Pelagic Fish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with
Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with
 Most epipelagic predator fish and their smaller prey fish are
Most epipelagic predator fish and their smaller prey fish are

 Oceanic fish (also called open ocean or offshore fish) live in the waters that are not above the continental shelf. Oceanic fish can be contrasted with
Oceanic fish (also called open ocean or offshore fish) live in the waters that are not above the continental shelf. Oceanic fish can be contrasted with
File:Sunfish.jpg, The huge
 In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone and support very different types of pelagic fishes adapted to living in these deeper zones.
In deep water,
In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone and support very different types of pelagic fishes adapted to living in these deeper zones.
In deep water,
 Below the epipelagic zone, conditions change rapidly. Between 200 metres and approximately 1000 metres, light continues to fade until there is almost none. Temperatures fall through a
Below the epipelagic zone, conditions change rapidly. Between 200 metres and approximately 1000 metres, light continues to fade until there is almost none. Temperatures fall through a
"Deep-sea creatures: The mesopelagic zone"
''Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Updated 21 September 2007. Most mesopelagic fish make daily vertical migrations, moving at night into the epipelagic zone, often following similar migrations of zooplankton, and returning to the depths for safety during the day. These vertical migrations often occur over a large vertical distances, and are undertaken with the assistance of a
File:Dmawsoni Head shot.jpg, The Antarctic toothfish have large, upward looking eyes, adapted to detecting the silhouettes of prey fish.
File:Opisthoproctus soleatus.png, The
The
"Fish with four eyes can see through the deep sea gloom"
''Times Online''. Times Newspapers Ltd. Retrieved 14 March 2009. Sampling via deep
File:Longnoselancetfish.jpg, Longnose lancetfish. Lancetfish are ambush predators that frequent the mesopelagic. They are among the largest mesopelagic fishes (up to 2 metres). Moyle and Cech, p. 336
File:gigantura chuni.png, The

 Below the mesopelagic zone it is pitch dark. This is the midnight or
Below the mesopelagic zone it is pitch dark. This is the midnight or
"Deep-sea creatures: The bathypelagic zone"
''Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Updated 21 September 2007. Bathypelagic fish are sedentary, adapted to outputting minimum energy in a habitat with very little food or available energy, not even sunlight, only bioluminescence. Their bodies are elongated with weak, watery muscles and
File:Eurypharynx pelecanoides.jpg, The

Carl . "Coastal fish – Fish of the open sea floor"
Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 Demersal fish are found by the

File:Pacific hagfish Myxine.jpg, Pacific hagfish resting on bottom. Hagfish coat themselves and any dead fish they find with noxious slime, making them inedible to other species.
File:Bathypterois grallator.jpg, The tripodfish (''
 At great depths, food scarcity and extreme pressure works to limit the survivability of fish. The deepest point of the ocean is about . Bathypelagic fishes are not normally found below . The greatest depth recorded for a benthic fish is . It may be that extreme pressures interfere with essential enzyme functions.
Benthic fishes are more diverse and are likely to be found on the
At great depths, food scarcity and extreme pressure works to limit the survivability of fish. The deepest point of the ocean is about . Bathypelagic fishes are not normally found below . The greatest depth recorded for a benthic fish is . It may be that extreme pressures interfere with essential enzyme functions.
Benthic fishes are more diverse and are likely to be found on the
Pelagic Freezer-trawler Association. Retrieved 22 July 2009. Around Iceland, three separate populations of herring were fished traditionally. These stocks collapsed in the late 1960s, although two have since recovered. After the collapse, Iceland turned to
File:Pacific sardine002.jpg, These
File:Yellowfin tuna nurp.jpg,


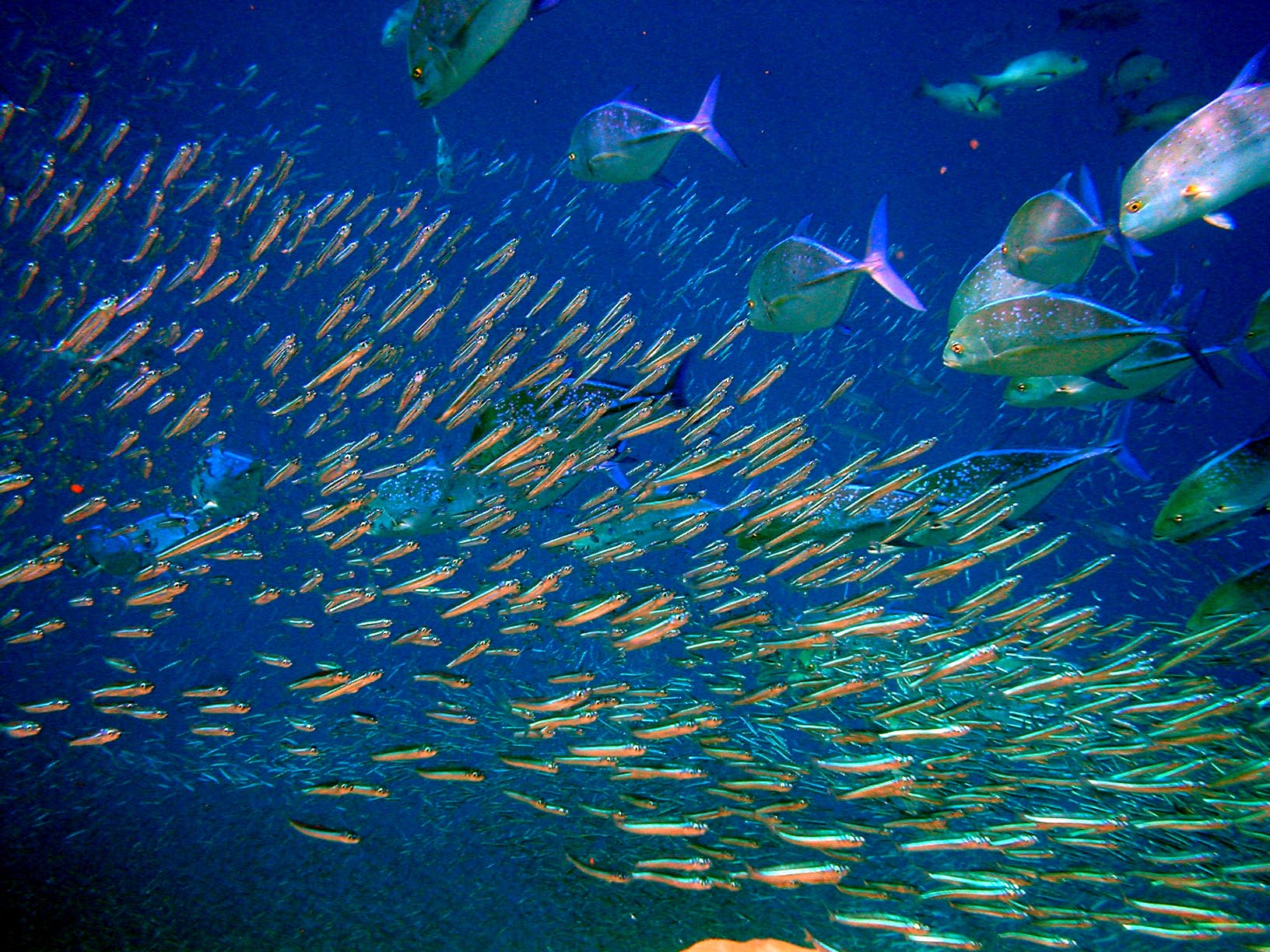
 Epipelagic fish generally move long distances between feeding and spawning areas, or as a response to changes in the ocean. Large ocean predators, such as salmon and tuna, can migrate thousands of kilometres, crossing oceans. Moyle and Cech, p. 578
In a 2001 study, the movements of
Epipelagic fish generally move long distances between feeding and spawning areas, or as a response to changes in the ocean. Large ocean predators, such as salmon and tuna, can migrate thousands of kilometres, crossing oceans. Moyle and Cech, p. 578
In a 2001 study, the movements of
Third of open ocean sharks threatened with extinction
There are 64 species of oceanic sharks and rays on the list, including hammerheads, giant devil rays, and
''
File:Sphyrnalewini.jpg, The
In parts of the world the
"Reproduction and development in epipelagic fishes"
In: Kathleen S Cole, ''Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes: Patterns and Processes'', pp. 21–64, University of California Press. . * Freon, Pierre (1998) ''Dynamics of Pelagic Fish Distribution and Behaviour: Effects on Fisheries and Stock Assessment'', Wiley-Blackwell. . * * * Pepperell J (2011
''Fishes of the Open Ocean: A Natural History and Illustrated Guide''
University of New South Wales Press, . * Salvanesa AGV and Kristoffersen J
"Mesopelagic Fishes"
In: ''Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences'', pp. 1711–1717.
''
One fish, two fish: New MIT sensor improves fish counts
''
Glowing life in an underwater world
TED video from
The Open Ocean
''MarineBio.org''. MarineBio.org. Updated 28 August 2011. TED video from
The Open Ocean
''MarineBio.org''. MarineBio.org. Updated 28 August 2011.
Pelagic Advisory Council
of the
 Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with
Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
that do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish
Coral reef fish are fish which live amongst or in close relation to coral reefs. Coral reefs form complex ecosystems with tremendous biodiversity. Among the myriad inhabitants, the fish stand out as colourful and interesting to watch. Hundreds ...
that are associated with coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s.
The marine pelagic environment is the largest aquatic habitat on Earth, occupying 1,370 million cubic kilometres (330 million cubic miles), and is the habitat for 11% of known fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
species. The ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s have a mean depth of . About 98% of the total water volume is below , and 75% is below . Moyle and Cech, p. 585
Marine pelagic fish can be divided into coastal (inshore) fish and oceanic (offshore) fish. Coastal pelagic fish inhabit the relatively shallow and sunlit waters above the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, while oceanic pelagic fish inhabit the vast and deep waters beyond the continental shelf (even though they also may swim inshore).
Pelagic fish range in size from small coastal forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food ...
, such as herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
s and sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
s, to large apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
oceanic fishes, such as bluefin tuna Bluefin tuna is a common name used to refer to several species of tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, th ...
and oceanic sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorp ...
. They are usually agile swimmers with streamlined bodies, capable of sustained cruising on long-distance migrations. Many pelagic fish swim in schools
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsor ...
weighing hundreds of tonnes. Others, such as the large ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish or common mola (''Mola mola'') is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It was misidentified as the heaviest bony fish, which was actually a different species, ''Mola alexandrini''. Adults typically weigh between . The spe ...
, are solitary . There are also freshwater pelagic fish in some of the larger lakes, such as the Lake Tanganyika sardine
The Lake Tanganyika sardine (''Limnothrissa miodon'') is a species of freshwater fish in the family Clupeidae which was endemic to Lake Tanganyika but which has now been introduced to other lakes in Africa as a food source. It is monotypic withi ...
.
Epipelagic fish
Epipelagic fish inhabit theepipelagic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
, the uppermost layer of the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
, ranging from sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
down to . It is also referred to as the ''surface waters'' or the ''sunlit zone'', and includes the photic zone. The photic zone is defined as the surface waters down to the depth where the sunlight is attenuated to 1% of the surface value. This depth depends on how turbid
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
the water is, but can extend to in clear water, coinciding with the epipelagic zone. The photic zone allows sufficient light for phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
to photosynthesize
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
.
A vast habitat for most pelagic fish, the epipelagic zone is well lit so visual predators can use their eyesight, is usually well mixed and oxygenated from wave action, and can be a good habitat for algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
to grow. However, it is an almost featureless habitat. This lack of habitat variation results in a lack of species diversity
Species diversity is the number of different species that are represented in a given community (a dataset). The effective number of species refers to the number of equally abundant species needed to obtain the same mean proportional species abundan ...
, so the zone supports less than 2% of the world's known fish species. Much of the zone lacks nutrients for supporting fish, so epipelagic fish tend to be found in coastal water above the continental shelves, where land runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the ...
can provide nutrients, or in those parts of the ocean where upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
moves nutrients into the area. Moyle and Cech, p. 571
Epipelagic fish can be divided broadly into small forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food ...
and larger predator fish
Predatory fish are hypercarnivorous fish that actively prey upon other fish or aquatic animals, with examples including shark, billfish, barracuda, pike/muskellunge, walleye, perch and salmon. Some omnivorous fish, such as the red-bellied piranh ...
that feed on them. Forage fish school
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compuls ...
and filter feed
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
on plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
. Most epipelagic fish have streamlined bodies capable of sustained cruising on migrations. In general, predatory and forage fish share the same morphological features. Predator fish are usually fusiform
Fusiform means having a spindle-like shape that is wide in the middle and tapers at both ends. It is similar to the lemon-shape, but often implies a focal broadening of a structure that continues from one or both ends, such as an aneurysm on a b ...
with large mouths, smooth bodies, and deeply forked tails. Many use vision to prey on zooplankton or smaller fish, while others filter feed on plankton.
countershaded
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, a ...
with silvery colours that reduce visibility by scattering incoming light. The silvering is achieved with reflective fish scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as ...
s that function as small mirrors. This may give an effect of transparency. At medium depths at sea, light comes from above, so a mirror that is oriented vertically makes animals such as fish invisible from the side.
In the shallower epipelagic waters, the mirrors must reflect a mixture of wavelengths, and the fish accordingly, has crystal stacks with a range of different spacings. A further complication for fish with bodies that are rounded in cross-section is that the mirrors would be ineffective if laid flat on the skin, as they would fail to reflect horizontally. The overall mirror effect is achieved with many small reflectors, all oriented vertically.
Although the number of species is limited, epipelagic fishes are abundant. What they lack in diversity they make up for in numbers. Forage fish occur in huge numbers, and large fish that prey on them often are sought after as premier food fish
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ing ...
. As a group, epipelagic fishes form the most valuable fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
in the world.
Many forage fish are facultative predators that can pick individual copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s or fish larvae out of the water column, and then change to filter feeding on phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
when energetically, that gives better results. Filter feeding fish usually use long fine gill raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the ...
s to strain small organisms from the water column. Some of the largest epipelagic fishes, such as the basking shark
The basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') is the second-largest living shark and fish, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach in leng ...
and whale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of .McClain CR, Balk MA, Benfield MC, Branch TA, Chen C, Cosgrove J, D ...
, are filter feeders, and so are some of the smallest, such as adult sprat
Sprat is the common name applied to a group of forage fish belonging to the genus '' Sprattus'' in the family Clupeidae. The term also is applied to a number of other small sprat-like forage fish ('' Clupeoides'', '' Clupeonella'', '' Corica'' ...
s and anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
. Moyle and Cech, p. 572
Ocean waters that are exceptionally clear contain little food. Areas of high productivity tend to be somewhat turbid from plankton blooms. These attract the filter feeding plankton eaters, which in turn attract the higher predators. Tuna fishing tends to be optimum when water turbidity, measured by the maximum depth a secchi disc
The Secchi disk (or Secchi disc), as created in 1865 by Angelo Secchi, is a plain white, circular disk in diameter used to measure water transparency or turbidity in bodies of water. The disc is mounted on a pole or line, and lowered slowly down ...
can be seen during a sunny day, is 15 to 35 metres.
Floating objects
Epipelagic fish are fascinated by floating objects. They aggregate in considerable numbers around objects such as drifting flotsam, rafts, jellyfish, and floating seaweed. The objects appear to provide a "visual stimulus in an optical void". Floating objects may offer refuge forjuvenile fish
Fish go through various life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawned eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable of feeding themselves and carry a yolk sac which ...
from predators. An abundance of drifting seaweed or jellyfish can result in significant increases in the survival rates of some juvenile species.
Many coastal juveniles use seaweed for the shelter and the food that is available from invertebrates and other fish associated with it. Drifting seaweed, particularly the pelagic ''Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae ( seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral ...
'', provide a niche habitat with its own shelter and food, and even supports its own unique fauna, such as the sargassum fish
The sargassum fish, anglerfish, or frog fish (''Histrio histrio'') is a frogfish of the family (biology), family Antennariidae, Monotypic taxon, the only species in its genus. It lives among ''Sargassum'' seaweed which floats in subtropical ocea ...
. One study, off Florida, found 54 species from 23 families living in flotsam from ''Sargassum'' mats. Jellyfish also are used by juvenile fish for shelter and food, even though jellyfish can prey on small fish. Moyle and Cech, p. 576
Mobile oceanic species such as tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
can be captured by travelling long distances in large fishing vessel
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was ...
s. A simpler alternative is to leverage off the fascination fish have with floating objects. When fishermen use such objects, they are called fish aggregating device
A fish aggregating (or aggregation) device (FAD) is a man-made object used to attract ocean-going pelagic fish such as marlin, tuna and mahi-mahi (dolphin fish). They usually consist of buoys or floats tethered to the ocean floor with concrete bloc ...
s (FADs). FADs are anchored rafts or objects of any type, floating on the surface or just below it. Fishermen in the Pacific and Indian oceans set up floating FADs, assembled from all sorts of debris, around tropical islands, and then use purse seine
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be dep ...
s to capture the fish attracted to them.
A study using sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect o ...
in French Polynesia, found large shoals of juvenile bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus '' Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are ...
and yellowfin tuna
The yellowfin tuna (''Thunnus albacares'') is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.
Yellowfin is often marketed as ahi, from the Hawaiian , a name also used there for the closely related bigeye ...
aggregated closest to the devices, 10 to 50 m. Farther out, 50 to 150 m, was a less dense group of larger yellowfin and albacore tuna
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct sto ...
. Yet farther out, to 500 m, was a dispersed group of various large adult tuna. The distribution and density of these groups was variable and overlapped. The FADs also were used by other fish, and the aggregations dispersed when it was dark.
Larger fish, even predator fish such as the great barracuda
''Sphyraena barracuda'', commonly known as the great barracuda, is a species of barracuda: large, predatory ray-finned fish found in subtropical oceans around the world.
Distribution and habitat
The great barracuda is present in tropical to warm ...
, often attract a retinue of small fish that accompany them in a strategically safe way. Skindivers who remain for long periods in the water also often attract a retinue of fish, with smaller fishes coming in close and larger fishes observing from a greater distance. Marine turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead ...
s, functioning as a mobile shelter for small fish, can be impaled accidentally by a swordfish trying to catch the fish.
Coastal fish

Coastal fish
Coastal fish, also called inshore fish or neritic fish, inhabit the sea between the shoreline and the edge of the continental shelf. Since the continental shelf is usually less than deep, it follows that pelagic coastal fish are generally epi ...
(also called neritic
The neritic zone (or sublittoral zone) is the relatively shallow part of the ocean above the drop-off of the continental shelf, approximately in depth.
From the point of view of marine biology it forms a relatively stable and well-illuminate ...
or inshore fish) inhabit the waters near the coast
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
and above the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
. Since the continental shelf is usually less than 200 metres deep, it follows that coastal fish that are not demersal fish, are usually epipelagic fish, inhabiting the sunlit epipelagic zone.
Coastal epipelagic fish are among the most abundant in the world. They include forage fish as well as the predator fish that feed on them. Forage fish thrive in those inshore waters where high productivity results from the upwelling and shoreline run off of nutrients. Some are partial residents that spawn in streams, estuaries, and bays, but most complete their life cycle in the zone.
Oceanic fish
coastal fish
Coastal fish, also called inshore fish or neritic fish, inhabit the sea between the shoreline and the edge of the continental shelf. Since the continental shelf is usually less than deep, it follows that pelagic coastal fish are generally epi ...
, who do live above the continental shelf. However, the two types are not mutually exclusive, since there are no firm boundaries between coastal and ocean regions, and many epipelagic fish move between coastal and oceanic waters, particularly in different stages in their life cycle.
Oceanic epipelagic fish can be true residents, partial residents, or accidental residents. True residents live their entire life in the open ocean. Only a few species are true residents, such as tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
, billfish
The term billfish refers to a group of saltwater predatory fish characterised by prominent pointed bills (rostra), and by their large size; some are longer than . Extant billfish include sailfish and marlin, which make up the family Istioph ...
, flying fish
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine fish in the order Beloniformes class Actinopterygii, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven to nine genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird d ...
, sauries
Sauries are fish of the family Scomberesocidae. There are two genera, each containing two species. The name Scomberesocidae is derived from the ''scomber'', which in turn is derived from the Greek ''skombros'', meaning "mackerel", and the Latin ...
, pilotfish, remora
The remora (), sometimes called suckerfish, is any of a family (Echeneidae) of ray-finned fish in the order Carangiformes. Depending on species, they grow to long. Their distinctive first dorsal fins take the form of a modified oval, sucker-li ...
s, dolphinfish
''Coryphaena'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes known as the dolphinfishes, and is currently the only known genus in the family Coryphaenidae. The generic name is from Greek κορυφή (''koryphē'', "crown, top") and -αινα (-''aina' ...
, ocean sharks, and ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish or common mola (''Mola mola'') is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It was misidentified as the heaviest bony fish, which was actually a different species, ''Mola alexandrini''. Adults typically weigh between . The spe ...
. Most of these species migrate back and forth across open oceans, rarely venturing over continental shelves. Some true residents associate with drifting jellyfish or seaweeds.
Partial residents occur in three groups: species that live in the zone only when they are juveniles (drifting with jellyfish and seaweeds); species that live in the zone only when they are adults (salmon, flying fish, dolphin, and whale sharks); and deep water species that make nightly migrations up into the surface waters (such as the lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represent ...
). Accidental residents occur occasionally when adults and juveniles of species from other environments are carried accidentally into the zone by currents.
ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish or common mola (''Mola mola'') is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It was misidentified as the heaviest bony fish, which was actually a different species, ''Mola alexandrini''. Adults typically weigh between . The spe ...
, a true resident of the ocean epipelagic zone, sometimes drifts with the current, eating jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
.
File:Whale shark Georgia aquarium.jpg, The giant whale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of .McClain CR, Balk MA, Benfield MC, Branch TA, Chen C, Cosgrove J, D ...
, another resident of the ocean epipelagic zone, filter feeds on plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
, and periodically dives deep into the mesopelagic zone.
File:Protomyctophum subparallelum (no common name).gif, Lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represent ...
are partial residents of the ocean epipelagic zone During the day they hide in deep waters, but at night they migrate up to surface waters to feed.
Deep water fish
 In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone and support very different types of pelagic fishes adapted to living in these deeper zones.
In deep water,
In the deep ocean, the waters extend far below the epipelagic zone and support very different types of pelagic fishes adapted to living in these deeper zones.
In deep water, marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus
In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as distinguished from dissolved organic material. Detritus typically includes the bodies or fragments of bodies of dead organisms, and fecal material. Detritus typically hosts commun ...
falling from the upper layers of the water column. Its origin lies in activities within the productive photic zone. Marine snow includes dead or dying plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
, protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s (diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s), fecal matter, sand, soot, and other inorganic dust. The "snowflakes" grow over time and may reach several centimetres in diameter, travelling for weeks before reaching the ocean floor. However, most organic components of marine snow are consumed by microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s, zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
, and other filter feeding animals within the first 1,000 metres of their journey, that is, within the epipelagic zone. In this way marine snow can be considered the foundation of deep-sea mesopelagic
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins ...
and benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s: As sunlight cannot reach them, deep-sea organisms rely heavily on marine snow as an energy source.
Some deep-sea pelagic groups, such as the lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represent ...
, ridgehead
Ridgeheads, also known as bigscales, are a family (Melamphaidae, from the Greek ''melanos'' lackand ''amphi'' y both sides of small, deep-sea stephanoberyciform fish. The family contains approximately 37 species in five genera; their distribut ...
, marine hatchetfish
Marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes are small deep-sea mesopelagic ray-finned fish of the stomiiform subfamily Sternoptychinae. They should not be confused with the freshwater hatchetfishes, which are not particularly closely related T ...
, and lightfish families are sometimes termed ''pseudoceanic'' because, rather than having an even distribution in open water, they occur in significantly higher abundances around structural oases, notably seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s, and over continental slope
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
s. The phenomenon is explained by the likewise abundance of prey species that also are attracted to the structures.
The fish in the different pelagic and deep water benthic zones are physically structured, and behave, in ways that differ markedly from each other. Groups of coexisting species within each zone all seem to operate in similar ways, such as the small mesopelagic vertically migrating plankton-feeders, the bathypelagic anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence ...
es, and the deep water benthic rattail
Grenadiers or rattails are generally large, brown to black gadiform marine fish of the subfamily Macrourinae, the largest subfamily of the family Macrouridae. Found at great depths from the Arctic to Antarctic, members of this subfamily are am ...
s. Moyle and Cech, p. 591
Ray finned species, with spiny fins, are rare among deep sea fishes, which suggests that deep sea fish are ancient and so well adapted to their environment that invasions by more modern fishes have been unsuccessful. The few ray fins that do exist are mainly in the Beryciformes
The Beryciformes are a poorly-understood order of carnivorous ray-finned fishes consisting of 7 families, 30 genera, and 161 species. They feed on small fish and invertebrates. Beyond this, little is known about the biology of most member specie ...
and Lampriformes
Lampriformes is an order of ray-finned fish. Members are collectively called lamprids (which is more properly used for the Lampridae) or lampriforms, and unite such open-ocean and partially deep-sea Teleostei as the crestfishes, oarfish, opah ...
, which also are ancient forms. Most deep sea pelagic fishes belong to their own orders, suggesting a long evolution in deep sea environments. In contrast, deep water benthic species are in orders that include many related shallow water fishes. Moyle and Cech, p. 586
Many species move daily between zones in vertical migrations. In the following table, they are listed in the middle or deeper zone where they regularly are found.
Mesopelagic fish
 Below the epipelagic zone, conditions change rapidly. Between 200 metres and approximately 1000 metres, light continues to fade until there is almost none. Temperatures fall through a
Below the epipelagic zone, conditions change rapidly. Between 200 metres and approximately 1000 metres, light continues to fade until there is almost none. Temperatures fall through a thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
to temperatures between and . This is the twilight or mesopelagic
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins ...
zone. Pressure continues to increase, at the rate of one atmosphere every 10 metres, while nutrient concentrations fall, along with dissolved oxygen and the rate at which the water circulates.
Sonar operators, using the sonar technology developed during World War II, were puzzled by what appeared to be a false sea floor 300–500 metres deep at day, and less deep at night. This turned out to be due to millions of marine organisms, most particularly small mesopelagic fish, with swimbladders that reflected the sonar. These organisms migrate up into shallower water at dusk to feed on plankton. The layer is deeper when the moon is out, and may become shallower when clouds pass over the moon. This phenomenon has come to be known as the deep scattering layer
The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and w ...
.Ryan "Deep-sea creatures: The mesopelagic zone"
''Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Updated 21 September 2007. Most mesopelagic fish make daily vertical migrations, moving at night into the epipelagic zone, often following similar migrations of zooplankton, and returning to the depths for safety during the day. These vertical migrations often occur over a large vertical distances, and are undertaken with the assistance of a
swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
. The swimbladder is inflated when the fish wants to move up, and, given the high pressures in the mesopelagic zone, this requires significant energy. As the fish ascends, the pressure in the swimbladder must adjust to prevent it from bursting. When the fish wants to return to the depths, the swimbladder is deflated. Some mesopelagic fishes make daily migrations through the thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
, where the temperature changes between 10 and 20 °C, thus displaying considerable tolerances for temperature change. Moyle and Cech, p. 590
These fish have muscular bodies, ossified bones, scales, well developed gills and central nervous systems, and large hearts and kidneys. Mesopelagic plankton feeders have small mouths with fine gill raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the ...
s, while the piscivore
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
s have larger mouths and coarser gill rakers. The vertically migratory fish have swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
s.
Mesopelagic fish are adapted for an active life under low light conditions. Most of them are visual predators with large eyes. Some of the deeper water fish have tubular eyes with big lenses and only rod cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in per ...
s that look upward. These give binocular vision and great sensitivity to small light signals. This adaptation gives improved terminal vision at the expense of lateral vision, and allows the predator to pick out squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting t ...
, cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of ...
, and smaller fish that are silhouetted against the gloom above them.
Mesopelagic fish usually lack defensive spines, and use colour to camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the ...
them from other fish. Ambush predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey ...
s are dark, black or red. Since the longer, red, wavelengths of light do not reach the deep sea, red effectively functions the same as black. Migratory forms use countershaded
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, a ...
silvery colours. On their bellies, they often display photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
s producing low grade light. For a predator from below, looking upward, this bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
camouflages the silhouette of the fish. However, some of these predators have yellow lenses that filter the (red deficient) ambient light, leaving the bioluminescence visible.
Barreleye
Barreleyes, also known as spook fish (a name also applied to several species of chimaera), are small deep-sea argentiniform fish comprising the family Opisthoproctidae found in tropical-to-temperate waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and I ...
has barrel-shaped, tubular eyes that generally are directed upward, but may be swivelled forward.
Image:Malacosteus niger.jpg, The stoplight loosejaw has a lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
one-quarter as long as its body. The jaw has no floor and is attached only by a hinge and a modified tongue bone. Large fang-like teeth in the front are followed by many small barbed teeth.
Image:Malacosteus.JPG, The stoplight loosejaw is also one of the few fishes that produce red bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
. As most of their prey cannot perceive red light, this allows it to hunt with an essentially invisible beam of light.
brownsnout spookfish
The brownsnout spookfish or brown-snout spookfish (''Dolichopteryx longipes'') is a species of barreleye in the family Opisthoproctidae. It and the glasshead barreleye fish are the only vertebrates known to employ a mirror, in addition to a lens ...
is a species of barreleye
Barreleyes, also known as spook fish (a name also applied to several species of chimaera), are small deep-sea argentiniform fish comprising the family Opisthoproctidae found in tropical-to-temperate waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and I ...
and is the only vertebrate known to employ a mirror, as opposed to a lens, to focus an image in its eyes.Smith, L. (8 January 2009)"Fish with four eyes can see through the deep sea gloom"
''Times Online''. Times Newspapers Ltd. Retrieved 14 March 2009. Sampling via deep
trawling
Trawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different spec ...
indicates that lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represent ...
account for as much as 65% of all deep sea fish biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
. Indeed, lanternfish are among the most widely distributed, populous, and diverse of all vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
s, playing an important ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
role as prey for larger organisms. The estimated global biomass of lanternfish is 550–660 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s, several times the entire world fisheries catch. Lanternfish also account for much of the biomass responsible for the deep scattering layer
The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and w ...
of the world's oceans. Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect o ...
reflects off the millions of lanternfish swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled Organ (anatomy), organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their curren ...
s, giving the appearance of a false bottom.
Bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus '' Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are ...
are an epipelagic/mesopelagic species that is carnivorous, eating other fish. Satellite tagging has shown that bigeye tuna often spend prolonged periods cruising deep below the surface during the daytime, sometimes making dives as deep as . These movements are thought to be in response to the vertical migrations of prey organisms in the deep scattering layer
The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and w ...
.
telescopefish
Telescopefish are small, deep-sea aulopiform fish comprising the small family Giganturidae. The two known species are within the genus ''Gigantura''. Though rarely captured, they are found in cold, deep tropical to subtropical waters worldwide ...
has large, forward-pointing telescoping eyes with large lenses.
File:Daggertooth.PNG, The daggertooth
The daggertooths (genus ''Anotopterus'') are a genus of marine mesopelagic fish in the order Aulopiformes, the sole genus of the family Anotopteridae. They are found in oceans worldwide, but prefer cooler waters.
Description
Daggertooths are not ...
slashes other mesopelagic fish when it bites them with its dagger-like teeth.
File:Thobe u0.gif, Bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus '' Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are ...
cruise the epipelagic zone at night and the mesopelagic zone during the day.
File:Lestidiops affinis (1).jpg, A collection of mesopelagic forage fishes trawled from the Gulf of Mexico that includes Myctophids
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represente ...
, larval anglerfishes, bristlemouth
The Gonostomatidae are a family of mesopelagic marine fish, commonly named bristlemouths, lightfishes, or anglemouths. It is a relatively small family, containing only eight known genera and 32 species. However, bristlemouths make up for their ...
s, and a barracudina
Barracudinas are any member of the marine mesopelagic fish family Paralepididae: 50 or so extant species are found almost worldwide in deep waters. Several genera are known only from fossils dating back to the Ypresian epoch.
The generic name ...
Bathypelagic fish

 Below the mesopelagic zone it is pitch dark. This is the midnight or
Below the mesopelagic zone it is pitch dark. This is the midnight or bathypelagic zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagi ...
, extending from 1000 m to the bottom deep water benthic zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning " ...
. If the water is exceptionally deep, the pelagic zone below sometimes is called the lower midnight or abyssopelagic zone.
Conditions are somewhat uniform throughout these zones, the darkness is complete, the pressure is crushing, and temperatures, nutrients, and dissolved oxygen levels are all low.
Bathypelagic fish have special adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
s to cope with these conditions – they have slow metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
s and unspecialized diets, being willing to eat anything that comes along. They prefer to sit and wait for food rather than waste energy searching for it. The behaviour of bathypelagic fish can be contrasted with the behaviour of mesopelagic fish. Mesopelagic are often highly mobile, whereas bathypelagic fish are almost all lie-in-wait predators, normally expending little energy in movement. Moyle and Cech, p. 594
The dominant bathypelagic fishes are small bristlemouth
The Gonostomatidae are a family of mesopelagic marine fish, commonly named bristlemouths, lightfishes, or anglemouths. It is a relatively small family, containing only eight known genera and 32 species. However, bristlemouths make up for their ...
and anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence ...
; fangtooth
Fangtooths are beryciform fish of the family Anoplogastridae (sometimes spelled "Anoplogasteridae") that live in the deep sea. The name is from the Greek , meaning "unarmed", and (), meaning "stomach". With a circumglobal distribution in tropica ...
, viperfish
A viperfish is any species of marine fish in the genus ''Chauliodus''. Viperfishes are mostly found in the mesopelagic zone and are characterized by long, needle-like teeth and hinged lower jaws. A typical viperfish grows to lengths of . Viperf ...
, daggertooth
The daggertooths (genus ''Anotopterus'') are a genus of marine mesopelagic fish in the order Aulopiformes, the sole genus of the family Anotopteridae. They are found in oceans worldwide, but prefer cooler waters.
Description
Daggertooths are not ...
, and barracudina
Barracudinas are any member of the marine mesopelagic fish family Paralepididae: 50 or so extant species are found almost worldwide in deep waters. Several genera are known only from fossils dating back to the Ypresian epoch.
The generic name ...
are also common. These fishes are small, many about long, and not many longer than . They spend most of their time waiting patiently in the water column for prey to appear or to be lured by their phosphors. What little energy is available in the bathypelagic zone filters from above in the form of detritus, faecal material, and the occasional invertebrate or mesopelagic fish. About 20% of the food that has its origins in the epipelagic zone falls down to the mesopelagic zone, but only about 5% filters down to the bathypelagic zone.Ryan "Deep-sea creatures: The bathypelagic zone"
''Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. Updated 21 September 2007. Bathypelagic fish are sedentary, adapted to outputting minimum energy in a habitat with very little food or available energy, not even sunlight, only bioluminescence. Their bodies are elongated with weak, watery muscles and
skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
structures. Since so much of the fish is water, they are not compressed by the great pressures at these depths. They often have extensible, hinged jaws
Jaws or Jaw may refer to:
Anatomy
* Jaw, an opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth
** Mandible, the lower jaw
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Jaws (James Bond), a character in ''The Spy Who Loved Me'' and ''Moonraker''
* ...
with recurved teeth. They are slimy, without scales. The central nervous system is confined to the lateral line and olfactory systems, the eyes are small and may not function, and gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s, kidneys and hearts, and swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
s are small or missing. Moyle and Cech, p. 587
These are the same features found in fish larvae
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
, which suggests that during their evolution, bathypelagic fish have acquired these features through neoteny
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compa ...
. As with larvae, these features allow the fish to remain suspended in the water with little expenditure of energy.
Despite their ferocious appearance, these beasts of the deep are mostly miniature fish with weak muscles, and are too small to represent any threat to humans.
The swimbladders of deep sea fish are either absent or scarcely operational, and bathypelagic fish do not normally undertake vertical migrations. Filling bladders at such great pressures incurs huge energy costs. Some deep sea fishes have swimbladders that function while they are young and inhabit the upper epipelagic zone, but they wither or fill with fat when the fish move down to their adult habitat.
The most important sensory systems are usually the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
, which responds to sound, and the lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
, which responds to changes in water pressure. The olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
system also can be important for males who find females by smell.
Bathypelagic fish are black, or sometimes red, with few photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
s. When photophores are used, it is usually to entice prey or attract a mate. Because food is so scarce, bathypelagic predators are not selective in their feeding habits, but grab whatever comes close enough. They accomplish this by having a large mouth with sharp teeth for grabbing large prey and overlapping gill raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the ...
s that prevent small prey that have been swallowed from escaping.
It is not easy finding a mate in this zone. Some species depend on bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
. Others are hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrate ...
s, which doubles their chances of producing both eggs and sperm when an encounter occurs. The female anglerfish releases pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s to attract tiny males. When a male finds her, he bites onto her and never lets go. When a male of the anglerfish species ''Haplophryne mollis
''Haplophryne mollis'', the ghostly seadevil or soft leftvent angler, is a species of anglerfish in the Family (biology), family Leftvent, Linophrynidae and is Monotypic taxon, the only species in the genus ''Haplophryne''. It is found in the B ...
'' bites into the skin of a female, he release an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
that digests the skin of his mouth and her body, fusing the pair to the point where the two circulatory systems join up. The male then atrophies into nothing more than a pair of gonads
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
. This extreme sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
ensures that, when the female is ready to spawn, she has a mate immediately available.
Many animal forms other than fish live in the bathypelagic zone, such as squid, large whales, octopuses, sponges, brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, w ...
s, sea stars, and echinoid
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
s, but this zone is difficult for fish to live in.
gulper eel
The saccopharyngiformes are a derived lineage of unusual eels within the order Anguilliformes, and includes families Cyematidae, Monognathidae, Eurypharyngidae, Saccopharyngidae, and the proposed family Neocyematidae. Most of the fish in this gro ...
uses its mouth like a net by opening its large mouth and swimming at its prey. It has a luminescent organ at the tip of its tail to attract prey.
Image:Chiasmodon niger.jpg, The black swallower, with its distensible stomach, is notable for its ability to swallow, whole, bony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilag ...
es ten times its mass.
Image:Hamol u0.gif, Female ''Haplophryne mollis
''Haplophryne mollis'', the ghostly seadevil or soft leftvent angler, is a species of anglerfish in the Family (biology), family Leftvent, Linophrynidae and is Monotypic taxon, the only species in the genus ''Haplophryne''. It is found in the B ...
'' anglerfish trailing attached males that have atrophied into a pair of gonads
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
, for use when the female is ready to spawn.
File:Anoplogaster cornuta 2.jpg, The widespread fangtooth
Fangtooths are beryciform fish of the family Anoplogastridae (sometimes spelled "Anoplogasteridae") that live in the deep sea. The name is from the Greek , meaning "unarmed", and (), meaning "stomach". With a circumglobal distribution in tropica ...
has the largest teeth of any fish, proportionate to body size. Despite their ferocious appearance, bathypelagic fish are usually weakly muscled and too small to represent any threat to humans.
File:Messina Straits Chauliodus sloani.jpg, The Sloane's viperfish can make nightly migrations from bathypelagic depths to near surface waters.
Demersal fish

Demersal fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
live on or near the bottom of the sea.Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish – Fish of the open sea floor"
Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 Demersal fish are found by the
seafloor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth an ...
in coastal areas on the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, and in the open ocean they are found along the outer continental margin
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
on the continental slope and the continental rise. They are not generally found at abyssopelagic
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. "Abyss" derives from the Greek word , meaning bottomless. At depths of , this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean ...
or hadopelagic
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions.
The cumula ...
depths or on the abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. ...
. They occupy a range of seafloors consisting of mud, sand, gravel, or rocks.
In deep waters, the fishes of the demersal zone are active and relatively abundant, compared to fishes of the bathypelagic zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagi ...
.
Rattail
Grenadiers or rattails are generally large, brown to black gadiform marine fish of the subfamily Macrourinae, the largest subfamily of the family Macrouridae. Found at great depths from the Arctic to Antarctic, members of this subfamily are am ...
s and brotulas are common, and other well-established families are eel
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
s, eelpout
The eelpouts are the ray-finned fish family Zoarcidae. As the common name suggests, they are somewhat eel-like in appearance. All of the roughly 300 species are marine and mostly bottom-dwelling, some at great depths. Eelpouts are predominantly ...
s, hagfish
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, a ...
es, greeneyes, batfishes, and lumpfishes.
The bodies of deep water benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
fishes are muscular with well developed organs. In this way they are closer to mesopelagic fishes than bathopelagic fishes. In other ways, they are more variable. Photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
s are usually absent, eyes and swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
s range from absent to well developed. They vary in size, with larger species greater than one metre not uncommon.
Deep sea benthic fish are usually long and narrow. Many are eels or shaped like eels. This may be because long bodies have long lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
s. Lateral lines detect low-frequency sounds, and some benthic fishes appear to have muscles that drum such sounds to attract mates. Smell is also important, as indicated by the rapidity with which benthic fish find traps baited with bait fish
300px, Feeder Goldfish are common baitfish.
Bait fish (or baitfish) are small-sized fish caught and used by anglers as bait to attract larger predatory fish, particularly game fish. Baitfish species are typically those that are common and bree ...
.
The main diet of deep sea benthic fish is invertebrates of the deep sea benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
. Smell, touch, and lateral line sensitivities seem to be the main sensory devices for locating these. Moyle and Cech, p. 588
Deep sea benthic fish can be divided into strictly benthic fish and benthopelagic fish. Usually, strictly benthic fish are negatively buoyant, while benthopelagic fish are neutrally buoyant. Strictly benthic fish stay in constant contact with the bottom. They either lie-and-wait as ambush predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey ...
s or move actively over the bottom in search for food.


Benthopelagic fish
Benthopelagic fish inhabit the water just above the bottom, feeding onbenthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
. Most dermersal fish are benthopelagic.
They can be divided into flabby or robust body types. Flabby benthopelagic fishes are like bathopelagic fishes, they have a reduced body mass, and low metabolic rates, expending minimal energy as they lie and wait to ambush
An ambush is a long-established military tactics, military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbru ...
prey. An example of a flabby fish is the cusk-eel '' Acanthonus armatus'', a predator with a huge head and a body that is 90% water. This fish has the largest ears (otolith
An otolith ( grc-gre, ὠτο-, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called statoconium or otoconium or statolith, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The sa ...
s) and the smallest brain in relation to its body size of all known vertebrates.
Robust benthopelagic fish are muscular swimmers that actively cruise the bottom searching for prey. They may live around features, such as seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s, which have strong currents. Examples are the orange roughy
The orange roughy (''Hoplostethus atlanticus''), also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categori ...
and Patagonian toothfish
The Patagonian toothfish (''Dissostichus eleginoides'') is a species of notothen found in cold waters () between depths of in the southern Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans and Southern Ocean on seamounts and continental shelves around most ...
. Because these fish were once abundant, and because their robust bodies are good to eat, these fish have been harvested commercially.
Benthic fish
Benthic fish are not pelagic fish, but they are discussed here briefly, by way of completeness and contrast. Some fishes do not fit into the above classification. For example, the family of nearly blind spiderfishes, common and widely distributed, feed on benthopelagic zooplankton. Yet they are strictly benthic fish, since they stay in contact with the bottom. Their fins have long rays they use to "stand" on the bottom while they face the current and grab zooplankton as it passes by. The deepest-living fish known, the strictly benthic ''Abyssobrotula galatheae
''Abyssobrotula galatheae'' is a species of cusk eel in the family Ophidiidae. It is the deepest-living fish known; one specimen, trawled from a depth of in the Puerto Rico Trench in 1970, holds the record for the deepest fish ever captured. Alt ...
'', eel-like and blind, feeds on benthic invertebrates.
Bathypterois grallator
The tripodfish or tripod spiderfish, ''Bathypterois grallator'', is a deep-sea benthic fish in the family Ipnopidae found at lower latitudes. It is now relatively well known from photographs and submersible observations, and seems to prefer to p ...
''), a species of spiderfish, uses its fin extensions to "stand" on the bottom.
File:Taeniura meyeni reef.jpg, The blotched fantail ray feeds on bottom-dwelling fish, bivalves, crabs, and shrimps.
continental slope
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
, where there is habitat diversity and often, food supplies. Approximately 40% of the ocean floor consists of abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. ...
s, but these flat, featureless regions are covered with sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
and largely devoid of benthic life (benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s) can intercept deep sea currents and cause productive upwellings that support benthic fish. Undersea mountain ranges may separate underwater regions into different ecosystems.
Pelagic fisheries
Forage fish
Small pelagic fish are usuallyforage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food ...
that are hunted by larger pelagic fish and other predators. Forage fish filter feed
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
on plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
and are usually less than long. They often stay together in schools
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsor ...
and may migrate large distances between spawning grounds and feeding grounds. They are found particularly in upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
regions around the northeast Atlantic, off the coast of Japan, and off the west coasts of Africa and the Americas. Forage fish are generally short-lived, and their stocks fluctuate markedly over the years.Checkley D, Alheit J and Oozeki Y (2009) ''Climate Change and Small Pelagic Fish'', Cambridge University Press. .
Herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
are found in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
and the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
at depths to . Important herring fisheries have existed in these areas for centuries. Herring of different sizes and growth rates belong to different populations, each of which have their own migration routes. When spawning, a female produces from 20,000 to 50,000 eggs. After spawning, the herrings are depleted of fat, and migrate back to feeding grounds rich in plankton.Pelagic speciesPelagic Freezer-trawler Association. Retrieved 22 July 2009. Around Iceland, three separate populations of herring were fished traditionally. These stocks collapsed in the late 1960s, although two have since recovered. After the collapse, Iceland turned to
capelin
The capelin or caplin (''Mallotus villosus'') is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin ...
, which now account for about half of Iceland's total catch.
Blue whiting
The blue whiting (''Micromesistius poutassou'') one of the two species in the genus '' Micromesistius'' in the family Gadidae, which also contains cod, haddock, whiting, and pollock. It is common in the northeast Atlantic Ocean from Morocco to ...
are found in the open ocean and above the continental slope
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
at depths between 100 and 1000 meters . They follow vertical migrations of the zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
they feed on to the bottom during daytime and to the surface at night time.
Traditional fisheries for anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
and sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
s also have operated in the Pacific, the Mediterranean, and the southeast Atlantic. Bone and Moore, p. 443 The world annual catch of forage fish in recent years has been approximately 22 million tonnes, or one quarter of the world's total catch.
schooling
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compuls ...
Pacific sardines are forage fish
Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food ...
.
File:Herringramkils.jpg, Herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
s ram feeding
Aquatic feeding mechanisms face a special difficulty as compared to feeding on land, because the density of water is about the same as that of the prey, so the prey tends to be pushed away when the mouth is closed. This problem was first identifi ...
on copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s
File:Mallotus villosus.gif, Capelin
The capelin or caplin (''Mallotus villosus'') is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin ...
File:Anchovy closeup.jpg, Anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
File:Enrin u0.png, Peruvian anchoveta
Predator fish
Medium size pelagic fishes includetrevally
The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish which includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only famil ...
, barracuda
A barracuda, or cuda for short, is a large, predatory, ray-finned fish known for its fearsome appearance and ferocious behaviour. The barracuda is a saltwater fish of the genus ''Sphyraena'', the only genus in the family Sphyraenidae, which was ...
, flying fish
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine fish in the order Beloniformes class Actinopterygii, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven to nine genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird d ...
, bonito, mahi mahi, and coastal mackerel. Many of these fish hunt forage fish, but are in turn, hunted by yet larger pelagic fish. Nearly all fish are predator fish to some measure, and apart from the top predators, the distinction between predator fish and prey or forage fish, is somewhat artificial.
Around Europe there are three populations of coastal mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
. One population migrates to the North Sea, another stays in the waters of the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, and the third population migrates southward along the west coast of Scotland and Ireland. The cruise speed of the mackerel is an impressive 10 kilometres per hour.MackerelInstitute of Marine Research
The Norwegian Institute of Marine Research ( no, Havforskningsinstituttet) is a national consultative research institute which is owned by the Ministry of Fisheries and Coastal Affairs. The institute performs research and provides advisory services ...
. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
Many large pelagic fish are oceanic nomadic species that undertake long offshore migrations. They feed on small pelagic forage fish, as well as medium-sized pelagic fish. At times, they follow their schooling prey, and many species form schools themselves.
Examples of larger pelagic fish are tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
, billfish
The term billfish refers to a group of saltwater predatory fish characterised by prominent pointed bills (rostra), and by their large size; some are longer than . Extant billfish include sailfish and marlin, which make up the family Istioph ...
, king mackerel
The king mackerel (''Scomberomorus cavalla'') or kingfish, is a migratory species of mackerel of the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. It is an important species to both the commercial and recreational fishing industries.
Description
Th ...
, sharks, and large rays.
Tuna in particular are of major importance to commercial fisheries. Although tuna migrate across oceans, trying to find them there is not the usual approach. Tuna tend to congregate in areas where food is abundant, along the boundaries of currents, around islands, near seamounts, and in some areas of upwelling along continental slopes. Tuna are captured by several methods: purse seine vessels enclose an entire surface school with special nets, pole and line vessels that use poles baited with other smaller pelagic fish as baitfish
300px, Feeder Goldfish are common baitfish.
Bait fish (or baitfish) are small-sized fish caught and used by anglers as bait to attract larger predatory fish, particularly game fish. Baitfish species are typically those that are common and b ...
, and rafts called fish aggregating device
A fish aggregating (or aggregation) device (FAD) is a man-made object used to attract ocean-going pelagic fish such as marlin, tuna and mahi-mahi (dolphin fish). They usually consist of buoys or floats tethered to the ocean floor with concrete bloc ...
s are set up, because tuna, as well as some other pelagic fish, tend to congregate under floating objects.
Other large pelagic fish are premier game fish
Game fish, sport fish or quarry refer to popular fish pursued by recreational anglers, and can be freshwater or saltwater fish. Game fish can be eaten after being caught, or released after capture. Some game fish are also targeted commerciall ...
, particularly marlin
Marlins are fish from the family Istiophoridae, which includes about 10 species. A marlin has an elongated body, a spear-like snout or bill, and a long, rigid dorsal fin which extends forward to form a crest. Its common name is thought to deri ...
and swordfish.
Yellowfin tuna
The yellowfin tuna (''Thunnus albacares'') is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.
Yellowfin is often marketed as ahi, from the Hawaiian , a name also used there for the closely related bigeye ...
are being fished as a replacement for the now largely depleted Southern bluefin tuna
The southern bluefin tuna (''Thunnus maccoyii'') is a tuna of the family (biology), family Scombridae found in open southern Hemisphere waters of all the world's oceans mainly between 30th parallel south, 30°S and 50th parallel south, 50°S, to ...
.
File:Brama brama.jpg, Atlantic pomfret
The Atlantic pomfret (''Brama brama''), also known as Ray's bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a pomfret of the family Bramidae. It is found in the Atlantic, Indian, and South Pacific Oceans, at depths down to .
Its length is betw ...
File:Xiphias gladius1.jpg, Swordfish
File:Sccav u0.gif, alt=King mackerels cruise on long migrations at 10 kilometres per hour, King mackerel
The king mackerel (''Scomberomorus cavalla'') or kingfish, is a migratory species of mackerel of the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. It is an important species to both the commercial and recreational fishing industries.
Description
Th ...
s cruise on long migrations at 10 kilometres per hour.



Productivity
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
occurs both along coastlines and in midocean when a collision of deep ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, s ...
s brings cold water that is rich in nutrients to the surface. These upwellings support blooms of phytoplankton, which in turn, produce zooplankton and support many of the world's main fisheries. If the upwelling fails, then fisheries in the area fail. Moyle and Cech, pp. 574–575
In the 1960s the Peruvian anchoveta
The Peruvian anchoveta (''Engraulis ringens'') is a species of fish of the anchovy family, Engraulidae, from the Southeast Pacific Ocean. It has yielded greater catches than any other single wild fish species in the world, with annual harvests ...
fishery was the world's largest fishery. The anchoveta population was greatly reduced during the 1972 El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date L ...
event, when warm water drifted over the cold Humboldt Current, as part of a 50-year cycle, lowering the depth of the thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
. The upwelling stopped and phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
production plummeted, as did the anchoveta population, and millions of seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same enviro ...
s, dependent on the anchoveta, died. Since the mid-1980s, the upwelling has resumed, and the Peruvian anchoveta catch levels have returned to the 1960s levels.
Off Japan, the collision of the Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean an ...
with the Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
produces nutrient-rich upwellings. Cyclic changes in these currents resulted in a decline in the sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
''sardinops melanosticta'' populations. Fisheries catches fell from 5 million tonnes in 1988 to 280 thousand tonnes in 1998. As a further consequence, Pacific bluefin tuna
The Pacific bluefin tuna (''Thunnus orientalis'') is a predatory species of tuna found widely in the northern Pacific Ocean, but it is migratory and also recorded as a visitor to the south Pacific.
In the past it was often included in '' T. thyn ...
stopped moving into the region to feed.
Ocean currents can shape how fish are distributed, both concentrating and dispersing them. Adjacent ocean currents can define distinct, if shifting, boundaries. These boundaries can even be visible, but usually their presence is marked by rapid changes in salinity, temperature, and turbidity.
For example, in the Asian northern Pacific, albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct s ...
are confined between two current systems. The northern boundary is determined by the cold North Pacific Current
The North Pacific Current (sometimes referred to as the North Pacific Drift) is a slow warm water current that flows west-to-east between 30 and 50 degrees north in the Pacific Ocean. The current forms the southern part of the North Pacific Su ...
and the southern boundary is determined by the North Equatorial Current
The North Equatorial Current (NEC) is a westward wind-driven current mostly located near the equator, but the location varies from different oceans. The NEC in the Pacific and the Atlantic is about 5°-20°N, while the NEC in the Indian Ocean is v ...
. To complicate things, their distribution is further modified within the area defined by the two current systems by another current, the Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
, whose flows fluctuate seasonally.
Epipelagic fish often spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: ...
in an area where the eggs and larvae drift downstream into suitable feeding areas, and eventually, drift into adult feeding areas.
Islands and banks
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Becaus ...
can interact with currents and upwellings in a manner that results in areas of high ocean productivity. Large eddies can form downcurrent or downwind from islands, concentrating plankton. Banks and reefs can intercept deep currents that upwell.
* Scombrid
The mackerel, tuna, and bonito family, Scombridae, includes many of the most important and familiar food fishes. The family consists of 51 species in 15 genera and two subfamilies. All species are in the subfamily Scombrinae, except the butterf ...
s
Highly migratory species
 Epipelagic fish generally move long distances between feeding and spawning areas, or as a response to changes in the ocean. Large ocean predators, such as salmon and tuna, can migrate thousands of kilometres, crossing oceans. Moyle and Cech, p. 578
In a 2001 study, the movements of
Epipelagic fish generally move long distances between feeding and spawning areas, or as a response to changes in the ocean. Large ocean predators, such as salmon and tuna, can migrate thousands of kilometres, crossing oceans. Moyle and Cech, p. 578
In a 2001 study, the movements of Atlantic bluefin tuna
The Atlantic bluefin tuna (''Thunnus thynnus'') is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It is variously known as the northern bluefin tuna (mainly when including Pacific bluefin as a subspecies), giant bluefin tuna or individuals excee ...
from an area off North Carolina were studied with the help of special popup tags. When attached to a tuna, these tags monitored the movements of the tuna for about a year, then detached and floated to the surface where they transmitted their information to a satellite. The study found that the tuna had four different migration patterns. One group confined itself to the western Atlantic for a year. Another group also stayed mainly in the western Atlantic, but migrated to the Gulf of Mexico for spawning. A third group moved across the Atlantic Ocean and back again. The fourth group crossed to the eastern Atlantic and then moved into the Mediterranean Sea for spawning. The study indicates that, while there is some differentiation by spawning areas, there is essentially only one population of Atlantic bluefin tuna, intermixing groups that between them, use all of the north Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Mediterranean Sea.
The term highly migratory species (HMS) is a legal term that has its origins in Article 64 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
(UNCLOS).
The highly migratory species include: tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
and tuna-like species (albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct s ...
, Atlantic bluefin, bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus '' Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are ...
, skipjack, yellowfin, blackfin, little tunny
The little tunny (''Euthynnus alletteratus''), also known as the false albacore, little tuna, bonita, bonito, or blue bonito, is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It can be found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean and Blac ...
, Pacific bluefin, southern bluefin and bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
), pomfret
Pomfrets are perciform fishes belonging to the family Bramidae. The family currently includes 20 species across seven genera. Several species are important food sources for humans, especially ''Brama brama'' in South Asia. The earlier form of ...
, marlin
Marlins are fish from the family Istiophoridae, which includes about 10 species. A marlin has an elongated body, a spear-like snout or bill, and a long, rigid dorsal fin which extends forward to form a crest. Its common name is thought to deri ...
, sailfish
The sailfish is one or two species of marine fish in the genus ''Istiophorus'', which belong to the family Istiophoridae ( marlins). They are predominantly blue to gray in colour and have a characteristically large dorsal fin known as the ...
, swordfish, saury
The saury (''Cololabis adocetus'') is a species of fish (not to be confused with the Pacific saury, another species in the genus ''Cololabis'') which is a member of the family Scomberesocidae, or the saury family. It is widespread in the Eastern P ...
and oceangoing shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
s, as well as mammals such as dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s, and other cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
s.
Essentially, highly migratory species coincide with the larger of the "large pelagic fish", discussed in the previous section, if cetaceans are added and some commercially unimportant fish, such as the sunfish, are excluded. These are high trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it ...
species that undertake migrations of significant, but variable distances across oceans for feeding, often on forage fish, or reproduction, and also have wide geographic distributions. Thus, these species are found both inside the exclusive economic zones and in the high seas
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regiona ...
outside these zones. They are pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or wa ...
species, which means they mostly live in the open ocean and do not live near the sea floor, although they may spend part of their life cycle in nearshore waters.
Capture production
According to theFood and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(FAO), the world harvest in 2005 consisted of 93.2 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s captured by commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often ...
in wild fisheries
A wild fishery is a natural body of water with a sizeable free-ranging fish or other aquatic animal (crustaceans and molluscs) population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries can be marine ( saltwater) or lacustrine/r ...
. Of this total, about 45% were pelagic fish. The following table shows the world capture production in tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s.
Threatened species
In 2009, theInternational Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
(IUCN) produced the first red list
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biologi ...
for threatened oceanic sharks and rays. They claim that approximately one third of open ocean sharks and rays are under threat of extinction.IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
. 25 June 2009.porbeagle
The porbeagle (''Lamna nasus'') is a species of mackerel shark in the family Lamnidae, distributed widely in the cold and temperate marine waters of the North Atlantic and Southern Hemisphere. In the North Pacific, its ecological equivalent is ...
.Fishing puts a third of all oceanic shark species at risk of extinction''
guardian.co.uk
TheGuardian.com, formerly known as Guardian.co.uk and ''Guardian Unlimited'', is a British news and media website owned by the Guardian Media Group. It contains nearly all of the content of the newspapers ''The Guardian'' and ''The Observer'', ...
'', 26 June 2009.
Oceanic sharks are captured incidentally by swordfish and tuna high seas
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regiona ...
fisheries. In the past there were few markets for sharks, which were regarded as worthless bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
. Now sharks are being increasingly targeted to supply emerging Asian markets, particularly for shark fins
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimor ...
, which are used in shark fin soup
Shark fin soup is a traditional soup or stewed dish served in parts of China, Taiwan, and Southeast Asia. The shark fins provide texture, while the taste comes from the other soup ingredients. It is commonly served at special occasions such as ...
.
The northwest Atlantic Ocean shark populations are estimated to have declined by 50% since the early 1970s. Oceanic sharks are vulnerable because they do not produce many young, and the young can take decades to mature.
scalloped hammerhead
The scalloped hammerhead (''Sphyrna lewini'') is a species of hammerhead shark in the family (biology), family Hammerhead shark, Sphyrnidae. It was originally known as ''Zygaena lewini''. The Greek language, Greek word ''sphyrna'' translates into ...
is classified as endangered.
File:Oceanic Whitetip Shark.png, alt=The oceanic whitetip shark has declined by 99% in the Gulf of Mexico, The oceanic whitetip shark
The oceanic whitetip shark (''Carcharhinus longimanus''), also known as shipwreck shark, Brown Milbert's sand bar shark, brown shark, lesser white shark, nigano shark, oceanic white-tipped whaler, and silvertip shark, is a large pelagic requiem ...
has declined by 99% in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
.
File:Atlantic mobula lisbon.jpg, The devil fish
The devil fish or giant devil ray (''Mobula mobular'') is a species of ray in the family Mobulidae. It is currently listed as endangered, mostly due to bycatch mortality in unrelated fisheries.
Description
The devil fish is larger than its clo ...
, a large ray, is threatened.
File:Lamna nasus.jpg, The porbeagle shark
The porbeagle (''Lamna nasus'') is a species of mackerel shark in the family Lamnidae, distributed widely in the cold and temperate marine waters of the North Atlantic and Southern Hemisphere. In the North Pacific, its ecological equivalent is ...
is threatened.
scalloped hammerhead
The scalloped hammerhead (''Sphyrna lewini'') is a species of hammerhead shark in the family (biology), family Hammerhead shark, Sphyrnidae. It was originally known as ''Zygaena lewini''. The Greek language, Greek word ''sphyrna'' translates into ...
shark has declined by 99% since the late 1970s. Its status on the red list is that it is globally endangered, meaning it is near extinction.
See also
*Deep sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
* Deep sea fish
* Demersal fish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
* Freshwater fish
Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine conditions in many ways, especially the difference in levels of s ...
* Nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) refers to the actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water. The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the passive organisms t ...
* Ocean Tracking Network The Ocean Tracking Network is a research effort using implanted acoustic transmitters to study fish migration
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, o ...
* Oily fish
Oily fish are fish species with oil (fats) in soft tissues and in the coelomic cavity around the gut. Their fillets may contain up to 30% oil, although this figure varies both within and between species. Examples of oily fish include smal ...
* Pacific Ocean Shelf Tracking Project
* Tagging of Pacific Predators
References
Notes Bibliography * *Further reading
* Collette, BB (2010"Reproduction and development in epipelagic fishes"
In: Kathleen S Cole, ''Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes: Patterns and Processes'', pp. 21–64, University of California Press. . * Freon, Pierre (1998) ''Dynamics of Pelagic Fish Distribution and Behaviour: Effects on Fisheries and Stock Assessment'', Wiley-Blackwell. . * * * Pepperell J (2011
''Fishes of the Open Ocean: A Natural History and Illustrated Guide''
University of New South Wales Press, . * Salvanesa AGV and Kristoffersen J
"Mesopelagic Fishes"
In: ''Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences'', pp. 1711–1717.
''
PhysOrg.com
Phys.org is an online science, research and technology news aggregator offering briefs from press releases and reports from news agencies (a form of journalism sometimes pejoratively called churnalism). The website also produces its own science ...
'', 26 March 2009.
One fish, two fish: New MIT sensor improves fish counts
''
PhysOrg.com
Phys.org is an online science, research and technology news aggregator offering briefs from press releases and reports from news agencies (a form of journalism sometimes pejoratively called churnalism). The website also produces its own science ...
'', 2 February 2006.
External links
Glowing life in an underwater world
TED video from
Edith Widder
Edith Anne "Edie" Widder Smith (born 1951) is an American oceanographer, marine biologist, author and the Co-founder, CEO and Senior Scientist at the Ocean Research & Conservation Association.
Books
* The Bioluminescence Coloring Book
Below ...
The Open Ocean
''MarineBio.org''. MarineBio.org. Updated 28 August 2011. TED video from
Edith Widder
Edith Anne "Edie" Widder Smith (born 1951) is an American oceanographer, marine biologist, author and the Co-founder, CEO and Senior Scientist at the Ocean Research & Conservation Association.
Books
* The Bioluminescence Coloring Book
Below ...
The Open Ocean
''MarineBio.org''. MarineBio.org. Updated 28 August 2011.
Pelagic Advisory Council
of the
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body o ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pelagic Fish
Ichthyology
Fishing industry