planktonic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Plankton are the diverse collection of
Plankton are the diverse collection of

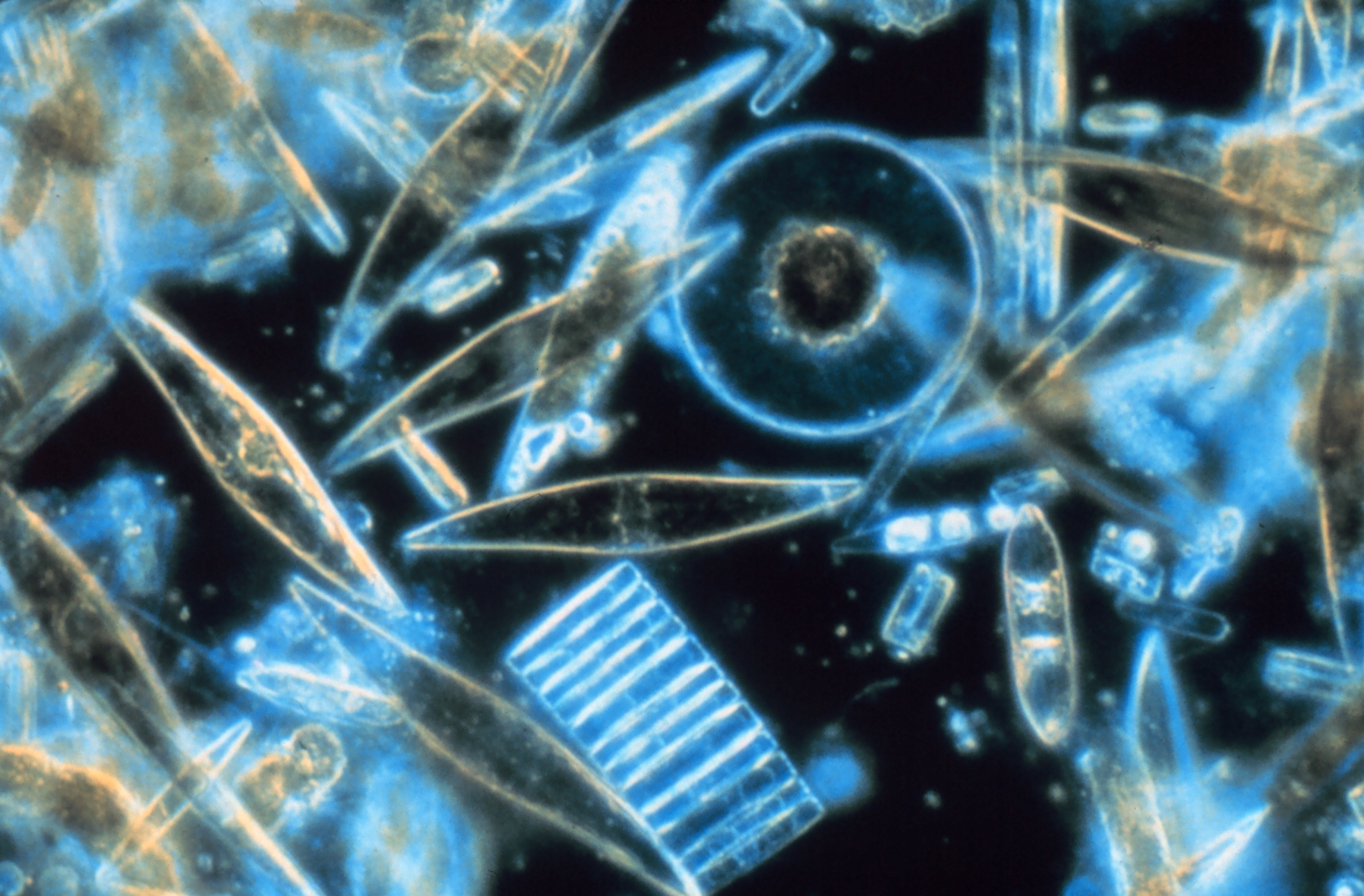 The name ''plankton'' is derived from the
The name ''plankton'' is derived from the
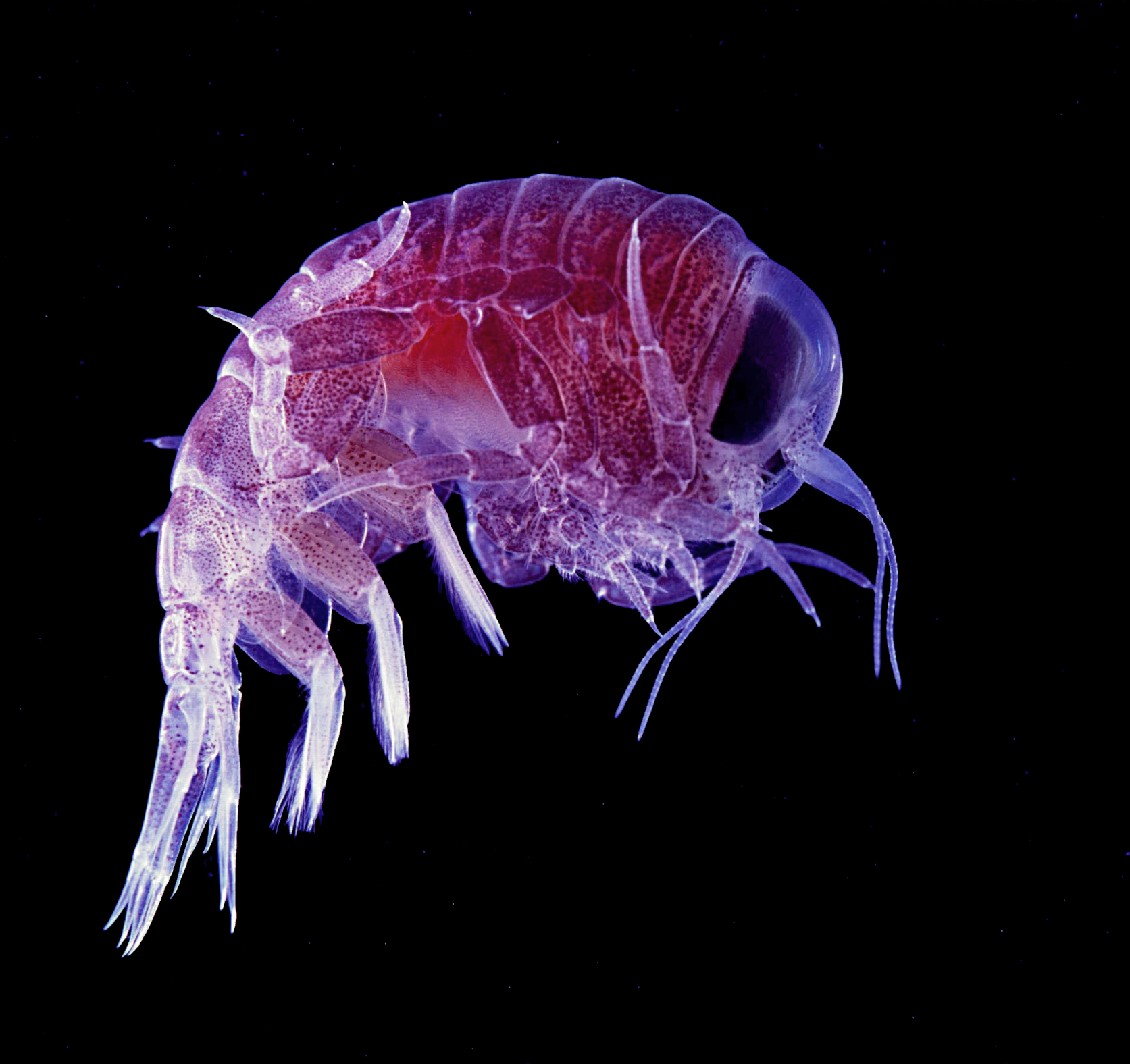 Plankton are primarily divided into broad functional (or
Plankton are primarily divided into broad functional (or
 Plankton are also often described in terms of size. Usually the following divisions are used:
::
However, some of these terms may be used with very different boundaries, especially on the larger end. The existence and importance of nano- and even smaller plankton was only discovered during the 1980s, but they are thought to make up the largest proportion of all plankton in number and diversity.
The microplankton and smaller groups are
Plankton are also often described in terms of size. Usually the following divisions are used:
::
However, some of these terms may be used with very different boundaries, especially on the larger end. The existence and importance of nano- and even smaller plankton was only discovered during the 1980s, but they are thought to make up the largest proportion of all plankton in number and diversity.
The microplankton and smaller groups are
File:Plankton size.png,
File:Ocean mist and spray 2.jpg,
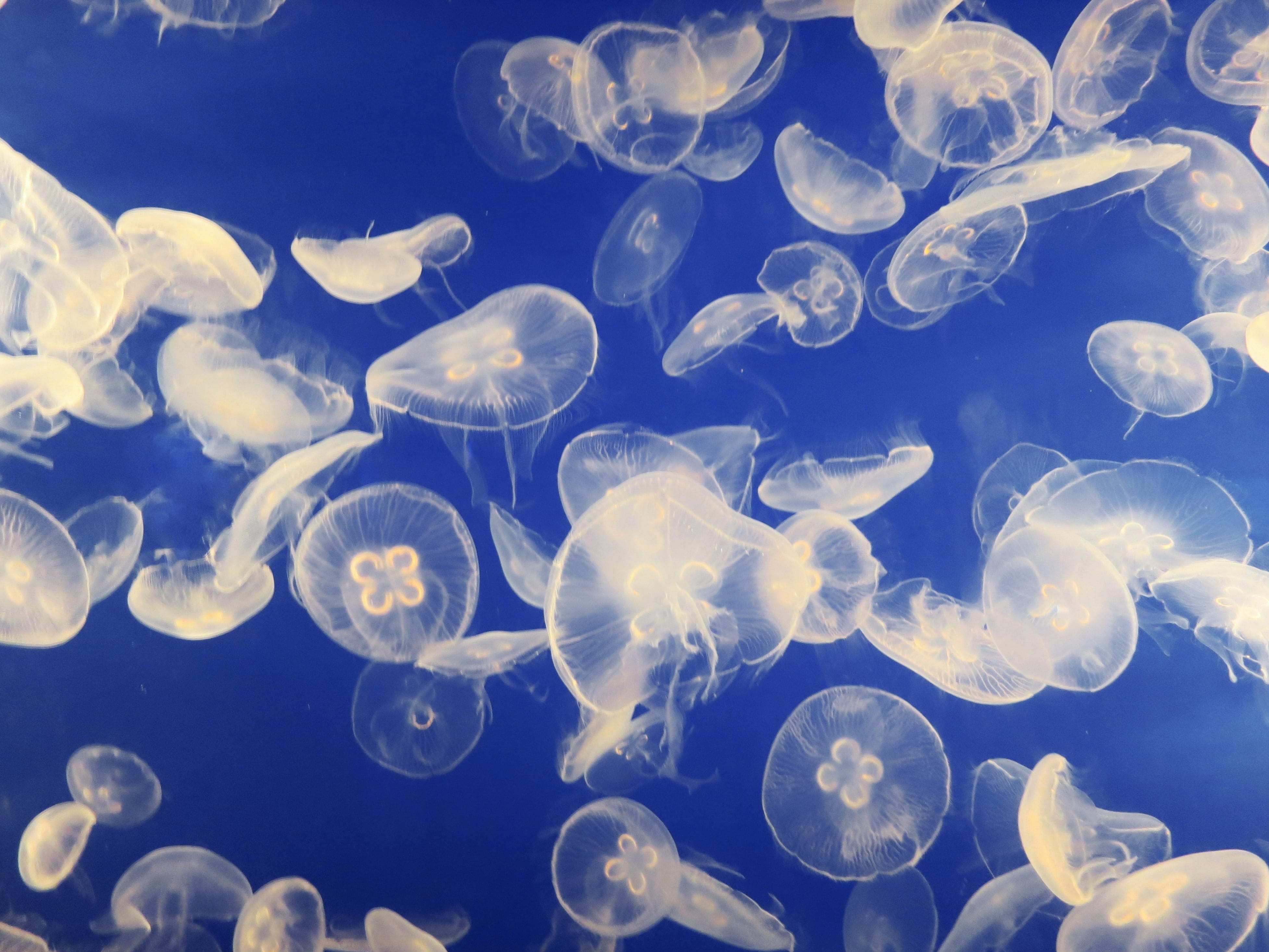

 Ichthyoplankton are the Fish eggs, eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into Juvenile fish, juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals.What are Ichthyoplankton?
Ichthyoplankton are the Fish eggs, eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into Juvenile fish, juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals.What are Ichthyoplankton?
Southwest Fisheries Science Center, NOAA. Modified 3 September 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2011. Fish can produce high numbers of eggs which are often released into the open water column. Fish eggs typically have a diameter of about . The newly hatched young of oviparous fish are called
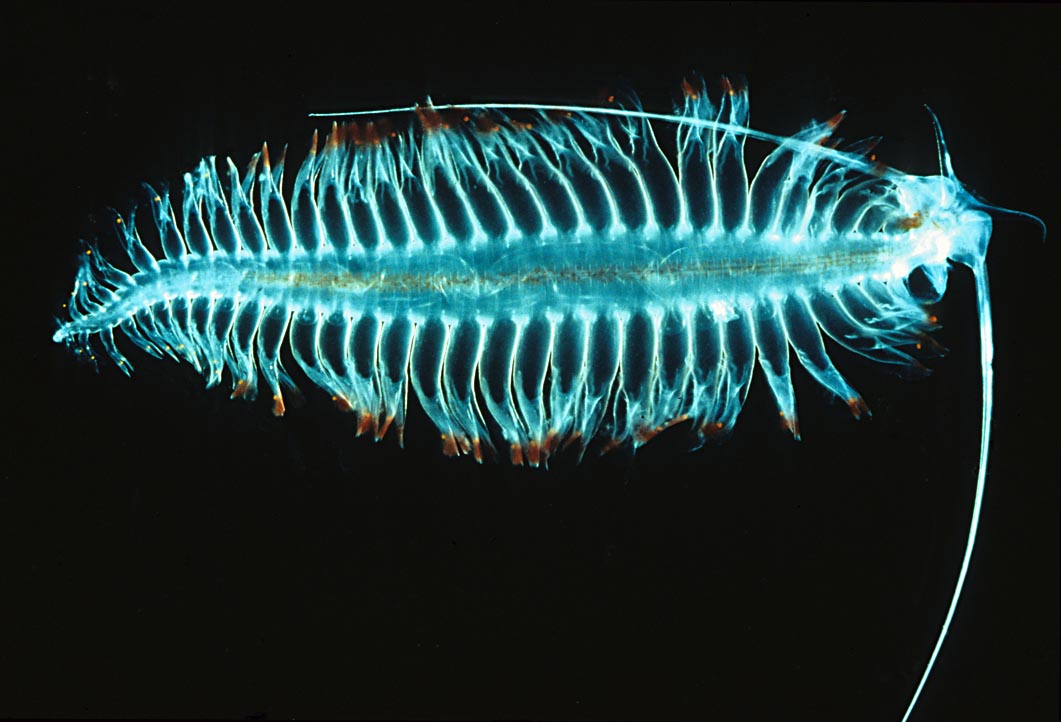 Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with
Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with
 Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and Benthic zone, benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of
Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and Benthic zone, benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of
File:Diatom Helipelta metil.jpg, Diatoms have glass shells (frustules) and produce much of the world's oxygen.
File:Haeckel Spumellaria detail.png, The elaborate silica shells of microscopic marine radiolarians can eventually produce opal.
File:Coccolithus pelagicus.jpg, Coccolithophores have chalk plates called coccoliths, and produced the Cliffs of Dover.
File:Cwall99 lg.jpg, Planktonic algae bloom of
 Apart from aeroplankton, plankton inhabits oceans, seas, lakes and ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see chemosynthesis), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the tropics, tropical and sub-tropical oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate and silicate. This results from large-scale ocean current, ocean circulation and water column Stratification (water), stratification. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant macronutrient concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called HNLC, HNLC regions). The micronutrient iron is deficient in these regions, and iron fertilization, adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton algal blooms. Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, arid land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where trade winds bring dust from the Sahara Desert in north Africa).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, zooplankton and bacterioplankton instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called marine snow, can be especially high following the termination of spring blooms.
The local distribution of plankton can be affected by wind-driven Langmuir circulation and the Langmuir circulation#Biological effects, biological effects of this physical process.
Apart from aeroplankton, plankton inhabits oceans, seas, lakes and ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see chemosynthesis), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the tropics, tropical and sub-tropical oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate and silicate. This results from large-scale ocean current, ocean circulation and water column Stratification (water), stratification. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant macronutrient concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called HNLC, HNLC regions). The micronutrient iron is deficient in these regions, and iron fertilization, adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton algal blooms. Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, arid land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where trade winds bring dust from the Sahara Desert in north Africa).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, zooplankton and bacterioplankton instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called marine snow, can be especially high following the termination of spring blooms.
The local distribution of plankton can be affected by wind-driven Langmuir circulation and the Langmuir circulation#Biological effects, biological effects of this physical process.
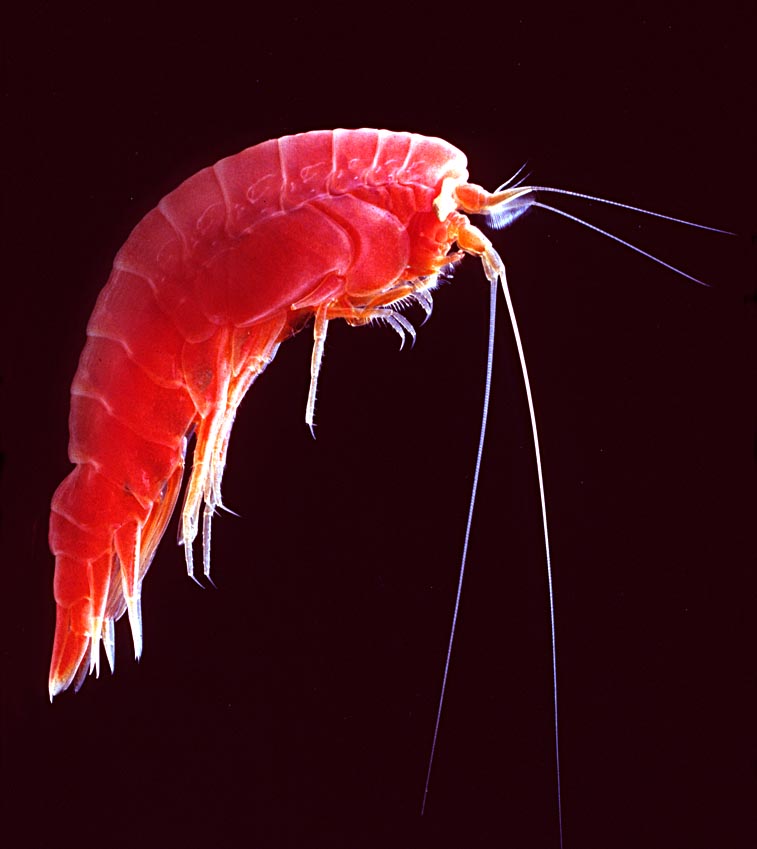 The growth of phytoplankton populations is dependent on light levels and nutrient availability. The chief factor limiting growth varies from region to region in the world's oceans. On a broad scale, growth of phytoplankton in the oligotrophic tropical and subtropical gyres is generally limited by nutrient supply, while light often limits phytoplankton growth in subarctic gyres. Environmental variability at multiple scales influences the nutrient and light available for phytoplankton, and as these organisms form the base of the marine food web, this variability in phytoplankton growth influences higher trophic levels. For example, at interannual scales phytoplankton levels temporarily plummet during El Niño periods, influencing populations of zooplankton, fishes, sea birds, and
The growth of phytoplankton populations is dependent on light levels and nutrient availability. The chief factor limiting growth varies from region to region in the world's oceans. On a broad scale, growth of phytoplankton in the oligotrophic tropical and subtropical gyres is generally limited by nutrient supply, while light often limits phytoplankton growth in subarctic gyres. Environmental variability at multiple scales influences the nutrient and light available for phytoplankton, and as these organisms form the base of the marine food web, this variability in phytoplankton growth influences higher trophic levels. For example, at interannual scales phytoplankton levels temporarily plummet during El Niño periods, influencing populations of zooplankton, fishes, sea birds, and 
File:Pelagibacter.jpg, ''Pelagibacter ubique'', the most common bacteria in the ocean, plays a major role in global carbon cycles
File:Prochlorococcus marinus (cropped).jpg, The tiny cyanobacterium ''Prochlorococcus'' is a major contributor to atmospheric oxygen
File:Noctiluca scintillans varias.jpg, The Noctiluca scintillans, sea sparkle dinoflagellate glows in the night to produce the milky seas effect
File:Copepodkils.jpg, Copepod from Antarctica, a translucent ovoid animal with two long antennae
File:Clupeaharenguslarvaeinsitukils.jpg, Herring larva imaged with the remains of the yolk and the long gut visible in the transparent animal
File:Icefishuk.jpg, Notothenioidei, Icefish larvae from Antarctica have no haemoglobin
File:Mnemiopsis leidyi 2.jpg, The sea walnut ctenophore has a transient anus which forms only when it needs to defecate
File:LeptocephalusConger.jpg, Eel larva drifting with the gulf stream
File:Krill666.jpg, Antarctic krill, probably the largest biomass of a single species on the planet
File:Dinoflagellates and a tintinnid ciliate.jpg, Microzooplankton are major grazers of the plankton: two dinoflagellates and a tintinnid ciliate.
File:Sargassum on the beach, Cuba.JPG, Sargassum seaweed drifts with currents using air bladders to stay afloat
File:Plankton creates sea foam 2.jpg, Planktonic sea foam bubbles with image of photographer
File:Janthina.jpg, Macroplankton: a ''Janthina janthina'' snail (with bubble float) cast up onto a beach in Maui
Ocean Drifters
– Short film narrated by David Attenborough about the varied roles of plankton
Plankton Chronicles
– Short documentary films and photos
COPEPOD: The Global Plankton Database
– Global coverage database of zooplankton biomass and abundance data
Plankton*Net
– Taxonomy (biology), Taxonomic database of images of plankton species
Guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
– Tasmanian Aquaculture and Fisheries Institute
Sir Alister Hardy Foundation for Ocean Science
– Continuous Plankton Recorder Survey
– Integrated Marine Observing System
Sea Drifters
– BBC Audio slideshow
– Images of planktonic microorganisms
Plankton, planktic, planktonic
– Essays on nomenclature
Journal of Plankton Research
– Scientific periodical devoted to plankton {{Authority control Plankton, Biological oceanography Planktology, Aquatic ecology Oceanographical terminology
 Plankton are the diverse collection of
Plankton are the diverse collection of organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
s found in water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
(or air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
) that are unable to propel themselves against a current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
(or wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
and whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s.
Marine plankton include bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
and drifting or floating animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s that inhabit the saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish water, ...
of ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s and the brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estu ...
waters of estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton
Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ...
, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
s, pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
and wind-scattered seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air by sea spray
Sea spray are aerosol particles formed from the ocean, mostly by ejection into Earth's atmosphere by bursting bubbles at the air-sea interface. Sea spray contains both organic matter and inorganic salts that form sea salt aerosol (SSA). SSA ha ...
.
Though many planktonic species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
are microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale be ...
in size, ''plankton'' includes organisms over a wide range of sizes, including large organisms such as jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
. Plankton are defined by their ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
and level of motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
rather than by any phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
or taxonomic classification. Technically the term does not include organisms on the surface of the water, which are called ''neuston
Neuston, also known as pleuston, are organisms that live at the surface of the ocean or an estuary, or at the surface of a lake, river or pond. Neuston can live on top of the water surface or may be attached to the underside of the water surface. ...
''—or those that swim actively in the water, which are called ''nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) refers to the actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water. The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the passive organisms t ...
''.
Terminology

 The name ''plankton'' is derived from the
The name ''plankton'' is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
adjective (), meaning ''errant
A knight-errant (or knight errant) is a figure of medieval Chivalric romance, chivalric romance literature. The adjective '':wikt:errant, errant'' (meaning "wandering, roving") indicates how the knight-errant would wander the land in search of adv ...
'', and by extension, ''wanderer'' or ''drifter'', and was coined by Victor Hensen
Christian Andreas Victor Hensen (10 February 1835 – 5 April 1924) was a German zoologist and marine biologist (planktology). He coined the term ''plankton'' and laid the foundation for biological oceanography and quantitative studies.
Family
...
in 1887. While some forms are capable of independent movement and can swim hundreds of meters vertically in a single day (a behavior called diel vertical migration), their horizontal position is primarily determined by the surrounding water movement, and plankton typically flow with ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, s ...
s. This is in contrast to nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) refers to the actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water. The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the passive organisms t ...
organisms, such as fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting t ...
and marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reli ...
s, which can swim against the ambient flow and control their position in the environment.
Within the plankton, holoplankton
Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic (they live in the water column and cannot swim against a current) for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with meroplankton, which are planktic organisms that spend part of their lif ...
spend their entire life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
as plankton (e.g. most algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s, salp
A salp (plural salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (plural salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktic tunicate. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body, one of the most efficient ...
s, and some jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
). By contrast, meroplankton
Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of larval stages of larger organism. Meroplankton can be contrasted with holoplankton, whi ...
are only planktic for part of their lives (usually the larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
l stage), and then graduate to either a nektic (swimming) or benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
(sea floor) existence. Examples of meroplankton include the larvae of sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
s, starfish, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s, marine worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete wo ...
s, and most fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
.
The amount
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a multitude or magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity and continuity. Quantities can be compared in terms of "more", "less", or "equal", or by assigning a numerical value multiple of a unit ...
and distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
of plankton depends on available nutrients, the state of water and a large amount of other plankton.
The study of plankton is termed planktology
Planktology is the study of plankton, various small drifting plants, animals and microorganisms that inhabit bodies of water. Planktology topics include primary production, energy flow and the carbon cycle.
Plankton drive the "biological pump", ...
and a planktonic individual is referred to as a plankter. The adjective ''planktonic'' is widely used in both the scientific and popular literature, and is a generally accepted term. However, from the standpoint of prescriptive grammar, the less-commonly used ''planktic'' is more strictly the correct adjective. When deriving English words from their Greek or Latin roots, the gender-specific ending (in this case, "-on" which indicates the word is neuter) is normally dropped, using only the root of the word in the derivation.
Trophic groups
 Plankton are primarily divided into broad functional (or
Plankton are primarily divided into broad functional (or trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it ...
) groups:
*Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
(from Greek ''phyton'', or plant), are autotroph
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
ic prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
or eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
alga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mi ...
e that live near the water surface where there is sufficient light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
to support photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
. Among the more important groups are the diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s, cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, dinoflagellates and coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
s.
*Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
(from Greek ''zoon'', or animal), are small protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
ns or metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
ns (e.g. crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s and other animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s) that feed on other plankton. Some of the eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
and larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
e of larger nektonic animals, such as fish, crustaceans, and annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecol ...
s, are included here.
* Mycoplankton include fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
and fungus-like organisms, which, like bacterioplankton, are also significant in remineralisation and nutrient cycling
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cycli ...
.
* Bacterioplankton include bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, which play an important role in remineralising organic material down the water column (note that prokaryotic phytoplankton are also bacterioplankton).
* Virioplankton are viruses. Viruses are more abundant in the plankton than bacteria and archaea, though much smaller.
Mixoplankton
*Mixotroph A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
s. Plankton have traditionally been categorized as producer, consumer and recycler groups, but some plankton are able to benefit from more than just one trophic level. In this mixed trophic strategy—known as mixotrophy—organisms act as both producers and consumers, either at the same time or switching between modes of nutrition in response to ambient conditions. This makes it possible to use photosynthesis for growth when nutrients and light are abundant, but switching to eat phytoplankton, zooplankton or each other when growing conditions are poor. Mixotrophs are divided into two groups; constitutive mixotrophs, CMs, which are able to perform photosynthesis on their own, and non-constitutive mixotrophs, NCMs, which use phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
to engulf phototrophic prey that are either kept alive inside the host cell which benefit from its photosynthesis, or they digest their prey except for the plastids which continues to perform photosynthesis (kleptoplasty
Kleptoplasty or kleptoplastidy is a symbiotic phenomenon whereby plastids, notably chloroplasts from algae, are sequestered by host organisms. The word is derived from ''Kleptes'' (κλέπτης) which is Greek for thief. The alga is eaten norma ...
).
Recognition of the importance of mixotrophy as an ecological strategy is increasing, as well as the wider role this may play in marine biogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, ...
. Studies have shown that mixotrophs are much more important for the marine ecology than previously assumed, and comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. Their presence act as a buffer that prevents the collapse of ecosystems during times with little to no light.
Size groups
 Plankton are also often described in terms of size. Usually the following divisions are used:
::
However, some of these terms may be used with very different boundaries, especially on the larger end. The existence and importance of nano- and even smaller plankton was only discovered during the 1980s, but they are thought to make up the largest proportion of all plankton in number and diversity.
The microplankton and smaller groups are
Plankton are also often described in terms of size. Usually the following divisions are used:
::
However, some of these terms may be used with very different boundaries, especially on the larger end. The existence and importance of nano- and even smaller plankton was only discovered during the 1980s, but they are thought to make up the largest proportion of all plankton in number and diversity.
The microplankton and smaller groups are microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s and operate at low Reynolds number
In fluid mechanics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be domi ...
s, where the viscosity of water is more important than its mass or inertia.
Habitat groups
Marine plankton
Marine plankton includes marine bacteria and archaea,algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries.
Freshwater plankton
Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found inland in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers.Aeroplankton
Sea spray
Sea spray are aerosol particles formed from the ocean, mostly by ejection into Earth's atmosphere by bursting bubbles at the air-sea interface. Sea spray contains both organic matter and inorganic salts that form sea salt aerosol (SSA). SSA ha ...
containing marine microorganisms
Marine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism (or microbe) is any microscopic livin ...
can be swept high into the atmosphere and may travel the globe as aeroplankton
Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ...
before falling back to earth.
Aeroplankton
Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ...
are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by the current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
of the wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
; they are the atmospheric analogue to oceanic plankton. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale be ...
in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of their tiny size. Scientists can collect them for study in traps and sweep nets from aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
, kites or balloons. Aeroplankton is made up of numerous microbes
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
, including virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
es, about 1000 different species of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, around 40,000 varieties of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and hundreds of species of protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
es and liverworts that live some part of their life cycle as aeroplankton, often as spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...
s, pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
, and wind-scattered seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s. Additionally, peripatetic microorganisms are swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms, and an even larger amount of airborne marine microorganisms are propelled high into the atmosphere in sea spray. Aeroplankton deposits hundreds of millions of airborne viruses and tens of millions of bacteria every day on every square meter around the planet.
The sea surface microlayer
The sea surface microlayer (SML) is the boundary interface between the atmosphere and ocean, covering about 70% of Earth's surface. With an operationally defined thickness between 1 and , the SML has physicochemical and biological properties that ...
, compared to the sub-surface waters, contains elevated concentration of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
.Blanchard, D.C., 1983. The production, distribution and bacterial enrichment of the sea-salt aerosol. In: Liss, P.S., Slinn, W.G.N. ŽEds.., Air–Sea Exchange of Gases and Particles. D. Reidel Publishing Co., Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 407-444. These materials can be transferred from the sea-surface to the atmosphere in the form of wind-generated aqueous aerosols due to their high vapour tension and a process known as volatilisation
Volatilization is the process whereby a dissolved sample is vaporised. In atomic spectroscopy this is usually a two-step process. The analyte is turned into small droplets in a nebuliser which are entrained in a gas flow which is in turn volatilis ...
.Wallace Jr., G.T., Duce, R.A., 1978. Transport of particulate organic matter by bubbles in marine waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23 Ž6., 1155–1167. When airborne, these microbes
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
can be transported long distances to coastal regions. If they hit land they can have affect animal, vegetation and human health.WHO, 1998. Draft guidelines for safe recreational water environments: coastal and fresh waters, draft for consultation. World Health Organization, Geneva, EOSrDRAFTr98 14, pp. 207–299. Marine aerosols that contain viruses can travel hundreds of kilometers from their source and remain in liquid form as long as the humidity is high enough (over 70%).Klassen, R. D., & Roberge, P. R. (1999). Aerosol transport modeling as an aid to understanding atmospheric corrosivity patterns. Materials & Design, 20, 159–168.Moorthy, K. K., Satheesh, S. K., & Krishna Murthy, B.V. (1998). Characteristics ofspectral optical depths and size distributions of aerosols over tropical oceanic regions. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar–Terrestrial Physics, 60, 981–992.
These aerosols are able to remain suspended in the atmosphere for about 31 days.Aller, J., Kuznetsova, M., Jahns, C., Kemp, P. (2005) The sea surface microlayer as a source of viral and bacterial enrichment in marine aerosols. Journal of aerosol science. Vol. 36, pp. 801-812. Evidence suggests that bacteria can remain viable after being transported inland through aerosols. Some reached as far as 200 meters at 30 meters above sea level. The process which transfers this material to the atmosphere causes further enrichment in both bacteria and viruses in comparison to either the SML or sub-surface waters (up to three orders of magnitude in some locations).Marks, R., Kruczalak, K., Jankowska, K., & Michalska, M. (2001). Bacteria and fungi in air over the GulfofGdansk and Baltic sea. Journal of Aerosol Science, 32, 237–250.
Geoplankton
Many animals live in terrestrial environments by thriving in transient often microscopic bodies of water and moisture, these includerotifer
The rotifers (, from the Latin , "wheel", and , "bearing"), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first described by Rev. John H ...
s and gastrotrich
The gastrotrichs (phylum Gastrotricha), commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, acoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environmen ...
s which lay resilient eggs capable of surviving years in dry environments, and some of which can go dormant themselves. Nematodes are usually microscopic with this lifestyle. Water bears, despite only having lifespans of a few months, famously can enter suspended animation during dry or hostile conditions and survive for decades. This allows them to be ubiquitous in terrestrial environments despite needing water to grow and reproduce. Many microscopic crustacean groups like copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s and amphipods
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far describ ...
(of which sandhoppers are members) and seed shrimp
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typical ...
are known to go dormant when dry and live in transient bodies of water too
Other groups
Gelatinous zooplankton

Gelatinous zooplankton
Gelatinous zooplankton are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish are gelatinous zoopla ...
are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
are gelatinous zooplankton, but not all gelatinous zooplankton are jellyfish. The most commonly encountered organisms include ctenophores, medusae
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
, salps, and Chaetognatha in coastal waters. However, almost all marine phyla, including Annelida, Mollusca and Arthropoda, contain gelatinous species, but many of those odd species live in the open ocean and the deep sea and are less available to the casual ocean observer.
Ichthyoplankton
 Ichthyoplankton are the Fish eggs, eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into Juvenile fish, juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals.What are Ichthyoplankton?
Ichthyoplankton are the Fish eggs, eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into Juvenile fish, juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals.What are Ichthyoplankton?Southwest Fisheries Science Center, NOAA. Modified 3 September 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2011. Fish can produce high numbers of eggs which are often released into the open water column. Fish eggs typically have a diameter of about . The newly hatched young of oviparous fish are called
larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
e. They are usually poorly formed, carry a large yolk sac (for nourishment) and are very different in appearance from juvenile and adult specimens. The larval period in oviparous fish is relatively short (usually only several weeks), and larvae rapidly grow and change appearance and structure (a process termed metamorphosis) to become juveniles. During this transition larvae must switch from their yolk sac to feeding on zooplankton prey, a process which depends on typically inadequate zooplankton density, starving many larvae. In time fish larvae become able to swim against currents, at which point they cease to be plankton and become juvenile fish.
Holoplankton
 Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with
Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with meroplankton
Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of larval stages of larger organism. Meroplankton can be contrasted with holoplankton, whi ...
, which are planktic organisms that spend part of their life cycle in the benthic zone. Examples of holoplankton include some diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s, radiolarians, some dinoflagellates, foraminifera, amphipods, krill, copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s, and salp
A salp (plural salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (plural salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktic tunicate. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body, one of the most efficient ...
s, as well as some gastropod mollusk species. Holoplankton dwell in the pelagic zone as opposed to the benthic zone. Holoplankton include both phytoplankton and zooplankton and vary in size. The most common plankton are protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s.
Meroplankton
 Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and Benthic zone, benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of
Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and Benthic zone, benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
l stages of larger organism. Meroplankton can be contrasted with holoplankton
Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic (they live in the water column and cannot swim against a current) for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with meroplankton, which are planktic organisms that spend part of their lif ...
, which are planktonic organisms that stay in the pelagic zone as plankton throughout their entire life cycle. After a period of time in the plankton, many meroplankton graduate to the nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) refers to the actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water. The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the passive organisms t ...
or adopt a benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
(often Sessility (zoology), sessile) lifestyle on the seafloor. The larval stages of benthic invertebrates make up a significant proportion of planktonic communities. The planktonic larval stage is particularly crucial to many benthic invertebrate in order to Dispersal vector, disperse their young. Depending on the particular species and the environmental conditions, larval or juvenile-stage meroplankton may remain in the pelagic zone for durations ranging from hour to months.
Pseudoplankton
Pseudoplankton are organisms that attach themselves to planktonic organisms or other floating objects, such as drifting wood, buoyant shells of organisms such as ''Spirula'', or man-made flotsam. Examples include goose barnacles and the bryozoan ''Jellyella''. By themselves these animals cannot Buoyancy, float, which contrasts them with true planktonic organisms, such as ''Velella'' and the Portuguese Man o' War, which are buoyant. Pseudoplankton are often found in the guts of filtering Zooplankton, zooplankters.Tychoplankton
Tychoplankton are organisms, such as free-living or attached Benthos, benthic organisms and other non-planktonic organisms, that are carried into the plankton through a disturbance of their benthic habitat, or by winds and currents. This can occur by direct turbulence or by disruption of the substrate and subsequent entrainment in the water column. Tychoplankton are, therefore, a primary subdivision for sorting planktonic organisms by duration of lifecycle spent in the plankton, as neither their entire lives nor particular reproductive portions are confined to planktonic existence. Tychoplankton are sometimes called ''accidental plankton''.Mineralized plankton
coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
s off the southern coast of England
File:Planktic Foraminifera of the northern Gulf of Mexico.jpg, Foraminiferans have calcium carbonate shells and produced the limestone in the Great Pyramids.
Distribution
 Apart from aeroplankton, plankton inhabits oceans, seas, lakes and ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see chemosynthesis), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the tropics, tropical and sub-tropical oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate and silicate. This results from large-scale ocean current, ocean circulation and water column Stratification (water), stratification. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant macronutrient concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called HNLC, HNLC regions). The micronutrient iron is deficient in these regions, and iron fertilization, adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton algal blooms. Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, arid land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where trade winds bring dust from the Sahara Desert in north Africa).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, zooplankton and bacterioplankton instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called marine snow, can be especially high following the termination of spring blooms.
The local distribution of plankton can be affected by wind-driven Langmuir circulation and the Langmuir circulation#Biological effects, biological effects of this physical process.
Apart from aeroplankton, plankton inhabits oceans, seas, lakes and ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see chemosynthesis), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the tropics, tropical and sub-tropical oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate and silicate. This results from large-scale ocean current, ocean circulation and water column Stratification (water), stratification. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant macronutrient concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called HNLC, HNLC regions). The micronutrient iron is deficient in these regions, and iron fertilization, adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton algal blooms. Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, arid land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where trade winds bring dust from the Sahara Desert in north Africa).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, zooplankton and bacterioplankton instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called marine snow, can be especially high following the termination of spring blooms.
The local distribution of plankton can be affected by wind-driven Langmuir circulation and the Langmuir circulation#Biological effects, biological effects of this physical process.
Ecological significance
Food chain
Aside from representing the bottom few levels of a food chain that supports commercially important Fishery, fisheries, plankton ecosystems play a role in the biogeochemical cycles of many important chemical elements, including the ocean's carbon cycle. Fish larvae mainly eat zooplankton, which eat phytoplanktonCarbon cycle
Primarily by grazing on phytoplankton, zooplankton provide carbon to the planktic foodweb, either Cellular respiration, respiring it to provide metabolism, metabolic energy, or upon death as Biomass (ecology), biomass or detritus. Organic material tends to be density, denser than seawater, so it sinks into open ocean ecosystems away from the coastlines, transporting carbon along with it. This process, called the biological pump, is one reason that oceans constitute the largest carbon sink on Earth science, Earth. However, it has been shown to be influenced by increments of temperature. In 2019, a study indicated that at ongoing rates of Ocean acidification, seawater acidification, Antarctic phytoplanktons could become smaller and less effective at storing carbon before the end of the century. It might be possible to increase the ocean's uptake of Carbon dioxide#In the Earth.27s atmosphere, carbon dioxide () generated through Human impact on the environment, human activities by increasing plankton production through iron fertilization – introducing amounts of iron into the ocean. However, this technique may not be practical at a large scale. Ocean Anoxic sea water, oxygen depletion and resultant methanogen, methane production (caused by the excess production remineralising at depth) is one potential drawback.Oxygen production
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
absorb energy from the Sun and nutrients from the water to produce their own nourishment or energy. In the process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
, phytoplankton release molecular oxygen () into the water as a waste byproduct. It is estimated that about 50% of the world's oxygen is produced via phytoplankton photosynthesis. The rest is produced via photosynthesis on land by plants. Furthermore, phytoplankton photosynthesis has controlled the atmospheric Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, /Oxygen#Build-up in the atmosphere, balance since the early Precambrian Eon.
Absorption efficiency
The ''absorption efficiency'' (AE) of plankton is the proportion of food absorbed by the plankton that determines how available the consumed organic materials are in meeting the required physiological demands. Depending on the feeding rate and prey composition, variations in absorption efficiency may lead to variations in fecal pellet production, and thus regulates how much organic material is recycled back to the marine environment. Low feeding rates typically lead to high absorption efficiency and small, dense pellets, while high feeding rates typically lead to low absorption efficiency and larger pellets with more organic content. Another contributing factor to dissolved organic matter (DOM) release is respiration rate. Physical factors such as oxygen availability, pH, and light conditions may affect overall oxygen consumption and how much carbon is loss from zooplankton in the form of respired . The relative sizes of zooplankton and prey also mediate how much carbon is released via sloppy feeding. Smaller prey are ingested whole, whereas larger prey may be fed on more “sloppily”, that is more biomatter is released through inefficient consumption. There is also evidence that diet composition can impact nutrient release, with carnivorous diets releasing more dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and ammonium than omnivorous diets.Biomass variability
 The growth of phytoplankton populations is dependent on light levels and nutrient availability. The chief factor limiting growth varies from region to region in the world's oceans. On a broad scale, growth of phytoplankton in the oligotrophic tropical and subtropical gyres is generally limited by nutrient supply, while light often limits phytoplankton growth in subarctic gyres. Environmental variability at multiple scales influences the nutrient and light available for phytoplankton, and as these organisms form the base of the marine food web, this variability in phytoplankton growth influences higher trophic levels. For example, at interannual scales phytoplankton levels temporarily plummet during El Niño periods, influencing populations of zooplankton, fishes, sea birds, and
The growth of phytoplankton populations is dependent on light levels and nutrient availability. The chief factor limiting growth varies from region to region in the world's oceans. On a broad scale, growth of phytoplankton in the oligotrophic tropical and subtropical gyres is generally limited by nutrient supply, while light often limits phytoplankton growth in subarctic gyres. Environmental variability at multiple scales influences the nutrient and light available for phytoplankton, and as these organisms form the base of the marine food web, this variability in phytoplankton growth influences higher trophic levels. For example, at interannual scales phytoplankton levels temporarily plummet during El Niño periods, influencing populations of zooplankton, fishes, sea birds, and marine mammal
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reli ...
s.
The effects of anthropogenic warming on the global population of phytoplankton is an area of active research. Changes in the vertical stratification of the water column, the rate of temperature-dependent biological reactions, and the atmospheric supply of nutrients are expected to have important impacts on future phytoplankton productivity. Additionally, changes in the mortality of phytoplankton due to rates of zooplankton grazing may be significant.

Plankton diversity
Planktonic Relationships
Fish & plankton Zooplankton are the initial prey item for almost all fish larvae as they switch from their yolk sacs to external feeding. Fish rely on the density and distribution of zooplankton to match that of new larvae, which can otherwise starve. Natural factors (e.g., current variations, temperature changes) and man-made factors (e.g. river dams, ocean acidification, rising temperatures) can strongly affect zooplankton, which can in turn strongly affect larval survival, and therefore breeding success. It's been shown that plankton can be patchy in marine environments where there aren't significant fish populations and additionally, where fish are abundant, zooplankton dynamics are influenced by the fish predation rate in their environment. Depending on the predation rate, they could express regular or chaotic behavior. A negative effect that fish larvae can have on planktonic algal blooms is that the larvae will prolong the blooming event by diminishing available zooplankton numbers; this in turn permits excessive phytoplankton growth allowing the bloom to flourish . The importance of both phytoplankton and zooplankton is also well-recognized in extensive and semi-intensive pond fish farming. Plankton population-based pond management strategies for fish rearing have been practiced by traditional fish farmers for decades, illustrating the importance of plankton even in man-made environments. Whales & plankton Of all animal fecal matter, it is whale feces that is the 'trophy' in terms of increasing nutrient availability. Phytoplankton are the powerhouse of open ocean primary production and they can acquire many nutrients from whale feces. In the marine food web, phytoplankton are at the base of the food web and are consumed by zooplankton & krill, which are preyed upon by larger and larger marine organisms, including whales, so it can be said that whale poop fuels the entire food web.Humans & plankton
Plankton have many direct and indirect effects on humans. Around 70% of the oxygen in the atmosphere is produced in the oceans from phytoplankton performing photosynthesis, meaning that the majority of the oxygen available for us and other organisms that Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, respire aerobically is produced by plankton. Plankton also make up the base of the marine food web, providing food for all the trophic levels above. Recent studies have analyzed the marine food web to see if the system runs on a Top-down and bottom-up design, top-down or bottom-up approach. Essentially, this research is focused on understanding whether changes in the food web are driven by nutrients at the bottom of the food web or predators at the top. The general conclusion is that the bottom-up approach seemed to be more predictive of food web behavior. This indicates that plankton have more sway in determining the success of the primary consumer species that prey on them than do the secondary consumers that prey on the primary consumers. In some cases, plankton act as an intermediate Host (biology), host for deadly parasites in humans. One such case is that of cholera, an infection caused by several strains of Vibrio cholerae. These species have been shown to have a symbiotic relationship with chitinous zooplankton species likecopepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s. These bacteria benefit not only from the food provided by the chiton from the zooplankton, but also from the protection from acidic environments. Once the copepods have been ingested by a human host, the chitinous exterior protects the bacteria from the stomach acids in the stomach and proceed to the intestines. Once there, the bacteria bind with the surface of the small intestine and the host will start developing symptoms, including extreme diarrhea, within five days.
See also
*Aeroplankton
Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ...
* Gelatinous zooplankton
Gelatinous zooplankton are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish are gelatinous zoopla ...
* Ichthyoplankton
* Nekton
* Paradox of the plankton
* Seston
* Veliger
References
Further reading
*Kirby, Richard R. (2010). ''Ocean Drifters: A Secret World Beneath the Waves''. Studio Cactus Ltd, UK. . *Dusenbery, David B. (2009). ''Living at Micro Scale: The Unexpected Physics of Being Small''. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts . *Kiørboe, Thomas (2008). ''A Mechanistic Approach to Plankton Ecology''. Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J. . *Dolan, J.R., Agatha, S., Coats, D.W., Montagnes, D.J.S., Stocker, D.K., eds. (2013).''Biology and Ecology of Tintinnid Ciliates: Models for Marine Plankton''. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, UK .External links
Ocean Drifters
– Short film narrated by David Attenborough about the varied roles of plankton
Plankton Chronicles
– Short documentary films and photos
COPEPOD: The Global Plankton Database
– Global coverage database of zooplankton biomass and abundance data
Plankton*Net
– Taxonomy (biology), Taxonomic database of images of plankton species
Guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
– Tasmanian Aquaculture and Fisheries Institute
Sir Alister Hardy Foundation for Ocean Science
– Continuous Plankton Recorder Survey
– Integrated Marine Observing System
Sea Drifters
– BBC Audio slideshow
– Images of planktonic microorganisms
Plankton, planktic, planktonic
– Essays on nomenclature
Journal of Plankton Research
– Scientific periodical devoted to plankton {{Authority control Plankton, Biological oceanography Planktology, Aquatic ecology Oceanographical terminology