Right Upper Quadrant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The human

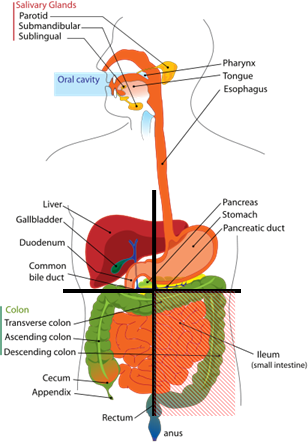 The left lower quadrant (LLQ) of the
The left lower quadrant (LLQ) of the

 Nine regions of the abdomen can be marked using two horizontal and two vertical dividing lines. The vertical lines are the mid-clavicular lines taken from the mid-point of each
Nine regions of the abdomen can be marked using two horizontal and two vertical dividing lines. The vertical lines are the mid-clavicular lines taken from the mid-point of each
abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
is divided into quadrants and regions by anatomists
Anatomy () is the branch of Morphology (biology), morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things ...
and physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
s for the purposes of study, diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
, and treatment. The division into four quadrants allows the localisation of pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
and tenderness, scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, t ...
s, lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
and tissues may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant. These terms are not used in comparative anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species).
The science began in the classical era, continuing in t ...
, since most other animals do not stand erect.
The left lower quadrant includes the left iliac fossa
The iliac fossa is a large, smooth, concave surface on the internal surface of the Ilium (bone), ilium (part of the three fused bones making the hip bone).
Structure
The iliac fossa is bounded above by the iliac crest, and below by the Arcuate ...
and half of the flank. The equivalent in other animals is ''left posterior quadrant''. The left upper quadrant extends from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage. This is the ''left anterior quadrant'' in other animals. The right upper quadrant extends from umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent in other animals is ''right anterior quadrant''. The right lower quadrant extends from the umbilical plane to the right inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may ...
. This in other animals is the ''right posterior quadrant''.
The nine regions offer more detailed anatomy and are delineated by two vertical and two horizontal lines.
Quadrants

human abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
is the area left of the midline and below the umbilicus. The LLQ includes the left iliac fossa
The iliac fossa is a large, smooth, concave surface on the internal surface of the Ilium (bone), ilium (part of the three fused bones making the hip bone).
Structure
The iliac fossa is bounded above by the iliac crest, and below by the Arcuate ...
and half of the left flank region. The equivalent term for animals is ''left posterior quadrant''.
Important organs here are:
* the descending colon
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest (whereupon it transitions into the sigmoid colon). The function of the descen ...
and sigmoid colon
The sigmoid colon (or pelvic colon) is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about in length. The loop is typically shaped like a Greek letter sigma (ς) or Latin letter S (thus ''s ...
* the left ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
and fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproduct ...
* the left ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
The left upper quadrant (LUQ) extends from the median plane
Whether in reference to the anatomy of the human or other members of the Bilateria, the median plane, also called the midsagittal plane and related terms, is used to describe the sagittal plane as it bisects the body vertically through the midline ...
to the left of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage. The equivalent term for animals is ''left anterior quadrant''. Important organs here are:
* Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
* Spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
* Left lobe of liver
In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface – the liver is divided into two lobes: the rig ...
* Body of pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine ...
* Left kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
and adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
* Splenic flexure
In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure.
St ...
of colon
* Parts of transverse and descending colon
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest (whereupon it transitions into the sigmoid colon). The function of the descen ...
The right upper quadrant (RUQ) extends from the median plane to the right of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent term for animals is ''right anterior quadrant''. Important organs here are:
* Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
* Gall bladder with biliary tree
The biliary tract (also biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids a ...
* Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
* Head of pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
* Right kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
and adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
* Hepatic flexure
In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure.
S ...
of colon
The right lower quadrant (RLQ) extends from the median plane to the right of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the right inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may ...
. The equivalent term for animals is ''right posterior quadrant''. Important organs here are:
* Cecum
The cecum ( caecum, ; plural ceca or caeca, ) is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix (a ...
* Appendix
* Ascending colon
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the ascending colon is the part of the colon located between the cecum and the transverse colon.
Characteristics and structure
The ascending colon is smaller in calibre than the cecum from wh ...
* Right ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
and fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproduct ...
* Right ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
Regions

 Nine regions of the abdomen can be marked using two horizontal and two vertical dividing lines. The vertical lines are the mid-clavicular lines taken from the mid-point of each
Nine regions of the abdomen can be marked using two horizontal and two vertical dividing lines. The vertical lines are the mid-clavicular lines taken from the mid-point of each clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
. The upper horizontal line is the subcostal line taken from the inferior parts of the lowest costal cartilages. The lower horizontal line is the transtubercular line connecting the tubercles of the pelvis.
The three main centrally positioned regions are the epigastric region, the umbilical region
The umbilical region is one of the nine regions of the abdomen. It is the region that surrounds the area around the umbilicus and is placed approximately halfway between the xiphoid process and the pubic symphysis. This region of the abdomen ...
, and the hypogastric region also known as the pubic region.
On the sides of the abdomen the other six regions are the left and right hypochondriac regions, on either side of the epigastrium; the left and right lumbar flank regions, on either side of the umbilical region, and the left and right iliac or inguinal regions on either side of the hypogastrium.
("Hypo-" means below; "epi-" means above; "chondron" means cartilage (in this case, the cartilage of the rib) and "gaster" means stomach. The reversal of "left" and "right" is intentional, because the anatomical designations reflect the patient's own right and left.)
Clinical significance
Ifabdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
or signs of peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and covering of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One pa ...
are localised in the LLQ, colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and ...
, diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, also called colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—Diverticulum, diverticula—that can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lo ...
, ureteral colic or pain due to ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. They usually cause no symptoms, but occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either #Cyst rupture, br ...
s or pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder, is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, mainly the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
may be suspected. Examples of tumors in the left lower quadrant include colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
and ovarian tumor.
The LUQ may be painful or tender in the case of intestinal malrotation
Intestinal malrotation is a congenital anomaly of rotation of the midgut. It occurs during the first trimester as the fetal gut undergoes a complex series of growth and development. Malrotation can lead to a dangerous complication called volvulus, ...
. The RUQ may be painful or tender in hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
, cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include Right upper quadrant (abdomen), right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede ...
, and peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while ...
. The RLQ, in particular the right inguinal region or right iliac fossa may be painful and tender in conditions such as appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the Appendix (anatomy), appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and anorexia (symptom), decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these t ...
.
Differential diagnosis
;Children *gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
, mesenteric adenitis, Meckel's diverticulitis, intussusception, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, lobar pneumonia
;Adults
* regional enteritis, renal colic, perforated peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while ...
, testicular torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher tha ...
, rectus sheath hematoma, pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder, is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, mainly the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
, ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these sympto ...
, endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which Tissue (biology), tissue similar to the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, grows in other places in the body, outside the uterus. It occurs in women and a limited number of other female mammals. Endomet ...
, torsion/rupture of ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. They usually cause no symptoms, but occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either #Cyst rupture, br ...
, appendicitis
;Elderly
* diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, also called colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—Diverticulum, diverticula—that can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lo ...
, intestinal obstruction, colonic carcinoma, mesenteric ischemia
Intestinal ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the large or small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute intestinal ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic intestinal ischemia. T ...
, leaking aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilatation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. Typically, there are no symptoms except when the aneurysm dissects or ruptures, which causes sudden, severe pain in the abdomen and lower back ...
See also
* Murphy's sign *McBurney's point
McBurney's point is the point over the right side of the abdomen that is one-third of the distance from the anterior superior iliac spine to the Navel, umbilicus (navel). This is near the most common location of the Vermiform appendix, appendix.
...
* Superficial anatomy
Surface anatomy (also called superficial anatomy and visual anatomy) is the study of the external features of the body of an animal.Seeley (2003) chap.1 p.2 In birds, this is termed ''topography''. Surface anatomy deals with anatomical features ...
References
{{Superficial abdominopelvic anatomy Abdomen