Reichsstraße (Middle Ages) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
{{About, the imperial medieval roads, other uses, Reichsstraße (disambiguation){{!Reichsstraße
 In
In
 In
In medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
times, imperial roads (german: Reichsstraße) were designated routes in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
that afforded protection to travellers in return for tolls collected for the emperor.
The ''Reichsstraße'' came under royal jurisdiction (''Königsbann {{Short description, Exercise of royal jurisdiction
''Königsbann'', literally king's ban ( lat, bannus, more rarely ''bannum'', from the OHG: ''ban''), was the exercise of royal jurisdiction in the Holy Roman Empire.
A specific ban (German: ''Ban ...
'') and travellers were afforded the protection of the ''Landfrieden
Under the law of the Holy Roman Empire, a ''Landfrieden'' or ''Landfriede'' (Latin: ''constitutio pacis'', ''pax instituta'' or ''pax jurata'', variously translated as "land peace", or "public peace") was a contractual waiver of the use of legiti ...
'', a law that was supposed to ensure peace and unhindered passage similar to the Queen's peace
The legal term peace, sometimes king's peace (Latin ''pax regis'')''Black's Law Dictionary'' (10th ed.: ed. Bryan A. Garner: Thomson Reuters, 2014), p. 1306. or queen's peace, is the common-law concept of the maintenance of public order.Markus D ...
. From the 10th century it was also extended to bridges and ferries. Under King Henry I of Germany
Henry the Fowler (german: Heinrich der Vogler or '; la, Henricus Auceps) (c. 876 – 2 July 936) was the Duke of Saxony from 912 and the King of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, h ...
the term ''Reichsstrasse'' (''des riches strâze'' in Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. High ...
) was used for the first time as a translation of ''strata imperialis''.
According to Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
's legislation, based on Gallic public law
Public law is the part of law that governs relations between legal persons and a government, between different institutions within a State (polity), state, between Separation of powers, different branches of governments, as well as relationship ...
, the maintenance of roads, the responsibility for transport infrastructure and security were part of the duties and privileges of the king, his "regalia
Regalia is a Latin plurale tantum word that has different definitions. In one rare definition, it refers to the exclusive privileges of a sovereign. The word originally referred to the elaborate formal dress and dress accessories of a sovereig ...
". In return the king received the taxes
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, o ...
. He invested the territorial rulers through whose lordships the roads ran, with the execution of these duties. A safe-conduct letter (''tote Geleit'') or an armed escort (''lebende Geleit''), ensured the safety of the travellers. The escort was provided on specified occasions, of which travelling to the election and coronation of Roman-German kings and emperors was the most important, whereas travelling to trade fair
A trade fair, also known as trade show, trade exhibition, or trade exposition, is an exhibition organized so that companies in a specific industry can showcase and demonstrate their latest products and services, meet with industry partners and ...
s and markets were the most common.
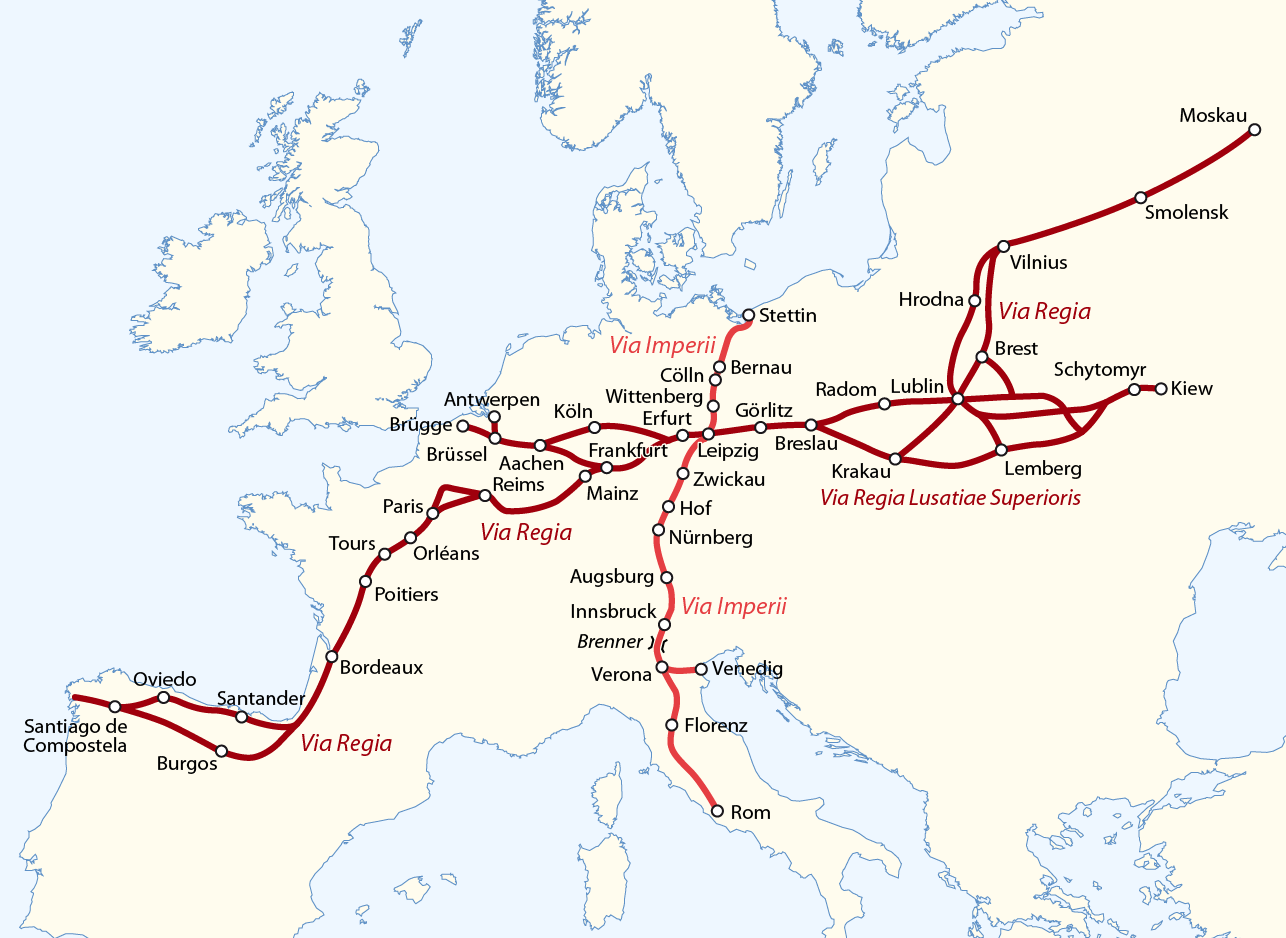
Important imperial roads were the north-south Via Imperii
Via Imperii (Imperial Road) was one of the most important of a class of roads known collectively as imperial roads (''german: Reichsstraßen'') of the Holy Roman Empire. This old trade route ran in a south–north direction from Venice on the Ad ...
and the east-west Via Regia
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a European Cultural Route following the route of the historic road of the Middle Ages. There were many such ''viae regiae'' associated with the king in the medieval Holy Roman Empire.
History Origins
The ...
meeting at Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, as well as the Via Carolina
Via or VIA may refer to the following:
Science and technology
* MOS Technology 6522, Versatile Interface Adapter
* ''Via'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Noctuidae
* Via (electronics), a through-connection
* VIA Technologies, a Tai ...
from the Imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
of Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
to Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
established by Emperor Charles IV, the Hellweg
In the Middle Ages, Hellweg was the official and common name given to main travelling routes in Germany. Their breadth was decreed as an unimpeded passageway a lance's width, about three metres, which the landholders through which the Hellweg pas ...
, the Burgundy Way
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former Regions of France, administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Duke of Burgundy, Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11 ...
and Italian Way/Via Francigena The Via Francigena () is an ancient road and pilgrimage route running from the cathedral city of Canterbury in England, through France and Switzerland, to Rome and then to Apulia, Italy, where there were ports of embarkation for the Holy Land. It w ...
.
Medieval roads and tracks
Economy of the Holy Roman Empire
Historic trails and roads in Germany