Riemann's minimal surface on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
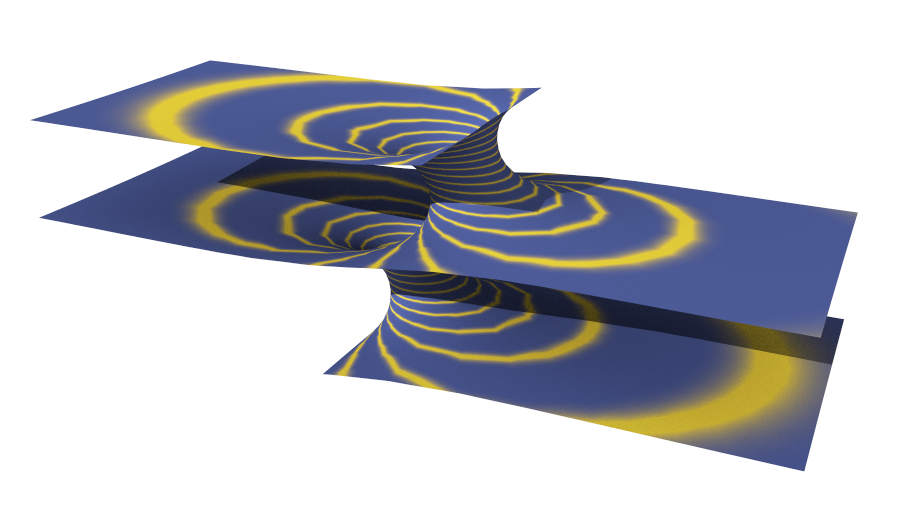 In
In
 In
In differential geometry
Differential geometry is a Mathematics, mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of Calculus, single variable calculus, vector calculus, lin ...
, Riemann's minimal surface is a one-parameter family of minimal surface
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface that locally minimizes its area. This is equivalent to having zero mean curvature (see definitions below).
The term "minimal surface" is used because these surfaces originally arose as surfaces that ...
s described by Bernhard Riemann
Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann (; ; 17September 182620July 1866) was a German mathematician who made profound contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. In the field of real analysis, he is mostly known for the f ...
in a posthumous paper published in 1867. Surfaces in the family are singly periodic minimal surfaces with an infinite number of ends
End, END, Ending, or ENDS may refer to:
End Mathematics
*End (category theory)
*End (topology)
*End (graph theory)
*End (graph_theory)#Cayley_graphs, End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
*End (endomorphism) Sports and games
*End (gridir ...
asymptotic to parallel planes, each plane "shelf" connected with catenoid
In geometry, a catenoid is a type of surface, arising by rotating a catenary curve about an axis (a surface of revolution). It is a minimal surface, meaning that it occupies the least area when bounded by a closed space. It was formally describ ...
-like bridges to the neighbouring ones. Their intersections with horizontal planes are circles or lines; Riemann proved that they were the only minimal surfaces fibered by circles in parallel planes besides the catenoid
In geometry, a catenoid is a type of surface, arising by rotating a catenary curve about an axis (a surface of revolution). It is a minimal surface, meaning that it occupies the least area when bounded by a closed space. It was formally describ ...
, helicoid
The helicoid, also known as helical surface, is a smooth Surface (differential geometry), surface embedded in three-dimensional space. It is the surface traced by an infinite line that is simultaneously being rotated and lifted along its Rotation ...
and plane. They are also the only nontrivial embedded minimal surfaces in Euclidean 3-space invariant under the group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
generated by a nontrivial translation. It is possible to attach extra handles to the surfaces, producing higher-genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
minimal surface families.
References
External links
* http://www.math.indiana.edu/gallery/minimalSurface.phtml * http://www.indiana.edu/~minimal/essays/riemann/index.html * http://virtualmathmuseum.org/Surface/riemann/riemann.html {{Bernhard Riemann Differential geometry Minimal surfaces Bernhard Riemann