safety net on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A safety net is a type of net designed to protect people from injury after falling from heights by limiting the distance they fall, and dissipating the impact energy. The term also refers to devices for arresting falling or flying objects for the safety of people beyond or below the net.
Safety nets are used in
A safety net is a type of net designed to protect people from injury after falling from heights by limiting the distance they fall, and dissipating the impact energy. The term also refers to devices for arresting falling or flying objects for the safety of people beyond or below the net.
Safety nets are used in
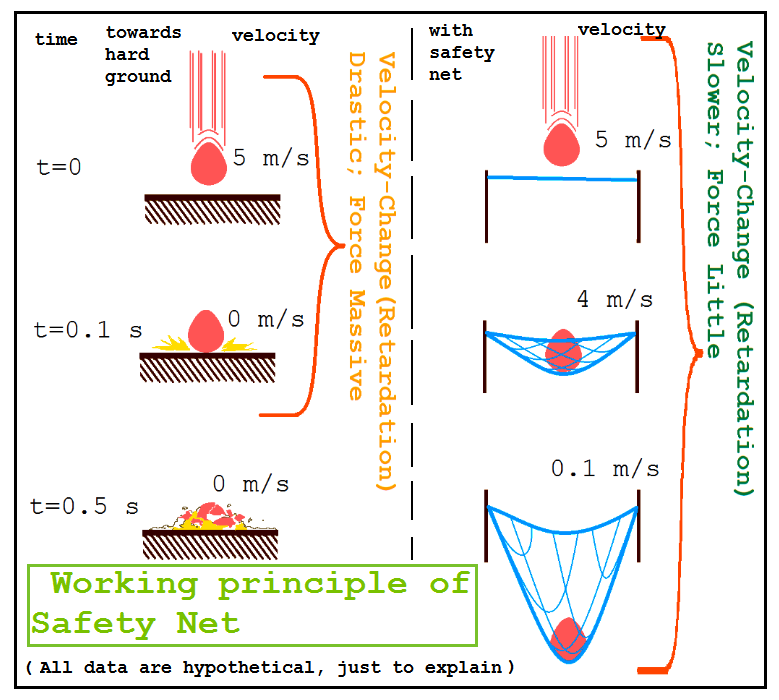 A safety net gives falling objects much more time to come to rest than hitting the hard ground directly. In physical terms, this means more time for deceleration and
A safety net gives falling objects much more time to come to rest than hitting the hard ground directly. In physical terms, this means more time for deceleration and
 Construction safety nets are used on
Construction safety nets are used on
Safety Net Systems
// Occupational Safety & Health Administration
Safety nets: Fall protection for the construction industry
/ National Safety Council Data Sheet 608, February 2006
Fall Protection in Construction, OSHA3146
/ U.S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration, 1998, page 6 "Fall Protection Systems Criteria and Practices", page 12 "Safety Net Systems"
Guide to Fall Protection Regulations
Workers Compensation Board, Canada, June 2013, page 11
A technical guide to the selection and use of fall prevention and arrest equipment
/ Glasgow Caledonian University for the Health and Safety Executive 2005 - "7.0 FALL ARREST NETTING (SAFETY NETS)" pp 107–138 Protective barriers Nets (devices)
 A safety net is a type of net designed to protect people from injury after falling from heights by limiting the distance they fall, and dissipating the impact energy. The term also refers to devices for arresting falling or flying objects for the safety of people beyond or below the net.
Safety nets are used in
A safety net is a type of net designed to protect people from injury after falling from heights by limiting the distance they fall, and dissipating the impact energy. The term also refers to devices for arresting falling or flying objects for the safety of people beyond or below the net.
Safety nets are used in construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
, building maintenance, entertainment, and other industries.
Action of a safety net
 A safety net gives falling objects much more time to come to rest than hitting the hard ground directly. In physical terms, this means more time for deceleration and
A safety net gives falling objects much more time to come to rest than hitting the hard ground directly. In physical terms, this means more time for deceleration and kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Rober ...
transfer, resulting in a softer landing and a much lower risk of damage.
The specific type of net to be used depends upon many factors, such as the falling object's speed and mass. To withstand more force, a greater total width of the net is required. The minimum distance between the spot on the net where the object impacted and the nearest edge of the net is also important and must be maintained above a certain limit. The materials used to make the net, and the tension of the net's ropes, are other important factors. Additionally, the net must be placed at an appropriate height from the hard ground, so that a falling object could not make contact with the ground. The hole size of the net should not be so big that falling objects could pass through its holes.
Construction safety net
 Construction safety nets are used on
Construction safety nets are used on high-rise building
A tower block, high-rise, apartment tower, residential tower, apartment block, block of flats, or office tower is a tall building, as opposed to a low-rise building and is defined differently in terms of height depending on the jurisdiction ...
construction sites to prevent the fall of people or objects from the site. Construction safety nets are the safest and most cost-effective fall prevention system in such an environment. Construction safety nets are typically made from high-density polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or " polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density rati ...
(or HDPE) fibers. The construction safety netting system, also known as debris netting, can be installed both horizontally and vertically according to the site requirements. The best practice of construction safety netting is to wrap up the whole construction site from bottom to top, which works as a protection wall to prevent anything from falling without blocking the view of workers on the site. Installation of a safety net at any building site requires professional expertise and technical knowledge.
Other uses of safety nets
Safety nets can also be used for escape from a building during a disaster (especially fires), action-sports and entertainment, etc.See also
* Construction site safety * Fall arrest harness * Roof edge protection *Shock absorber
A shock absorber or damper is a mechanical or hydraulics, hydraulic device designed to absorb and Damping ratio, damp shock (mechanics), shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typic ...
* Buffer (disambiguation)
* Buffer stop
A buffer stop, bumper, bumping post, bumper block or stopblock (US), is a device to prevent Railroad car, railway vehicles from going past the end of a physical section of Track (rail transport), track.
The design of the buffer stop is dependen ...
* Buffer (rail transport)
A buffer is a part of the buffers and chain coupler system used on the railway systems of many countries, among them most of those in Europe, for attaching railway vehicles together (in North America, rolling stock instead has draft gear built ...
* Damping ratio
In physical systems, damping is the loss of energy of an oscillating system by dissipation. Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. Examples of damping include ...
* Damper (disambiguation)
* Damped wave
* Cushioning
* Shock (mechanics)
In mechanics and physics, shock is a sudden acceleration caused, for example, by impact (mechanics), impact, drop, kick, earthquake, or explosion. Shock is a transient physical excitation.
Shock describes matter subject to extreme rates of for ...
* Impact (mechanics)
In mechanics, an impact is when two bodies Collision, collide. During this collision, both bodies decelerate. The deceleration causes a high force or Shock (mechanics), shock, applied over a short time period. A high force, over a short durat ...
* Jerk (physics)
Jerk (also known as jolt) is the rate of change of an object's acceleration over time. It is a vector quantity (having both magnitude and direction). Jerk is most commonly denoted by the symbol and expressed in m/s3 (SI units) or standard gra ...
* Impulse (physics)
In classical mechanics, impulse (symbolized by or Imp) is the change in momentum of an object. If the initial momentum of an object is , and a subsequent momentum is , the object has received an impulse :
\mathbf=\mathbf_2 - \mathbf_1.
Moment ...
* Collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great for ...
* Brake
A brake is a machine, mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for Acceleration, slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of ...
* Terminal velocity
Terminal velocity is the maximum speed attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid (air is the most common example). It is reached when the sum of the drag force (''Fd'') and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity (''FG ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Safety Net Systems
// Occupational Safety & Health Administration
Safety nets: Fall protection for the construction industry
/ National Safety Council Data Sheet 608, February 2006
Fall Protection in Construction, OSHA3146
/ U.S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration, 1998, page 6 "Fall Protection Systems Criteria and Practices", page 12 "Safety Net Systems"
Guide to Fall Protection Regulations
Workers Compensation Board, Canada, June 2013, page 11
A technical guide to the selection and use of fall prevention and arrest equipment
/ Glasgow Caledonian University for the Health and Safety Executive 2005 - "7.0 FALL ARREST NETTING (SAFETY NETS)" pp 107–138 Protective barriers Nets (devices)