Radiogram (medicine) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Radiography is an imaging technique using
 The creation of images by exposing an object to
The creation of images by exposing an object to
 Computed tomography or CT scan (previously known as CAT scan, the "A" standing for "axial") uses ionizing radiation (x-ray radiation) in conjunction with a computer to create images of both soft and hard tissues. These images look as though the patient was sliced like bread (thus, "tomography" – "tomo" means "slice"). Though CT uses a higher amount of ionizing x-radiation than diagnostic x-rays (both utilising X-ray radiation), with advances in technology, levels of CT radiation dose and scan times have reduced. CT exams are generally short, most lasting only as long as a breath-hold,
Computed tomography or CT scan (previously known as CAT scan, the "A" standing for "axial") uses ionizing radiation (x-ray radiation) in conjunction with a computer to create images of both soft and hard tissues. These images look as though the patient was sliced like bread (thus, "tomography" – "tomo" means "slice"). Though CT uses a higher amount of ionizing x-radiation than diagnostic x-rays (both utilising X-ray radiation), with advances in technology, levels of CT radiation dose and scan times have reduced. CT exams are generally short, most lasting only as long as a breath-hold,
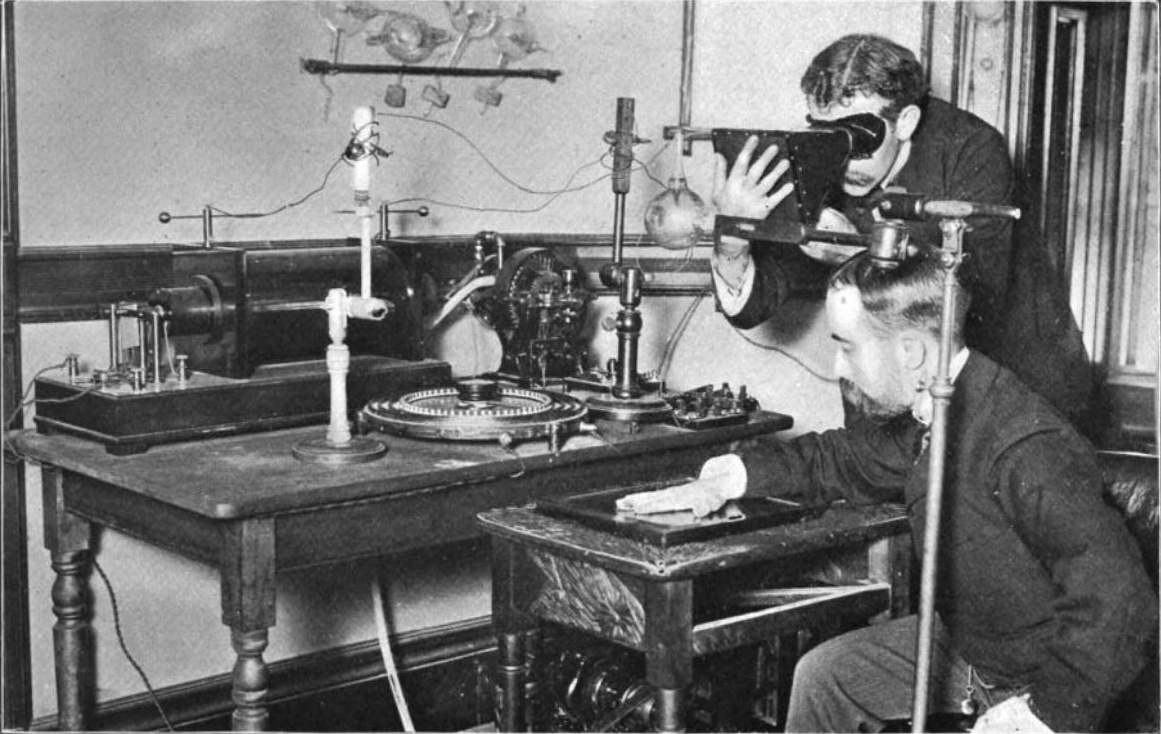

 Radiography's origins and fluoroscopy's origins can both be traced to 8 November 1895, when German physics professor
Radiography's origins and fluoroscopy's origins can both be traced to 8 November 1895, when German physics professor  Röntgen discovered X-rays' medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first ever photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said, "I have seen my death."
The first use of X-rays under clinical conditions was by John Hall-Edwards in
Röntgen discovered X-rays' medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first ever photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said, "I have seen my death."
The first use of X-rays under clinical conditions was by John Hall-Edwards in  X-rays were put to diagnostic use very early; for example,
X-rays were put to diagnostic use very early; for example,
MedPix
Medical Image Database
Video on X-ray inspection and industrial computed tomography
Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences
* ttp://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Xcom/Text/XCOM.html NIST's XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database
NIST's FAST: Attenuation and Scattering Tables
RadiologyInfo -
The radiology information resource for patients: Radiography (X-rays) {{Authority control
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s, gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
. Similar techniques are used in airport security
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.
Aviation security is a combination of measures and hum ...
(where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray
Backscatter X-ray is an advanced X-ray imaging technology. Traditional X-ray machines detect hard and soft materials by the variation in x-ray intensity transmitted through the target. In contrast, backscatter X-ray detects the radiation that ...
). To create an image in conventional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images ...
, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thicknes ...
and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
(either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean ( flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise a ...
images by this technique is called projectional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the subject which itself moves through the conical X-ray beam produced. Any given point within the subject is crossed from many directions by many different beams at different times. Information regarding attenuation of these beams is collated and subjected to computation to generate two dimensional images in three planes (axial, coronal, and sagittal) which can be further processed to produce a three dimensional image.
Medical uses
Since the body is made up of various substances with differing densities, ionising and non-ionising radiation can be used to reveal the internal structure of the body on an image receptor by highlighting these differences usingattenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variabl ...
, or in the case of ionising radiation, the absorption of X-ray photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s by the denser substances (like calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
-rich bones). The discipline involving the study of anatomy through the use of radiographic images is known as radiographic anatomy
File:Chest.jpg
File:Chestxp illustrated.jpg, Human chest radiographic anatomy.
Radioanatomy (x-ray anatomy) is anatomy discipline which involves the study of anatomy through the use of radiographic films.
The x-ray film represents two-dimens ...
. Medical radiography acquisition is generally carried out by radiographer
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radi ...
s, while image analysis is generally done by radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
s. Some radiographers also specialise in image interpretation. Medical radiography includes a range of modalities producing many different types of image, each of which has a different clinical application.
Projectional radiography
 The creation of images by exposing an object to
The creation of images by exposing an object to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s or other high-energy forms of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
and capturing the resulting remnant beam (or "shadow") as a latent image is known as "projection radiography". The "shadow" may be converted to light using a fluorescent screen, which is then captured on photographic film, it may be captured by a phosphor screen to be "read" later by a laser (CR), or it may directly activate a matrix of solid-state
Solid state, or solid matter, is one of the four fundamental states of matter.
Solid state may also refer to:
Electronics
* Solid-state electronics, circuits built of solid materials
* Solid state ionics, study of ionic conductors and their use ...
detectors (DR—similar to a very large version of a CCD in a digital camera). Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
and some organs (such as lungs) especially lend themselves to projection radiography. It is a relatively low-cost investigation with a high diagnostic
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
yield. The difference between ''soft'' and ''hard'' body parts stems mostly from the fact that carbon has a very low X-ray cross section compared to calcium.
Computed tomography
 Computed tomography or CT scan (previously known as CAT scan, the "A" standing for "axial") uses ionizing radiation (x-ray radiation) in conjunction with a computer to create images of both soft and hard tissues. These images look as though the patient was sliced like bread (thus, "tomography" – "tomo" means "slice"). Though CT uses a higher amount of ionizing x-radiation than diagnostic x-rays (both utilising X-ray radiation), with advances in technology, levels of CT radiation dose and scan times have reduced. CT exams are generally short, most lasting only as long as a breath-hold,
Computed tomography or CT scan (previously known as CAT scan, the "A" standing for "axial") uses ionizing radiation (x-ray radiation) in conjunction with a computer to create images of both soft and hard tissues. These images look as though the patient was sliced like bread (thus, "tomography" – "tomo" means "slice"). Though CT uses a higher amount of ionizing x-radiation than diagnostic x-rays (both utilising X-ray radiation), with advances in technology, levels of CT radiation dose and scan times have reduced. CT exams are generally short, most lasting only as long as a breath-hold, Contrast agents
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
are also often used, depending on the tissues needing to be seen. Radiographers perform these examinations, sometimes in conjunction with a radiologist (for instance, when a radiologist performs a CT-guided biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
).
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
, or bone densitometry, is used primarily for osteoporosis tests. It is not projection radiography, as the X-rays are emitted in 2 narrow beams that are scanned across the patient, 90 degrees from each other. Usually the hip (head of the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
), lower back (lumbar spine
The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse p ...
), or heel (calcaneum
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
...
) are imaged, and the bone density (amount of calcium) is determined and given a number (a T-score). It is not used for bone imaging, as the image quality is not good enough to make an accurate diagnostic image for fractures, inflammation, etc. It can also be used to measure total body fat, though this is not common. The radiation dose received from DEXA scans is very low, much lower than projection radiography examinations.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is a term invented by Thomas Edison during his early X-ray studies. The name refers to the fluorescence he saw while looking at a glowing plate bombarded with X-rays. The technique provides moving projection radiographs. Fluoroscopy is mainly performed to view movement (of tissue or a contrast agent), or to guide a medical intervention, such as angioplasty, pacemaker insertion, or joint repair/replacement. The last can often be carried out in the operating theatre, using a portable fluoroscopy machine called a C-arm. It can move around the surgery table and make digital images for the surgeon. Biplanar Fluoroscopy works the same as single plane fluoroscopy except displaying two planes at the same time. The ability to work in two planes is important for orthopedic and spinal surgery and can reduce operating times by eliminating re-positioning.Angiography
Angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
is the use of fluoroscopy to view the cardiovascular system. An iodine-based contrast is injected into the bloodstream and watched as it travels around. Since liquid blood and the vessels are not very dense, a contrast with high density (like the large iodine atoms) is used to view the vessels under X-ray. Angiography is used to find aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus ( ...
s, leaks, blockages ( thromboses), new vessel growth, and placement of catheters and stents. Balloon angioplasty
Angioplasty, is also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclero ...
is often done with angiography.
Contrast radiography
Contrast radiography uses a radiocontrast agent, a type ofcontrast medium
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radio ...
, to make the structures of interest stand out visually from their background. Contrast agents are required in conventional angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
, and can be used in both projectional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
and computed tomography (called ''contrast CT
Contrast CT, or contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT), is X-ray computed tomography (CT) using radiocontrast. Radiocontrasts for X-ray CT are generally iodine-based types. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that ...
'').
Other medical imaging
Although not technically radiographic techniques due to not using X-rays, imaging modalities such asPET
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive appearances, intelligence ...
and MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
are sometimes grouped in radiography because the radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
department of hospitals handle all forms of imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
. Treatment using radiation is known as radiotherapy.
Industrial radiography
Industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
is a method of non-destructive testing where many types of manufactured components can be examined to verify the internal structure and integrity of the specimen. Industrial Radiography can be performed utilizing either X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
or gamma rays
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
. Both are forms of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
. The difference between various forms of electromagnetic energy is related to the wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
. X and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and this property leads to the ability to penetrate, travel through, and exit various materials such as carbon steel and other metals. Specific methods include industrial computed tomography
Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT ...
.

Image quality
Image quality will depend on resolution and density. Resolution is the ability an image to show closely spaced structure in the object as separate entities in the image while density is the blackening power of the image. Sharpness of a radiographic image is strongly determined by the size of the X-ray source. This is determined by the area of the electron beam hitting the anode. A large photon source results in more blurring in the final image and is worsened by an increase in image formation distance. This blurring can be measured as a contribution to the modulation transfer function of the imaging system. The memory devices used in large-scale radiographic systems are also very important. They work efficiently to store the crucial data of contrast and density in the radiography image and produce the output accordingly. Smaller capacity memory drives with high-density connectors are also important to deal with internal vibration or shock.Radiation dose
The dosage of radiation applied in radiography varies by procedure. For example, the effective dosage of a chest x-ray is 0.1 mSv, while an abdominal CT is 10 mSv. TheAmerican Association of Physicists in Medicine
The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) is a scientific, educational, and professional organization of Medical Physicists. In 2011, it absorbed the American College of Medical Physics
Their headquarters are located at 1631 Princ ...
(AAPM) have stated that the "risks of medical imaging at patient doses below 50 mSv for single procedures or 100 mSv for multiple procedures over short time periods are too low to be detectable and may be nonexistent." Other scientific bodies sharing this conclusion include the International Organization of Medical Physicists, the UN Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, and the International Commission on Radiological Protection
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) is an independent, international, non-governmental organization, with the mission to protect people, animals, and the environment from the harmful effects of ionising radiation. Its r ...
. Nonetheless, radiological organizations, including the Radiological Society of North America
The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) is a non-profit organization and an international society of radiologists, medical physicists and other medical imaging professionals representing 31 radiologic subspecialties from 145 countries a ...
(RSNA) and the American College of Radiology (ACR), as well as multiple government agencies, indicate safety standards to ensure that radiation dosage is as low as possible.
Shielding
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
is the most common shield against X-rays because of its high density (11340 kg/m3), stopping power, ease of installation and low cost. The maximum range of a high-energy photon such as an X-ray in matter is infinite; at every point in the matter traversed by the photon, there is a probability of interaction. Thus there is a very small probability of no interaction over very large distances. The shielding of photon beam is therefore exponential (with an attenuation length
In physics, the attenuation length or absorption length is the distance \lambda into a material when the probability has dropped to 1/e that a particle has ''not'' been absorbed. Alternatively, if there is a beam of particles incident on the mate ...
being close to the radiation length In physics, the radiation length is a characteristic of a material, related to the energy loss of high energy particles electromagnetically interacting with it.
Definition
In materials of high atomic number (e.g. W, U, Pu) the electrons of energie ...
of the material); doubling the thickness of shielding will square the shielding effect.
Table in this section shows the recommended thickness of lead shielding in function of X-ray energy, from the Recommendations by the Second International Congress of Radiology.
Campaigns
In response to increased concern by the public over radiation doses and the ongoing progress of best practices, The Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging was formed within the Society for Pediatric Radiology. In concert with theAmerican Society of Radiologic Technologists
The American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), located in Albuquerque, New Mexico, is a professional membership association for medical imaging technologists, radiation therapists, and radiologic science students.
ASRT members may spec ...
, the American College of Radiology, and the American Association of Physicists in Medicine
The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) is a scientific, educational, and professional organization of Medical Physicists. In 2011, it absorbed the American College of Medical Physics
Their headquarters are located at 1631 Princ ...
, the Society for Pediatric Radiology developed and launched the Image Gently campaign which is designed to maintain high quality imaging studies while using the lowest doses and best radiation safety practices available on pediatric patients. This initiative has been endorsed and applied by a growing list of various professional medical organizations around the world and has received support and assistance from companies that manufacture equipment used in radiology.
Following upon the success of the Image Gently campaign, the American College of Radiology, the Radiological Society of North America, the American Association of Physicists in Medicine, and the American Society of Radiologic Technologists have launched a similar campaign to address this issue in the adult population called Image Wisely. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) of the United Nations have also been working in this area and have ongoing projects designed to broaden best practices and lower patient radiation dose.
Provider payment
Contrary to advice that emphasises only conducting radiographs when in the patient's interest, recent evidence suggests that they are used more frequently when dentists are paid under fee-for-service.Equipment


Sources
In medicine and dentistry,projectional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
and computed tomography images generally use X-rays created by X-ray generator
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thicknes ...
s, which generate X-rays from X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
s. The resultant images from the radiograph (X-ray generator/machine) or CT scanner are correctly referred to as "radiograms"/"roentgenograms" and "tomograms" respectively.
A number of other sources of X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s are possible, and may be used in industrial radiography or research; these include betatron
A betatron is a type of cyclic particle accelerator. It is essentially a transformer with a torus-shaped vacuum tube as its secondary coil. An alternating current in the primary coils accelerates electrons in the vacuum around a circular path. Th ...
s, and linear accelerators
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear be ...
(linacs) and synchrotrons. For gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s, radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
sources such as 192Ir, 60Co or 137Cs are used.
Grid
An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the quantity of scattered x-rays that reach the detector. This improves the contrast resolution of the image, but also increases radiation exposure for the patient.Detectors
Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film ( photographic film), now mostly replaced by variousdigitizing
DigitizationTech Target. (2011, April). Definition: digitization. ''WhatIs.com''. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer- ...
devices like image plate Photostimulated luminescence (PSL) is the release of stored energy within a phosphor by stimulation with visible light, to produce a luminescent signal. X-rays may induce such an energy storage. A plate based on this mechanism is called a photostim ...
s or flat panel detector
Flat-panel detectors are a class of solid-state x-ray digital radiography devices similar in principle to the image sensors used in digital photography and video. They are used in both projectional radiography and as an alternative to x-ray ima ...
s) and dose measurement devices (such as ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gas-filled radiation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term ...
s, Geiger counters, and dosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern electronic personal d ...
s used to measure the local radiation exposure, dose, and/or dose rate, for example, for verifying that radiation protection
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Expos ...
equipment and procedures are effective on an ongoing basis).
Side markers
A radiopaque anatomical side marker is added to each image. For example, if the patient has their right hand x-rayed, the radiographer includes a radiopaque "R" marker within the field of the x-ray beam as an indicator of which hand has been imaged. If a physical marker is not included, the radiographer may add the correct side marker later as part of digital post-processing.Image intensifiers and array detectors
As an alternative to X-ray detectors, image intensifiers are analog devices that readily convert the acquired X-ray image into one visible on a video screen. This device is made of a vacuum tube with a wide input surface coated on the inside withcaesium iodide
Caesium iodide or cesium iodide (chemical formula CsI) is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly ...
(CsI). When hit by X-rays material phosphors which causes the photocathode
A photocathode is a surface engineered to convert light ( photons) into electrons using the photoelectric effect. Photocathodes are important in accelerator physics where they are utilised in a photoinjector to generate high brightness electron ...
adjacent to it to emit electrons. These electron are then focus using electron lenses inside the intensifier to an output screen coated with phosphorescent materials. The image from the output can then be recorded via a camera and displayed.
Digital devices known as array detectors are becoming more common in fluoroscopy. These devices are made of discrete pixelated detectors known as thin-film transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, becaus ...
s (TFT) which can either work ''indirectly'' by using photo detectors that detect light emitted from a scintillator material such as CsI, or ''directly'' by capturing the electrons produced when the X-rays hit the detector. Direct detector do not tend to experience the blurring or spreading effect caused by phosphorescent scintillators of or film screens since the detectors are activated directly by X-ray photons.
Dual-energy
''Dual-energy'' radiography is where images are acquired using two separate tube voltages. This is the standard method for bone densitometry. It is also used inCT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
to decrease the required dose of iodinated contrast
Iodinated contrast is a form of intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have particularly improved visib ...
.
History
 Radiography's origins and fluoroscopy's origins can both be traced to 8 November 1895, when German physics professor
Radiography's origins and fluoroscopy's origins can both be traced to 8 November 1895, when German physics professor Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Mount ...
discovered the X-ray and noted that, while it could pass through human tissue, it could not pass through bone or metal. Röntgen referred to the radiation as "X", to indicate that it was an unknown type of radiation. He received the first Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
for his discovery.
There are conflicting accounts of his discovery because Röntgen had his lab notes burned after his death, but this is a likely reconstruction by his biographers: Röntgen was investigating cathode rays
Cathode rays or electron beam (e-beam) are streams of electrons observed in discharge tubes. If an evacuated glass tube is equipped with two electrodes and a voltage is applied, glass behind the positive electrode is observed to glow, due to el ...
using a fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
screen painted with barium platinocyanide Platinocyanide, also known as tetracyanoplatinate (IUPAC), cyanoplatinate, or platinocyanate, is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula t(CN)4sup>2−. The name also applies to compounds containing this ion, which are salts of the hypothetical ...
and a Crookes tube
A Crookes tube (also Crookes–Hittorf tube) is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, with partial vacuum, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, streams of electrons, were ...
which he had wrapped in black cardboard to shield its fluorescent glow. He noticed a faint green glow from the screen, about 1 metre away. Röntgen realized some invisible rays coming from the tube were passing through the cardboard to make the screen glow: they were passing through an opaque object to affect the film behind it.
 Röntgen discovered X-rays' medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first ever photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said, "I have seen my death."
The first use of X-rays under clinical conditions was by John Hall-Edwards in
Röntgen discovered X-rays' medical use when he made a picture of his wife's hand on a photographic plate formed due to X-rays. The photograph of his wife's hand was the first ever photograph of a human body part using X-rays. When she saw the picture, she said, "I have seen my death."
The first use of X-rays under clinical conditions was by John Hall-Edwards in Birmingham, England
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
on 11 January 1896, when he radiographed a needle stuck in the hand of an associate. On 14 February 1896, Hall-Edwards also became the first to use X-rays in a surgical operation.
The United States saw its first medical X-ray obtained using a discharge tube
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric ...
of Ivan Pulyui
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgari ...
's design. In January 1896, on reading of Röntgen's discovery, Frank Austin of Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
tested all of the discharge tubes in the physics laboratory and found that only the Pulyui tube produced X-rays. This was a result of Pulyui's inclusion of an oblique "target" of mica, used for holding samples of fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
material, within the tube. On 3 February 1896 Gilman Frost, professor of medicine at the college, and his brother Edwin Frost, professor of physics, exposed the wrist of Eddie McCarthy, whom Gilman had treated some weeks earlier for a fracture, to the X-rays and collected the resulting image of the broken bone on gelatin photographic plates obtained from Howard Langill, a local photographer also interested in Röntgen's work.
 X-rays were put to diagnostic use very early; for example,
X-rays were put to diagnostic use very early; for example, Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton
Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton FRS (18 October 1863 – 19 February 1930) was a Scottish consulting electrical engineer, who provided the theoretical basis for the electronic television, two decades before the technology existed to implement ...
opened a radiographic laboratory in the United Kingdom in 1896, before the dangers of ionizing radiation were discovered. Indeed, Marie Curie
Marie Salomea Skłodowska–Curie ( , , ; born Maria Salomea Skłodowska, ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934) was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first ...
pushed for radiography to be used to treat wounded soldiers in World War I. Initially, many kinds of staff conducted radiography in hospitals, including physicists, photographers, physicians, nurses, and engineers. The medical speciality of radiology grew up over many years around the new technology. When new diagnostic tests were developed, it was natural for the radiographer
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radi ...
s to be trained in and to adopt this new technology. Radiographers now perform fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function ...
, computed tomography, mammography, ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is " radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emi ...
and magnetic resonance imaging as well. Although a nonspecialist dictionary might define radiography quite narrowly as "taking X-ray images", this has long been only part of the work of "X-ray departments", radiographers, and radiologists. Initially, radiographs were known as roentgenograms, while ''skiagrapher'' (from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
words for "shadow" and "writer") was used until about 1918 to mean ''radiographer''. The Japanese term for the radiograph, レントゲン (rentogen), shares its etymology with the original English term.
See also
*Autoradiograph
An autoradiograph is an image on an X-ray film or nuclear emulsion produced by the pattern of decay emissions (e.g., beta particles or gamma rays) from a distribution of a radioactive substance. Alternatively, the autoradiograph is also available ...
* Background radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
Background radiation originates from a variety of source ...
* Computer-aided diagnosis
Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal o ...
* Imaging science
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
* List of civilian radiation accidents
This article lists notable civilian accidents involving radioactive materials or involving ionizing radiation from artificial sources such as x-ray tubes and particle accelerators. Accidents related to nuclear power that involve fissile materia ...
* Medical imaging in pregnancy
Medical imaging in pregnancy may be indicated because of pregnancy complications, intercurrent diseases or routine prenatal care.
Options
Options for medical imaging in pregnancy include the following:
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without ...
* Radiation
* Digital radiography
Digital radiography is a form of radiography that uses x-ray–sensitive plates to directly capture data during the patient examination, immediately transferring it to a computer system without the use of an intermediate cassette. Advantages inclu ...
* Radiation contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirab ...
* Radiographer
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radi ...
* Thermography
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared i ...
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
MedPix
Medical Image Database
Video on X-ray inspection and industrial computed tomography
Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences
* ttp://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Xcom/Text/XCOM.html NIST's XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database
NIST's FAST: Attenuation and Scattering Tables
RadiologyInfo -
The radiology information resource for patients: Radiography (X-rays) {{Authority control