Russian Traditional Music on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Russian folk music specifically deals with the folk music traditions of the ethnic
 The performance and promulgation of ethnic music in Russia has a long tradition. Initially it was intertwined with various forms of art music, however, in the late 19th century it began to take on a life of its own with the rise in popularity of folkloric ensembles, such as the folk choir movement led by
The performance and promulgation of ethnic music in Russia has a long tradition. Initially it was intertwined with various forms of art music, however, in the late 19th century it began to take on a life of its own with the rise in popularity of folkloric ensembles, such as the folk choir movement led by  In the 1960s, folk music in Russia continued to receive significant state support and was often seen as the antithesis of Western
In the 1960s, folk music in Russia continued to receive significant state support and was often seen as the antithesis of Western
 *
*
 *
*
Golosá: Russian Folk Choir of the University of ChicagoOfficial Website of the Osipov State Russian Folk Orchestra
– one of Russia's leading folk orchestras with about 80 members. Some mp3 clips can be downloaded.
Music from Russia and Nearby RegionsRussian folk musicAndreyev State Russian OrchestraChicago Cossacks
– Russian Folk Group in Chicago
State Academic North-Russian Folk Ensemble / www.sevhor.ru
{{European musical instruments Folk music by country
Russian people
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
.
Ethnic styles in the modern era
 The performance and promulgation of ethnic music in Russia has a long tradition. Initially it was intertwined with various forms of art music, however, in the late 19th century it began to take on a life of its own with the rise in popularity of folkloric ensembles, such as the folk choir movement led by
The performance and promulgation of ethnic music in Russia has a long tradition. Initially it was intertwined with various forms of art music, however, in the late 19th century it began to take on a life of its own with the rise in popularity of folkloric ensembles, such as the folk choir movement led by Mitrofan Pyatnitsky
 Mitrofan (Mitrophan) Yefimovich Pyatnitsky (rus ...
Mitrofan (Mitrophan) Yefimovich Pyatnitsky (rus ...
and the Russian folk instrument movement pioneered by  Mitrofan (Mitrophan) Yefimovich Pyatnitsky (rus ...
Mitrofan (Mitrophan) Yefimovich Pyatnitsky (rus ...Vasily Andreyev
Vasily Vasilievich Andreyev (russian: Василий Васильевич Андреев; 26 December 1918)
article on the city ...
.
In article on the city ...
Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
, folk music was categorized as being democratic (of the people) or proletarian (of the working class) as opposed to art music, which was often regarded as being bourgeois. After the revolution, along with proletarian
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose only possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian. Marxist philoso ...
"mass music" (music for the proletarian masses) it received significant support from the state. In Post World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
Russia, proletarian mass music however lost its appeal, whereas folkloric music continued to have a widespread support among the population, inside and outside of the Soviet Union. However the authentic nature of folk music was severely distorted by the drive to 'professionalise' performers, regardless of the genre they worked in: thus all folk singers were obliged to both learn Western-style classical notation, and to learn to perform classical repertoire – or else risk losing their right to perform as 'professionals'.
 In the 1960s, folk music in Russia continued to receive significant state support and was often seen as the antithesis of Western
In the 1960s, folk music in Russia continued to receive significant state support and was often seen as the antithesis of Western pop music
Pop music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. The terms ''popular music'' and ''pop music'' are often used interchangeably, although the former describe ...
. The fact that numerous Soviet folkloric ensembles were invited for foreign tours raised the prestige of the folk performer to that of academic musicians, and in some cases even higher because access to the West and Western goods was very desirable.
Ethnic (folk) music in Russia can often be categorized according to the amount of authenticity in the performance: truly authentic folk music (reproductive performances of traditional music), folkloric and "fakeloric" performance.
Russia is a multi-ethnic country with some 300 different ethnic groups, many of them non-Slavic, living within its borders. This article deals specifically with just Russian ethnic music.
Authentic folk music
This music is closely tied in with village life and traditions. It was usually not performed by professional musicians. From the Central Committee's resolution of 1932, which prescribed musical literacy (in parallel to the drive to industrialise the Soviet Union), there has been a marked decline in authentic folk performance practice. Festivals, competitions and the work ofethnomusicologists
Ethnomusicology is the study of music from the cultural and social aspects of the people who make it. It encompasses distinct theoretical and methodical approaches that emphasize cultural, social, material, cognitive, biological, and other dim ...
have made attempts at preserving what has survived. In recent times there has been a movement by musicologists to study and reproduce authentic folk music in an authentic performance style on the concert stage. This movement in Russia is spearheaded by members of the faculty of folk music at the Moscow Conservatory
The Moscow Conservatory, also officially Moscow State Tchaikovsky Conservatory (russian: Московская государственная консерватория им. П. И. Чайковского, link=no) is a musical educational inst ...
under the direction of Dmitri Pokrovsky
Dmitri Viktorovich Pokrovsky (, 3 May 1944 – 29 June 1996) was a Russian folk music researcher and musician, best known for his efforts to rediscover authentic, and often near extinct rural musical traditions, from many different regions of Russi ...
. More recently, Russian folk songs with strong religious (spiritual) components have been performed by singers like Zhanna Bichevskaya
Zhanna Vladimirovna Bichevskaya ( en, Jeanne Bichevskaya; russian: Жанна Владимировна Бичевская; born June 17, 1944) is a prominent Russian singer and folk musician.
She was born in Moscow. In 1971 she graduated from th ...
, Olga Arefieva and Elena Frolova
Folkloric music
This category includes music by groups led by music professionals, past and present, who have taken authentic musical material, and then arranged and performed it in a manner formulated by Vasily Andreyev and subsequently refined under Stalin's regime, yet widely accepted as 'authentically Russian' by Western audiences (conditioned, for instance, by performances by the Red Army Song and Dance Ensemble). The category includes many of the regional folkloric ensembles and dance companies popular in the Russian Federation. Often these folkloric ensembles specialize in collecting and maintaining the folk music traditions of the area of their origins which they service. They perform in stylized stage costumes based on the authentic costume designs used in the village but modified for stage use. Most inauthentic – but widespread – was the practice of performing so-called Cossack prisiadki (low-squatting dances) in perfect synchronization; as Professor Laura J. Olson observes, 'this situation did not reflect actual Cossack traditions so much as it borrowed from the traditions of Russian ballet that dated to the late nineteenth century'.Artistic folklore music
This includes music composed by city intelligentsia and professional composers in a folkloric manner. Much of the music of the Russian folk instrument orchestras can also be categorized in this group as it is based on academic music traditions and playing techniques only taking a folk element as its inspiration. As in all western folklore traditions, the distinction is difficult to draw, as in the 19th century, intellectuals would both collect folk music (not always being accurate about their source material) and conflate it with original compositions. In recent times music professionals who have completed diplomas in noted conservatories performing on Russian folk instruments are now questioning their "folkiness" when they perform, as none of their music was ever really performed originally by the (village) folk. Some now refer to their music as being academic folk music which to many academic musicians is anoxymoron
An oxymoron (usual plural oxymorons, more rarely oxymora) is a figure of speech that juxtaposes concepts with opposing meanings within a word or phrase that creates an ostensible self-contradiction. An oxymoron can be used as a rhetorical devi ...
.
Vocal music
Authentic Russian folk music is primarily vocal. Russian folk song was an integral part of daily village life. It was sung from morning to night, and reflected the four seasons and significant events in villagers' lives. Its roots are in the Orthodox church services where significant parts are sung. Most of the population was also illiterate and poverty-stricken, so musical instruments were rare, and notation (which is more relevant for instrumentals than vocals) could not be read. Authentic village singing differs from academic singing styles. It is usually done using just the chest register and is often called "white sound" or "white" voice. It is often described as controlled screaming or shouting. Female chest register singers have only a low diapason of one octave to 12 notes. Chest register singing has evolved into a style used by many of Russia's folk choirs and neighbouring countries. It was pioneered by Pyatnitsky and Ukrainian folk choir director Demutsky in the early 1900s. Notable ensembles include the Pyatnitsky Russian Folk Chorus, the Northern Russian Folk Chorus, theOmsk State Russian Folk Chorus
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk ...
, Beloe Zlato Beloe may refer to:
People
* Gerald Beloe (1877–1944), English cricket player
* William Beloe (1756–1817), English writer
* William Beloe (Royal Navy officer) (1909–1966), British navy officer
Other
* Beloe Report
* Krasnoe & Beloe
{{da ...
, the Alexandrov Song and Dance Ensemble of the Soviet Army
The Alexandrov Ensemble ( rus, Ансамбль Александрова, r=Ansambl' Aleksandrova; commonly known as the Red Army Choir in the West) is an official army choir of the Russian armed forces. Founded during the Soviet era, the en ...
and the Moscow Military Area Song and Dance Ensemble
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million re ...
.
Instrumental music
Instrumental music for a long period was suppressed in Russia. In 1648, TsarAlexis I of Russia
Aleksey Mikhaylovich ( rus, Алексе́й Миха́йлович, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsʲej mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ; – ) was the Tsar of Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. While finding success in foreign affairs, his reign saw several wars ...
banned the use of certain musical instruments. Some historians believe that skomorokh
A skomorokh ( in Russian, in Old East Slavic, in Church Slavonic. Compare with the Old Polish , ) was a medieval East Slavic harlequin, or actor, who could also sing, dance, play musical instruments and compose for oral/musical and dramatic pe ...
s singing disrespectful songs about the Tsar to instrumental accompaniment could have been the reason. As a result of the ban, instrumental music traditions disappeared and did not have a fertile ground for development in Russia for many years. No musical instruments are used in Orthodox churches (in Russia).
In the late 19th century, Vasily Andreyev
Vasily Vasilievich Andreyev (russian: Василий Васильевич Андреев; 26 December 1918)
article on the city ...
, a salon violinist, took up the balalaika in his performances for French tourists to Petersburg. The music became popular and soon Andreyev had organized a club of balalaika players. This club grew into an orchestra, which in time grew into a movement.
article on the city ...
Alexey Arhipovsky
Alexey Vitalyevich Arkhipovsky (also spelled as Arhipovskiy, russian: Алексей Витальевич Архиповский; born 15 May 1967) is a modern-day Russian balalaika player.
Personal life
Alexey Arkhipovsky was born in 1967 in t ...
is considered the modern-day Russian Paganini of the balalaika, but with a Pat Metheny
Patrick Bruce Metheny ( ; born August 12, 1954) is an American jazz guitarist and composer.
He is the leader of the Pat Metheny Group and is also involved in duets, solo works, and other side projects. His style incorporates elements of progre ...
approach. During his tours he has gained many admiring fans who compared him with Paganini and Jimi Hendrix
James Marshall "Jimi" Hendrix (born Johnny Allen Hendrix; November 27, 1942September 18, 1970) was an American guitarist, singer and songwriter. Although his mainstream career spanned only four years, he is widely regarded as one of the most ...
: “One would icthink that a three string instrument tuned E-E-A would have much potential, but you then haven’t heard Alexei Arkhipovskiy yet... hoshows that he is the Russian Paganini.” “ ebecame a sensation immediately after the first appearance in front of the general public. He practically wrecked the Guitar
The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected stri ...
festival ... showing incredible musical mastery. It was a real Theatre of inexpressible play and giddy performing numbers, MIME and gesture. Many hearers compared imno less than with great Jimi Hendrix"
From a simple unsophisticated three-stringed instrument, combined with an awakening 'Russianness' in the last phases of the Tsarist Empire, the movement led to the development and implementation of many other Russian folk instruments. The Russian folk instrument movement had its resonance in the cultures of other ethnic groups within Russia, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, and the Soviet Bloc countries. Folk instrument orchestras appeared in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
, and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
.
Traditional instruments
Chordophones
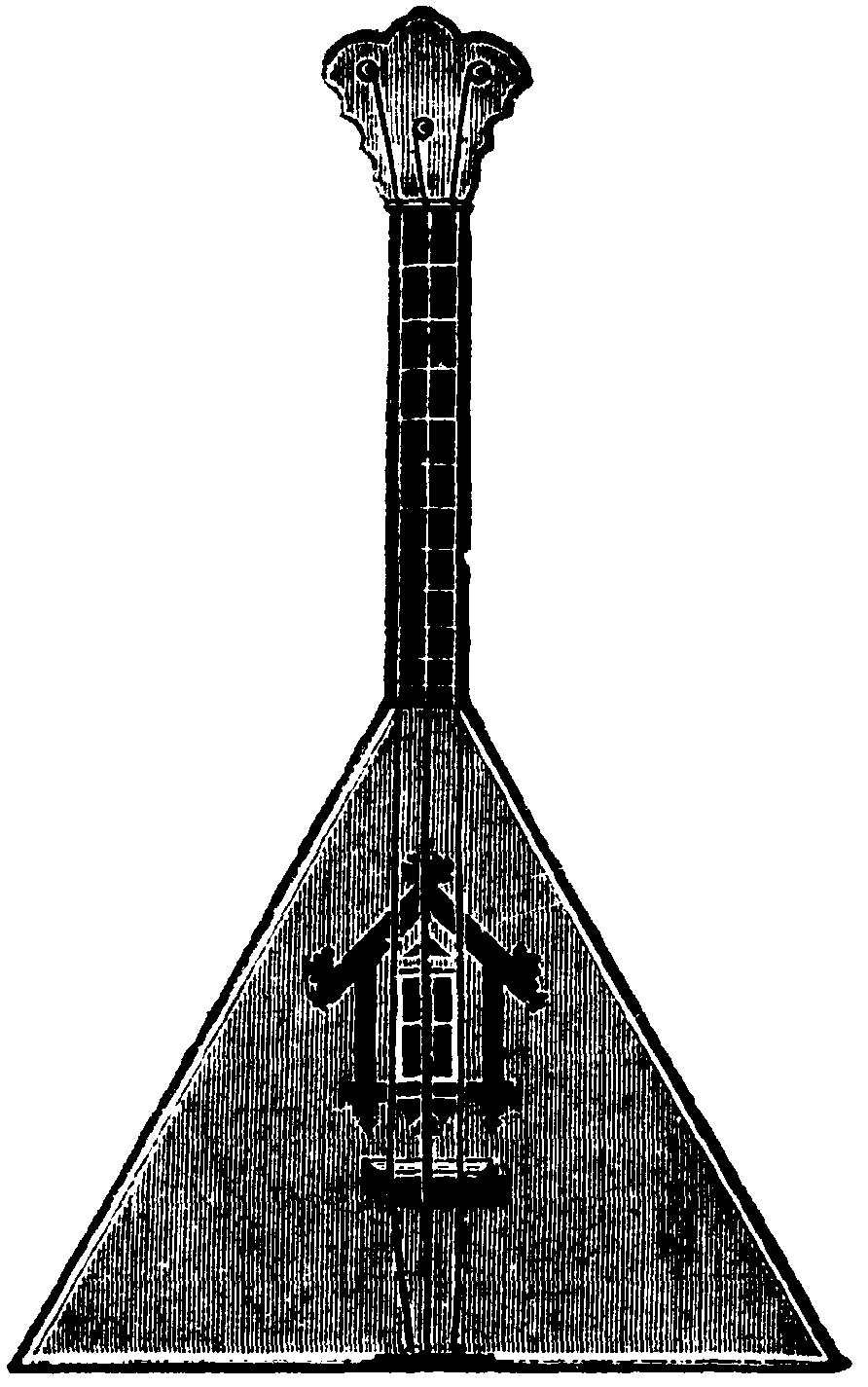
*Balalaika
The balalaika (russian: link=no, балала́йка, ) is a Russian stringed musical instrument with a characteristic triangular wooden, hollow body, fretted neck and three strings. Two strings are usually tuned to the same note and the thir ...
, a three-stringed, triangular sound-board, played with the fingers. It comes in many different sizes, prima being the most common. Two of the strings are tuned alike in descant, prima, secunda, and alto balalaikas. *
*Domra
The ''domra'' (Cyrillic: до́мра, ) is a long-necked Belarusian, Russian, and Ukrainian folk string instrument of the lute family with a round body and three or four metal strings.
History
The first known mention of domra is in ''Admonit ...
, a small three- or four-stringed Russian variant of the mandolin
A mandolin ( it, mandolino ; literally "small mandola") is a stringed musical instrument in the lute family and is generally plucked with a pick. It most commonly has four courses of doubled strings tuned in unison, thus giving a total of 8 ...
with a rounded soundboard, plucked or strummed with a plectrum
A plectrum is a small flat tool used for plucking or strumming of a stringed instrument. For hand-held instruments such as guitars and mandolins, the plectrum is often called a pick and is held as a separate tool in the player's hand. In harpsic ...
. It is also made in various orchestral sizes. Originally they were all three-stringed (E-A-D). The four-string variety was developed by in the early 20th century and became popular in Ukraine.
*Gudok
The gudok (, russian: гудок), gudochek (, russian: гудочек) is an ancient Eastern Slavic string musical instrument, played with a bow.
(also ''hudok''), a three-stringed, pear-shaped Russian bowed instrument tuned in fifths which is usually held vertically. *
*Gusli
''Gusli'' ( rus, гусли, p=ˈɡuslʲɪ) is the oldest East Slavic multi-string plucked instrument, belonging to the zither family, due to its strings being parallel to its resonance board. Its roots lie in Veliky Novgorod in Novgorodian Ru ...
, one of the oldest known Eastern Slav musical instruments, described by the Greeks as early as the 6th century AD. Many different varieties of this plucked string instrument exist.
* Kolyosnaya lira (Wheeled Lyre), a Russian version of the hurdy-gurdy
The hurdy-gurdy is a string instrument that produces sound by a hand-crank-turned, rosined wheel rubbing against the strings. The wheel functions much like a violin bow, and single notes played on the instrument sound similar to those of a vio ...
usually made with a violoncello
The cello ( ; plural ''celli'' or ''cellos'') or violoncello ( ; ) is a bowed (sometimes plucked and occasionally hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually tuned in perfect fifths: from low to high, C2, G2, D ...
body.
* Semistrunnaya gitara (Semistrunka, Russian guitar), a seven string version of the acoustic guitar with its own preferred method of construction and unique open G major tuning.
Aerophones
* Bayan, achromatic button accordion
A chromatic button accordion is a type of button accordion where the melody-side keyboard consists of rows of buttons arranged chromatically. The bass-side keyboard is usually the Stradella system or one of the various free-bass systems. Incl ...
*Garmon
The garmon ( rus, гармо́нь, p=gɐˈrmonʲ, links=yes, from rus, гармо́ника, p=gɐˈrmonʲɪkə, r=garmonika, cognate of English ''harmonica''), commonly called garmoshka, is a kind of Russian button accordion, a free-reed wi ...
, a kind of diatonic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize Scale (music), scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical sty ...
Russian button accordion
A button accordion is a type of accordion on which the melody-side keyboard consists of a series of buttons. This differs from the piano accordion, which has piano-style keys. Erich von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs categorize it as a free reed aerop ...
, featuring a unique unisonoric design
* Kalyuki (russian: Калюки), a hollow pipe with no additional air holes, used for whistling sounds
* Kugikli/ Kuvikly (russian: Куги́клы (куви́клы)), simple panpipes
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth). Multiple varieties of pan flutes have been ...
* Svirel, a Russian flute
* Vladimirsky rozhok, a type of horn made in Russia's Vladimir Oblast
Vladimir Oblast (russian: Влади́мирская о́бласть, ''Vladimirskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its closest border 66 Meter, km east of central Moscow, the administrative cen ...
by shepherds who composed melodious calls on it. It has a range of two octaves and a very distinctive idiosyncratic sound.
*Volynka
The volynka ( uk, волинка, коза, russian: волынка, crh, tulup zurna – see also duda, and koza) is a bagpipe. Its etymology comes from the region Volyn, Ukraine, where it was borrowed from Romania.
The ''volynka'' is constr ...
, a traditional Slavic bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Nor ...
*Zhaleika
The ''zhaleika'' (russian: жале́йка), also known as bryolka (''брёлка''), is the Slavic wind instrument, most used in Belarusian, Russian and sometimes Ukrainian ethnic music. Also known as a "folk clarinet" or hornpipe. The zhaleik ...
, a Russian folk clarinet
The clarinet is a musical instrument in the woodwind family. The instrument has a nearly cylindrical bore and a flared bell, and uses a single reed to produce sound.
Clarinets comprise a family of instruments of differing sizes and pitches ...
/hornpipe
The hornpipe is any of several dance forms played and danced in Britain and Ireland and elsewhere from the 16th century until the present day. The earliest references to hornpipes are from England with Hugh Aston's Hornepype of 1522 and others r ...
Idiophones
*Buben
The tambourine is a musical instrument in the Percussion instrument, percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingle (percussion), jingles, called "zills". Classically the term tambourine deno ...
, an equivalent of the tambourine
The tambourine is a musical instrument in the percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingles, called "zills". Classically the term tambourine denotes an instrument with a drumhead, though ...
* Bubentsy (russian: бубенцы)
* Vargan, an equivalent of the jew's harp
*Korobochka
Anatoliy Vasylyovych Korobochka (russian: Анатолий Васильевич Коробочка) (born 5 January 1955 in Simferopol, USSR, now Ukraine) is a former midfielder, and was formerly the Director of Football at Heart of Midlothian ...
, an equivalent of the wood block
* Derevaynnie Lozhki, an equivalent of spoons
Spoons may refer to:
* Spoon, a utensil commonly used with soup
* Spoons (card game), the card game of Donkey, but using spoons
Film and TV
* ''Spoons'' (TV series), a 2005 UK comedy sketch show
*Spoons, a minor character from ''The Sopranos''
...
* Rubel, an equivalent of the washboard
*Treshchotka
A treshchotka ( rus, трещо́тка, p=trʲɪˈɕːɵtkə, singular; sometimes referred to in the plural, treshchotki, rus, трещо́тки, p=trʲɪˈɕːɵtkʲɪ) is a Russian folk music idiophone percussion instrument which is used to i ...
, an equivalent of the clapper
* Zvonchalka
Recurring elements in singing
The "Ahy luli luli lui” or "Ohy loli loli loi" phrase is characteristic for Russian folk songs and is sung by women. Whistling is very common in Russian folk songs. The exclamation "Opa", also "Op op" and sometimes "Ota" is also a common characteristic of Russian folk music and is used by female and male singers. Also, various exclamations of the Cossacks are represented in many Russian folk songs.See also
*Sergey Nikolaevich Starostin
Sergey Nikolaevich Starostin (Russian: Сергей Николаевич Старостин; born 1 January 1956 in Moscow) is a Russian folk and jazz composer and performer, famous for his modern interpretations of archaic Russian (as well as Sá ...
* Ivan Kupala (band)
* Pelageya
Pelageya Sergeyevna Telegina (russian: link=no, Пелаге́я Серге́евна Теле́гина; before marriage Pelageya Sergeyevna Khanova; born Polina Sergeyevna Smirnova; 14 July 1986), known mononymously as Pelageya, is а Russia ...
* Zhanna Bichevskaya
Zhanna Vladimirovna Bichevskaya ( en, Jeanne Bichevskaya; russian: Жанна Владимировна Бичевская; born June 17, 1944) is a prominent Russian singer and folk musician.
She was born in Moscow. In 1971 she graduated from th ...
* Olga Glazova
Olga Gennadievna Glazova (russian: link=no, Ольга Геннадьевна Глазова, born 26 November 1993 in Pskov) is a Russian singer-songwriter, composer and poet. She performed an academic repertoire of gusli and Russian folk songs ...
* Music of Russia
Music of Russia denotes music produced from Russia and/or by Russians. Russia is a large and culturally diverse country, with many ethnic groups, each with their own locally developed music. Russian music also includes significant contributions ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
*, and by trio ofGolosá: Russian Folk Choir of the University of Chicago
– one of Russia's leading folk orchestras with about 80 members. Some mp3 clips can be downloaded.
Music from Russia and Nearby Regions
– Russian Folk Group in Chicago
State Academic North-Russian Folk Ensemble / www.sevhor.ru
{{European musical instruments Folk music by country