Pulse Sequence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
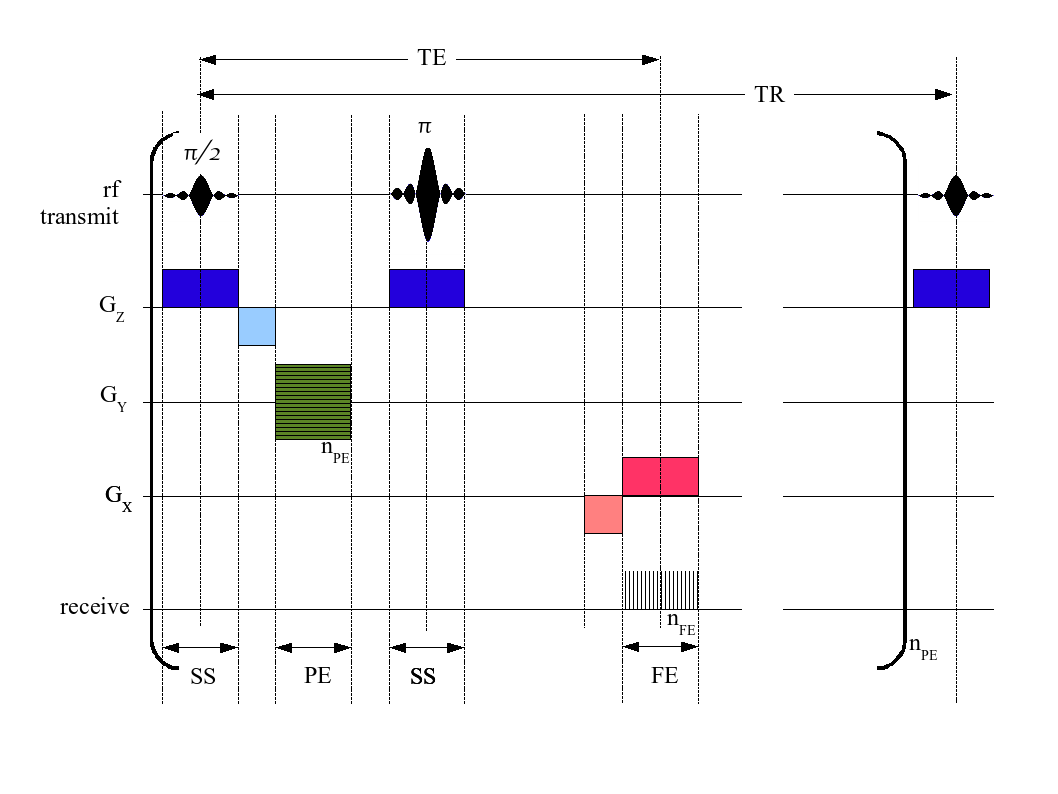

 In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
Pulse sequences
in the online textbook
The Basics of NMR
(by Joseph Hornak) Nuclear magnetic resonance {{NMR-stub


 In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
pulses applied to the sample, such that the free induction decay is related to the characteristic frequencies of the desired signals. After applying a Fourier transform, the signal can be represented in the frequency domain as the NMR spectrum. In magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
, additional '' gradient pulses'' are applied by switching magnetic fields that exhibit a space-dependent gradient which can be used to reconstruct spatially resolved images after applying Fourier transforms.
The outcome of pulse sequences is often analyzed using the product operator formalism.
See also
* Spin echo * Insensitive nuclei enhanced by polarization transfer * MRI sequenceReferences
External links
Pulse sequences
in the online textbook
The Basics of NMR
(by Joseph Hornak) Nuclear magnetic resonance {{NMR-stub