Radio Control (7inch) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Radio control (often abbreviated to RC) is the use of
 Getting rid of the wires via using a new wireless technology, radio, appeared in the late 1890s. In 1897 British engineer Ernest Wilson and C. J. Evans patented a radio-controlled torpedo or demonstrated radio-controlled boats on the
Getting rid of the wires via using a new wireless technology, radio, appeared in the late 1890s. In 1897 British engineer Ernest Wilson and C. J. Evans patented a radio-controlled torpedo or demonstrated radio-controlled boats on the  In 1903, the Spanish engineer
In 1903, the Spanish engineer
Electrical Engineering Hall of Fame. Early Developments of Wireless Remote Control: The Telekino of Torres-Quevedo
''(pdf) vol. 96, No. 1, January 2008, Proceedings of the IEEE. and so up to 19 different actions. In 1904, Torres chose to carry out the first test on a three-wheeled land vehicle with a range of 20 to 30 meters. In 1906, in the presence of an audience which included King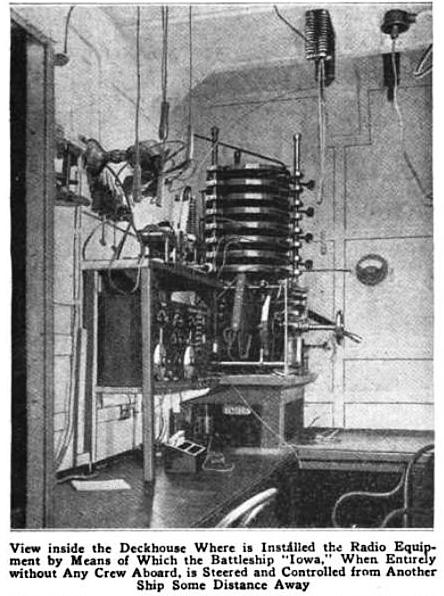 During World War I American inventor John Hays Hammond, Jr. developed many techniques used in subsequent radio control including developing remote controlled torpedoes, ships, anti-jamming systems and even a system allowing his remote-controlled ship targeting an enemy ship's searchlights. In 1922 he installed radio control gear on the obsolete US Navy battleship USS ''Iowa'' so it could be used as a
During World War I American inventor John Hays Hammond, Jr. developed many techniques used in subsequent radio control including developing remote controlled torpedoes, ships, anti-jamming systems and even a system allowing his remote-controlled ship targeting an enemy ship's searchlights. In 1922 he installed radio control gear on the obsolete US Navy battleship USS ''Iowa'' so it could be used as a
 The first general use of radio control systems in models started in the early 1950s with single-channel self-built equipment; commercial equipment came later. The advent of
The first general use of radio control systems in models started in the early 1950s with single-channel self-built equipment; commercial equipment came later. The advent of
 Remote control military applications are typically not radio control in the direct sense, directly operating flight control surfaces and propulsion power settings, but instead take the form of instructions sent to a completely
Remote control military applications are typically not radio control in the direct sense, directly operating flight control surfaces and propulsion power settings, but instead take the form of instructions sent to a completely
control signal
In telecommunications, signaling is the use of signals for controlling communications. This may constitute an information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a telecommunication circuit and the management of the network.
Classi ...
s transmitted by radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
to remotely operate a device. Examples of simple radio control systems are garage door opener
A garage door opener is a motorized device that opens and closes a garage door controlled by switches on the garage wall. Most also include a handheld radio remote control carried by the owner, which can be used to open and close the door from ...
s and keyless entry system
A remote keyless system (RKS), also known as remote keyless entry (RKE) or remote central locking, is an electronic lock that controls access to a building or vehicle by using an electronic remote control (activated by a handheld device or a ...
s for vehicles, in which a small handheld radio transmitter unlocks or opens doors. Radio control is also used for control of model vehicles from a hand-held radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmissio ...
. Industrial, military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
, and scientific research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and medieval world. The ...
organizations make use of radio-controlled vehicles as well. A rapidly growing application is control of unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron ...
s (UAVs or drones) for both civilian and military uses, although these have more sophisticated control systems than traditional applications.
History
The idea of controlling unmanned vehicles (for the most part in an attempt to improve the accuracy oftorpedoes
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
for military purposes) predates the invention of radio. The latter half of the 1800s saw development of many such devices, connected to an operator by wires, including the first practical application invented by German engineer Werner von Siemens
Ernst Werner Siemens ( von Siemens from 1888; ; ; 13 December 1816 – 6 December 1892) was a German electrical engineer, inventor and industrialist. Siemens's name has been adopted as the SI unit of electrical conductance, the siemens. He ...
in 1870.
 Getting rid of the wires via using a new wireless technology, radio, appeared in the late 1890s. In 1897 British engineer Ernest Wilson and C. J. Evans patented a radio-controlled torpedo or demonstrated radio-controlled boats on the
Getting rid of the wires via using a new wireless technology, radio, appeared in the late 1890s. In 1897 British engineer Ernest Wilson and C. J. Evans patented a radio-controlled torpedo or demonstrated radio-controlled boats on the Thames river
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the ...
(accounts of what they did vary). At an 1898 exhibition at Madison Square Garden
Madison Square Garden, colloquially known as the Garden or by its initials MSG, is a multi-purpose indoor arena in New York City. It is located in Midtown Manhattan between Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh and Eighth Avenue (Manhattan), Eig ...
, Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla (;"Tesla"
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
demonstrated a small boat that used a . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
coherer
The coherer was a primitive form of radio signal detector used in the first radio receivers during the wireless telegraphy era at the beginning of the 20th century. Its use in radio was based on the 1890 findings of French physicist Édouard Bra ...
-based radio control. With an eye towards selling the idea to the US government as a torpedo, Tesla's 1898 patent included a clockwork frequency changer so an enemy could not take control of the device.
Leonardo Torres Quevedo
Leonardo Torres Quevedo (; 28 December 1852 – 18 December 1936) was a Spanish civil engineer, mathematician and inventor, known for his numerous engineering innovations, including Aerial tramway, aerial trams, airships, catamarans, and remote ...
introduced a radio based control system called the "''Telekino''" at the Paris Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific d ...
. In the same year, he applied for several patents in other countries. It was intended as a way of testing Astra-Torres airship
The Astra-Torres airships were non-rigid airships built by Société Astra in France between about 1908 and 1922 to a design by the Spaniard Leonardo Torres Quevedo.Francisco A. González Redond''Leonardo Torres Quevedo, 1902-1908. The Foundatio ...
, a dirigible of his own design, without risking human lives. Unlike the previous mechanisms, which carried out actions of the 'on/off' type, Torres established a system for controlling any mechanical or electrical device with different states of operation. This method required a transmitter capable of sending a family of different code words by means of a binary telegraph key
A telegraph key, clacker, tapper or morse key is a specialized electrical switch used by a trained operator to transmit text messages in Morse code in a telegraphy system. Keys are used in all forms of electrical telegraph systems, includ ...
signal, and a receiver, which was able to set up a different state of operation in the device being used, depending on the code word. It was able to select different positions for the steering engine
A steering engine is a power steering device for ships.
History
Prior to the invention of the steering engine, large steam-powered warships with manual steering needed huge crews to turn the rudder rapidly. The Royal Navy once used 78 men hauli ...
and different velocities for the propelling engine
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
independently, and also to act over other mechanisms such an electric light
Electric light is an artificial light source powered by electricity.
Electric Light may also refer to:
* Light fixture, a decorative enclosure for an electric light source
* Electric Light (album), ''Electric Light'' (album), a 2018 album by James ...
, for switching it, and a flag
A flag is a piece of textile, fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and fla ...
, for raising or dropping it, at the same time,A. P. Yuste. Electrical Engineering Hall of Fame. Early Developments of Wireless Remote Control: The Telekino of Torres-Quevedo
''(pdf) vol. 96, No. 1, January 2008, Proceedings of the IEEE. and so up to 19 different actions. In 1904, Torres chose to carry out the first test on a three-wheeled land vehicle with a range of 20 to 30 meters. In 1906, in the presence of an audience which included King
Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Alfonso León Fernando María Jaime Isidro Pascual Antonio de Borbón y Habsburgo-Lorena''; French language, French: ''Alphonse Léon Ferdinand Marie Jacques Isidore Pascal Antoine de Bourbon''; 17 May ...
of Spain, Torres demonstrated the invention in the Port of Bilbao, guiding the electrically powered launch ''Vizcaya'' from the shore with people on board, which was controlled at a distance over 2 km.
In 1904, ''Bat'', a Windermere
Windermere (historically Winder Mere) is a ribbon lake in Cumbria, England, and part of the Lake District. It is the largest lake in England by length, area, and volume, but considerably smaller than the List of lakes and lochs of the United Ki ...
steam launch, was controlled using experimental radio control by its inventor, ack Kitchen In 1909 French inventor abet
ABET (pronounced A-bet), formerly known as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., is a non-governmental accreditation organization for post-secondary programs in engineering, engineering technology, computing, and applied ...
demonstrated what he called his "''Torpille Radio-Automatique''", a radio-controlled torpedo.
In 1917, Archibald Low
Archibald Montgomery Low (17 October 1888 – 13 September 1956) developed the first powered drone aircraft. He was an English consulting engineer, research physicist and inventor, and author of more than 40 books.
Low has been called the "f ...
, as head of the secret Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
(RFC) experimental works at Feltham
Feltham () is a town in West London, England, from Charing Cross. Historically part of Middlesex, it became part of the London Borough of Hounslow in 1965. The parliamentary constituency of Feltham and Heston (UK Parliament constituency), Felt ...
, was the first person to use radio control successfully on an aircraft, a 1917 Aerial Target. It was "piloted" from the ground by future world aerial speed record holder Henry Segrave
Sir Henry O'Neal de Hane Segrave (22 September 1896 – 13 June 1930) was an early British pioneer in land speed and water speed records. Segrave, who set three land and one water record, was the first person to hold both titles simultaneou ...
. Low's systems encoded the command transmissions as a countermeasure to prevent enemy intervention. By 1918 the secret D.C.B. Section of the Royal Navy's Signals School, Portsmouth under the command of Eric Robinson V.C. used a variant of the Aerial Target’s radio control system to control from ‘mother’ aircraft different types of naval vessels including a submarine.UK National Archives ADM 1/8539/253 Capabilities of distantly controlled boats. Reports of trials at Dover 28 - 31 May 1918
target ship
A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunit ...
(sunk in gunnery exercise in March 1923).
The Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
used remotely controlled teletank
Teletanks were a series of experimental wireless remotely controlled unmanned tanks produced in the Soviet Union in the 1930s and early 1940s so as to reduce combat risk to soldiers. A teletank is controlled by radio from a control tank at a dis ...
s during the 1930s in the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
against Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
and fielded at least two teletank battalions at the beginning of the Great Patriotic War
The Eastern Front, also known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union and its successor states, and the German–Soviet War in modern Germany and Ukraine, was a Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II ...
. A teletank is controlled by radio from a control tank at a distance of 500–1500 m, the two constituting a ''telemechanical group''. There were also remotely controlled cutters and experimental remotely controlled planes in the Red Army.
The United Kingdom's World War One development of their radio-controlled 1917 'Aerial Target' (AT) and 1918 'Distant Control Boat' (DCB) using Low's control systems led eventually to their 1930s fleet of "Queen Bee
A queen bee is typically an adult, mated female ( gyne) that lives in a colony or hive of honey bees. With fully developed reproductive organs, the queen is usually the mother of most, if not all, of the bees in the beehive. Queens are develope ...
". This was a remotely controlled unmanned version of the de Havilland
The de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited (pronounced , ) was a British aviation manufacturer established in late 1920 by Geoffrey de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome Edgware on the outskirts of North London. Operations were later moved to ...
"Tiger Moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. ...
" aircraft for Navy fleet gunnery firing practice. The "Queen Bee" was superseded by the similarly named ''Airspeed Queen Wasp
The Airspeed AS.30 Queen Wasp was a British pilotless target aircraft built by Airspeed Limited at Portsmouth during the Second World War. Although intended for both Royal Air Force and Royal Navy use, the aircraft never went into series pro ...
'', a purpose-built target aircraft of higher performance.
Second World War
Radio control was further developed during World War II, primarily by the Germans who used it in a number ofmissile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
projects. Their main effort was the development of radio-controlled missiles and glide bomb
A glide bomb or stand-off bomb is a standoff weapon with flight control surfaces to give it a flatter, gliding flight path than that of a conventional bomb without such surfaces. This allows it to be released at a distance from the target rat ...
s for use against shipping, a target otherwise both difficult and dangerous to attack. However, by the end of the war, the ''Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
'' was having similar problems attacking Allied bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes
air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles.
There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strateg ...
s and developed a number of radio command guided
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its ...
surface-to-air anti-aircraft missiles, none of which saw service.
The effectiveness of the Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
's systems, primarily comprising the series of Telefunken
Telefunken was a German radio and television producer, founded in Berlin in 1903 as a joint venture between Siemens & Halske and the ''AEG (German company), Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft'' (AEG) ("General electricity company").
Prior to ...
''Funk-Gerät'' (or FuG) 203 ''Kehl'' twin-axis, single joystick-equipped transmitters mounted in the deploying aircraft, and Telefunken's companion FuG 230 ''Straßburg'' receiver placed in the ordnance to be controlled during deployment and used by both the Fritz X
Fritz X was a German guided anti-ship glide bomb used during World War II. Developed alongside the Henschel Hs 293, ''Fritz X'' was one of the first precision guided weapons deployed in combat. ''Fritz X'' was a nickname used both by Allied an ...
unpowered, armored anti-ship bomb and the powered Henschel Hs 293
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II Nazi Germany, German Command guidance, radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next y ...
guided bomb, was greatly reduced by British efforts to jam their radio signals, eventually with American assistance. After initial successes, the British launched a number of commando
A commando is a combatant, or operative of an elite light infantry or special operations force, specially trained for carrying out raids and operating in small teams behind enemy lines.
Originally, "a commando" was a type of combat unit, as oppo ...
raids to collect the missile radio sets. Jammers were then installed on British ships, and the weapons basically "stopped working". The German development teams then turned to wire-guided missiles once they realized what was going on, but the systems were not ready for deployment until the war had already moved to France.
The German ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branche ...
'' operated ''FL-Boote'' (''ferngelenkte Sprengboote'') which were radio controlled motor boats filled with explosives to attack enemy shipping from 1944.
Both the British and US also developed radio control systems for similar tasks, to avoid the huge anti-aircraft batteries set up around German targets. However, no system proved usable in practice, and the one major US effort, ''Operation Aphrodite
Aphrodite was the World War II code name of a United States Army Air Forces operation to use worn out Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress and Consolidated PB4Y bombers as radio controlled flying bombs against bunkers and other hardened or reinforced e ...
'', proved to be far more dangerous to its users than to the target. The American Azon
AZON (or Azon), from "azimuth only", was one of the world's first guided weapons, deployed by the Allies and contemporary with the German Fritz X.
Officially designated VB-1 ("Vertical Bomb 1"), it was invented by Major Henry J. Rand and Tho ...
guided free-fall ordnance, however, proved useful in both the European and CBI Theater
China Burma India Theater (CBI) was the United States military designation during World War II for the China and Southeast Asian or India–Burma (IBT) theaters. Operational command of Allied forces (including U.S. forces) in the CBI was ...
s of World War II.
Radio control systems of this era were generally electromechanical in nature, using small metal "fingers" or " reeds" with different resonant
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
frequencies each of which would operate one of a number of different relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
s when a particular frequency was received. The relays would in turn then activate various actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an ...
s acting on the control surfaces of the missile. The controller's radio transmitter would transmit the different frequencies in response to the movements of a control stick; these were typically on/off signals. The radio gear used to control the rudder function on the American-developed Azon
AZON (or Azon), from "azimuth only", was one of the world's first guided weapons, deployed by the Allies and contemporary with the German Fritz X.
Officially designated VB-1 ("Vertical Bomb 1"), it was invented by Major Henry J. Rand and Tho ...
guided ordnance, however, was a fully proportional control, with the "ailerons", solely under the control of an on-board gyroscope, serving merely to keep the ordnance from rolling.
These systems were widely used until the 1960s, when the increasing use of solid state systems greatly simplified radio control. The electromechanical systems using reed relay
A reed relay is a type of relay that uses an electromagnet to control one or more reed switches. The contacts are of magnetic material and the electromagnet acts directly on them without requiring an armature to move them. Sealed in a long, narro ...
s were replaced by similar electronic ones, and the continued miniaturization of electronics allowed more signals, referred to as ''control channels'', to be packed into the same package. While early control systems might have two or three channels using amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion t ...
, modern systems include twenty or more using frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
.
Radio-controlled models
 The first general use of radio control systems in models started in the early 1950s with single-channel self-built equipment; commercial equipment came later. The advent of
The first general use of radio control systems in models started in the early 1950s with single-channel self-built equipment; commercial equipment came later. The advent of transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s greatly reduced the battery requirements, since the current requirements at low voltage were greatly reduced and the high voltage battery was eliminated. In both tube and early transistor sets the model's control surfaces were usually operated by an electromagnetic 'escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to t ...
' controlling the stored energy in a rubber-band loop, allowing simple on/off rudder control (right, left, and neutral) and sometimes other functions such as motor speed.
Crystal-controlled superheterodyne receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original car ...
s with better selectivity and stability made control equipment more capable and at lower cost. Multi-channel developments were of particular use to aircraft, which really needed a minimum of three control dimensions (yaw, pitch and motor speed), as opposed to boats, which required only two or one.
As the electronics revolution took off, single-signal channel circuit design became redundant, and instead radios provided proportionally coded signal streams which a servomechanism
In mechanical and control engineering, a servomechanism (also called servo system, or simply servo) is a control system for the position and its time derivatives, such as velocity, of a mechanical system. It often includes a servomotor, and ...
could interpret, using pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying peri ...
(PWM).
More recently, high-end hobby
A hobby is considered to be a regular activity that is done for enjoyment, typically during one's leisure time. Hobbies include collecting themed items and objects, engaging in creative and artistic pursuits, playing sports, or pursuing other ...
systems using pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitud ...
(PCM) features have come on the market that provide a computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
ized digital data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of Discrete mathematics, discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet (formal languages ...
bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
-stream signal to the receiving device, instead of the earlier PWM encoding type. However, even with this coding, loss of transmission during flight has become more common, in part because of the ever more wireless society. Some more modern FM-signal receivers that still use "PWM" encoding instead can, thanks to the use of more advanced computer chips in them, be made to lock onto and use the individual signal characteristics of a particular PWM-type RC transmitter's emissions alone, ''without'' needing a special "code" transmitted along with the control information as PCM encoding has always required.
In the early 21st century, 2.4 gigahertz spread spectrum
In telecommunications, especially radio communication, spread spectrum are techniques by which a signal (electrical engineering), signal (e.g., an electrical, electromagnetic, or acoustic) generated with a particular Bandwidth (signal processi ...
RC control systems have become increasingly utilized in control of model vehicles and aircraft. Now, these 2.4 GHz systems are being made by most radio manufacturers. These radio systems range in price from a couple thousand dollar
Dollar is the name of more than 25 currencies. The United States dollar, named after the international currency known as the Spanish dollar, was established in 1792 and is the first so named that still survives. Others include the Australian d ...
s, all the way down to under US$30 for some. Some manufacturers even offer conversion kits for older digital 72 MHz or 35 MHz receivers and radios. As the emerging multitude of 2.4 GHz band spread spectrum RC systems usually use a "frequency-agile
Frequency agility is the ability of a radar system to quickly shift its operating frequency to account for atmospheric effects, Radar jamming and deception, jamming, mutual interference with friendly sources, or to make it more difficult to locate ...
" mode of operations, like FHSS
Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) is a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly changing the carrier frequency among many frequencies occupying a large spectral band. The changes are controlled by a code known to both transmitter ...
that do not stay on one set frequency any longer while in use, the older "exclusive use" provisions at model flying sites needed for VHF-band RC control systems' frequency control, for VHF-band RC systems that only used one set frequency unless serviced to change it, are not as mandatory as before.
Modern military and aerospace applications
 Remote control military applications are typically not radio control in the direct sense, directly operating flight control surfaces and propulsion power settings, but instead take the form of instructions sent to a completely
Remote control military applications are typically not radio control in the direct sense, directly operating flight control surfaces and propulsion power settings, but instead take the form of instructions sent to a completely autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defi ...
, computerized automatic pilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of a vehicle without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allow ...
. Instead of a "turn left" signal that is applied until the aircraft is flying in the right direction, the system sends a single instruction that says "fly to this point".
Some of the most outstanding examples of remote radio control of a vehicle are the Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rove ...
s such as Sojourner
A sojourner is a person who resides temporarily in a place.
Sojourner may also refer to:
People
* Sojourner Truth (1797–1883), abolitionist and women's rights activist
* Albert Sojourner (1872–1951), member of the Mississippi House of Rep ...
.
Industrial radio remote control
Today radio control is used in industry for such devices as overhead cranes and switchyardlocomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for ...
s. Radio-controlled teleoperators are used for such purposes as inspections, and special vehicles for disarming of bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechan ...
s. Some remotely controlled devices are loosely called robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s, but are more properly categorized as teleoperators since they do not operate autonomously, but only under control of a human operator.
An industrial radio remote control can either be operated by a person, or by a computer control system in a machine to machine
Machine to machine (M2M) is direct communication between devices using any communications channel, including wired communication, wired and wireless.
Machine to machine communication can include industrial instrumentation, enabling a sensor or met ...
(M2M) mode. For example, an automated warehouse may use a radio-controlled crane that is operated by a computer to retrieve a particular item. Industrial radio controls for some applications, such as lifting machinery, are required to be of a fail-safe design in many jurisdictions.
Industrial remote controls work differently from most consumer products. When the receiver receives the radio signal which the transmitter sent, it checks it so that it is the correct frequency and that any security codes match. Once the verification is complete, the receiver sends an instruction to a relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
which is activated. The relay activates a function in the application corresponding to the transmitters button. This could be to engage an electrical directional motor in an overhead crane
An overhead crane, commonly called a bridge crane, is a type of crane found in industrial environments. An overhead crane consists of two parallel rails seated on longitudinal I-beams attached to opposite steel columns by means of brackets. ...
.
In a receiver there are usually several relays, and in something as complex as an overhead crane, perhaps up to twelve or more relays are required to control all directions. In a receiver which opens a gate, two relays are often sufficient.
Industrial remote controls are getting more and higher safety requirements. For example: a remote control may not lose the safety functionality in case of malfunction. This can be avoided by using redundant relays with forced contacts.
See also
*Precision-guided munition
A precision-guided munition (PGM), also called a smart weapon, smart munition, or smart bomb, is a type of weapon system that integrates advanced guidance and control systems, such as Global Positioning System, GPS, laser guidance, or Infrared ...
* Radio-controlled airplane
* Radio-controlled boat
* Radio-controlled car
Radio-controlled cars, or RC cars for short, are miniature vehicles (cars, vans, buses, buggies, etc.) controlled via radio.
Nitro powered models use glow plug engines, small internal combustion engines fuelled by a special mixture of n ...
* Radio-controlled helicopter
A radio-controlled helicopter (also '' RC helicopter'') is model aircraft which is distinct from an RC airplane because of the differences in construction, aerodynamics, and flight training. Several basic designs of RC helicopters exist, of ...
* Remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
* Remote control vehicle
A remote-control vehicle, is defined as any vehicle that is teleoperated by a means that does not restrict its motion with an origin external to the device. This is often a radio-control device, a cable between the controller and the vehicle ...
* Telecommand
A telecommand or telecontrol is a command sent to control a remote system or systems not directly connected (e.g. via wires) to the place from which the telecommand is sent. The word is derived from ''tele'' = remote (Greek), and ''command'' = to ...
* Teletank
Teletanks were a series of experimental wireless remotely controlled unmanned tanks produced in the Soviet Union in the 1930s and early 1940s so as to reduce combat risk to soldiers. A teletank is controlled by radio from a control tank at a dis ...
Notes and references
Further reading
* Bill Yenne, ''Attack of the drones: a history of unmanned aerial combat'', Zenith Imprint, 2004, * Laurence R. Newcome ''Unmanned aviation: a brief history of unmanned aerial vehicles'', AIAA, 2004, , {{DEFAULTSORT:Radio Control