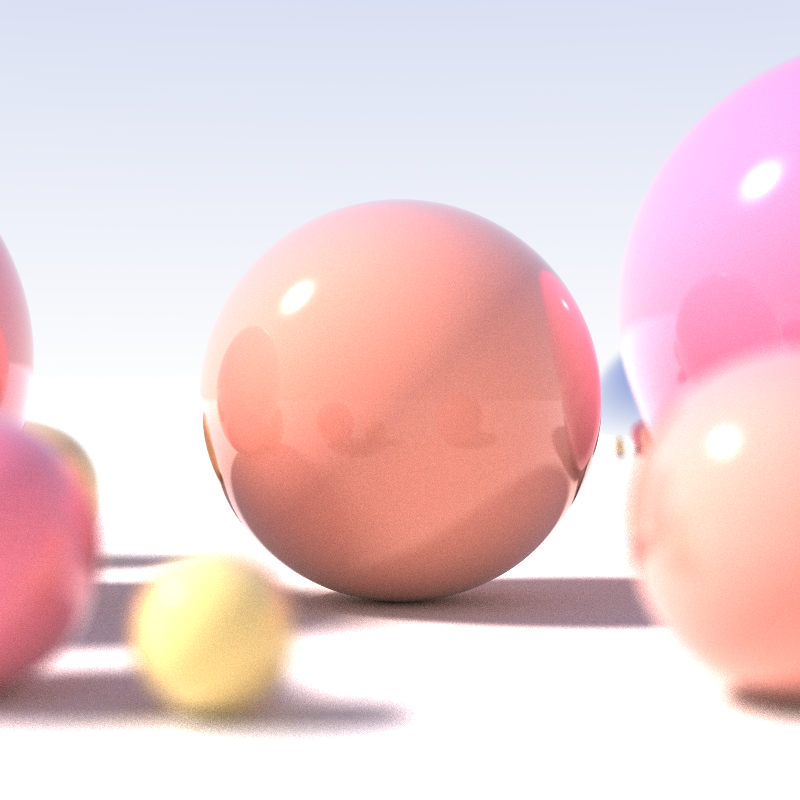
In
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
, ray tracing is a technique for modeling
light transport for use in a wide variety of
rendering algorithms for generating
digital images
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with '' finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions f ...
.
On a spectrum of
computational cost
A computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that is well-defined. Common examples of computation are mathematical equation solving and the execution of computer algorithms.
Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historic ...
and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as
ray casting
Ray casting is the methodological basis for 3D CAD/CAM solid modeling and image rendering. It is essentially the same as ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing for computer graphics where virtual light rays are "cast" or "traced" on their path from th ...
,
recursive ray tracing,
distribution ray tracing,
photon mapping
In computer graphics, photon mapping is a two-pass global illumination rendering algorithm developed by Henrik Wann Jensen between 1995 and 2001Jensen, H. (1996). ''Global Illumination using Photon Maps''. nlineAvailable at: http://graphics.sta ...
and
path tracing
Path tracing is a rendering algorithm in computer graphics that Simulation, simulates how light interacts with Physical object, objects, voxels, and Volumetric_path_tracing, participating media to generate realistic (''physically plausible'') R ...
, are generally slower and higher fidelity than
scanline rendering
Scanline rendering (also scan line rendering and scan-line rendering) is an algorithm for visible surface determination, in 3D computer graphics, that works on a row-by-row basis rather than a polygon-by-polygon or pixel-by-pixel basis. All of ...
methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as still
CGI images, and film and television
visual effects
Visual effects (sometimes abbreviated as VFX) is the process by which imagery is created or manipulated outside the context of
a live-action shot in filmmaking and video production.
The integration of live-action footage and other live-action fo ...
(VFX), but was less suited to
real-time
Real-time, realtime, or real time may refer to:
Computing
* Real-time computing, hardware and software systems subject to a specified time constraint
* Real-time clock, a computer clock that keeps track of the current time
* Real-time Control Syst ...
applications such as
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s, where
speed is critical in rendering each
frame
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
.
Since 2018, however,
hardware acceleration for real-time ray tracing has become standard on new commercial graphics cards, and graphics APIs have followed suit, allowing developers to use hybrid ray tracing and
rasterization
In computer graphics, rasterisation (British English) or rasterization (American English) is the task of taking an image described in a vector graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, whic ...
-based rendering in games and other real-time applications with a lesser hit to frame render times.
Ray tracing is capable of simulating a variety of
optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
effects, such as
reflection,
refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo ...
,
soft shadows
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after impinging on an opaque object of lesser size. In cases of equal or smaller impinging objects, only an umbra and penumba are generated. As ...
,
scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
,
depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus (optics), focus in an image captured with a camera. See also the closely related depth of focus.
Factors affecting depth ...
,
motion blur
Motion blur is the apparent streaking of moving objects in a photograph or a sequence of frames, such as a film or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single exposure, due to rapid movement or l ...
,
caustics,
ambient occlusion
In 3D computer graphics, modeling, and animation, ambient occlusion is a shading and rendering technique used to calculate how exposed each point in a scene is to ambient lighting. For example, the interior of a tube is typically more occlude ...
and
dispersion phenomena (such as
chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
). It can also be used to trace the path of
sound waves
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
in a similar fashion to light waves, making it a viable option for more immersive sound design in video games by rendering realistic
reverberation
In acoustics, reverberation (commonly shortened to reverb) is a persistence of sound after it is produced. It is often created when a sound is reflection (physics), reflected on surfaces, causing multiple reflections that build up and then de ...
and
echo
In audio signal processing and acoustics, an echo is a reflection of sound that arrives at the listener with a delay after the direct sound. The delay is directly proportional to the distance of the reflecting surface from the source and the lis ...
es. In fact, any physical
wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
or
particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
phenomenon with approximately linear motion can be simulated with
ray tracing.
Ray tracing-based rendering techniques that involve sampling light over a domain generate rays or using
denoising
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an u ...
techniques.
History

The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer ( , ;; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer or Duerer, was a German painter, Old master prin ...
, who is credited for its invention.
[.]
Dürer described multiple techniques for projecting 3-D scenes onto an image plane. Some of these project chosen geometry onto the image plane, as is done with
rasterization
In computer graphics, rasterisation (British English) or rasterization (American English) is the task of taking an image described in a vector graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, whic ...
today. Others determine what geometry is visible along a given ray, as is done with ray tracing.
Using a computer for ray tracing to generate shaded pictures was first accomplished by
Arthur Appel in 1968. Appel used ray tracing for primary visibility (determining the closest surface to the camera at each image point) by tracing a ray through each point to be shaded into the scene to identify the visible surface. The closest surface intersected by the ray was the visible one. This non-recursive ray tracing-based rendering algorithm is today called "
ray casting
Ray casting is the methodological basis for 3D CAD/CAM solid modeling and image rendering. It is essentially the same as ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing for computer graphics where virtual light rays are "cast" or "traced" on their path from th ...
". His algorithm then traced secondary rays to the light source from each point being shaded to determine whether the point was in shadow or not.
Later, in 1971, Goldstein and Nagel of
MAGI (Mathematical Applications Group, Inc.) published "3-D Visual Simulation", wherein ray tracing was used to make shaded pictures of solids. At the ray-surface intersection point found, they computed the surface normal and, knowing the position of the light source, computed the brightness of the pixel on the screen. Their publication describes a short (30 second) film “made using the University of Maryland’s display hardware outfitted with a 16mm camera. The film showed the helicopter and a simple ground level gun emplacement. The helicopter was programmed to undergo a series of maneuvers including turns, take-offs, and landings, etc., until it eventually is shot down and crashed.” A ''
CDC 6600
The CDC 6600 was the flagship of the 6000 series of mainframe computer systems manufactured by Control Data Corporation. Generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer, it outperformed the industry's prior recordholder, the I ...
'' computer was used. MAGI produced an animation video called ''MAGI/SynthaVision Sampler'' in 1974.
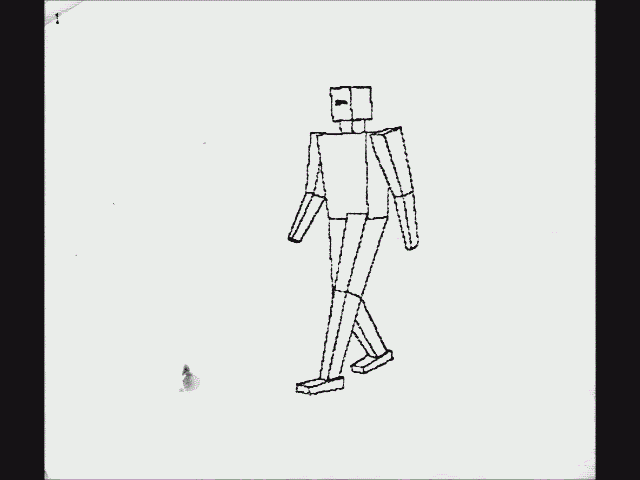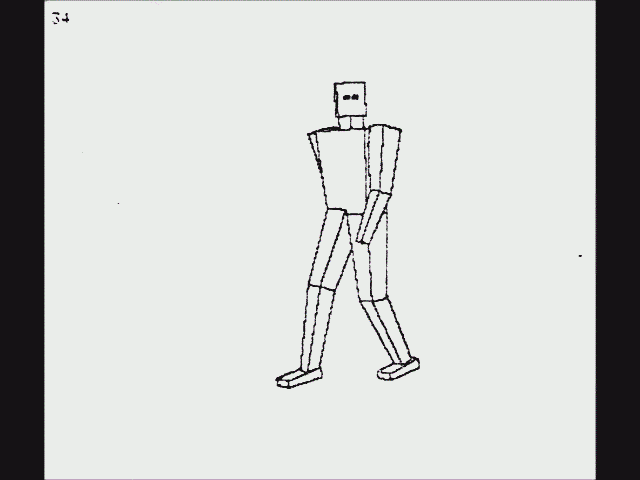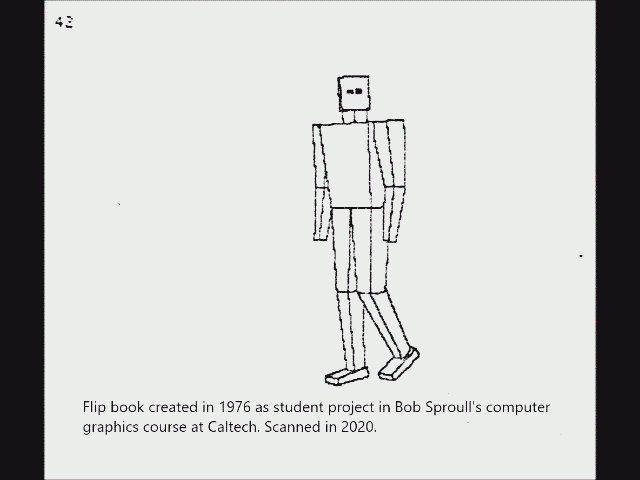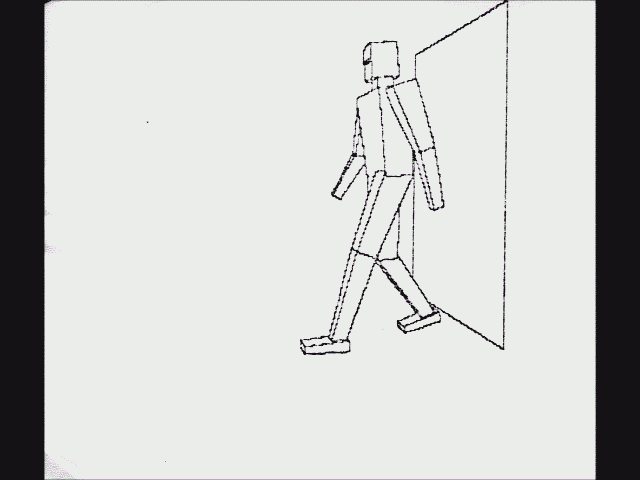
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in
Bob Sproull
Robert Fletcher "Bob" Sproull (born c. 1945) is an American computer scientist, who worked for Oracle Corporation where he was director of Oracle Labs in Burlington, Massachusetts. He is currently an adjunct professor at the College of Informa ...
's computer graphics course at
Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small g ...
. The scanned pages are shown as a video in the accompanying image. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The platform was a DEC
PDP-10
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especi ...
, a
Tektronix
Tektronix, Inc., historically widely known as Tek, is an American company best known for manufacturing test and measurement devices such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and video and mobile test protocol equipment. Originally an independent c ...
storage-tube display, and a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term ''
ray casting
Ray casting is the methodological basis for 3D CAD/CAM solid modeling and image rendering. It is essentially the same as ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing for computer graphics where virtual light rays are "cast" or "traced" on their path from th ...
'' in the context of
computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
and
solid modeling
Solid modeling (or solid modelling) is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional shapes '' (solids)''. Solid modeling is distinguished within the broader related areas of geometric modeling and ...
, and in 1982 published his work while at GM Research Labs.
Turner Whitted was the first to show recursive ray tracing for mirror reflection and for refraction through translucent objects, with an angle determined by the solid's index of refraction, and to use ray tracing for
anti-aliasing Anti-aliasing may refer to any of a number of techniques to combat the problems of aliasing in a sampled signal such as a digital image or digital audio recording.
Specific topics in anti-aliasing include:
* Anti-aliasing filter, a filter used b ...
. Whitted also showed ray traced shadows. He produced a recursive ray-traced film called ''The Compleat Angler'' in 1979 while an engineer at Bell Labs. Whitted's deeply recursive ray tracing algorithm reframed rendering from being primarily a matter of surface visibility determination to being a matter of light transport. His paper inspired a series of subsequent work by others that included
distribution ray tracing and finally
unbiased
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is inaccurate, closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individ ...
path tracing
Path tracing is a rendering algorithm in computer graphics that Simulation, simulates how light interacts with Physical object, objects, voxels, and Volumetric_path_tracing, participating media to generate realistic (''physically plausible'') R ...
, which provides the ''
rendering equation
In computer graphics, the rendering equation is an integral equation that expresses the amount of light leaving a point on a surface as the sum of emitted light and reflected light. It was independently introduced into computer graphics by David ...
'' framework that has allowed computer generated imagery to be faithful to reality.
For decades,
global illumination
Global illumination (GI), or indirect illumination, is a group of algorithms used in 3D computer graphics that are meant to add more realistic lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aest ...
in major films using
computer-generated imagery
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in Digital art, art, Publishing, printed media, Training simulation, simulators, videos and video games. These images ...
was approximated with additional lights. Ray tracing-based rendering eventually changed that by enabling physically-based light transport. Early feature films rendered entirely using path tracing include ''
Monster House'' (2006), ''
Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs
''Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs'' is a children's book written by Judi Barrett and illustrated by Ron Barrett. It was first published in 1978 by Atheneum Books, followed by a 1982 trade paperback edition from sister company Aladdin Pap ...
'' (2009), and ''
Monsters University
''Monsters University'' is a 2013 American animated Coming-of-age film, coming-of-age comedy film produced by Pixar Animation Studios for Walt Disney Pictures. A prequel to ''Monsters, Inc.'' (2001), it was directed by Dan Scanlon (in his fea ...
'' (2013).
Algorithm overview

Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in
3-D computer graphics environments, with more photorealism than either
ray casting
Ray casting is the methodological basis for 3D CAD/CAM solid modeling and image rendering. It is essentially the same as ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing for computer graphics where virtual light rays are "cast" or "traced" on their path from th ...
or
scanline rendering
Scanline rendering (also scan line rendering and scan-line rendering) is an algorithm for visible surface determination, in 3D computer graphics, that works on a row-by-row basis rather than a polygon-by-polygon or pixel-by-pixel basis. All of ...
techniques. It works by tracing a path from an imaginary eye through each
pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
in a virtual screen, and calculating the color of the object visible through it.
Scenes in ray tracing are described mathematically by a programmer or by a visual artist (normally using intermediary tools). Scenes may also incorporate data from images and models captured by means such as digital photography.
Typically, each ray must be tested for
intersection
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects simultaneously. For example, in Euclidean geometry, when two lines in a plane are not parallel, their ...
with some subset of all the objects in the scene. Once the nearest object has been identified, the algorithm will estimate the incoming
light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
at the point of intersection, examine the material properties of the object, and combine this information to calculate the final color of the pixel. Certain illumination algorithms and reflective or translucent materials may require more rays to be re-cast into the scene.
It may at first seem counterintuitive or "backward" to send rays ''away'' from the camera, rather than ''into'' it (as actual light does in reality), but doing so is many orders of magnitude more efficient. Since the overwhelming majority of light rays from a given light source do not make it directly into the viewer's eye, a "forward" simulation could potentially waste a tremendous amount of computation on light paths that are never recorded.
Therefore, the shortcut taken in ray tracing is to presuppose that a given ray intersects the view frame. After either a maximum number of reflections or a ray traveling a certain distance without intersection, the ray ceases to travel and the pixel's value is updated.
Calculate rays for rectangular viewport
On input we have (in calculation we use vector
normalization
Normalization or normalisation refers to a process that makes something more normal or regular. Science
* Normalization process theory, a sociological theory of the implementation of new technologies or innovations
* Normalization model, used in ...
and
cross product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and ...
):
*
eye position
*
target position
*
field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
- for humans, we can assume
*
numbers of square pixels on viewport vertical and horizontal direction
*
numbers of actual pixel
*
vertical vector which indicates where is up and down, usually
 In
In  The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by  Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in  Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in 3-D computer graphics environments, with more photorealism than either
Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in 3-D computer graphics environments, with more photorealism than either  In
In  The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by  Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in