Rectangular Wave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

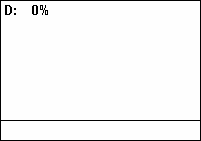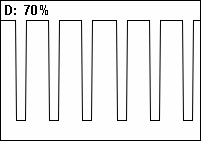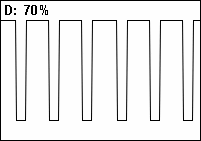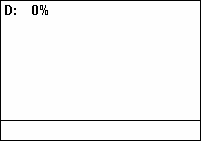 A pulse wave or pulse train is a type of
A pulse wave or pulse train is a type of
Synth Secrets: Modulation
, ''SoundOnSound.com''. Retrieved May 4, 2018. The pulse wave is also known as the rectangular wave, the periodic version of the

How to Make a Noise
', . BookBaby. .Aikin, Jim (2004). ''Power Tools for Synthesizer Programming'', p.55-56. Hal Leonard. .Hurtig, Brent (1988). ''Synthesizer Basics'', p.23. Hal Leonard. . nasal/buzzy/biting, clear,Holmes, Thom (2015). ''Electronic and Experimental Music'', p.230. Routledge. . resonant, rich, round and bright

 A pulse wave or pulse train is a type of
A pulse wave or pulse train is a type of non-sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mat ...
waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its graph as a function of time, independent of its time and magnitude scales and of any displacement in time.David Crecraft, David Gorham, ''Electron ...
that includes square wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
s (duty cycle of 50%) and similarly periodic but asymmetrical waves (duty cycles other than 50%). It is a term used in synthesizer
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis ...
programming, and is a typical waveform available on many synthesizers. The exact shape of the wave is determined by the duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formu ...
or pulse width
The pulse width is a measure of the elapsed time between the leading and trailing edges of a single pulse of energy. The measure is typically used with electrical signals and is widely used in the fields of radar and power supplies. There are two c ...
of the oscillator output. In many synthesizers, the duty cycle can be modulated (pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed ...
) for a more dynamic timbre.Reid, Gordon (February 2000).Synth Secrets: Modulation
, ''SoundOnSound.com''. Retrieved May 4, 2018. The pulse wave is also known as the rectangular wave, the periodic version of the
rectangular function
The rectangular function (also known as the rectangle function, rect function, Pi function, Heaviside Pi function, gate function, unit pulse, or the normalized boxcar function) is defined as
\operatorname(t) = \Pi(t) =
\left\{\begin{array}{r ...
.
The average level of a rectangular wave is also given by the duty cycle, therefore by varying the on and off periods and then averaging these said periods, it is possible to represent any value between the two limiting levels. This is the basis of pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed ...
.
Frequency-domain representation
TheFourier series
A Fourier series () is a summation of harmonically related sinusoidal functions, also known as components or harmonics. The result of the summation is a periodic function whose functional form is determined by the choices of cycle length (or '' ...
expansion for a rectangular pulse wave with period , amplitude and pulse length is
where .
Equivalently, if duty cycle is used, and :
Note that, for symmetry, the starting time () in this expansion is halfway through the first pulse.
Alternatively, can be written using the Sinc function
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized..
In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by
\operatornamex = \frac.
Alternatively, the ...
, using the definition , as
or with as
Generation
A pulse wave can be created by subtracting asawtooth wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ...
from a phase-shifted version of itself. If the sawtooth waves are bandlimited
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a signal's frequency domain representation or spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency.
A band-limited signal is one whose Fourier transform or spectral density has bounded support.
A bandlimi ...
, the resulting pulse wave is bandlimited, too. A single ramp wave (sawtooth or triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- colli ...
) applied to an input of a comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals V_+ and V_- and one binary digital output V_\text. The output is ideally
: ...
produces a pulse wave that is not bandlimited. A voltage applied to the other input of the comparator determines the pulse width.

Applications
The harmonic spectrum of a pulse wave is determined by the duty cycle. Acoustically, the rectangular wave has been described variously as having a narrow/thin,Souvignier, Todd (2003). ''Loops and Grooves'', p.12. Hal Leonard. .Cann, Simon (2011).How to Make a Noise
', . BookBaby. .Aikin, Jim (2004). ''Power Tools for Synthesizer Programming'', p.55-56. Hal Leonard. .Hurtig, Brent (1988). ''Synthesizer Basics'', p.23. Hal Leonard. . nasal/buzzy/biting, clear,Holmes, Thom (2015). ''Electronic and Experimental Music'', p.230. Routledge. . resonant, rich, round and bright
sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by ...
. Pulse waves are used in many Steve Winwood
Stephen Lawrence Winwood (born 12 May 1948) is an English musician, singer, and songwriter whose genres include blue-eyed soul, rhythm and blues, blues rock, and pop rock. Though primarily a keyboard player and vocalist prominent for his distin ...
songs, such as " While You See a Chance".
In digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usual ...
, a digital signal is a pulse train (a pulse amplitude modulated
Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation where the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses. It is an analog pulse modulation scheme in which the amplitudes of a train of carrier pulse ...
signal), a sequence of fixed-width square wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
electrical pulses or light pulses, each occupying one of two discrete levels of amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of a ...
. These electronic pulse trains are typically generated by metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
(MOSFET) devices due to their rapid on–off electronic switch
In electronics, an electronic switch is an electronic component or device that can switch an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another. Electronic switches are considered binary devices because the ...
ing behavior, in contrast to BJT transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
which slowly generate signals more closely resembling sine waves
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
.
See also
*Gibbs phenomenon
In mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon, discovered by Available on-line at:National Chiao Tung University: Open Course Ware: Hewitt & Hewitt, 1979. and rediscovered by , is the oscillatory behavior of the Fourier series of a piecewise continuou ...
*Pulse shaping In electronics and telecommunications, pulse shaping is the process of changing the waveform of transmitted pulses to optimize the signal for its intended purpose or the communication channel. This is often done by limiting the bandwidth of the tra ...
*Sinc function
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized..
In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by
\operatornamex = \frac.
Alternatively, the ...
*Sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pulse Wave Waves