pr ...
(r. 1735–95), a trade post existed at Delen, upstream of Kiji (Kizi) Lake, according to Rinzo Mamiya. There were 500–600 people at the market during Mamiya's stay there.
Local native Sakhalin chiefs had their daughters taken as wives by Manchu officials as sanctioned by the Qing dynasty when the Qing exercised jurisdiction in Sakhalin and took tribute from them.
Japanese exploration and colonization
In 1635, Matsumae Kinhiro, the second daimyō of Matsumae Domain in Hokkaidō, sent Satō Kamoemon and Kakizaki Kuroudo on an expedition to Sakhalin. One of the Matsumae explorers, Kodō Shōzaemon, stayed on the island in the winter of 1636 and sailed along the east coast to Taraika (now Poronaysk) in the spring of 1637. In an early colonization attempt, a Japanese settlement was established at Ōtomari on Sakhalin's southern end in 1679. Cartographers of theMatsumae clan
The was a Japanese aristocratic family who were daimyo of Matsumae Domain, in present-day Matsumae, Hokkaidō, from the Azuchi–Momoyama period until the Meiji Restoration. They were given the domain as a march fief in 1590 by Toyotomi ...
drew a map of the island and called it "Kita-Ezo" (Northern Ezo, Ezo being the old Japanese name for the islands north of Honshu
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the list of islands by area, seventh-largest island in the world, and the list of islands by ...
).
In the 1780s, the influence of the Japanese Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
on the Ainu of southern Sakhalin increased significantly. By the beginning of the 19th century, the Japanese economic zone extended midway up the east coast, to Taraika. With the exception of the Nayoro Ainu located on the west coast in close proximity to China, most Ainu stopped paying tribute to the Qing dynasty. The Matsumae clan
The was a Japanese aristocratic family who were daimyo of Matsumae Domain, in present-day Matsumae, Hokkaidō, from the Azuchi–Momoyama period until the Meiji Restoration. They were given the domain as a march fief in 1590 by Toyotomi ...
was nominally in charge of Sakhalin, but they neither protected nor governed the Ainu there. Instead they extorted the Ainu for Chinese silk, which they sold in Honshu
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the list of islands by area, seventh-largest island in the world, and the list of islands by ...
as Matsumae's special product. To obtain Chinese silk, the Ainu fell into debt, owing much fur to the Santan ( Ulch people), who lived near the Qing office. The Ainu also sold the silk uniforms (''mangpao'', ''bufu'', and ''chaofu'') given to them by the Qing, which made up the majority of what the Japanese knew as ''nishiki'' and ''jittoku''. As dynastic uniforms, the silk was of considerably higher quality than that traded at Nagasaki
, officially , is the capital and the largest Cities of Japan, city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
Founded by the Portuguese, the port of Portuguese_Nagasaki, Nagasaki became the sole Nanban trade, port used for tr ...
, and enhanced Matsumae prestige as exotic items. Eventually the Tokugawa government, realizing that they could not depend on the Matsumae, took control of Sakhalin in 1807.
Japan proclaimed sovereignty over Sakhalin in 1807; in 1809, Mamiya Rinzō claimed that it was an island.
European exploration
 The first European known to visit Sakhalin was Martin Gerritz de Vries, who mapped Cape Patience and Cape Aniva on the island's east coast in 1643. The Dutch captain, however, was unaware that it was an island, and 17th-century maps usually showed these points (and often Hokkaido as well) as part of the mainland. As part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program,
The first European known to visit Sakhalin was Martin Gerritz de Vries, who mapped Cape Patience and Cape Aniva on the island's east coast in 1643. The Dutch captain, however, was unaware that it was an island, and 17th-century maps usually showed these points (and often Hokkaido as well) as part of the mainland. As part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program, Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
Jean-Baptiste Régis, Pierre Jartoux, and Xavier Ehrenbert Fridelli joined a Chinese team visiting the lower Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
(known to them under its Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
name, Sahaliyan Ula, "the Black River"), in 1709, and learned of the existence of the nearby offshore island from the Nanai natives of the lower Amur.
The Jesuits did not have a chance to visit the island, and the geographical information provided by the Nanai people and Manchus who had been to the island was insufficient to allow them to identify it as the land visited by de Vries in 1643. As a result, many 17th-century maps showed a rather strangely shaped Sakhalin, which included only the northern half of the island (with Cape Patience), while Cape Aniva, discovered by de Vries, and the "Black Cape" (Cape Crillon) were thought to form part of the mainland.
Only with the 1787 expedition of Jean-François de La Pérouse did the island began to resemble something of its true shape on European maps. Though unable to pass through its northern "bottleneck" due to contrary winds, La Perouse charted most of the Strait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary or Gulf of Tartary (; ; ; ) is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia (South-East Russia), connecting the Sea of Okhotsk ( Nevelskoy Strait) on the north with the Sea of Japan ...
, and islanders he encountered near today's Nevelskoy Strait told him that the island was called "Tchoka" (or at least that is how he recorded the name in French), and "Tchoka" appears on some maps thereafter.
19th century
Russo-Japanese rivalry
 On the basis of its belief that it was an extension of Hokkaido, both geographically and culturally, Japan again proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island (as well as the
On the basis of its belief that it was an extension of Hokkaido, both geographically and culturally, Japan again proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island (as well as the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands are a volcanic archipelago administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. The islands stretch approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, separating the ...
chain) in 1845, in the face of competing claims from Russia. In 1849, however, the Russian navigator Gennady Nevelskoy
Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy (; in Drakino, Soligalichsky Uyezd, Kostroma Governorate – in St. Petersburg) was a Russian navigator and naval officer.
In 1829 he joined the Naval Cadet Corps and in 1846 was given the rank of ...
recorded the existence and navigability of the strait later given his name, and Russian settlers began establishing coal mines, administration facilities, schools, and churches on the island. In 1853–54, Nikolay Rudanovsky surveyed and mapped the island.
In 1855, Russia and Japan signed the Treaty of Shimoda, which declared that nationals of both countries could inhabit the island: Russians in the north, and Japanese in the south, without a clearly defined boundary between. Russia also agreed to dismantle its military base at Ootomari. Following the Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Chinese War or ''Arrow'' War, was fought between the United Kingdom, France, Russia, and the United States against the Qing dynasty of China between 1856 and 1860. It was the second major ...
, Russia forced China to sign the Treaty of Aigun (1858) and the Convention of Peking (1860), under which China lost to Russia all claims to territories north of Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang is a province in northeast China. It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the confluence of the Amur and Us ...
(Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
) and east of Ussuri.
In 1857, the Russians established a penal colony, or '' katorga'', on Sakhalin. The island remained under shared sovereignty until the signing of the 1875 Treaty of Saint Petersburg, in which Japan surrendered its claims in Sakhalin to Russia. In 1890, the author Anton Chekhov
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (; ; 29 January 1860 – 15 July 1904) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer, widely considered to be one of the greatest writers of all time. His career as a playwright produced four classics, and his b ...
visited the penal colony on Sakhalin. He spent three months there interviewing thousands of convicts and settlers for a census and published his memoir ''Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
'' () of his journey.
Division along 50th parallel
 Japanese forces invaded and occupied Sakhalin in the closing stages of the
Japanese forces invaded and occupied Sakhalin in the closing stages of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
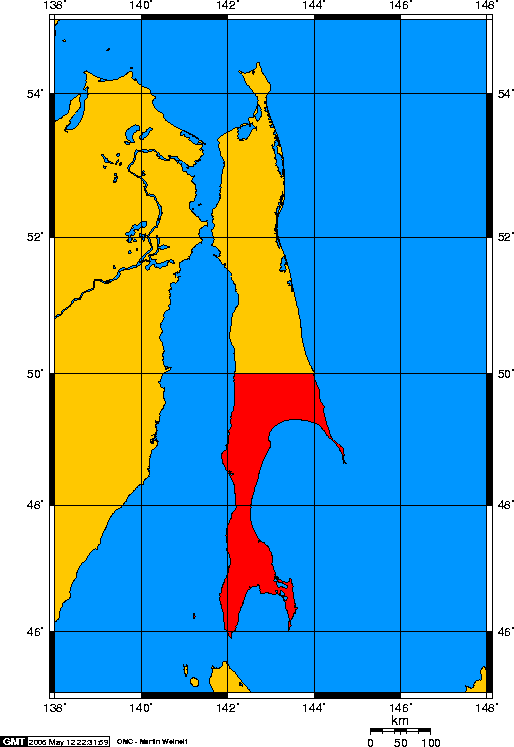
. In accordance with the Treaty of Portsmouth of 1905, the southern part of the island below the 50th parallel north
Following are circles of latitude between the 45th parallel north and the 50th parallel north:
46th parallel north
The 46th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 46 degree (angle), degrees true north, north of the Earth, Earth's equat ...
reverted to Japan, while Russia retained the northern three-fifths.
South Sakhalin was administered by Japan as Karafuto Prefecture (), with the capital at Toyohara (today's Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk). A large number of migrants were brought in from Korea.
The northern, Russian, half of the island formed Sakhalin Oblast, with the capital at Aleksandrovsk-Sakhalinsky. In response to the United States opening of Japan by Commodore Matthew C. Perry in 1853 and, later, the subsequent signing of the Convention of Kanagawa on March 31, 1854, Tsar Nicholas I
Nicholas I, group=pron (Russian language, Russian: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia, List of rulers of Partitioned Poland#Kings of the Kingdom of Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 18 ...
, who was personally involved in the "Sakhalin issue", in April 1853 ordered the Russian-American Company (RAC) to immediately occupy the Sakhalin Island and begin colonization by constructing two redoubts armed with cannons on the western and southern coasts of the island. On September 20, 1853, the RAC ship " Emperor Nikolai I" () under the command of skipper Martin Fyodorovich Klinkowström () and under the general guidance of Captain Nevelskoy arrived at Tomari-Aniva on Aniva Bay, not far from the main Japanese settlement on the island, and put ashore men and materials to form a military outpost.
At the oldest stettlement on Sakhlin Island, Sakhalin Oblast had a Czarist era penal colony named Due () on Cape Douai which had the 1853 established Makaryevka () coal mine, which was supported by both the Muravyovsky post (), now known as Korsakov (), at Aniva Bay (), which was named after Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky who had sponsored the expedition commanded by Gennady Nevelskoy
Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy (; in Drakino, Soligalichsky Uyezd, Kostroma Governorate – in St. Petersburg) was a Russian navigator and naval officer.
In 1829 he joined the Naval Cadet Corps and in 1846 was given the rank of ...
that explored the coast of Sakhalin Island from 1849 to 1853, and the Russian-American Company, and hosted its first prisoner beginning in 1876. On April 18, 1869, Tsar Alexander II approved the "Regulations of the Committee on the Arrangement of Hard Labor" () which formed the legal basis for Sakhalin Island to be a penal colony.
In 1920, during the Siberian Intervention, Japan again occupied the northern part of the island, returning it to the Soviet Union in 1925 after the Treaty of Beijing was signed on January 20, 1925. However, Japan formed the state owned firm North Sakhalin Oil () which extracted oil from the OKHA Oil Field () near Okha on North Sakhalin from 1926 to 1944.
Whaling
Between 1848 and 1902, American whaleships huntedwhale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s off Sakhalin. They cruised for bowhead and gray whale
The gray whale (''Eschrichtius robustus''), also known as the grey whale,Britannica Micro.: v. IV, p. 693. is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and breeding grounds yearly. It reaches a length of , a weight of up to and lives between ...
s to the north and right whale
Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus ''Eubalaena'': the North Atlantic right whale (''E. glacialis''), the North Pacific right whale (''E. japonica'') and the southern right whale (''E. australis''). They are class ...
s to the east and south.
On June 7, 1855, the ship ''Jefferson'' (396 tons), of New London, was wrecked on Cape Levenshtern, on the northeastern side of the island, during a fog. All hands were saved as well as 300 barrels of whale oil
Whale oil is oil obtained from the blubber of whales. Oil from the bowhead whale was sometimes known as train-oil, which comes from the Dutch word ''traan'' ("tear drop").
Sperm oil, a special kind of oil used in the cavities of sperm whales, ...
.
Second World War
In August 1945, after repudiating the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, the Soviet Union invaded southern Sakhalin, an action planned secretly at theYalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (), held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the postwar reorganization of Germany and Europe. The three sta ...
. The Soviet attack started on August 11, 1945, a few days before the surrender of Japan. The Soviet 56th Rifle Corps, part of the 16th Army, consisting of the 79th Rifle Division, the 2nd Rifle Brigade, the 5th Rifle Brigade and the 214 Armored Brigade, attacked the Japanese 88th Infantry Division. Although the Soviet Red Army outnumbered the Japanese by three to one, they advanced only slowly due to strong Japanese resistance. It was not until the 113th Rifle Brigade and the 365th Independent Naval Infantry Rifle Battalion from Sovetskaya Gavan landed on Tōro, a seashore village of western Karafuto, on August 16 that the Soviets broke the Japanese defense line. Japanese resistance grew weaker after this landing. Actual fighting continued until August 21. From August 22 to August 23, most remaining Japanese units agreed to a ceasefire. The Soviets completed the conquest of Karafuto on August 25, 1945, by occupying the capital of Toyohara.
Of the approximately 400,000 people – mostly Japanese and Korean – who lived on South Sakhalin in 1944, about 100,000 were evacuated to Japan during the last days of the war. The remaining 300,000 stayed behind, some for several more years.
While the vast majority of Sakhalin Japanese and Koreans were gradually repatriated between 1946 and 1950, tens of thousands of Sakhalin Koreans (and a number of their Japanese spouses) remained in the Soviet Union.
No final peace treaty has been signed and the status of four neighboring islands remains disputed. Japan renounced its claims of sovereignty over southern Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Treaty of San Francisco
The , also called the , re-established peaceful relations between Japan and the Allied Powers on behalf of the United Nations by ending the legal state of war, military occupation and providing for redress for hostile actions up to and inclu ...
(1951), but maintains that the four offshore islands of Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
currently administered by Russia were not subject to this renunciation. Japan granted mutual exchange visas for Japanese and Ainu families divided by the change in status. Recently, economic and political cooperation has gradually improved between the two nations despite disagreements.
Recent history
 On 1 September 1983, Korean Air Flight 007, a South Korean civilian airliner, flew over Sakhalin and was shot down by the Soviet Union, just west of Sakhalin Island, near the smaller Moneron Island. The Soviet Union claimed it was a spy plane; however, commanders on the ground realized it was a commercial aircraft. All 269 passengers and crew died, including a U.S. Congressman, Larry McDonald.
On 27 May 1995, the 7.0 Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former Russian settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt.
On 1 September 1983, Korean Air Flight 007, a South Korean civilian airliner, flew over Sakhalin and was shot down by the Soviet Union, just west of Sakhalin Island, near the smaller Moneron Island. The Soviet Union claimed it was a spy plane; however, commanders on the ground realized it was a commercial aircraft. All 269 passengers and crew died, including a U.S. Congressman, Larry McDonald.
On 27 May 1995, the 7.0 Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former Russian settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt.
Geography
Sakhalin is separated from the mainland by the narrow and shallowStrait of Tartary
Strait of Tartary or Gulf of Tartary (; ; ; ) is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia (South-East Russia), connecting the Sea of Okhotsk ( Nevelskoy Strait) on the north with the Sea of Japan ...
, which often freezes in winter in its narrower part, and from Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
, Japan, by the Soya Strait or La Pérouse Strait
La Pérouse Strait (), or , is a strait dividing the southern part of the Russian island of Sakhalin from the northern part of the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, and connecting the Sea of Japan on the west with the Sea of Okhotsk on the east.
...
. Sakhalin is the largest island in Russia, being long, and wide, with an area of . It lies at similar latitudes to England, Wales and Ireland.
Its orography and geological structure are imperfectly known. One theory is that Sakhalin arose from the Sakhalin Island Arc. Nearly two-thirds of Sakhalin is mountainous. Two parallel ranges of mountains traverse it from north to south, reaching . The Western Sakhalin Mountains peak in Mount Ichara, , while the Eastern Sakhalin Mountains's highest peak, Mount Lopatin , is also the island's highest mountain. Tym-Poronaiskaya Valley separates the two ranges. Susuanaisky and Tonino-Anivsky ranges traverse the island in the south, while the swampy Northern-Sakhalin plain occupies most of its north.Ivlev, A. M. Soils of Sakhalin. New Delhi: Indian National Scientific Documentation Centre, 1974. Pages 9–28.
Crystalline rocks crop out at several capes; Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
s, containing an abundant and specific fauna of gigantic ammonite
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family N ...
s, occur at Dui on the west coast; and Tertiary
Tertiary (from Latin, meaning 'third' or 'of the third degree/order..') may refer to:
* Tertiary period, an obsolete geologic period spanning from 66 to 2.6 million years ago
* Tertiary (chemistry), a term describing bonding patterns in organic ch ...
conglomerates, sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
s, marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, Clay minerals, clays, and silt. When Lithification, hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
M ...
s, and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
s, folded by subsequent upheavals, are found in many parts of the island. The clays, which contain layers of good coal and abundant fossilized vegetation, show that during the Miocene period, Sakhalin formed part of a continent which comprised north Asia, Alaska, and Japan, and enjoyed a comparatively warm climate. The Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
s was probably broader than it is now.
Main rivers: The Tym, long and navigable by rafts and light boats for , flows north and northeast with numerous rapids and shallows, and enters the Sea of Okhotsk.Тымь– an article in the ''
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
''. (In Russian, retrieved 21 June 2020.) The Poronay flows south-southeast to the Gulf of Patience or Shichiro Bay, on the southeastern coast. Three other small streams enter the wide semicircular Aniva Bay or Higashifushimi Bay at the southern extremity of the island.
The northernmost point of Sakhalin is Cape Elizabeth on the Schmidt Peninsula, while Cape Crillon is the southernmost point of the island. The Khalpili Islands are off Cape Khalpili.
Sakhalin has two smaller islands associated with it, Moneron Island and Ush Island. Moneron, the only land mass in the Tatar strait, long and wide, is about west from the nearest coast of Sakhalin and from the port city of Nevelsk. Ush Island is an island off of the northern coast of Sakhalin.
Demographics
 According to the 1897 census, Sakhalin had a population of 28,113, of which 56.2% were Russians, 8.4%
According to the 1897 census, Sakhalin had a population of 28,113, of which 56.2% were Russians, 8.4% Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, 7.0% Nivkh, 5.8% Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, 5.4% Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
, 5.1% Ainu, 2.82% Oroks, 0.95% in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, 0.81% Japanese, with the non-indigenous people living mainly from agriculture, or being convicts or exiles. The majority of Nivkh, Ainu and Japanese lived from fishing or hunting, whereas the Oroks lived mainly by livestock (reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
) breeding. The Ainu, Japanese and Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
lived almost exclusively in the southern part of the island. Since 1925, many Poles fled Soviet Russian persecution in the north to the then Japanese south.
The 400,000 Japanese inhabitants of Sakhalin (including the Japanized indigenous Ainu) who had not already been evacuated during the war were deported following the invasion of the southern portion of the island by the Soviet Union in 1945 at the end of World War II.
In 2010, the island's population was recorded at 497,973, 83% of whom were ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, followed by about 30,000 Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
(5.5%). Smaller minorities were the Ainu, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
, Sakhas and in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Evenks
The Evenki, also known as the Evenks and formerly as the Tungus, are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic people of North Asia. In Russia, the Evenki are recognised as one of the Indigenous peoples of the Russian North, indigenous peoples of the Russi ...
. The native inhabitants currently consist of some 2,000 Nivkhs and 750 Oroks. The Nivkhs in the north support themselves by fishing and hunting.
The administrative center of the oblast, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, a city of about 175,000, has a large Korean minority, typically referred to as Sakhalin Koreans, who were forcibly brought by the Japanese during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
to work in the coal mines. Most of the population lives in the southern half of the island, centered mainly around Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk and two ports, Kholmsk and Korsakov (population about 40,000 each). In 2008 there were 6,416 births and 7,572 deaths.
Climate
The Sea of Okhotsk ensures that Sakhalin has a cold and humid climate, ranging from humid continental (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''Dfb'') in the south to subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
(''Dfc'') in the centre and north. The maritime influence makes summers much cooler than in similar-latitude inland cities such as Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
or Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
, but makes the winters much snowier and a few degrees warmer than in interior East Asian cities at the same latitude. Summers are foggy with little sunshine.
Precipitation is heavy, owing to the strong onshore winds in summer and the high frequency of North Pacific storms affecting the island in the autumn. It ranges from around on the northwest coast to over in southern mountainous regions. In contrast to interior east Asia with its pronounced summer maximum, onshore winds ensure Sakhalin has year-round precipitation with a peak in the autumn.
Flora and fauna

 The whole of the island is covered with dense
The whole of the island is covered with dense forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
s, mostly conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
ous. The Yezo (or Yeddo) spruce (''Picea jezoensis''), the Sakhalin fir (''Abies sachalinensis''), the Dahurian larch (''Larix gmelinii''), and '' Picea glehnii'' are the chief trees; on the upper parts of the mountains are the Siberian dwarf pine
''Pinus pumila'', commonly known as the Siberian dwarf pine, dwarf Siberian pine, dwarf stone pine, Japanese stone pine, or creeping pine, is a tree in the family Pinaceae native plant, native to northeastern Asia and the Japan, Japanese isles. ...
(''Pinus pumila'') and the Kurile bamboo (''Sasa kurilensis''). Birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
es, both Siberian silver birch ('' Betula platyphylla'') and Erman's birch (''B. ermanii''), poplar, elm ('' Ulmus laciniata''), bird cherry (''Prunus padus''), Japanese yew (''Taxus cuspidata''), and several willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, of the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 350 species (plus numerous hybrids) of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions.
Most species are known ...
s are mixed with the conifers; while farther south the maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
, rowan and oak, as also the Japanese '' Kalopanax septemlobus'', the Amur cork tree (''Phellodendron amurense''), the spindle ('' Euonymus macropterus'') and the vine ('' Vitis thunbergii'') make their appearance. The underwoods abound in berry-bearing plants (e.g. cloudberry, cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. Cranberries are low, creeping shrubs or vines up to long and in height; they have slender stems that are not th ...
, crowberry, red whortleberry), red-berried elder ('' Sambucus racemosa''), wild raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of several plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the Rosaceae, rose family, most of which are in the subgenus ''Rubus#Modern classification, Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Ras ...
, and Spiraea.
Brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear native to Eurasia and North America. Of the land carnivorans, it is rivaled in size only by its closest relative, the polar bear, which is much less variable in size and slightly bigger on av ...
, Eurasian river otter, red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
, eurasian lynx
The Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx'') is one of the four wikt:extant, extant species within the medium-sized wild Felidae, cat genus ''Lynx''. It is widely distributed from Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe to Cent ...
, leopard cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a Felinae, small wild cat native to continental South Asia, South, Southeast Asia, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely di ...
and sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaz ...
are fairly numerous (as are reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
in the north); rarely seen, but still present, is the elusive Sakhalin musk deer, a subspecies of Siberian musk deer. Smaller mammals include hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores and live Solitary animal, solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are precociality, able to fend for themselves ...
, squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrel ...
s, and various rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
(including rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include '' Neotoma'' (pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandicoo ...
s and mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
) nearly everywhere. The bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
population is made-up of mostly the common eastern Siberian forms, but there are some endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
or near-endemic breeding species, notably the endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
Nordmann's greenshank (''Tringa guttifer'') and the Sakhalin leaf warbler (''Phylloscopus borealoides''). The rivers swarm with fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, especially species of salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
(''Oncorhynchus''). Numerous cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
s visit the sea coast, including the endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
Western Pacific gray whale
The gray whale (''Eschrichtius robustus''), also known as the grey whale,Britannica Micro.: v. IV, p. 693. is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and breeding grounds yearly. It reaches a length of , a weight of up to and lives between ...
, for which the waters off of Sakhalin are their only known feeding ground, thus being a vitally important region for their population's longevity. Other cetaceans known to occur in this area are the North Pacific right whale
The North Pacific right whale (''Eubalaena japonica'') is a very large, thickset baleen whale species that is extremely rare and endangered.
The Northeast Pacific population, which summers in the southeastern Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska, may ...
, the bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus''), sometimes called the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and polar whale, is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena' ...
, and the beluga whale, the latter two generally preferring icy waters and colder conditions to the north. All are potential prey species for the highly social killer whale, or orca. The once-common Japanese sea lion and Japanese sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of ...
, both hunted to extinction, formerly ranged from Japan's coastline to Sakhalin, Korea, Kamchatka, and the Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea, also known as the North Sea, is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea.
Names
It is one of four ...
; however, over-harvesting depleted their numbers in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Today, ringed seals and the giant Steller sea lion can be spotted around Sakhalin Island.
Transport
Sea
Transport, especially by sea, is an important segment of the economy. Nearly all the cargo arriving for Sakhalin (and theKuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands are a volcanic archipelago administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. The islands stretch approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, separating the ...
) is delivered by cargo boats, or by ferries, in railway wagons, through the Vanino-Kholmsk train ferry from the mainland port of Vanino to Kholmsk. The ports of Korsakov and Kholmsk are the largest and handle all kinds of goods, while coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
and timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
shipments often go through other ports. In 1999, a ferry service was opened between the ports of Korsakov and Wakkanai, Japan, and operated through the autumn of 2015, when service was suspended.
For the 2016 summer season, this route will be served by a highspeed catamaran ferry from Singapore named Penguin 33. The ferry is owned by Penguin International Limited and operated by Sakhalin Shipping Company.
Sakhalin's main shipping company is Sakhalin Shipping Company, headquartered in Kholmsk on the island's west coast.
Rail
About 30% of all inland transport volume is carried by the island's railways, most of which are organized as the Sakhalin Railway ( Сахалинская железная дорога), which is one of the 17 territorial divisions of the Russian Railways. The Sakhalin Railway network extends from Nogliki in the north to Korsakov in the south. Sakhalin's railway has a connection with the rest of Russia via atrain ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry Railroad car, railway vehicles, as well as their cargoes and passengers. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with Track (rail transport), railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the f ...
operating between Vanino and Kholmsk.
The process of converting the railways from the Japanese gauge to the Russian gauge began in 2004 and
was completed in 2019.
The original Japanese D51 steam locomotives were used by the Soviet Railways until 1979.
Besides the main network run by the Russian Railways, until December 2006 the local oil company (Sakhalinmorneftegaz) operated a corporate narrow-gauge line extending for from Nogliki further north to Okha ( Узкоколейная железная дорога Оха – Ноглики). During the last years of its service, it gradually deteriorated; the service was terminated in December 2006, and the line was dismantled in 2007–2008.
Air
Sakhalin is connected by regular flights toMoscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, Khabarovsk, Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
and other cities of Russia. Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Airport has regularly scheduled international flights to Hakodate
is a Cities of Japan, city and seaports of Japan, port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of January 31, 2024, the city had an estimated population of 239,813 with 138,807 househol ...
, Japan, and Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
and Busan
Busan (), officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second list of cities in South Korea by population, most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.3 million as of 2024. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economi ...
, South Korea. There are also charter flights to the Japanese cities of Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
, Niigata, and Sapporo
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in Hokkaido, Japan. Located in the southwest of Hokkaido, it lies within the alluvial fan of the Toyohira River, a tributary of the Ishikari River. Sapporo is the capital ...
and to the Chinese cities of Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
, Dalian
Dalian ( ) is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China (after Shenyang ...
and Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
. The island was formerly served by Alaska Airlines from Anchorage
Anchorage, officially the Municipality of Anchorage, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Alaska. With a population of 291,247 at the 2020 census, it contains nearly 40 percent of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolita ...
, Petropavlovsk, and Magadan
Magadan ( rus, Магадан, p=məɡɐˈdan) is a Port of Magadan, port types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative centre of Magadan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the isthmus of the Staritsky Peninsula by the ...
.
Fixed links
The idea of building a fixed link between Sakhalin and the Russian mainland was first put forward in the 1930s. In the 1940s, an abortive attempt was made to link the island via a underseatunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ve ...
. The project was abandoned under Premier Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
. In 2000, the Russian government revived the idea, adding a suggestion that a 40-km (25 mile) long bridge could be constructed between Sakhalin and the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, providing Japan with a direct connection to the Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
n railway network. It was claimed that construction work could begin as early as 2001. The idea was received skeptically by the Japanese government and appears to have been shelved, probably permanently, after the cost was estimated at as much as $50 billion.
In November 2008, Russian president Dmitry Medvedev
Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev (born 14 September 1965) is a Russian politician and lawyer who has served as Deputy Chairman of the Security Council of Russia since 2020. Medvedev was also President of Russia between 2008 and 2012 and Prime Mini ...
announced government support for the construction of the Sakhalin Tunnel, along with the required regauging of the island's railways to Russian standard gauge, at an estimated cost of 300–330 billion rouble
The ruble or rouble (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is a currency unit. Currently, currencies named ''ruble'' in circulation include the Russian ruble (RUB, ₽) in Russia and the Belarusian ruble (BYN, Rbl) in Belarus. These currencies are s ...
s.
In July 2013, Russian Far East development minister Viktor Ishayev proposed a railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
bridge to link Sakhalin with the Russian mainland. He also again suggested a bridge between Sakhalin and Hokkaidō, which could potentially create a continuous rail corridor between Europe and Japan. In 2018, president Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
ordered a feasibility study for a mainland bridge project.
Economy
 The economy of Sakhalin relies primarily on oil and gas exports,
The economy of Sakhalin relies primarily on oil and gas exports, coal mining
Coal mining is the process of resource extraction, extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its Energy value of coal, energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to Electricity generation, generate electr ...
, forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and Natural environment, environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and ...
, and fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
. Limited quantities of rye, wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, oats, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
and vegetable
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including edible flower, flo ...
s grow there, although the growing season
A season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The growing season is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal plant growth. Whi ...
averages less than 100 days.
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and the subsequent economic liberalization
Economic liberalization, or economic liberalisation, is the lessening of government regulations and restrictions in an economy in exchange for greater participation by private entities. In politics, the doctrine is associated with classical liber ...
, Sakhalin has experienced an oil boom with extensive petroleum-exploration and mining by most large oil multinational corporations
A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or stateless corporation, is a corporate organization that owns and cont ...
. The oil and natural- gas reserves contain an estimated 14 billion
Billion is a word for a large number, and it has two distinct definitions:
* 1,000,000,000, i.e. one thousand million, or (ten to the ninth power), as defined on the short scale. This is now the most common sense of the word in all varieties of ...
barrels (2.2 km3) of oil and 2,700 km3 (96 trillion
''Trillion'' is a number with two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000,000, i.e. one million 1,000,000, million, or (ten to the twelfth Exponentiation, power), as defined on the long and short scales, short scale. This is now the meaning in bot ...
cubic feet) of gas and are being developed under production-sharing agreement contracts involving international oil- companies like ExxonMobil
Exxon Mobil Corporation ( ) is an American multinational List of oil exploration and production companies, oil and gas corporation headquartered in Spring, Texas, a suburb of Houston. Founded as the Successors of Standard Oil, largest direct s ...
and Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard outer layer of a marine ani ...
.
In 1996, two large consortia, Sakhalin-I and Sakhalin-II, signed contracts to explore for oil and gas off the northeast coast of the island. The two consortia's pre-project estimate of costs were a combined US$
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
21 billion on the two projects; costs had almost doubled to $37 billion as of September 2006, triggering Russian governmental opposition. The cost will include an estimated US$1 billion to upgrade the island's infrastructure: roads, bridges, waste management
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste, together with monitor ...
sites, airports, railways, communications systems, and ports. In addition, Sakhalin-III-through-VI are in various early stages of development.
The Sakhalin I project, managed by Exxon Neftegas, completed a production-sharing agreement (PSA) between the Sakhalin I consortium, the Russian Federation, and the Sakhalin government. Russia is in the process of building a pipeline across the Tatar Strait from Sakhalin Island to De-Kastri terminal on the Russian mainland. From De-Kastri, the resource will be loaded onto tankers for transport to East Asian markets, namely Japan, South Korea and China.
A second consortium, Sakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd (Sakhalin Energy), is managing the Sakhalin II project. It has completed the first production-sharing agreement (PSA) with the Russian Federation. Sakhalin Energy will build two 800-km pipelines running from the northeast of the island to Prigorodnoye (Prigorodnoe) in Aniva Bay at the southern end. The consortium will also build, at Prigorodnoye, the first liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume o ...
(LNG) plant to be built in Russia. The oil and gas are also bound for East Asian markets.
Sakhalin II has come under fire from environmental groups, namely Sakhalin Environment Watch, for dumping dredging material in Aniva Bay. These groups were also worried about the offshore pipelines interfering with the migration of whales off the island. The consortium has () rerouted the pipeline to avoid the whale migration. After a doubling in the projected cost, the Russian government threatened to halt the project for environmental reasons. There have been suggestions that the Russian government is using the environmental issues as a pretext for obtaining a greater share of revenues from the project and/or forcing involvement by the state-controlled Gazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐsˈprom) is a Russian State-owned enterprise, majority state-owned multinational Energy industry, energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. The Gazprom name is a contract ...
. The cost overruns (at least partly due to Shell's response to environmental concerns), are reducing the share of profits flowing to the Russian treasury.
In 2000, the oil-and-gas industry accounted for 57.5% of Sakhalin's industrial output. By 2006 it is expected to account for 80% of the island's industrial output. Sakhalin's economy is growing rapidly thanks to its oil-and-gas industry.
, Gazprom had taken a 50% plus one share interest in Sakhalin II by purchasing 50% of Shell, Mitsui and Mitsubishi's shares.
In June 2021, it was announced that Russia aims to make Sakhalin Island carbon neutral by 2025.
International partnerships
* Gig Harbor, Washington, United States *Jeju Province
Jeju Province (; ), officially Jeju Special Self-Governing Province (Jeju language, Jeju: ; ), is the southernmost Provinces of South Korea, province of South Korea, consisting of eight inhabited and 55 uninhabited islands, including Marado, Udo ...
, South Korea
Claimed by
*Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
18th Century to 1875
* Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
, Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
1840–1875
* Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, 1636–1872
See also
* List of islands of Russia * Ryugase Group – a geological formation on the island * Winter storms of 2009–10 in East AsiaCitations
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Anton Chekhov
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (; ; 29 January 1860 – 15 July 1904) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer, widely considered to be one of the greatest writers of all time. His career as a playwright produced four classics, and his b ...
, ''A Journey to Sakhalin'' (1895), including:
** ''Saghalien r SakhalinIsland'' (1891–1895)
** ''Across Siberia''
* C. H. Hawes, ''In the Uttermost East'' (London, 1903). (quoted in EB1911, see below)
* Ajay Kamalakaran, ''Sakhalin Unplugged'' (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, 2006)
* Ajay Kamalakaran, ''Globetrotting for Love and Other Stories from Sakhalin Island'' (Times Group Books, 2017)
*
* John J. Stephan, ''Sakhalin: A History''. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1971.
External links
Map of the Sakhalin Hydrocarbon Region
– at Blackbourn Geoconsulting
TransGlobal Highway
– Proposed Sakhalin–Hokkaidō Friendship Tunnel
Maps of Ezo, Sakhalin and Kuril Islands
from 1854 {{Chinese historical placenames in Outer Manchuria Ainu geography Geography of Northeast Asia Islands of Sakhalin Oblast Islands of the Pacific Ocean Islands of the Russian Far East Islands of the Sea of Okhotsk Pacific Coast of Russia Physiographic provinces Former Japanese colonies