Quick Charge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Quick Charge (QC) is a proprietary battery charging protocol developed by
Quick Charge (QC) is a proprietary battery charging protocol developed by
 Though not publicly documented, the voltage negotiation between device and charger has been
Though not publicly documented, the voltage negotiation between device and charger has been
Qualcomm Quick Charge
Qualcomm Quick Charge Technology Device List
Consumer electronics Qualcomm Battery chargers
 Quick Charge (QC) is a proprietary battery charging protocol developed by
Quick Charge (QC) is a proprietary battery charging protocol developed by Qualcomm
Qualcomm Incorporated () is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software and services related to wireless techn ...
, used for managing power delivered over USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
, mainly by communicating to the power supply and negotiating a voltage.
Quick Charge is supported by devices such as mobile phones which run on Qualcomm system-on-chip
A system on a chip (SoC) is an integrated circuit that combines most or all key components of a computer or electronic system onto a single microchip. Typically, an SoC includes a central processing unit (CPU) with memory, input/output, and da ...
(SoCs), and by some chargers; both device and charger must support QC, otherwise QC charging is not attained. It charges batteries in devices faster than standard USB allows by increasing the output voltage supplied by the USB charger, while adopting techniques to prevent the battery damage caused by uncontrolled fast charging and regulating the incoming voltage internally. Many chargers supporting Quick Charge 2.0 and later are wall adaptors, but it is implemented on some in-car chargers, and some power banks use it to both receive and deliver charge.
Quick Charge is also used by other manufacturers' proprietary rapid-charging systems.
Details
Quick Charge is a proprietary technology that can charge battery-powered devices, primarily mobile phones, at power levels exceeding the 7.5watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s (5 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Uni ...
s at 1.5 amps) supported by the USB BC 1.2 standard, using existing USB cables. The higher voltage available allows more power (watts) to be supplied through wires without excessive heating. As current is lower for the same power if voltage is increased, there is less resistive loss, which becomes significant for longer cables.
Numerous other companies have competing technologies, including MediaTek
MediaTek Inc. (), sometimes informally abbreviated as MTK, is a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company that designs and manufactures a range of semiconductor products, providing chips for wireless communications, high-definition television, h ...
Pump Express and '' OPPO VOOC'' (licensed to OnePlus as ''Dash Charge''), the latter of which supplies higher current without voltage increase, relying on thicker USB wires to handle the current without overheating, as described in .
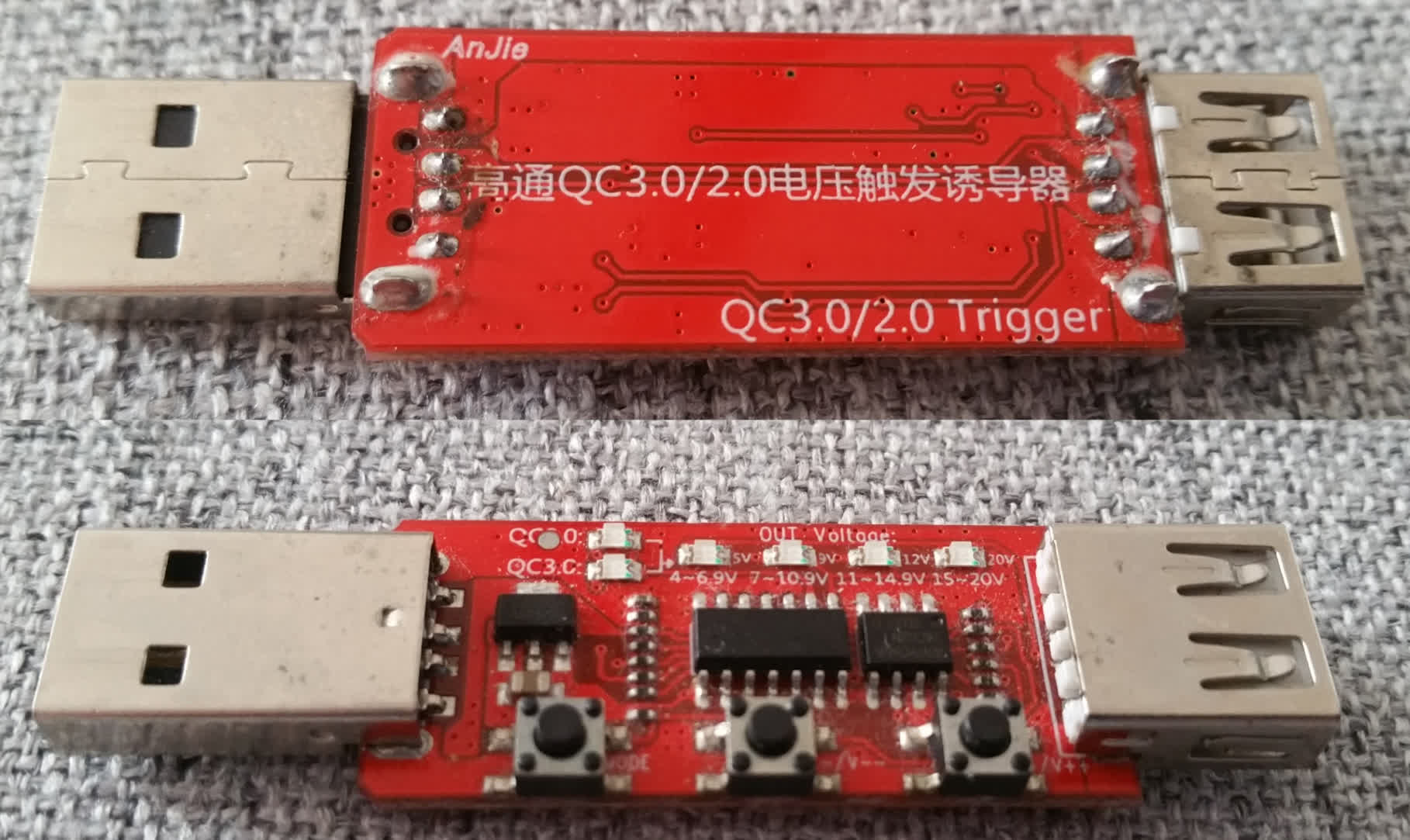
 Though not publicly documented, the voltage negotiation between device and charger has been
Though not publicly documented, the voltage negotiation between device and charger has been reverse-engineered
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accompl ...
, and a custom voltage can be manually requested from the charger using a ''trigger circuit'' that simulates the negotiation to an end device.
Quick Charge requires both the power supply and the device being charged to support it, otherwise charging falls back to the standard USB ten watts.
Quick Charge 2.0 introduced an optional feature called Dual Charge (initially called Parallel Charging), using two PMICs to split the power into 2 streams to reduce phone temperature.
Quick Charge 3.0 introduced ''INOV'' (''Intelligent Negotiation for Optimal Voltage''), Battery Saver Technologies, HVDCP+, and optional Dual Charge+. INOV is an algorithm that determines the optimum power transfer while maximizing efficiency. Battery Saver Technologies aims to maintain at least 80% of the battery's original charge capacity after 500 charge cycles. Qualcomm claims Quick Charge 3.0 is up to 4–6 °C cooler, 16% faster and 38% more efficient than Quick Charge 2.0, and that Quick Charge 3.0 with Dual Charge+ is up to 7–8 °C cooler, 27% faster and 45% more efficient than Quick Charge 2.0 with Dual Charge.
Quick Charge 4 was announced in December 2016 for the Snapdragon 835
The Qualcomm Snapdragon suite of System on a chip, systems on chips (SoCs) are designed for use in smartphones, Tablet computer, tablets, laptops, 2-in-1 PCs, smartwatches, and smartbooks devices.
Before Snapdragon
SoC made by Qualcomm before ...
and later chips. Quick Charge 4 supports HVDCP++, optional Dual Charge++, INOV 3.0, and Battery Saver Technologies 2. It is cross-compatible with both USB-C
USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a 24-pin reversible Electrical connector, connector (not a Communication protocol, protocol) that supersedes previous USB hardware#Connectors, USB connectors (also supersedes Mini DisplayPort and Lightning (connector) ...
and USB-PD specifications, supporting fallback to USB-PD if either the charger or device is not QC-compatible. However, Quick Charge 4 chargers are not backward compatible with Quick Charge. It also features additional safety measures to protect against over-voltage, over-current and overheating, as well as cable quality detection. Qualcomm claims Quick Charge 4 with Dual Charge++ is up to 5 °C cooler, 20% faster and 30% more efficient than Quick Charge 3.0 with Dual Charge+.
Quick Charge 4+ was announced on June 1, 2017. It introduces Intelligent Thermal Balancing and Advanced Safety Features to eliminate hot spots and protect against overheating and short-circuit or damage to the USB-C connector. Dual Charge++ is mandatory, while in prior versions Dual Charge was optional. Unlike Quick Charge 4, Quick Charge 4+ is fully backward compatible with Quick Charge C 2.0 and 3.0 devices.
Quick Charge 5 was announced on July 27, 2020. With up to 100W of power, on a mobile phone with a 4500mAh battery, Qualcomm claims 50% charge in just 5 minutes. Qualcomm announced that this standard is cross-compatible with USB PD PPS programmable power supply, and that its technology can communicate with the charger when charging double cells and double the voltage and current out. For instance, a single battery requests 8.8V; the dual cell can then ask the PPS charger to output 17.6 volts and split it in half to the two separate batteries, providing 5.6 amps total to achieve 100 watts. The first phone supporting this technology was the Xiaomi Mi 10 Ultra.
Quick Charge for Wireless Power
On February 25, 2019, Qualcomm announced Quick Charge for Wireless Power. Quick Charge for Wireless Power falls back on the Qi standard by theWireless Power Consortium
The Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) is a Multinational corporation, multinational technology consortium formed on December 17, 2008. WPC is a virtual corporation with administrative offices in Washington, DC. Its mission is to create and promote ...
if either the charger or device is not compatible.
Versions
Other charging protocols
Compatible with QC-enabled chargers
* Adaptive Fast Charging (Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
)
* Super Fast Charging (Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
)
* BoostMaster (Asus
ASUSTeK Computer Inc. (, , , ; stylized as ASUSTeK or ASUS) is a Taiwanese Multinational corporation, multinational computer, phone hardware and electronics manufacturer headquartered in Beitou District, Taipei, Taiwan. Its products include deskto ...
)
* Dual-Engine Fast Charging ( Vivo, pre-2020 models only) – interchangeable with Dash Charge and VOOC
* Mi Fast Charge (Xiaomi
Xiaomi (; ) is a Chinese multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Beijing, China. It is best known for consumer electronics software electric vehicles. It is the second-largest manufacturer of smartphones in the worl ...
)
* TurboPower (Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois. It was founded by brothers Paul and Joseph Galvin in 1928 and had been named Motorola since 1947. Many of Motorola's products had been ...
)
Other proprietary protocols
* DART (Realme, 2020 to 2022 ) – interchangeable with SuperVOOC, Super Flash Charge, and Warp Charge * Pump Express (MediaTek
MediaTek Inc. (), sometimes informally abbreviated as MTK, is a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company that designs and manufactures a range of semiconductor products, providing chips for wireless communications, high-definition television, h ...
)
* Super Flash Charge (Vivo, 2020 onwards) – interchangeable with SuperVOOC, DART, and Warp Charge
* SuperCharge (Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ("Huawei" sometimes stylized as "HUAWEI"; ; zh, c=华为, p= ) is a Chinese multinational corporationtechnology company in Longgang, Shenzhen, Longgang, Shenzhen, Guangdong. Its main product lines include teleco ...
)
* SuperVOOC (OPPO
Oppo (sometimes stylized as OPPO) is a private company, private China, Chinese consumer electronics manufacturer headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong.
Founded in 2004, its major product lines include Oppo phones, smartphones, Smart device, sm ...
, from 2019 to present and Realme
Realme (stylized in all lowercase as гealme) is a multinational Chinese consumer electronics manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong. It was founded by Li Bingzhong (known as Sky Li) on May 4, 2018, who was a former vice president of Oppo. ...
, from 2022 to present) – interchangeable with DART, Super Flash Charge, and Warp Charge
* VOOC (OPPO
Oppo (sometimes stylized as OPPO) is a private company, private China, Chinese consumer electronics manufacturer headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong.
Founded in 2004, its major product lines include Oppo phones, smartphones, Smart device, sm ...
, until 2019 and pre-2020 Realme
Realme (stylized in all lowercase as гealme) is a multinational Chinese consumer electronics manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong. It was founded by Li Bingzhong (known as Sky Li) on May 4, 2018, who was a former vice president of Oppo. ...
models) – interchangeable with Dash Charge and Dual-Engine Fast Charging
* Warp Charge, formerly Dash Charge ( OnePlus) – interchangeable with Super Flash Charge, SuperVOOC, VOOC, Dual-Engine Fast Charging, and DART
* XCharge ( Infinix)
* Apple Lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
Notes
References
{{reflistExternal links
Qualcomm Quick Charge
Qualcomm Quick Charge Technology Device List
Consumer electronics Qualcomm Battery chargers