Pericynthion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In


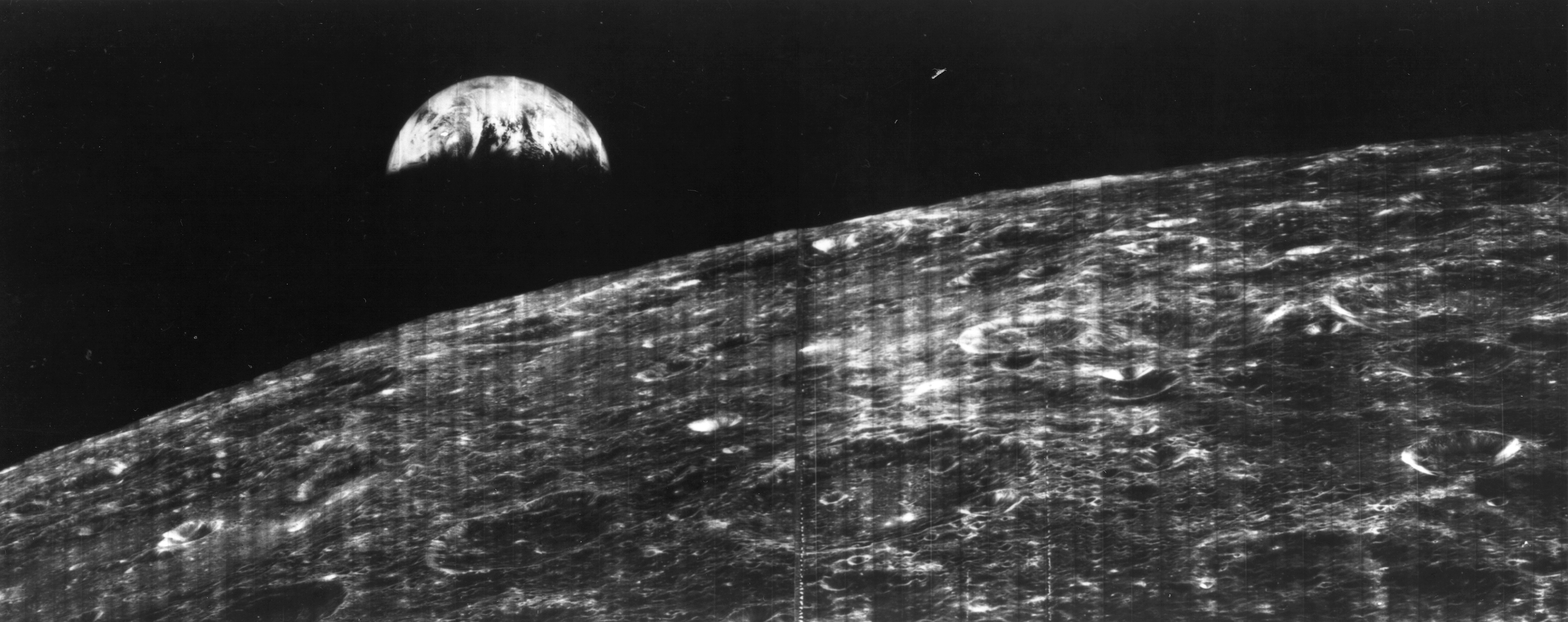 The
The
 In
In astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
and spaceflight, a lunar orbit (also known as a selenocentric orbit) is an orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
by an object around Earth's Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
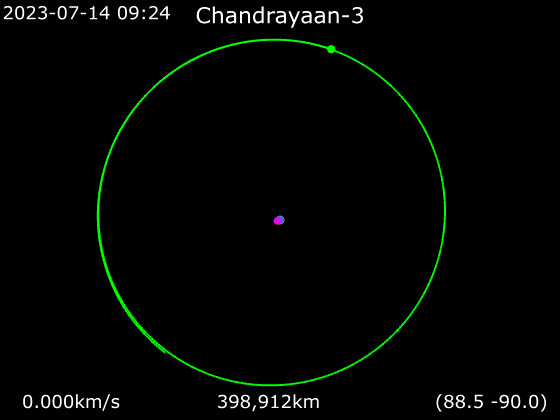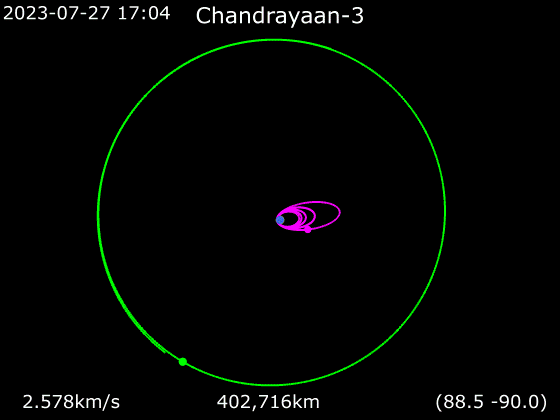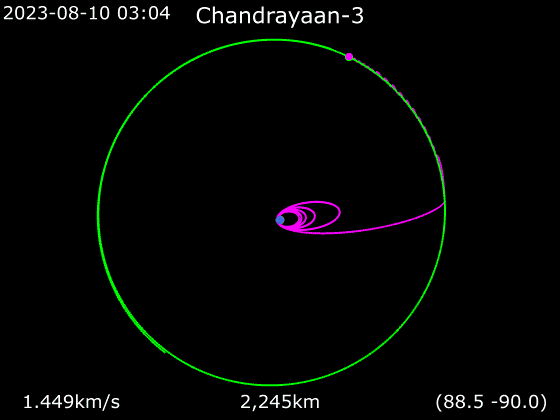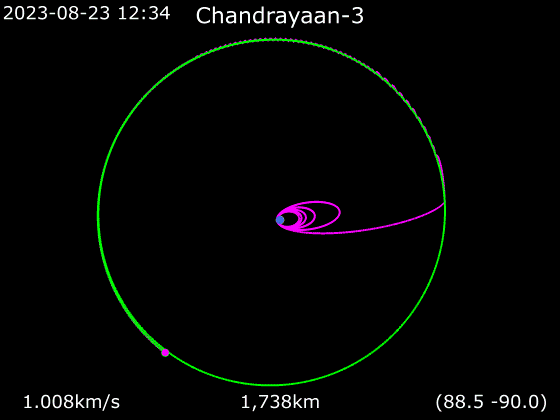
. In general these orbits are not circular. When farthest from the Moon (at apoapsis) a spacecraft is said to be at apolune, apocynthion, or aposelene. When closest to the Moon (at periapsis) it is said to be at perilune, pericynthion, or periselene. These derive from names or epithets of the moon goddess.
Lunar orbit insertion (LOI) is an orbit insertion maneuver used to achieve lunar orbit.
Low lunar orbit (LLO) is an orbit below altitude. These have a period of about 2 hours. They are of particular interest in the exploration of the Moon, but suffer from gravitational perturbations that make most unstable, and leave only a few orbital trajectories possible for indefinite '' frozen orbits''. These would be useful for long-term stays in LLO.
Perturbation effects and low orbits
Most lunar low orbits below 100 km (60 mi) are unstable. Gravitational anomalies slightly distorting the orbits of some Lunar Orbiters led to the discovery of mass concentrations (dubbed mascons) beneath the lunar surface caused by large impacting bodies at some remote time in the past. These anomalies are large enough to cause a lunar orbit to change significantly over the course of several days. They can cause a plumb bob to hang about a third of a degree off vertical, pointing toward the mascon, and increase the force of gravity by one-half percent. TheApollo 11
Apollo 11 was a spaceflight conducted from July 16 to 24, 1969, by the United States and launched by NASA. It marked the first time that humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin l ...
first manned landing mission employed the first attempt to correct for the perturbation effect (the frozen orbits were not known at that time). The parking orbit was "circularized" at by , which was expected to become the nominal circular when the LM made its return rendezvous with the CSM. But the effect was overestimated by a factor of two; at rendezvous, the orbit was calculated to be by .
Stable low orbits
Study of the mascons' effect on lunar spacecraft led to the discovery in 2001 of frozen orbits occurring at four orbital inclinations: 27°, 50°, 76°, and 86°, in which a spacecraft can stay in a low orbit indefinitely. TheApollo 15
Apollo 15 (July 26August 7, 1971) was the ninth crewed mission in the Apollo program and the fourth Moon landing. It was the first List of Apollo missions#Alphabetical mission types, J mission, with a longer stay on the Moon and a greate ...
subsatellite PFS-1 and the Apollo 16
Apollo 16 (April 1627, 1972) was the tenth human spaceflight, crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, Apollo space program, administered by NASA, and the fifth and penultimate to Moon landing, land on the Moon. It was the second o ...
subsatellite PFS-2, both small satellites released from the Apollo Service Module, contributed to this discovery. PFS-1 ended up in a long-lasting orbit, at 28° inclination, and successfully completed its mission after one and a half years. PFS-2 was placed in a particularly unstable orbital inclination of 11°, and lasted only 35 days in orbit before crashing into the lunar surface.
Lunar high orbits
For lunar orbits with altitudes in the 500 to 20,000 km (300 to 12,000 mi) range, the gravity of Earth leads to orbit perturbations. At altitudes higher than that perturbed two-body astrodynamics models are insufficient and three-body models are required. Although the Moon's Hill sphere extends to a radius of , the gravity of Earth intervenes enough to make lunar orbits unstable at a distance of . The Lagrange points of the Earth-Moon system can provide stable orbits in the lunar vicinity, such as halo orbits and distant retrograde orbits. Some halo orbits remain over particular regions of the lunar surface. These can be used by lunar relay satellites to communicate with surface stations on the far side of the Moon. The first to do this was the 2019 Queqiao relay satellite. It was placed around Earth-Moon L2 at roughly from the Moon. Since 2022 ( CAPSTONE) near-rectilinear halo orbits, using as well a Lagrange point, have been used and are planned to be employed by the Lunar Gateway.Orbital transfer
There are three main ways to get to lunar orbit from Earth: direct transfer, low thrust transfer and low-energy transfer. These take 3–4 days, months or 2.5–4 months respectively.


History of missions to lunar orbit
First orbiters
 The
The Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
sent the first spacecraft to the vicinity of the Moon (or any extraterrestrial object), the robotic vehicle Luna 1
''Luna 1'', also known as ''Mechta'' ( , ''Literal translation, lit.'': ''Dream''), ''E-1 No.4'' and ''First Lunar Rover'', was the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of Earth's Moon, the first spacecraft to leave Earth's orbit, and the fi ...
, on January 4, 1959. It passed within of the Moon's surface, but did not achieve lunar orbit. Luna 3, launched on October 4, 1959, was the first robotic spacecraft to complete a circumlunar free return trajectory, still not a lunar orbit, but a figure-8 trajectory which swung around the far side of the Moon and returned to the Earth. This craft provided the first pictures of the far side of the Lunar surface.
Luna 10 became the first spacecraft to actually orbit the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
and any extraterrestrial body in April 1966. It studied micrometeoroid flux, and lunar environment until May 30, 1966. A follow-on mission, Luna 11, was launched on August 24, 1966, and studied lunar gravitational anomalies, radiation and solar wind measurements.
The first United States spacecraft to orbit the Moon was Lunar Orbiter 1 on August 14, 1966. The first orbit was an elliptical orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some or ...
, with an apolune of and a perilune
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides pert ...
of . Then the orbit was circularized at around to obtain suitable imagery. Five such spacecraft were launched over a period of thirteen months, all of which successfully mapped the Moon, primarily for the purpose of finding suitable Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
landing sites.
Crewed and later orbiters
TheApollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
's Command/Service Module (CSM) remained in a lunar parking orbit while the Lunar Module (LM) landed.
The combined CSM/LM would first enter an elliptical orbit, nominally by , which was then changed to a circular parking orbit of about . Orbital periods vary according to the sum of apoapsis and periapsis, and for the CSM were about two hours. The LM began its landing sequence with a Descent Orbit Insertion (DOI) burn to lower their periapsis to about , chosen to avoid hitting lunar mountains reaching heights of . After the second landing mission, the procedure was changed on Apollo 14
Apollo 14 (January 31February 9, 1971) was the eighth crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, the third to Moon landing, land on the Moon, and the first to land in the Geology of the Moon#Highlands, lunar highlands. It was the las ...
to save more of the LM fuel for its powered descent, by using the CSM's fuel to perform the DOI burn, and later raising its periapsis back to a circular orbit after the LM had made its landing.
See also
* Cislunar space * List of orbits *Orbital mechanics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to rockets, satellites, and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and the law of universal ...
* Distant retrograde orbit
* Near-rectilinear halo orbit
References
{{orbits Orbit of the Moon