Regional integration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

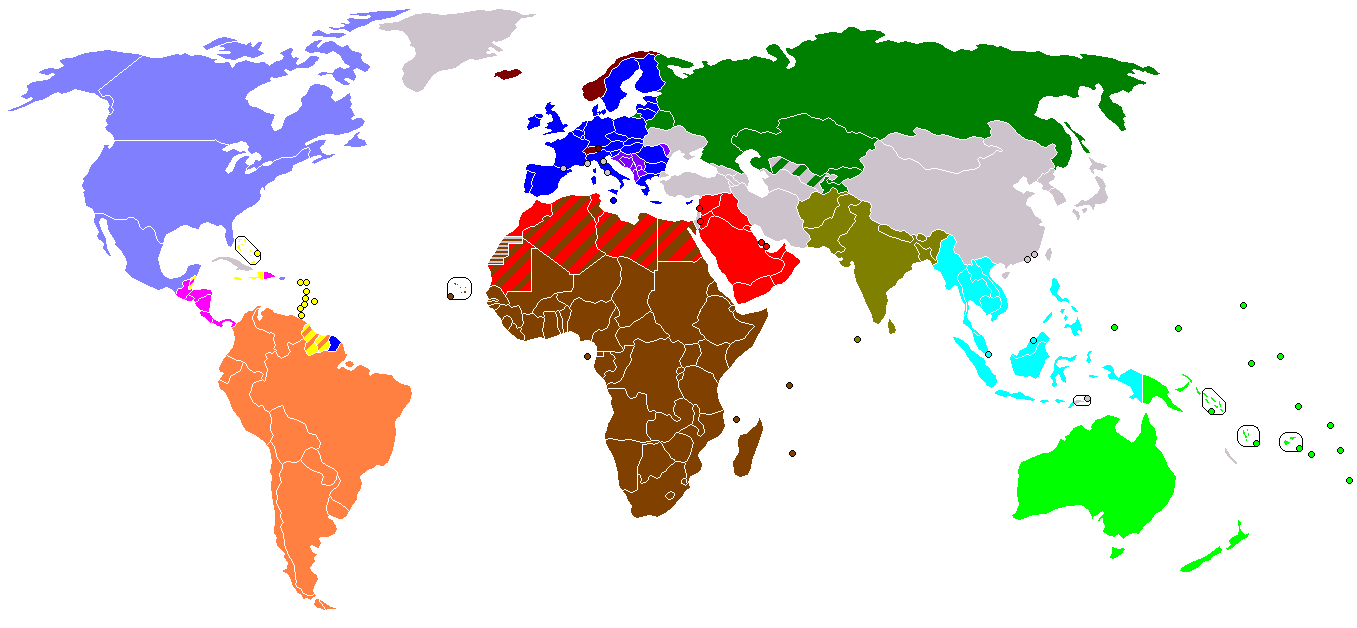 Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a
Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a

 Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a
Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
initiative where commercial interests are the focus for achieving broader socio-political and security objectives, as defined by national governments. Regional integration has been organized either via supranational institutional structures or through intergovernmental decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
, or a combination of both.
Past efforts at regional integration have often focused on removing barriers to free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold Economic liberalism, economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist politica ...
in the region, increasing the free movement of people, labour, goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
, and capital across national borders, reducing the possibility of regional armed conflict
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
(for example, through Confidence and Security-Building Measures), and adopting cohesive regional stances on policy issues, such as the environment, climate change and migration.
Intra-regional trade refers to trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
which focuses on economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
exchange primarily between countries of the same region or economic zone. In recent years countries within economic-trade regimes such as ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
for example have increased the level of trade and commodity exchange between themselves which reduces the inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
and tariff
A tariff or import tax is a duty (tax), duty imposed by a national Government, government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods ...
barriers associated with foreign markets resulting in growing prosperity.
Overview
Regional integration has been defined as the process through which independent national states "voluntarily mingle, merge and mix with their neighbours so as to lose the factual attributes of sovereignty while acquiring new techniques for resolving conflicts among themselves." De Lombaerde and Van Langenhove describe it as a worldwide phenomenon of territorial systems that increases the interactions between their components and creates new forms oforganization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
, co-existing with traditional forms of state-led organization at the national level.De Lombaerde, P. and Van Langenhove, L: "Regional Integration, Poverty and Social Policy." ''Global Social Policy'' 7 (3): 377-383, 2007. Some scholars see regional integration simply as the process by which states within a particular region increase their level of interaction with regard to economic, security, political, or social and cultural issues.
In short, regional integration is the joining of individual states within a region into a larger whole. The degree of integration depends upon the willingness and commitment of independent sovereign states to share their sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
. The deep integration that focuses on regulating the business environment in a more general sense is faced with many difficulties.
Regional integration initiatives, according to Van Langenhove, should fulfill at least eight important functions:
* The strengthening of trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
integration in the region
* The creation of an appropriate enabling environment for private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The private sector employs most of the workfo ...
development
* The development of infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
programmes in support of economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
and regional integration
* The development of strong public sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, pu ...
institutions and good governance;
* The reduction of social exclusion
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. In the EU context, the Euro ...
and the development of an inclusive civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere.environment programmes at the regional level
* The strengthening of the region's interaction with other regions of the world.
The crisis of the post-war order led to a new global political structure. This new global political structure made obsolete the classical Westphalian concept of a system of sovereign states to conceptualize world politics. The concept of sovereignty became looser and the old legal definitions of the ultimate and fully autonomous power of a
Regional integration arrangements are a part and parcel of the present global economic order and this trend is now an acknowledged future of the international scene. It has achieved a new meaning and new significance. Regional integration arrangements are mainly the outcome of the necessity felt by nation-states to integrate their economies in order to achieve rapid economic development, decrease conflict, and build mutual trust between the integrated units. The nation-state system, which has been the predominant pattern of international relations since the Peace of Westphalia in 1648 is evolving towards a system in which regional groupings of states are becoming increasingly important vis-a-vis sovereign states. Some have argued that the idea of the state and its sovereignty has been made irrelevant by processes that are taking place at both the global and local levels. Walter Lippmann believes that "the true constituent members of the international order of the future are communities of states." E.H. Carr shares Lippmann's views about the rise of regionalism and regional arrangements and comments that "the concept of sovereignty is likely to become in the future even more blurred and indistinct than it is at present."
Deep Integration
In: D+C, 2010/03, 114–117. * Duina, Francesco (2007). ''The Social Construction of Free Trade: The EU, NAFTA, and Mercosur''. Princeton: Princeton University Press. * Haas, Ernst B. (1964). ''Beyond the Nation State: Functionalism and International Organization''. Stanford: Stanford University Press. * Lindberg, Leon N., and Stuart A. Scheingold (eds.) (1971). ''Regional Integration: Theory and Research''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. * Michael, Arndt (2013). ''India's Foreign Policy and Regional Multilateralism''. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. . * Nye, Joseph S. (1971). ''Peace in Parts''. Boston: Little, Brown.
Towards UnityAsia Regional Integration CenterTransnational Institute, Video: Global crises, Regional SolutionsPeople's Agenda for Alternative Regionalisms
{{DEFAULTSORT:Regional Integration Economic integration Integration Supranational unions
nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
are no longer meaningful. Sovereignty, which gained meaning as an affirmation of cultural identity, has lost meaning as power over the economy. All regional integration projects during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
were built on the Westphalian state system and were designed to serve economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
as well as security motives in their assistance to state-building goals. Regional integration and globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
are two phenomena that have challenged the pre-existing global order based upon sovereign states since the beginning of the twenty-first century. The two processes deeply affect the stability of the Westphalian state system, thus contributing to both disorder and a new global order.
Closer integration of neighbouring economies has often been seen by governments as a first step in creating a larger regional market for trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
and investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broade ...
. This is claimed to spur greater efficiency, productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
gain and competitiveness, not just by lowering border barriers, but by reducing other costs and risks of trade and investment. Bilateral and sub-regional trading arrangements have been advocated by governments as economic development tools, as they have been designed to promote economic deregulation. Such agreements have also aimed to reduce the risk of reversion towards protectionism
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations ...
, locking in reforms already made and encouraging further structural adjustment
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
.
Some claim the desire for closer integration is usually related to a more significant passion for opening nation-states to the outside world, or that regional economic cooperation is pursued as a means of promoting development through greater efficiency, rather than as a means of disadvantaging others. It is also claimed that the members of these arrangements hope that they will succeed as building blocks for progress with a growing range of partners and towards a generally freer and open global environment for trade and investment and that integration is not an end in itself, but a process to support economic growth strategies, greater social equality
Social equality is a state of affairs in which all individuals within society have equal rights, liberties, and status, possibly including civil rights, freedom of expression, autonomy, and equal access to certain public goods and social servi ...
and democratization
Democratization, or democratisation, is the structural government transition from an democratic transition, authoritarian government to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction ...
. However, regional integration strategies as pursued by economic and national interests, particularly in the last 30 years, have also been highly contested across civil society. There is no conclusive evidence to suggest that the strategies of economic deregulation or increased investor protection implemented as forms of regional integration have succeeded in contributing to "progress" in sustainable economic growth, as the number of economic crises around the world has increased in frequency and intensity over the past decades. Also, there is increasing evidence that the forms of regional integration employed by nation-states have actually worsened social inequality and diminished democratic accountability. As a result of the persisting contradiction between the old promises of regional integration and real-world experience, the demand from across global civil society for alternative forms of regional integration has growRegional integration arrangements are a part and parcel of the present global economic order and this trend is now an acknowledged future of the international scene. It has achieved a new meaning and new significance. Regional integration arrangements are mainly the outcome of the necessity felt by nation-states to integrate their economies in order to achieve rapid economic development, decrease conflict, and build mutual trust between the integrated units. The nation-state system, which has been the predominant pattern of international relations since the Peace of Westphalia in 1648 is evolving towards a system in which regional groupings of states are becoming increasingly important vis-a-vis sovereign states. Some have argued that the idea of the state and its sovereignty has been made irrelevant by processes that are taking place at both the global and local levels. Walter Lippmann believes that "the true constituent members of the international order of the future are communities of states." E.H. Carr shares Lippmann's views about the rise of regionalism and regional arrangements and comments that "the concept of sovereignty is likely to become in the future even more blurred and indistinct than it is at present."
Regional integration agreements
Regional integration agreements (RIAs) have led to major developments in international relations between and among many countries, specifically increases in international trade and investment and in the formation of regional trading blocs. As fundamental to the multi-faceted process of globalization, regional integration has been a major development in the international relations of recent years. As such, Regional Integration Agreements has gained high importance. Not only are almost all the industrial nations part of such agreements, but also a huge number of developing nations too are a part of at least one, and in cases, more than one such agreement. The amount of trade that takes place within the scope of such agreements is about 35%, which accounts to more than one-third of the trade in the world. The main objective of these agreements is to reduce trade barriers among those nations concerned, but the structure may vary from one agreement to another. The removal of the trade barriers or liberalization of many economies has had multiple impacts, in some cases increasing Gross domestic product (GDP), but also resulting in greater global inequality, concentration of wealth and an increasing frequency and intensity of economic crises. The number of agreements agreed under the rules of the GATT and the WTO and signed in each year has dramatically increased since the 1990s. There were 194 agreements ratified in 1999 and it contained 94 agreements form the early 1990s. The last few years have experienced huge qualitative as well as quantitative changes in the agreements related to the Regional Integration Scheme. The top three major changes were the following: * Deep Integration Recognition * Closed regionalism to open model * Advent of trade blocsDeep Integration Recognition
Deep Integration Recognition analyses the aspect that effective integration is a much broader aspect, surpassing the idea that reducing tariffs, quotas and barriers will provide effective solutions. Rather, it recognizes the concept that additional barriers tend to segment the markets. That impedes the free flow of goods and services, along with ideas and investments. Hence, it is now recognized that the current framework of traditional trade policies are not adequate enough to tackle these barriers. Such deep-integration was first implemented in the Single Market Program in the European Union. However, in the light of the modern context, that debate is being propounded into the clauses of different regional integration agreements arising out of increase in international trade. (EU).Closed regionalism to open model
The change from a system of closed regionalism to a more open model had arisen out of the fact that the section of trading blocs that were created among the developing countries during the 1960s and 1970s were based on certain specific models such as those of import substitution as well as regional agreements coupled with the prevalence generally high external trade barriers. The positive aspects of such shifting is that there has been some restructuring of certain old agreements. The agreements tend to be more forward in their outward approach as well as show commitment in trying to advance international trade and commerce instead to trying to put a cap on it by way of strict control.Trade blocks
The Advent of Trade Blocks tend to draw in some parity between high-income industrial countries and developing countries with a much lower income base in that they tend to serve as equal partners under such a system. The concept of equal partners grew out of the concept of providing reinforcement to the economies to all the member countries. The various countries then agree upon the fact that they will help economies to maintain the balance of trade between and prohibit the entry of other countries in their trade process. An important example would be the North American Free Trade Area, formed in 1994 when the Canada - USFree Trade Agreement
A free trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating state (polity), states. There are two types of trade agreements: Bilateralism, bilateral and Multilateralism, m ...
was extended to Mexico. Another vibrant example would entail as to how EU has formed linkages incorporating the transition economies of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
through the Europe Agreements. It has signed agreements with the majority of Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
countries by highly developing the EU-Turkey customs union and a Mediterranean policy. Vysegrád four is a group of states co-operating in order to achieve higher economic results
Recent regional integration
Regional integration in Europe was consolidated in the Treaty on the European Union (theMaastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
), which came into force in November 1993 and established the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. The European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Europe, European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. ...
is a free trade bloc of four countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Norway) which operates in parallel and is linked to the European Union. In January 1994, the North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
was formed when Mexico acceded to a prior-existing bilateral free trade agreement between the US and Canada. In The Pacific there was the ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
Free Trade Area (AFTA) in 1993 which looked into reducing the tariffs. The AFTA started in full swing in 2000.
Alternative Regional Integration
In the last decade regional integration has accelerated and deepened around the world, in Latin America and North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia, with the formation of new alliances and trading blocks. However, critics of the forms this integration has taken have consistently pointed out that the forms of regional integration promoted have often beenneoliberal
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pej ...
in character, in line with the motives and values of the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
, the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
and the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
- promoting financial deregulation, the removal of barriers to capital and global corporations, their owners and investors; focusing on industrialisation
Industrialisation ( UK) or industrialization ( US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for th ...
, boosting global trade volumes and increasing GDP. This has been accompanied by a stark increase in global inequality, growing environmental problems as a result of industrial development, the displacement of formerly rural communities, ever-expanding urban slum
A slum is a highly populated Urban area, urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are p ...
s, rising unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
and the dismantling of social and environmental protections. Global financial deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a ...
has also contributed to the increasing frequency and severity of economic crises, while Governments have increasingly lost the sovereignty to take action to protect and foster weakened economies, as they are held to the rules of free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold Economic liberalism, economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist politica ...
implemented by the WTO and IMF.
Advocates of alternative regional integration argue strongly that the solutions to global crises (financial
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
, economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
, environmental, climate, energy, health, food, social, etc.) must involve regional solutions and regional integration, since they transcend national borders and territories, and require the cooperation of different peoples across geography. However, they propose alternatives to the dominant forms of neoliberal integration, which attends primarily to the needs of transnational corporations and investors. Economist, Harvard professor, former senior vice president and chief economist of the World Bank, Joseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, political activist, and a professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2 ...
has also argued strongly against neoliberal globalisation
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
(see Neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
). Stiglitz argues that the deregulation, free trade, and social spending cuts or austerity policies of neoliberal economics have actually created and worsened global crises. In his 2002 book Globalization and Its Discontents he explains how the industrialized economies of the US, Europe, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan developed not with the neoliberal policies promoted in developing countries and the global South by the WTO, IMF and World Bank, but rather with a careful mix of protection, regulation, social support and intervention from national governments in the market.
The People’s Agenda for Alternative Regionalisms
The ''People’s Agenda for Alternative Regionalisms'' is a network of civil society, social movement and community-based organisations from around the world, calling for alternative forms of regional integration. PAAR strives to "promote cross-fertilisation of experiences on regional alternatives among social movements and civil society organisations from Asia, Africa, South America and Europe." Further " aims to contribute to the understanding of alternative regional integration as a key strategy to struggle against neoliberal globalisation and to broaden the base among key social actors for political debate and action around regional integration" and is thus committed to expanding and deepening global democracy. PAAR aims to "build trans-regional processes to develop the concept of “people’s integration”, articulate the development of new analyses and insights on key regional issues, expose the problems of neoliberal regional integration and the limits of the export-led integration model, share and develop joint tactics and strategies for critical engagement with regional integration processes as well as the development of people's alternatives." It draws on and extends the work of such, Southern African People's Solidarity Network- SAPSN (Southern Africa). The PAAR initiative aims to develop these networks and support their efforts to reclaim democracy in the regions, recreate processes of regional integration and advance people-centred regional alternatives. In the video Global Crises, Regional Solutions the network argues that regional integration and cooperation is essential for tackling the many dimensions of the current global crises and that no country can face these crises alone. The video also calls for countries to break their dependency on the global markets, as well as the dominant development model that has failed to address increasing global hunger, poverty and environmental destruction, resulting instead in greater inequality and social unrest. Regional integration, the video argues, should be much more than macro-economic cooperation between states and corporations; it should protect shared ecological resources and should promote human development - health, wellbeing and democracy - as the base of economic development.See also
*Economic integration
Economic integration is the unification of economic policies between different states, through the partial or full abolition of tariff and Non-tariff barriers to trade, non-tariff restrictions on trade.
The trade-stimulation effects intended by ...
* Freedom of movement
Freedom of movement, mobility rights, or the right to travel is a human rights concept encompassing the right of individuals to travel from place to place within the territory of a country,Jérémiee Gilbert, ''Nomadic Peoples and Human Rights'' ...
* Free trade area
A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and ...
* Globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
* European integration
European integration is the process of political, legal, social, regional and economic integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union ...
References
Bibliography
* Bösl, Anton, Breytenbach, Willie, Hartzenberg, Trudi, McCarthy, Colin, Schade, Klaus (Eds), ''Monitoring Regional Integration in Southern Africa'', Yearbook Vol 8 (2008), Stellenbosch 2009. * Claar, Simone and Noelke Andreas (2010)Deep Integration
In: D+C, 2010/03, 114–117. * Duina, Francesco (2007). ''The Social Construction of Free Trade: The EU, NAFTA, and Mercosur''. Princeton: Princeton University Press. * Haas, Ernst B. (1964). ''Beyond the Nation State: Functionalism and International Organization''. Stanford: Stanford University Press. * Lindberg, Leon N., and Stuart A. Scheingold (eds.) (1971). ''Regional Integration: Theory and Research''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. * Michael, Arndt (2013). ''India's Foreign Policy and Regional Multilateralism''. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. . * Nye, Joseph S. (1971). ''Peace in Parts''. Boston: Little, Brown.
External links
* United Nations University Institute on Comparative Regional Integration Studies (UNU-CRIS)Towards Unity
{{DEFAULTSORT:Regional Integration Economic integration Integration Supranational unions