Ruby laser on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A ruby laser is a
 The ruby laser was the first laser to be made functional. Built by Theodore Maiman in 1960, the device was created out of the concept of an "optical maser," a maser that could operate in the visual or infrared regions of the spectrum.
In 1958, after the inventor of the maser,
The ruby laser was the first laser to be made functional. Built by Theodore Maiman in 1960, the device was created out of the concept of an "optical maser," a maser that could operate in the visual or infrared regions of the spectrum.
In 1958, after the inventor of the maser, 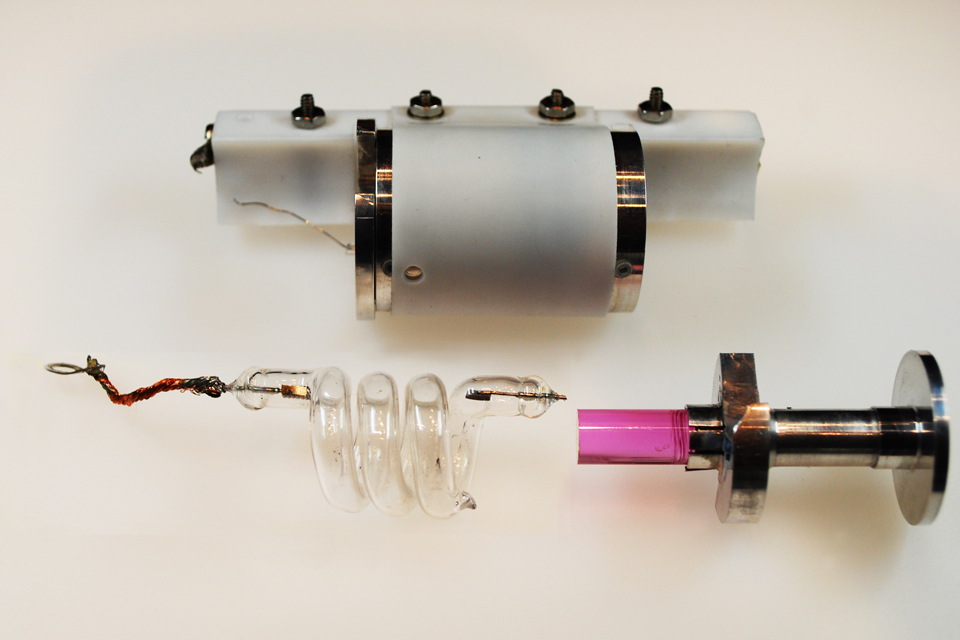 As time went on, many scientists began to doubt the usefulness of any color ruby as a laser medium. Maiman, too, felt his own doubts, but, being a very "single-minded person," he kept working on his project in secret. He searched to find a light source that would be intense enough to pump the rod, and an elliptical pumping cavity of high reflectivity, to direct the energy into the rod. He found his light source when a salesman from General Electric showed him a few xenon
As time went on, many scientists began to doubt the usefulness of any color ruby as a laser medium. Maiman, too, felt his own doubts, but, being a very "single-minded person," he kept working on his project in secret. He searched to find a light source that would be intense enough to pump the rod, and an elliptical pumping cavity of high reflectivity, to direct the energy into the rod. He found his light source when a salesman from General Electric showed him a few xenon  In 1962, Willard Boyle, working at
In 1962, Willard Boyle, working at
solid-state laser
A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a active laser medium, gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as ...
that uses a synthetic ruby crystal as its gain medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
. The first working laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
was a ruby laser made by Theodore H. "Ted" Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories on May 16, 1960.
Ruby lasers produce pulses of coherent visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
at a wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of 694.3 nm, which is a deep red color. Typical ruby laser pulse lengths are on the order of a millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second or 1000 microseconds.
A millisecond is to one second, as one second i ...
.
Design
A ruby laser most often consists of a ruby rod that must be pumped with very high energy, usually from aflashtube
A flashtube (flashlamp) produces an electrostatic discharge with an extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for a very short time. A flashtube is a glass tube with an electrode at each end and is filled with a gas that, when tr ...
, to achieve a population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system (such as a group of atoms or molecules) exists in a state in which more members of the system are in higher, excited states than in lower, unexcited energy ...
. The rod is often placed between two mirrors, forming an optical cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
, which oscillate the light produced by the ruby's fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
, causing stimulated emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to ...
. Ruby is one of the few solid state lasers that produce light in the visible range of the spectrum, lasing at 694.3 nanometers, in a deep red color, with a very narrow linewidth of 0.53 nm.''Principles of Lasers'' By Orazio Svelto – Plenum Press 1976 Page 367–370.
The ruby laser is a three level solid state laser. The active laser medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
(laser gain/ amplification medium) is a synthetic ruby rod that is energized through optical pumping
Optical pumping is a process in which light is used to raise (or "pump") electrons from a lower energy level in an atom or molecule to a higher one. It is commonly used in laser construction to pump the active laser medium so as to achieve popu ...
, typically by a xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
flashtube. Ruby has very broad and powerful absorption bands in the visual spectrum, at 400 and 550 nm, and a very long fluorescence lifetime of 3 milliseconds. This allows for very high energy pumping, since the pulse duration can be much longer than with other materials. While ruby has a very wide absorption profile, its conversion efficiency is much lower than other mediums.
In early examples, the rod's ends had to be polished with great precision, such that the ends of the rod were flat to within a quarter of a wavelength of the output light, and parallel to each other within a few seconds of arc. The finely polished ends of the rod were silvered
Silvering is the chemical process of coating a non-conductive substrate such as glass with a reflective substance, to produce a mirror. While the metal is often silver, the term is used for the application of any reflective metal.
Process
...
; one end completely, the other only partially. The rod, with its reflective ends, then acts as a Fabry–Pérot etalon (or a Gires-Tournois etalon). Modern lasers often use rods with antireflection coatings, or with the ends cut and polished at Brewster's angle instead. This eliminates the reflections from the ends of the rod. External dielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin film, thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type a ...
s then are used to form the optical cavity. Curved mirror
A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either ''convex'' (bulging outward) or ''concave'' (recessed inward). Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are ...
s are typically used to relax the alignment tolerances and to form a stable resonator, often compensating for thermal lensing of the rod.''Laser Fundamentals'' by William Thomas Silfvast – Cambridge University Press 1996 Page 547-549.
Ruby also absorbs some of the light at its lasing wavelength. To overcome this absorption, the entire length of the rod needs to be pumped, leaving no shaded areas near the mountings. The active part of the ruby is the dopant
A dopant (also called a doping agent) is a small amount of a substance added to a material to alter its physical properties, such as electrical or optics, optical properties. The amount of dopant is typically very low compared to the material b ...
, which consists of chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
ions suspended in a synthetic sapphire crystal. The dopant often comprises around only 0.05% of the crystal, but is responsible for all of the absorption and emission of radiation. Depending on the concentration of the dopant, synthetic ruby usually comes in either pink or red.
Applications
One of the first applications for the ruby laser was in rangefinding. By 1964, ruby lasers with rotating prism q-switches became the standard for militaryrangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to Length measurement, measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, suc ...
s, until the introduction of more efficient Nd:YAG rangefinders a decade later. Ruby lasers were used mainly in research.''Solid-State Laser Engineering'' by Walter Koechner – Springer-Verlag 1965, p. 2. The ruby laser was the first laser used to optically pump tunable dye lasers and is particularly well suited to excite laser dyes emitting in the near infrared. Ruby lasers are rarely used in industry, mainly due to low efficiency and low repetition rates. One of the main industrial uses is drilling holes through diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
, because ruby's high-powered beam closely matches diamond's broad absorption band (the GR1 band) in the red.
Ruby lasers have declined in use with the discovery of better lasing media. They are still used in a number of applications where short pulses of red light are required. Holographers around the world produce holographic
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interfe ...
portraits with ruby lasers, in sizes up to a meter square. Because of its high pulsed power and good coherence length, the red 694 nm laser light is preferred to the 532 nm green light of frequency-doubled Nd:YAG, which often requires multiple pulses for large holograms. Many non-destructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
labs use ruby lasers to create holograms of large objects such as aircraft tires to look for weaknesses in the lining. Ruby lasers were used extensively in tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing processes ...
and hair removal
Hair removal is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair. This process is also known as epilation or depilation.
Hair is a common feature of the human body, exhibiting considerable variation in thickness and length across different po ...
, but are being replaced by alexandrite and Nd:YAG lasers in this application.
History
 The ruby laser was the first laser to be made functional. Built by Theodore Maiman in 1960, the device was created out of the concept of an "optical maser," a maser that could operate in the visual or infrared regions of the spectrum.
In 1958, after the inventor of the maser,
The ruby laser was the first laser to be made functional. Built by Theodore Maiman in 1960, the device was created out of the concept of an "optical maser," a maser that could operate in the visual or infrared regions of the spectrum.
In 1958, after the inventor of the maser, Charles Townes
Charles Hard Townes (July 28, 1915 – January 27, 2015) was an American physicist. Townes worked on the theory and application of the maser, for which he obtained the fundamental patent, and other work in quantum electronics associated with b ...
, and his colleague, Arthur Schawlow, published an article in the ''Physical Review'' regarding the idea of optical masers, the race to build a working model began. Ruby had been used successfully in masers, so it was a first choice as a possible medium. While attending a conference in 1959, Maiman listened to a speech given by Schawlow, describing the use of ruby as a lasing medium. Schawlow stated that pink ruby, having a lowest energy-state that was too close to the ground-state, would require too much pumping energy for laser operation, suggesting red ruby as a possible alternative. Maiman, having worked with ruby for many years, and having written a paper on ruby fluorescence, felt that Schawlow was being "too pessimistic." His measurements indicated that the lowest energy level of pink ruby could at least be partially depleted by pumping with a very intense light source, and, since ruby was readily available, he decided to try it anyway.
Also attending the conference was Gordon Gould
Richard Gordon Gould (July 17, 1920 – September 16, 2005) was an American physicist who is sometimes credited with the invention of the laser and the optical amplifier. (Credit for the invention of the laser is disputed, since Charles Towne ...
. Gould suggested that, by pulsing the laser, peak outputs as high as a megawatt could be produced.
 As time went on, many scientists began to doubt the usefulness of any color ruby as a laser medium. Maiman, too, felt his own doubts, but, being a very "single-minded person," he kept working on his project in secret. He searched to find a light source that would be intense enough to pump the rod, and an elliptical pumping cavity of high reflectivity, to direct the energy into the rod. He found his light source when a salesman from General Electric showed him a few xenon
As time went on, many scientists began to doubt the usefulness of any color ruby as a laser medium. Maiman, too, felt his own doubts, but, being a very "single-minded person," he kept working on his project in secret. He searched to find a light source that would be intense enough to pump the rod, and an elliptical pumping cavity of high reflectivity, to direct the energy into the rod. He found his light source when a salesman from General Electric showed him a few xenon flashtube
A flashtube (flashlamp) produces an electrostatic discharge with an extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for a very short time. A flashtube is a glass tube with an electrode at each end and is filled with a gas that, when tr ...
s, claiming that the largest could ignite steel wool if placed near the tube. Maiman realized that, with such intensity, he did not need such a highly reflective pumping cavity, and, with the helical lamp, would not need it to have an elliptical shape. Maiman constructed his ruby laser at Hughes Research Laboratories, in Malibu, California. He used a pink ruby rod, measuring 1 cm by 1.5 cm, and, on May 16, 1960, fired the device, producing the first beam of laser light.
Theodore Maiman's original ruby laser is still operational. It was demonstrated on May 15, 2010, at a symposium co-hosted in Vancouver, British Columbia
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
by the Dr. Theodore Maiman Memorial Foundation and Simon Fraser University
Simon Fraser University (SFU) is a Public university, public research university in British Columbia, Canada. It maintains three campuses in Greater Vancouver, respectively located in Burnaby (main campus), Surrey, British Columbia, Surrey, and ...
, where Dr. Maiman was adjunct professor at the School of Engineering Science. Maiman's original laser was fired at a projector screen in a darkened room. In the center of a white flash (leakage from the xenon flashtube), a red spot was briefly visible.
The ruby lasers did not deliver a single pulse, but rather delivered a series of pulses, consisting of a series of irregular spikes within the pulse duration. In 1961, R.W. Hellwarth invented a method of q-switching, to concentrate the output into a single pulse.
 In 1962, Willard Boyle, working at
In 1962, Willard Boyle, working at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
, produced the first continuous output from a ruby laser. Unlike the usual side-pumping method, the light from a mercury arc lamp was pumped into the end of a very small rod, to achieve the necessary population inversion. The laser did not emit a continuous wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. It may refer to e.g. a laser or particl ...
, but rather a continuous train of pulses, giving scientists the opportunity to study the spiked output of ruby. The continuous ruby laser was the first laser to be used in medicine. It was used by Leon Goldman, a pioneer in laser medicine
Laser medicine is the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
The word ''laser'' stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiat ...
, for treatments such as tattoo removal, scar treatments, and to induce healing. Due to its limits in output power, tunability, and complications in operating and cooling the units, the continuous ruby laser was quickly replaced with more versatile dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
, Nd:YAG, and argon laser
An ion laser is a gas laser that uses an ionized gas as its lasing medium.
Like other gas lasers, ion lasers feature a sealed cavity containing the laser medium and mirrors forming a Fabry–Pérot resonator. Unlike helium–neon lasers, the ...
s.''Lasers in Aesthetic Surgery'' by Gregory S. Keller, Kenneth M. Toft, Victor Lacombe, Patrick Lee, James Watson – Thieme Medical Publishers 2001 p. 254.
References
External links
{{Solid-state laser Solid-state lasers