Prince Edward Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prince Edward Island is an island
 The coastline has a combination of long beaches, dunes, red
The coastline has a combination of long beaches, dunes, red
 Between 250 and 300 million years ago, freshwater streams flowing from ancient mountains brought silt, sand and gravel into what is now the Gulf of St. Lawrence. These sediments accumulated to form a sedimentary basin, and make up the island's bedrock. When the
Between 250 and 300 million years ago, freshwater streams flowing from ancient mountains brought silt, sand and gravel into what is now the Gulf of St. Lawrence. These sediments accumulated to form a sedimentary basin, and make up the island's bedrock. When the
, November 30, 2011.cbc.ca: "Charlottetown opens emergency water supply"
, July 10, 2012.cbc.ca: "Charlottetown relies on secondary water source"
, August 14, 2013. until water meters were installed. Government tabled a discussion paper on the proposed ''Water Act'' for the province on July 8, 2015. The use of groundwater came under scrutiny as the potato industry, which accounts for $1 billion every year and 50% of farm receipts, has pressed the government to lift a moratorium on high-capacity water wells for irrigation. The release of the discussion paper was to set off a consultation process in the autumn of 2015. Detailed information about the quality of drinking water in PEI communities and watersheds can be found on the provincial government's official website. It provides a summary of the ongoing testing of drinking water done by the Prince Edward Island Analytical Laboratories. Average drinking-water quality results are available, and information on the following parameters are provided: alkalinity; cadmium; calcium; chloride; chromium; iron; magnesium; manganese; nickel; nitrate; pH; phosphorus; potassium; sodium; and sulfate, as well as the presence of pesticides. Water-testing services are provided for a variety of clients through the PEI Analytical Laboratories which assesses according to the recommendations of the Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality published by
, website of the Government of Prince Edward Island, April 27, 2010. Retrieved on October 25, 2010. Another name is ''Minegoo''. The Mi'kmaq's legend is that the island was formed by the Great Spirit placing on the Blue Waters some dark red crescent-shaped clay. The two Mi'kmaq First Nation communities of Prince Edward Island today are Abegweit First Nation and Lennox Island First Nation.
 During the 18th century, the French were engaged in a series of conflicts with the
During the 18th century, the French were engaged in a series of conflicts with the
 During the
During the
 As a result of having hosted the inaugural meeting of Confederation, the Charlottetown Conference, Prince Edward Island presents itself as the "Birthplace of Confederation" and this is commemorated through several buildings, a
As a result of having hosted the inaugural meeting of Confederation, the Charlottetown Conference, Prince Edward Island presents itself as the "Birthplace of Confederation" and this is commemorated through several buildings, a
 According to the 2016 Canadian Census of the 139,690 people who self-identified with an ethnic origin, 98,615 were of European origins and 85,145 chose British Isles Origins. The largest ethnic group consists of people of Scottish descent (36%), followed by English (29%), Irish (28%), French (21%), German (5%), and Dutch (3%) descent.
Prince Edward Island's population is largely white; there are few visible minorities. Chinese Canadians are the largest visible minority group of Prince Edward Island, comprising 1.3% of the province's population. Almost half of respondents identified their ethnicity as "
According to the 2016 Canadian Census of the 139,690 people who self-identified with an ethnic origin, 98,615 were of European origins and 85,145 chose British Isles Origins. The largest ethnic group consists of people of Scottish descent (36%), followed by English (29%), Irish (28%), French (21%), German (5%), and Dutch (3%) descent.
Prince Edward Island's population is largely white; there are few visible minorities. Chinese Canadians are the largest visible minority group of Prince Edward Island, comprising 1.3% of the province's population. Almost half of respondents identified their ethnicity as "
''Source:
 As of the
As of the
 Agriculture remains the dominant industry in the provincial economy, as it has since colonial times. In 2015, agriculture and agri-food manufacturing was responsible for 7.6% of the province's GDP. The Island has a total land area of with approximately cleared for agricultural use. In 2016, the Census of Agriculture counted 1,353 farms on the Island, which is a 9.5% decrease from the previous census (2011). During the 20th century, potatoes were grown as a
Agriculture remains the dominant industry in the provincial economy, as it has since colonial times. In 2015, agriculture and agri-food manufacturing was responsible for 7.6% of the province's GDP. The Island has a total land area of with approximately cleared for agricultural use. In 2016, the Census of Agriculture counted 1,353 farms on the Island, which is a 9.5% decrease from the previous census (2011). During the 20th century, potatoes were grown as a

 Until May 1997, the province was linked by two passenger-vehicle ferry services to the mainland: one, provided by Marine Atlantic, operated year-round between Borden and Cape Tormentine, New Brunswick; the other, provided by Northumberland Ferries Limited, operates seasonally between Wood Islands and Caribou, Nova Scotia. A third ferry service provided by CTMA operates all year round with seasonal times between Souris and Cap-aux-Meules, Quebec, in the Magdalen Islands. In May 1997, the Confederation Bridge opened, connecting Borden-Carleton to Cape Jourimain, New Brunswick. The world's longest bridge over ice-covered waters, it replaced the Marine Atlantic ferry service. Since then, the Confederation Bridge's assured transportation link to the mainland has altered the province's tourism and agricultural and fisheries export economies.
The Island has the highest concentration of roadways in Canada. The provincially managed portion of the network consists of of paved roadways and of non-paved or clay roads. The province has very strict laws regarding use of roadside signs. Billboards and the use of portable signs are banned. There are standard direction information signs on roads in the province for various businesses and attractions in the immediate area. The by-laws of some municipalities also restrict the types of permanent signs that may be installed on private property.
Several airlines service the Charlottetown Airport (CYYG); the Summerside Airport (CYSU) is an additional option for general aviation.
There is an extensive bicycling and hiking trail that spans the island. The Confederation Trail is a recreational trail system. The land was once owned and used by Canadian National Railway (CN) as a rail line on the island.
Until May 1997, the province was linked by two passenger-vehicle ferry services to the mainland: one, provided by Marine Atlantic, operated year-round between Borden and Cape Tormentine, New Brunswick; the other, provided by Northumberland Ferries Limited, operates seasonally between Wood Islands and Caribou, Nova Scotia. A third ferry service provided by CTMA operates all year round with seasonal times between Souris and Cap-aux-Meules, Quebec, in the Magdalen Islands. In May 1997, the Confederation Bridge opened, connecting Borden-Carleton to Cape Jourimain, New Brunswick. The world's longest bridge over ice-covered waters, it replaced the Marine Atlantic ferry service. Since then, the Confederation Bridge's assured transportation link to the mainland has altered the province's tourism and agricultural and fisheries export economies.
The Island has the highest concentration of roadways in Canada. The provincially managed portion of the network consists of of paved roadways and of non-paved or clay roads. The province has very strict laws regarding use of roadside signs. Billboards and the use of portable signs are banned. There are standard direction information signs on roads in the province for various businesses and attractions in the immediate area. The by-laws of some municipalities also restrict the types of permanent signs that may be installed on private property.
Several airlines service the Charlottetown Airport (CYYG); the Summerside Airport (CYSU) is an additional option for general aviation.
There is an extensive bicycling and hiking trail that spans the island. The Confederation Trail is a recreational trail system. The land was once owned and used by Canadian National Railway (CN) as a rail line on the island.
 Lucy Maud Montgomery, who was born in Clifton (now New London) in 1874, drew inspiration from the land during the late
Lucy Maud Montgomery, who was born in Clifton (now New London) in 1874, drew inspiration from the land during the late
 There is an annual arts festival, the Charlottetown Festival, hosted at the Confederation Centre of the Arts as well as the Island Fringe Festival that takes place around Charlottetown. An annual jazz festival, the P.E.I. Jazz and Blues Festival. is a week-long series of concerts taking place at several venues including Murphy's Community Centre, outdoor stages, and churches in Charlottetown. The moving of its date to mid-August caused in 2011 a serious loss in funding from Ottawa's regional development agency ACOA. The musician's line up in 2011 included Oliver Jones, Sophie Milman, Matt Dusk, Jack de Keyzer, Jack Semple, Meaghan Smith and Jimmy Bowskill. There is also Canada Rocks, and the Cavendish Beach Music Festival. With agriculture and fishery playing a large role in the economy, P.E.I. has been marketed as a food tourism destination. Several food festivals have become popular such as the Fall Flavours festival and the Shellfish Festival.
There is an annual arts festival, the Charlottetown Festival, hosted at the Confederation Centre of the Arts as well as the Island Fringe Festival that takes place around Charlottetown. An annual jazz festival, the P.E.I. Jazz and Blues Festival. is a week-long series of concerts taking place at several venues including Murphy's Community Centre, outdoor stages, and churches in Charlottetown. The moving of its date to mid-August caused in 2011 a serious loss in funding from Ottawa's regional development agency ACOA. The musician's line up in 2011 included Oliver Jones, Sophie Milman, Matt Dusk, Jack de Keyzer, Jack Semple, Meaghan Smith and Jimmy Bowskill. There is also Canada Rocks, and the Cavendish Beach Music Festival. With agriculture and fishery playing a large role in the economy, P.E.I. has been marketed as a food tourism destination. Several food festivals have become popular such as the Fall Flavours festival and the Shellfish Festival.
University of Prince Edward Island Digital Historical Archives
The Government Prince Edward Island Visitor's Guide
PEI info
Mi'kmaq Confederacy home page
{{Authority control 1873 establishments in Canada Atlantic Canada British North America Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas The Maritimes States and territories established in 1873 Provinces and territories of Canada
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.
Part of the traditional lands of the Mi'kmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
. The island, known as Isle St-Jean (St. John's Island), was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
. In 1769, St. John's Island became its own British colony and its name was changed to Prince Edward Island (PEI) in 1798. PEI hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a union of the Maritime provinces; however, the conference became the first in a series of meetings which led to Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
on July 1, 1867. Prince Edward Island initially balked at Confederation but, facing bankruptcy from the Land Question and construction of a railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
, joined as Canada's seventh province on July 1, 1873.
According to Statistics Canada, the province of Prince Edward Island had 179,280 residents in 2025. The backbone of the island economy is farming; it produces 25% of Canada's potatoes. Other important industries include fisheries, tourism, aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
, biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
, information technology and renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
. As Prince Edward Island is one of Canada's older settled areas, its population still reflects the origins of its earliest settlers, with Acadian
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American region of Acadia, ...
, Scottish, Irish, and English surnames being dominant.
Prince Edward Island is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, about 10 km (6 miles) across the Northumberland Strait from both Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
and New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
. It is about north of Halifax and east of Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
. It has a land area of , is the 104th-largest island in the world and Canada's 23rd-largest island. It is the only Canadian province consisting entirely of islands.
Etymology
The island is known in the Mi'kmaq language of its historic indigenous occupants as ''Abegweit'' or ''Epekwitk'', roughly translated as "land cradled on the waves". When the island was part ofAcadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
, originally settled by French colonists, its French name was '' Île Saint-Jean'' (St. John's Island). In French, the island is today called ''Île-du-Prince-Édouard (ÎPÉ).''
The island was split from the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1769, and renamed in 1798 after Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (1767–1820), the fourth son of King George III and, in 1819, father of the future Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
. Thus, Prince Edward has been called "Father of the Canadian Crown". The following island landmarks are also named after the Duke of Kent:
* Prince Edward Battery, Victoria Park, Charlottetown
* Kent College, established in 1804 by Lieutenant Governor Edmund Fanning and his Legislative Council, the college would eventually become the University of Prince Edward Island
* Kent Street, Charlottetown
* West Kent Elementary School
* Kent Street, Georgetown
In Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
, the island's name is ''Eilean a' Phrionnsa'' (lit. "the Island of the Prince", the local form of the longer 'Eilean a' Phrionnsa Iomhair/Eideard'), or ''Eilean Eòin'' (literally, "John's Island" in reference to the island's former French name) for some Gaelic speakers in Nova Scotia, though not on PEI.
Geography
Prince Edward Island is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, west ofCape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
, north of the Nova Scotia peninsula, and northeast of New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
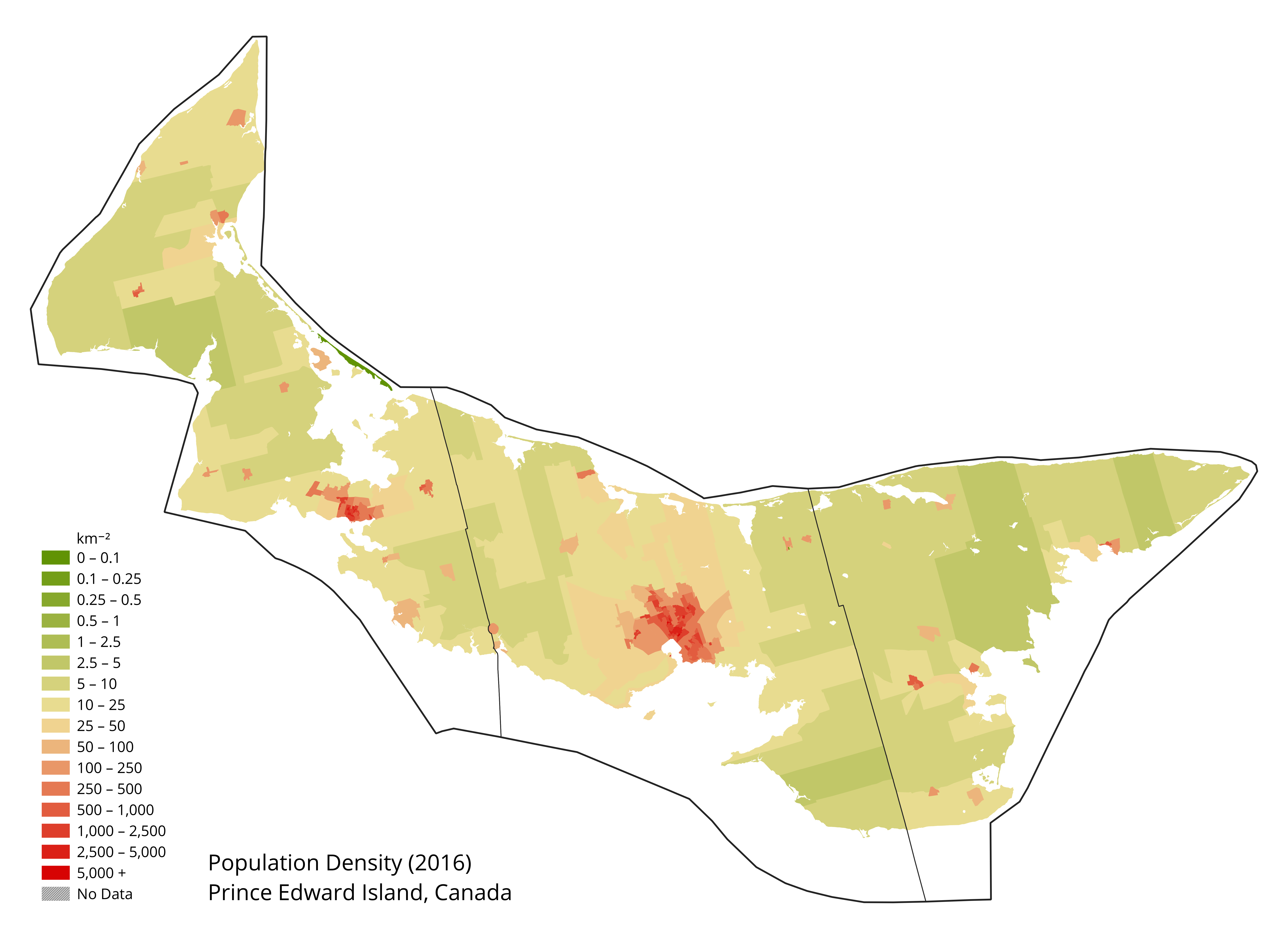
. Its southern shore bounds the Northumberland Strait. The island has two urban areas, and in total, is the most densely populated province in Canada.
The larger urban area surrounds Charlottetown Harbour, situated centrally on the island's southern shore. It consists of the capital city Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
, the suburban towns of Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
and Stratford, and a developing urban fringe. A much smaller urban area developed around Summerside Harbour, situated on the southern shore west of Charlottetown. This consists primarily of the city of Summerside. As with all natural harbours on the island, Charlottetown and Summerside harbours are created by rias.
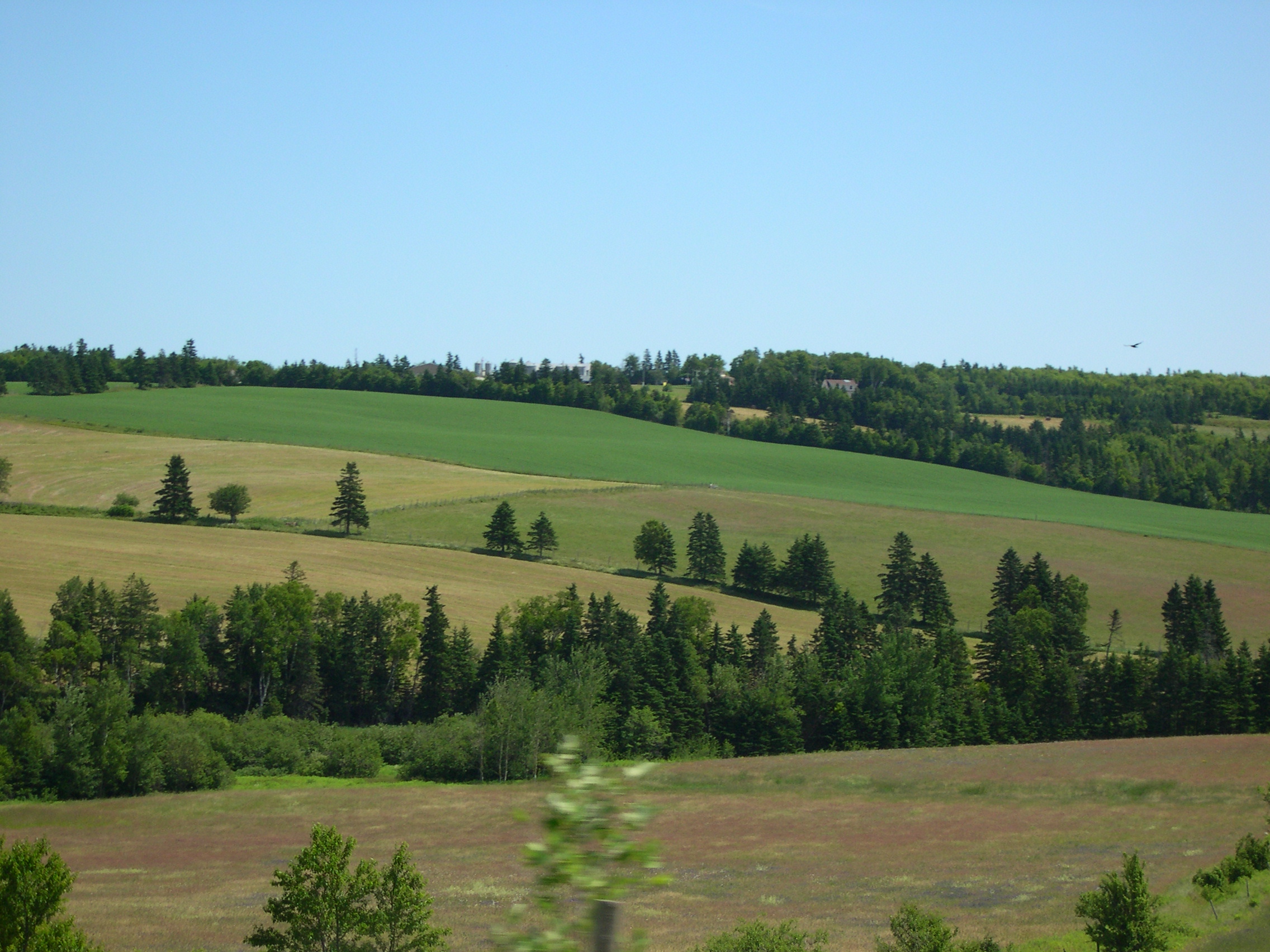
 The coastline has a combination of long beaches, dunes, red
The coastline has a combination of long beaches, dunes, red sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
cliffs, salt water marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in genera ...
es, and numerous bays and harbours. The beaches, dunes and sandstone cliffs consist of sedimentary rock and other material with a high iron concentration, which oxidizes upon exposure to the air. The geological properties of the white silica sand found at Basin Head are unique in the province; the sand grains cause a scrubbing noise as they rub against each other when walked on, and have been called the "singing sands". Large dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
fields on the north shore can be found on barrier islands at the entrances to various bays and harbours. The sand dunes at Greenwich
Greenwich ( , , ) is an List of areas of London, area in south-east London, England, within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, east-south-east of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime hi ...
are of particular significance as the shifting, parabolic dune system is home to a variety of birds and rare plants, and it is also a site of significant archeological interest.
Climate
The climate of the island is a maritime climate considered to be moderate and strongly influenced by the surrounding Gulf of St. Lawrence. As such, it is generally milder than many areas of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia due to the warmer waters of the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The climate is characterized by changeable weather throughout the year; in which specific weather conditions seldom last for long. During July and August, the average daytime high in PEI is ; however, the temperature can sometimes exceed during these months. In the winter months of January and February, the average daytime high is . The Island receives an average yearly rainfall of and an average yearly snowfall of . Winters are moderately cold and long but are milder than inland locations, with clashes of cold Arctic air and milder Atlantic air causing frequent temperature swings. The climate is considered to be morehumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
than oceanic since the Gulf of St. Lawrence freezes over, thus eliminating any moderation. The mean temperature is in January. During the winter months, the island usually has many storms (which may produce rain as well as snow) and blizzards since during this time, storms originating from the North Atlantic or the Gulf of Mexico frequently pass through. Springtime temperatures typically remain cool until the sea ice has melted, usually in late April or early May.
Summers are moderately warm, with the daily maximum temperature only occasionally reaching as high as . Autumn is a pleasant season, as the moderating Gulf waters delay the onset of frost, although storm activity increases compared to the summer. There is ample precipitation throughout the year, although it is heaviest in the late autumn, early winter and mid spring.
The following climate chart depicts the average conditions of Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
, as an example of the province's climate.
Geology
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s receded about 15,000 years ago, glacial debris such as till were left behind to cover most of the area that would become the island. This area was connected to the mainland by a strip of land, but when ocean levels rose as the glaciers melted, this land strip was flooded, forming the island. As the land rebounded from the weight of the ice, the island rose up to elevate it farther from the surrounding water.
Most of the bedrock in Prince Edward Island is composed of red sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
, part of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
age Pictou Group.
Although commercial deposits of minerals have not been found, exploration in the 1940s for natural gas beneath the northeastern end of the province resulted in the discovery of an undisclosed quantity of gas. The Island was reported by government to have only 0.08 tcf of "technically recoverable" natural gas. Twenty exploration wells for hydrocarbon resources have been drilled on Prince Edward Island and offshore. The first reported well was Hillsborough No.#1, drilled in Charlottetown Harbour in 1944 (the world's first offshore well), and the most recent was New Harmony No.#1 in 2007. Since the resurgence of exploration in the mid-1990s, all wells that have shown promising gas deposits have been stimulated through hydraulic fracture or "fracking". All oil and natural gas exploration and exploitation activities on the Island are governed by the ''Oil and Natural Gas Act'' R.S.P.E.I. 1988, Cap. 0-5 and its associated regulations and orders.
Water supply
The Province of Prince Edward Island is completely dependent on groundwater for its source of drinking water, with approximately 305 high capacity wells in use as of December 2018. As groundwater flows through an aquifer, it is naturally filtered. The water for the city of Charlottetown is extracted from thirteen wells in three wellfields and distributed to customers. The water removed is replenished by precipitation. Infrastructure in Charlottetown that was installed in 1888 is still in existence. With the age of the system in the older part of Charlottetown, concern has been raised regarding lead pipes. The Utility has been working with its residents on a lead-replacement program. A plebiscite in 1967 was held in Charlottetown over fluoridation, and residents voted in favour. Under provincial legislation, the Utility is required to report to its residents on an annual basis. It is also required to do regular sampling of the water and an overview is included in each annual report. The Winter River watershed provides about 92 per cent of the water supply for the city of Charlottetown, which had difficulty in each of 2011, 2012 and 2013 with its supply,cbc.ca: "Water supply worries prompt Charlottetown meeting", November 30, 2011.cbc.ca: "Charlottetown opens emergency water supply"
, July 10, 2012.cbc.ca: "Charlottetown relies on secondary water source"
, August 14, 2013. until water meters were installed. Government tabled a discussion paper on the proposed ''Water Act'' for the province on July 8, 2015. The use of groundwater came under scrutiny as the potato industry, which accounts for $1 billion every year and 50% of farm receipts, has pressed the government to lift a moratorium on high-capacity water wells for irrigation. The release of the discussion paper was to set off a consultation process in the autumn of 2015. Detailed information about the quality of drinking water in PEI communities and watersheds can be found on the provincial government's official website. It provides a summary of the ongoing testing of drinking water done by the Prince Edward Island Analytical Laboratories. Average drinking-water quality results are available, and information on the following parameters are provided: alkalinity; cadmium; calcium; chloride; chromium; iron; magnesium; manganese; nickel; nitrate; pH; phosphorus; potassium; sodium; and sulfate, as well as the presence of pesticides. Water-testing services are provided for a variety of clients through the PEI Analytical Laboratories which assesses according to the recommendations of the Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality published by
Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; )Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Gove ...
.
Flora and fauna
Prince Edward Island used to have native moose, bear, caribou, wolf, and other larger species. Due to hunting and habitat disruption these species are no longer found on the island. Some species common to P.E.I. arered fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
es, coyote, blue jays, and robins. Skunks and raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
s are common non-native species. Species at risk in P.E.I. include piping plovers, American eel, bobolinks, little brown bat, and beach pinweed.
Some species are unique to the province. In 2008, a new ascomycete species, '' Jahnula apiospora'' ( Jahnulales, Dothideomycetes
Dothideomycetes is the largest and most diverse class of ascomycete fungi. It comprises 11 orders 90 families, 1,300 genera and over 19,000 known species.
Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more orders to the class.
Traditionally, most of it ...
), was collected from submerged wood in a freshwater creek on Prince Edward Island.
North Atlantic right whales, one of the rarest whale species, once thought to be rare visitors into St. Lawrence regions until 1994, have been showing dramatic increases (annual concentrations were discovered off Percé in 1995 and gradual increases across the regions since 1998), and since 2014, notable numbers of whales have been recorded around Cape Breton to Prince Edward Island as 35 to 40 whales were seen in these areas in 2015.
History
Before the influx of Europeans, the Mi'kmaqFirst Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
have inhabited Prince Edward Island as part of the region of Mi'kma'ki
Mi'kma'ki or Mi'gma'gi is composed of the traditional and current territories, or country, of the Mi'kmaq people, in what is now Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and eastern Quebec, Canada. It is shared by an Non-governmental ...
. They named the Island ''Epekwitk'', meaning "cradled on the waves"; Europeans represented the pronunciation as ''Abegweit''.Island Information: Quick Facts, website of the Government of Prince Edward Island, April 27, 2010. Retrieved on October 25, 2010. Another name is ''Minegoo''. The Mi'kmaq's legend is that the island was formed by the Great Spirit placing on the Blue Waters some dark red crescent-shaped clay. The two Mi'kmaq First Nation communities of Prince Edward Island today are Abegweit First Nation and Lennox Island First Nation.
French colony
In 1534,Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
was the first European to see the island. In 1604, the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
laid claim to the lands of the Maritimes under the discovery doctrine, including Prince Edward Island, establishing the French colony of Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
. The island was named ''Île Saint-Jean'' (St. John's Island) by the French. The Mi'kmaq never recognized the claim but welcomed the French as trading partners and allies.
 During the 18th century, the French were engaged in a series of conflicts with the
During the 18th century, the French were engaged in a series of conflicts with the Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
and its colonies. Several battles between the two belligerents occurred on Prince Edward Island during this period. Following the British capture of Louisbourg during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
, New Englanders launched an attack on Île Saint-Jean (now Prince Edward Island); with a British detachment landed at Port-la-Joye. The island's capital had a garrison of 20 French soldiers under the command of Joseph du Pont Duvivier. The troops fled the settlement, and the New Englanders burned the settlement to the ground. Duvivier and the twenty men retreated up the Northeast River (Hillsborough River), pursued by the New Englanders until the French troops were reinforced with the arrival of the Acadian militia and the Mi'kmaq.Harvey, p. 111. The French troops and their allies were able to drive the New Englanders to their boats. Nine New Englanders were killed, wounded or made prisoner. The New Englanders took six Acadian hostages, who would be executed if the Acadians or Mi'kmaq rebelled against New England control. The New England troops left for Louisbourg. Duvivier and his 20 troops left for Quebec. After the fall of Louisbourg, the resident French population of Île Royale (now Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
) were deported to France, with the remaining Acadians of Île Saint-Jean living under the threat of deportation for the remainder of the war.
New Englanders had a force of 200 soldiers stationed at Port-La-Joye, as well as two warships boarding supplies for its journey of Louisbourg. To regain Acadia, Ramezay was sent from Quebec to the region to join forces with the Duc d'Anville expedition. Upon arriving at Chignecto, he sent Boishebert to Île Saint-Jean to ascertain the size of the New England force. After Boishebert returned, Ramezay sent Joseph-Michel Legardeur de Croisille et de Montesson along with over 500 men, 200 of whom were Mi'kmaq, to Port-La-Joye. In July 1746, the battle happened near York River. Montesson and his troops killed forty New Englanders and captured the rest. Montesson was commended for having distinguished himself in his first independent command. Hostilities between the British and French were ended in 1748 with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748.
Roughly one thousand Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
lived on the island prior to the Acadian Exodus from Nova Scotia. The population grew to nearly 5,000 the late 1740s and early 1750s, as Acadians from Nova Scotia fled to the island during the Acadian Exodus, and the subsequent British-ordered expulsions beginning in 1755.
Hostilities between British and French colonial forces resumed in 1754, although formal declarations of war were not issued until 1756. After French forces were defeated at the siege of Louisbourg, the British performed a military campaign on Ile Saint-Jean (now Prince Edward Island) to secure the island. The campaign was led by Colonel Andrew Rollo under orders from General Jeffery Amherst. The following campaigns saw the deportation of most Acadians from the island. Many Acadians died in the expulsion en route to France; on December 13, 1758, the transport ship '' Duke William'' sank and 364 died. A day earlier the '' Violet'' sank and 280 died; several days later sank with 213 on board. The French formally ceded the island, and most of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
to the British in the Treaty of Paris of 1763.
British colony
Initially named St. John's Island by the British, the island was administered as part of the colony of Nova Scotia, until it was split into a separate colony in 1769. In the mid-1760s, a survey team led by Samuel Holland divided the Island into 67 lots. On July 1, 1767, these properties were allocated to supporters of King George III by means of a lottery. Ownership of the land remained in the hands of landlords in England, angering Island settlers who were unable to gain title to land on which they worked and lived. Significant rent charges (to absentee landlords) created further anger. The land had been given to the absentee landlords with a number of conditions attached regarding upkeep and settlement terms, many of which were not satisfied. Islanders spent decades trying to convince the Crown to confiscate the lots; however, the descendants of the original owners were generally well connected to the British government and refused to give up the land. After the island was detached from Nova Scotia to become a separate colony, Walter Patterson was appointed the first British governor of St. John's Island in 1769. Assuming the office in 1770, he had a controversial career during which land title disputes and factional conflict slowed the initial attempts to populate and develop the island under afeudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring socie ...
. In an attempt to attract settlers from Ireland, in one of his first acts (1770) Patterson led the island's colonial assembly to rename the island "New Ireland", but the British Government promptly vetoed this as it exceeded the authority vested in the colonial government; only the Privy Council in London could change the name of a colony.
 During the
During the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
Charlottetown was raided in 1775 by a pair of American-employed privateers. Two armed schooners, ''Franklin'' and ''Hancock'', from Beverly, Massachusetts, made prisoner of the attorney-general at Charlottetown, on advice given them by some Pictou residents after they had taken eight fishing vessels in the Gut of Canso.
During and after the American Revolutionary War, from 1776 to 1783, the colony's efforts to attract exiled Loyalist refugees from the rebellious North American colonies met with some success. Walter Patterson's brother, John Patterson, one of the original grantees of land on the island, was a temporarily exiled Loyalist and led efforts to persuade others to come. Governor Patterson dismissal in 1787, and his recall to London in 1789 dampened his brother's efforts, leading John to focus on his interests in the United States. Edmund Fanning, also a Loyalist exiled by the Revolution, took over as the second governor, serving until 1804. His tenure was more successful than Patterson's. A large influx of Scottish Highlanders in the late 1700s also resulted in St. John's Island having the highest proportion of Scottish immigrants in Canada. This led to a higher proportion of Scottish Gaelic speakers and thriving culture surviving on the island than in Scotland itself, as the settlers could more easily avoid English influence overseas.
On November 29, 1798, during Fanning's administration, the British government granted approval to change the colony's name from St. John's Island to Prince Edward Island to distinguish it from areas with similar names in what is now Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
, such as the cities of Saint John in New Brunswick and St. John's in Newfoundland. The colony's new name honoured the fourth son of King George III, Prince Edward Augustus, the Duke of Kent (1767–1820), who subsequently led the British military forces on the continent as Commander-in-Chief, North America (1799–1800), with his headquarters in Halifax.
In 1853, the Island government passed the Land Purchase Act which empowered them to purchase lands from those owners who were willing to sell, and then resell the land to settlers for low prices. This scheme collapsed when the Island ran short of money to continue with the purchases. Many of these lands also were fertile, and were some of the key factors to sustaining Prince Edward Island's economy.
Confederation
From September 1 to 7, 1864, Prince Edward Island hosted the Charlottetown Conference, which was the first meeting in the process leading to the Quebec Resolutions and the creation of Canada in 1867. Prince Edward Island found the terms of union unfavourable and balked at joining in 1867, choosing to remain a colony of the United Kingdom. In the late 1860s, the colony examined various options, including the possibility of becoming a discrete dominion unto itself, as well as entertaining delegations from the United States, who were interested in Prince Edward Island joining the United States. In 1871, the colony began construction of the Prince Edward Island Railway (PEIR) and, frustrated by Great Britain's Colonial Office, began negotiations with the United States. In 1873, Canadian Prime Minister John A. Macdonald, anxious to thwart American expansionism and facing the distraction of the Pacific Scandal, negotiated for Prince Edward Island to join Canada. The Dominion Government of Canada assumed the colony's extensive railway debts and agreed to finance a buy-out of the last of the colony's absentee landlords to free the island of leasehold tenure and from any new immigrants entering the island (accomplished through the passage of the '' Land Purchase Act, 1875''). Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873. As a result of having hosted the inaugural meeting of Confederation, the Charlottetown Conference, Prince Edward Island presents itself as the "Birthplace of Confederation" and this is commemorated through several buildings, a
As a result of having hosted the inaugural meeting of Confederation, the Charlottetown Conference, Prince Edward Island presents itself as the "Birthplace of Confederation" and this is commemorated through several buildings, a ferry
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus ...
vessel, and the Confederation Bridge (constructed 1993 to 1997). The most prominent building in the province honouring this event is the Confederation Centre of the Arts, presented as a gift to Prince Edward Islanders by the 10 provincial governments and the Federal Government upon the centenary of the Charlottetown Conference, where it stands in Charlottetown as a national monument to the " Fathers of Confederation". The centre is one of the 22 National Historic Sites of Canada located in Prince Edward Island.
Demographics

Ethnicity
 According to the 2016 Canadian Census of the 139,690 people who self-identified with an ethnic origin, 98,615 were of European origins and 85,145 chose British Isles Origins. The largest ethnic group consists of people of Scottish descent (36%), followed by English (29%), Irish (28%), French (21%), German (5%), and Dutch (3%) descent.
Prince Edward Island's population is largely white; there are few visible minorities. Chinese Canadians are the largest visible minority group of Prince Edward Island, comprising 1.3% of the province's population. Almost half of respondents identified their ethnicity as "
According to the 2016 Canadian Census of the 139,690 people who self-identified with an ethnic origin, 98,615 were of European origins and 85,145 chose British Isles Origins. The largest ethnic group consists of people of Scottish descent (36%), followed by English (29%), Irish (28%), French (21%), German (5%), and Dutch (3%) descent.
Prince Edward Island's population is largely white; there are few visible minorities. Chinese Canadians are the largest visible minority group of Prince Edward Island, comprising 1.3% of the province's population. Almost half of respondents identified their ethnicity as "Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
".
''Source:
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
''
Language
 As of the
As of the 2021 Canadian Census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canada, Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, whic ...
, the ten most spoken languages in the province included English (149,525 or 99.36%), French (19,445 or 12.92%), Mandarin (2,940 or 1.95%), Hindi (1,660 or 1.1%), Tagalog (1,630 or 1.08%), Punjabi (1,550 or 1.03%), Spanish (1,425 or 0.95%), Arabic (1,165 or 0.77%), German (1,040 or 0.69%), and Vietnamese (785 or 0.52%). The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses.
The Canada 2016 Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial censu ...
showed a population of 142,910. Of the 140,020 singular responses to the census question concerning mother tongue, the most commonly reported languages were as follows:
In addition, there were 460 responses of both English and a "non-official language"; 30 of both French and a "non-official language"; 485 of both English and French; and 20 of English, French, and a "non-official language". (Figures shown are for the number of single language responses and the percentage of total single-language responses.)
Religion
According to the 2021 census, religious groups in Prince Edward Island included: *Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
(101,755 persons or 67.6%)
* Irreligion
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, ...
(42,830 persons or 28.5%)
* Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(1,720 persons or 1.1%)
* Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(1,245 persons or 0.8%)
* Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
(1,165 persons or 0.8%)
* Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(755 persons or 0.5%)
* Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
(165 persons or 0.1%)
* Indigenous Spirituality (75 persons or <0.1%)
* Other (765 persons or 0.5%)
Traditionally, the population has been evenly divided between Catholic and Protestant affiliations. The 2001 census indicated number of adherents for the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
with 63,240 (47%) and various Protestant churches with 57,805 (43%). This included the United Church of Canada
The United Church of Canada (UCC; ) is a mainline Protestant denomination that is the largest Protestant Christian denomination in Canada and the second largest Canadian Christian denomination after the Catholic Church in Canada.
The United Chu ...
with 26,570 (20%); the Presbyterian Church with 7,885 (6%) and the Anglican Church of Canada
The Anglican Church of Canada (ACC or ACoC) is the Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, province of the Anglican Communion in Canada. The official French-language name is ''l'Église anglicane du Canada''. In 2016, the Anglican Church of ...
with 6,525 (5%); those with no religion were among the lowest of the provinces with 8,705 (6.5%). If one considers that the founders of the United Church of Canada were largely Presbyterians in Prince Edward Island, the Island has one of the highest percentages of Presbyterians in the country. Since 2016 there are two Amish
The Amish (, also or ; ; ), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, church fellowships with Swiss people, Swiss and Alsace, Alsatian origins. As they ...
settlements on Prince Edward Island.
Economy
The provincial economy is dominated by the seasonal industries of agriculture, tourism, and thefishery
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish far ...
. The island also has tourists who visit year-round. Tourists engage in a variety of leisure activities, including the beaches, various golf course
A golf course is the grounds on which the sport of golf is played. It consists of a series of holes, each consisting of a teeing ground, tee box, a #Fairway and rough, fairway, the #Fairway and rough, rough and other hazard (golf), hazards, and ...
s, eco-tourism adventures, touring the countryside, and varied cultural events in local communities around the island. The economy of most rural communities on the island is based on small-scale agriculture. Industrial farming has increased as businesses buy and consolidate older farm properties. The province is limited in terms of heavy industry and manufacturing, though Cavendish Farms runs extensive food manufacturing operations on PEI.
 Agriculture remains the dominant industry in the provincial economy, as it has since colonial times. In 2015, agriculture and agri-food manufacturing was responsible for 7.6% of the province's GDP. The Island has a total land area of with approximately cleared for agricultural use. In 2016, the Census of Agriculture counted 1,353 farms on the Island, which is a 9.5% decrease from the previous census (2011). During the 20th century, potatoes were grown as a
Agriculture remains the dominant industry in the provincial economy, as it has since colonial times. In 2015, agriculture and agri-food manufacturing was responsible for 7.6% of the province's GDP. The Island has a total land area of with approximately cleared for agricultural use. In 2016, the Census of Agriculture counted 1,353 farms on the Island, which is a 9.5% decrease from the previous census (2011). During the 20th century, potatoes were grown as a cash crop
A cash crop, also called profit crop, is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate a marketed crop from a staple crop ("subsi ...
across more than a million acres of farmland. Traditionally, crops were grown on a rotational basis: common examples would be either potatoes, hay, clover, or oats being grown on a piece of land at any given time. More recently, the total amount of farms used for potatoes has decreased, but the province is still Canada's largest supplier of the crop. The number of acres under potato production in 2010 was 88,000, while soy accounted for 55,000. There are approximately 330 potato growers on PEI, with the grand majority of these being family farms, often with multiple generations working together. The province currently accounts for a quarter of Canada's total potato production, producing approximately annually. Comparatively, the state of Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
produces approximately annually, with a population approximately 9.5 times greater. The province is a major producer of seed potatoes, exporting to more than twenty countries around the world. An estimated total of 70% of the land is cultivated and 25% of all potatoes grown in Canada originate from P.E.I. The processing of frozen fried potatoes, green vegetables, and berries is a leading business activity.
As a legacy of the island's colonial history, the provincial government enforces extremely strict rules for non-resident land ownership, especially since the PEI ''Lands Protection Act'' of 1982. Residents and corporations are limited to maximum holdings of 400 and 1,200 hectares respectively. There are also restrictions on non-resident ownership of shorelines.
Many of the province's coastal communities rely upon shellfish harvesting, particularly lobster fishing as well as oyster fishing and mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
farming.
The island's economy has grown significantly over the last decade in key areas of innovation. Aerospace, bioscience, information and communications technology
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals) and computer ...
, and renewable energy have been a focus for growth and diversification. Aerospace alone now accounts for over 25% of the province's international exports and is the island's fourth largest industry at $355 million in annual sales. The bioscience industry employs over 1,300 people and generates over $150 million in sales.
The sale of carbonated beverages such as beer and soft drinks in non-refillable containers, such as aluminum cans or plastic bottles, was banned in 1976 as an environmental measure in response to public concerns over litter. Beer and soft drink companies opted to use refillable glass bottles for their products which were redeemable at stores and bottle depots.
Though often environmental and economic agendas may be at odds, the ‘ban the can’ legislation, along with being environmentally driven, was also economically motivated as it protected jobs. Seaman's Beverages, a bottling company and carbonated beverage manufacturer, was established in 1939 and a major employer in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. Making it illegal to retail cans led to a bigger share of the carbonated beverage market for Seamans. Seamans Beverages was eventually acquired by Pepsi Bottling Group Inc in 2002 prior to the lifting of the legislation.
The introduction of recycling programs for cans and plastic bottles in neighbouring provinces in recent years (also using a redemption system) has seen the provincial government introduce legislation to reverse this ban with the restriction lifted on May 3, 2008.
Prior to harmonization in 2013, Prince Edward Island had one of Canada's highest provincial retail sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
rates at 10%. On April 1, 2013, the provincial tax was harmonized with the federal Goods and Services Tax, and became known as the '' harmonized sales tax''. The 15% tax is applied to almost all goods and services except some clothing, food and home heating fuel. This rate is the same as the neighbouring Atlantic provinces.
The provincial government provides consumer protection in the form of regulation for certain items, ranging from apartment rent increases to petroleum products including gas, diesel, propane
Propane () is a three-carbon chain alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but becomes liquid when compressed for transportation and storage. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum ref ...
and heating oil. These are regulated through the Prince Edward Island Regulatory and Appeals Commission (IRAC). IRAC is authorized to limit the number of companies who are permitted to sell petroleum products.
, the median family income on Prince Edward Island is $76,607/year. The minimum wage is $16.00/hour .
Energy
Since 1918, Maritime Electric has delivered electricity to customers on the Island. The utility is currently owned and operated by Fortis Inc. Approximately twenty-five percent of electricity consumed on the island is generated fromrenewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
(largely wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that wind power, converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. , hundreds of thousands of list of most powerful wind turbines, large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over ...
s); the provincial government had set a renewable energy target for 30–50% for electricity consumed by 2015, though this goal has not been met. The total capacity of wind power on the island is 204 MW from 89 turbines. There are eight wind farms on the island, the largest being West Cape Wind Park with a capacity of 99 MW from 55 turbines. All of the turbines have been manufactured by Vestas: the Vestas V-80, Vestas V90, and Vestas V-47. A thermal oil-fired generating station, the Charlottetown Thermal Generating Station, is used sometimes for emergencies. It is being decommissioned. A second thermal generation station exists in Borden, the Borden Generating Station. The majority of electricity consumed on Prince Edward Island comes from New Brunswick through undersea cables. A recent $140M upgrade brought the capacity of the cable system from 200 MW to 560 MW.
The Point Lepreau nuclear plant in New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
was closed for refurbishments from 2008 to 2012, resulting in a steep price hike of about 25 per cent, but the province later subsidized rates. Residents were to pay 11.2 per cent more for electricity when the harmonized sales tax was adopted in April 2013, according to the P.E.I. Energy Accord that was tabled in the legislature on December 7, 2012. and passed as the ''Electric Power (Energy Accord Continuation) Amendment Act'', which establishes electric pricing from April 1, 2013, to March 1, 2016. Regulatory powers are derived for IRAC from the ''Electric Power Act''.
Education
Prince Edward Island's public school system has an English school district named the Public Schools Branch (previously the English Language School Board), as well as a Francophone district, the Commission scolaire de langue française. The English language district has a total of 10 secondary schools and 54 intermediate and elementary schools while the Francophone district has 6 schools covering all grades. 22 per cent of the student population is enrolled in French immersion. This is one of the highest levels in the country. Threepublic
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociology, sociological concept of the ''Öf ...
post-secondary institutions operate in the province, including one university, and two colleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary education, tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding academic degree, degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further educatio ...
. The University of Prince Edward Island is the province's only public university, and is located in the city of Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
. The university was created by the Island legislature to replace Prince of Wales College and St. Dunstan's University. UPEI is also home to the Atlantic Veterinary College, which offers the region's only veterinary medicine program.
Collège de l'Île, and Holland College are two public colleges that operate in the province; the former being a French first language
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period hypothesis, critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' ...
institution, while the latter is an English first language institution. Holland College includes specialized facilities such as the Atlantic Police Academy, Marine Training Centre, and the Culinary Institute of Canada. In addition to public post-secondary institutions, Prince Edward Island is also home to a private post-secondary institution, Maritime Christian College.
Today 23.5 per cent of residents aged 15 to 19 have bilingual skills, an increase of 100 per cent in a decade. Prince Edward Island, along with most rural regions in North America, is experiencing an accelerated rate of youth emigration. The provincial government .
Government and politics
The provincial government is responsible for such areas as health and social services, education, economic development, labour legislation and civil law. These matters of government are overseen in the provincial capital, Charlottetown. Prince Edward Island is governed by a parliamentary government within the construct ofconstitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
; the monarchy in Prince Edward Island is the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
branches. The sovereign is King Charles III, who also serves as head of state of 14 other Commonwealth countries, each of Canada's nine other provinces, and the Canadian federal realm, and resides in the United Kingdom. As such, the King's representative, the Lieutenant Governor of Prince Edward Island (presently Wassim Salamoun), carries out most of the royal duties in Prince Edward Island.
The direct participation of the royal and viceroyal figures in any of these areas of governance is limited; in practice, their use of the executive powers is directed by the Executive Council, a committee of ministers of the Crown responsible to the unicameral, elected Legislative Assembly and chosen and headed by the Premier of Prince Edward Island (presently Rob Lantz), the head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
. To ensure the stability of government, the lieutenant governor will usually appoint as premier the person who is the current leader of the political party that can obtain the confidence of a plurality in the Legislative Assembly. The leader of the party with the second-most seats usually becomes the Leader of His Majesty's Loyal Opposition (presently Hal Perry) and is part of an adversarial parliamentary system intended to keep the government in check.
Each of the 27 Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is elected by simple plurality in an electoral district
An electoral (congressional, legislative, etc.) district, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provi ...
. General elections are called by the lieutenant governor for the first Monday in October four years after the previous election, or may be called earlier on the advice of the premier. Historically, politics in the province have been dominated by the Liberal and the Progressive Conservative Parties since the province joined Confederation. From the 2015 election, the Green Party of Prince Edward Island gained a small representation in the Legislative Assembly, and in the 2019 election gained an additional six seats to form the Official Opposition.
The Mi'kmaq Confederacy of PEI is the tribal council and provincial-territorial organization in the province that represents both the Lennox Island and Abegweit First Nations.
Administrative divisions
Prince Edward Island is divided into threecounties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
that have historically been used as administrative divisions for the provincial government, and prior to Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
(in 1873), the colonial government.
Today, the counties are no longer used as administrative boundaries for the provincial government, though they continue to be used as census division
Census divisions, in Canada and the United States, are areas delineated for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation; they have no government in and of themselves. The census divisions of Canada are second-level census geographic uni ...
s by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
for statistical purposes in administering the Canadian census.
Municipalities

Zoning
Rolling hills, woods, reddish white sand beaches, ocean coves and the famous red soil have given Prince Edward Island a reputation as a province of outstanding natural beauty. As a result, the provincial government has enacted laws to preserve the landscape through regulation, although there is a lack of consistent enforcement. There is no province-widezoning
In urban planning, zoning is a method in which a municipality or other tier of government divides land into land-use "zones", each of which has a set of regulations for new development that differs from other zones. Zones may be defined for ...
and land-use planning. Under the Planning Act of the province, municipalities have the option to assume responsibility for land-use planning through the development and adoption of official plans and land use bylaws. Thirty-one municipalities have taken responsibility for planning. In areas where municipalities have not assumed responsibility for planning, the Province remains responsible for development control.
Health care and sanitation
The province has a single health administrative region (or district health authority) called Health PEI. Health PEI receives funding for its operations and is regulated by the Department of Health and Wellness. Many PEI homes and businesses are served by central sewage collection and treatment systems. These are operated either by a municipality or a private utility. Many industrial operations have their own wastewater treatment facilities. Staff members with the Department of Environment, Water and Climate Change provide advice to operators, as needed, on proper system maintenance. The IRAC regulates municipal water and sewer in the province, now under the ''Environmental Protection Act''. Since around 1900, the residents of the City of Charlottetown have benefited from a central sanitary sewer service. Early disposal practices, while advanced for their time, eventually were found to compromise the ecological integrity of the nearby Hillsborough River and the Charlottetown Harbour. By 1974, the commission had spearheaded the development of a primary wastewater treatment plant, known as the Charlottetown Pollution Control Plant, together with the construction of several pumping stations along the city's waterfront, and outfall piping deep into the Hillsborough River. There are eight hospitals in the province. * Queen Elizabeth Hospital (Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County, Prince Edward Island, Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlott ...
)
* Prince County Hospital ( Summerside)
* Kings County Memorial Hospital ( Montague)
* Community Hospital ( O'Leary)
* Souris Hospital ( Souris)
* Western Hospital ( Alberton)
* Hillsborough Hospital (Charlottetown) - the province's only psychiatric hospital
Prince Edward Island offers programs and services in areas such as acute care, primary care, home care, palliative care, public health, chronic disease prevention, and mental health and addictions, to name a few. The provincial government has opened several family health centres in recent years in various rural and urban communities. A provincial cancer treatment centre at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital provides support to those dealing with various types of cancer-related illnesses. A family medicine residency program was established in 2009 with the Dalhousie University Faculty of Medicine as a means to encourage new physicians to work in Prince Edward Island.
Long-term-care services are also available with several programs in place to support seniors wishing to remain independent in their communities. Many medications for seniors are subsidized through a provincial pharmaceutical plan.
The provincial government has several programs for early illness detection, including mammography and pap screening clinics. There are also asthma education and diabetes education programs, as well as prenatal programs, immunization programs and dental health risk prevention programs for children. The government is also attempting to implement a comprehensive integrated Electronic Health Record
An electronic health record (EHR) is the systematized collection of electronically stored patient and population health information in a digital format. These records can be shared across different health care settings. Records are shared thro ...
system.
The provincial government has recently committed to enhancing primary care and home care services and has invested in health care facilities in recent capital budgets; mostly replacements and upgrades to provincial government operated nursing homes and hospitals.
Some specialist services require patients to be referred to clinics and specialists in neighbouring provinces. Specialist operations and treatments are also provided at larger tertiary referral hospitals in neighbouring provinces such as the IWK Health Centre and Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
or the Saint John Regional Hospital, Moncton Hospital, and Dr. Georges-L.-Dumont University Hospital Centre in New Brunswick.
Ground ambulance service in Prince Edward Island is provided under contract by Island EMS. Air ambulance service is provided under contract by LifeFlight.
In recent decades, Prince Edward Island's population has shown statistically significant and abnormally high rates of diagnosed rare cancers, particularly in rural areas. Health officials, ecologists and environmental activists point to the use of pesticides
Pesticides are substances that are used to pest control, control pest (organism), pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for a ...
for industrial potato farming as a primary contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, wiktionary:Workplace, workplace, etc.
Types of contamina ...
.
Until 2016, Prince Edward Island was the only province in Canada that did not provide abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
services through its hospitals. Until that time, the last abortion that had been performed in the province was in 1982 prior to the opening of the Queen Elizabeth Hospital which saw the closure of the Roman Catholic-affiliated Charlottetown Hospital and the non-denominational Prince Edward Island Hospital; a condition of the "merger" being that abortions not be performed in the province. In 1988, following the court decision '' R. v. Morgentaler'', the then-opposition Progressive Conservative Party of Prince Edward Island tabled a motion demanding that the ban on abortions be upheld at the province's hospitals; the then-governing Prince Edward Island Liberal Party under Premier Joe Ghiz acquiesced and the ban was upheld. Until more local access was guaranteed, the Government of Prince Edward Island funded abortions for women who travelled to another province. Women from Prince Edward Island also travelled to the nearest private user-pay clinic, where they were required pay for the procedure using their own funds. Formerly this was the Morgentaler Clinic in Fredericton
Fredericton (; ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of New Brunswick. The city is situated in the west-central portion of the province along the Saint John River (Bay of Fundy), Saint John River, ...
, New Brunswick until this clinic closed due to lack of funds in July 2014. The clinic was reopened under new ownership in 2016 as Clinic 554 with expanded services. During that gap, women had to travel to Halifax or further. In 2016, the Liberal government led by Premier Wade MacLauchlan announced they would open a women's reproductive health clinic to provide abortions within the province. Abortions are now provided in Prince Edward Island.
Transportation
Prince Edward Island's transportation network has traditionally revolved around its seaports of Charlottetown, Summerside, Borden, Georgetown, and Souris —linked to its railway system, and the two main airports in Charlottetown and Summerside, for communication with mainland North America. The Prince Edward Island Railway system was abandoned by CN in 1989 in favour of an agreement with the federal government to improve major highways. Until May 1997, the province was linked by two passenger-vehicle ferry services to the mainland: one, provided by Marine Atlantic, operated year-round between Borden and Cape Tormentine, New Brunswick; the other, provided by Northumberland Ferries Limited, operates seasonally between Wood Islands and Caribou, Nova Scotia. A third ferry service provided by CTMA operates all year round with seasonal times between Souris and Cap-aux-Meules, Quebec, in the Magdalen Islands. In May 1997, the Confederation Bridge opened, connecting Borden-Carleton to Cape Jourimain, New Brunswick. The world's longest bridge over ice-covered waters, it replaced the Marine Atlantic ferry service. Since then, the Confederation Bridge's assured transportation link to the mainland has altered the province's tourism and agricultural and fisheries export economies.
The Island has the highest concentration of roadways in Canada. The provincially managed portion of the network consists of of paved roadways and of non-paved or clay roads. The province has very strict laws regarding use of roadside signs. Billboards and the use of portable signs are banned. There are standard direction information signs on roads in the province for various businesses and attractions in the immediate area. The by-laws of some municipalities also restrict the types of permanent signs that may be installed on private property.
Several airlines service the Charlottetown Airport (CYYG); the Summerside Airport (CYSU) is an additional option for general aviation.
There is an extensive bicycling and hiking trail that spans the island. The Confederation Trail is a recreational trail system. The land was once owned and used by Canadian National Railway (CN) as a rail line on the island.
Until May 1997, the province was linked by two passenger-vehicle ferry services to the mainland: one, provided by Marine Atlantic, operated year-round between Borden and Cape Tormentine, New Brunswick; the other, provided by Northumberland Ferries Limited, operates seasonally between Wood Islands and Caribou, Nova Scotia. A third ferry service provided by CTMA operates all year round with seasonal times between Souris and Cap-aux-Meules, Quebec, in the Magdalen Islands. In May 1997, the Confederation Bridge opened, connecting Borden-Carleton to Cape Jourimain, New Brunswick. The world's longest bridge over ice-covered waters, it replaced the Marine Atlantic ferry service. Since then, the Confederation Bridge's assured transportation link to the mainland has altered the province's tourism and agricultural and fisheries export economies.
The Island has the highest concentration of roadways in Canada. The provincially managed portion of the network consists of of paved roadways and of non-paved or clay roads. The province has very strict laws regarding use of roadside signs. Billboards and the use of portable signs are banned. There are standard direction information signs on roads in the province for various businesses and attractions in the immediate area. The by-laws of some municipalities also restrict the types of permanent signs that may be installed on private property.
Several airlines service the Charlottetown Airport (CYYG); the Summerside Airport (CYSU) is an additional option for general aviation.
There is an extensive bicycling and hiking trail that spans the island. The Confederation Trail is a recreational trail system. The land was once owned and used by Canadian National Railway (CN) as a rail line on the island.
Culture
Arts
The island's cultural traditions of art, music and creative writing are supported through the public education system. There is an annual arts festival, the Charlottetown Festival, hosted at the Confederation Centre of the Arts. Lucy Maud Montgomery, who was born in Clifton (now New London) in 1874, drew inspiration from the land during the late
Lucy Maud Montgomery, who was born in Clifton (now New London) in 1874, drew inspiration from the land during the late Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
for the setting of her classic novel '' Anne of Green Gables'' (1908). The musical play '' Anne of Green Gables'' has run every year at the Charlottetown festival for more than four decades. The sequel, '' Anne & Gilbert'', premiered in the Playhouse in Victoria in 2005. The actual location of Green Gables, the house featured in Montgomery's ''Anne'' books, is in Cavendish, on the north shore of PEI.
Elmer Blaney Harris founded an artists colony at Fortune Bridge and set his famous play '' Johnny Belinda'' on the island. Robert Harris was a well-known artist.
Prince Edward Island's documented music history begins in the 19th century with religious music, some written by the local pump and block maker and organ-importer Watson Duchemin. Several big bands including the Sons of Temperance Band and the Charlottetown Brass Band were active. Today, Acadian, Celtic, folk, and rock music prevail, with exponents including Gene MacLellan, his daughter Catherine MacLellan, Al Tuck, Lennie Gallant, Two Hours Traffic and Paper Lions. The celebrated singer-songwriter Stompin' Tom Connors
Charles Thomas "Stompin' Tom" Connors, Order of Canada, OC (February 9, 1936 – March 6, 2013) was a Canadian country music, country and folk music, folk singer-songwriter. Focusing his career exclusively on his native Canada, he is credited wi ...
spent his formative years in Skinners Pond. Celtic music is certainly the most common traditional music on the island, with fiddling and step dancing being very common. This tradition, largely Scottish, Irish and Acadian in origin is very similar to the music of Cape Breton and to a lesser extent, Newfoundland and is unique to the region. Due to the Islands influence as a former Highlander Clans Scottish colony, a March 4/4 for bagpipes was composed in honour of Prince Edward Island.
Festivals
 There is an annual arts festival, the Charlottetown Festival, hosted at the Confederation Centre of the Arts as well as the Island Fringe Festival that takes place around Charlottetown. An annual jazz festival, the P.E.I. Jazz and Blues Festival. is a week-long series of concerts taking place at several venues including Murphy's Community Centre, outdoor stages, and churches in Charlottetown. The moving of its date to mid-August caused in 2011 a serious loss in funding from Ottawa's regional development agency ACOA. The musician's line up in 2011 included Oliver Jones, Sophie Milman, Matt Dusk, Jack de Keyzer, Jack Semple, Meaghan Smith and Jimmy Bowskill. There is also Canada Rocks, and the Cavendish Beach Music Festival. With agriculture and fishery playing a large role in the economy, P.E.I. has been marketed as a food tourism destination. Several food festivals have become popular such as the Fall Flavours festival and the Shellfish Festival.
There is an annual arts festival, the Charlottetown Festival, hosted at the Confederation Centre of the Arts as well as the Island Fringe Festival that takes place around Charlottetown. An annual jazz festival, the P.E.I. Jazz and Blues Festival. is a week-long series of concerts taking place at several venues including Murphy's Community Centre, outdoor stages, and churches in Charlottetown. The moving of its date to mid-August caused in 2011 a serious loss in funding from Ottawa's regional development agency ACOA. The musician's line up in 2011 included Oliver Jones, Sophie Milman, Matt Dusk, Jack de Keyzer, Jack Semple, Meaghan Smith and Jimmy Bowskill. There is also Canada Rocks, and the Cavendish Beach Music Festival. With agriculture and fishery playing a large role in the economy, P.E.I. has been marketed as a food tourism destination. Several food festivals have become popular such as the Fall Flavours festival and the Shellfish Festival.
Sports
The most common sports played on the Island are hockey, curling, golf, horse racing, baseball, soccer, rugby, football and basketball. Water sports are also popular on Prince Edward Island during the summer. The province is home to a major junior ice hockey team, the Charlottetown Islanders of the Quebec Maritimes Junior Hockey League, and a Junior A ice hockey team, the Summerside Western Capitals, which play in the Maritime Junior A Hockey League. The Prince Edward Island Senators played in theAmerican Hockey League
The American Hockey League (AHL) is a professional ice hockey league in North America that serves as the primary developmental league of the National Hockey League (NHL). The league comprises 32 teams, with 26 in the United States and 6 in Cana ...
from 1993 to 1996. Relocated from New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is List ...
, the team was affiliated with the Ottawa Senators. The team eventually ended up in Binghamton, New York and became the Binghamton Senators in 2002.
The Island Storm were a professional basketball team that played in the National Basketball League of Canada
The National Basketball League of Canada (NBL Canada; ) was a Canadian professional men's minor league basketball organization. The NBL Canada was founded in 2011, when three existing Premier Basketball League teams joined with four new franchis ...
. The team was founded in 2011 as the Summerside Storm for the league's inaugural season and became the Island Storm in 2013. The team was granted a one-year leave of absence in 2021 but have not returned since.
In 2008 and 2009, Prince Edward Island hosted the Tour de PEI, a province-wide cycling race consisting of women from around the world.
Prince Edward Island has also hosted three Canada Games: two winter editions in 1991 and 2023; and a summer edition in 2009
2009 was designated as the International Year of Astronomy by the United Nations to coincide with the 400th anniversary of Galileo Galilei's first known astronomical studies with a telescope and the publication of Astronomia Nova by Joha ...
.
The two major indoor arenas in the province are: the Eastlink Centre (formerly the Civic Centre) in Charlottetown, home to the Charlottetown Islanders; and the Consolidated Credit Union Place in Summerside, home to the Summerside Western Capitals. The Credit Union Place was built to replace Cahill Stadium.
The UPEI Panthers represent the University of Prince Edward Island in the Atlantic University Sport conference of U Sports
U Sports (stylized as U SPORTS) is the national sport governing body for universities in Canada, comprising the majority of degree-granting universities in the country and four regional conferences: Ontario University Athletics (OUA), Résea ...
. The Holland Hurricanes represent Holland College in the Atlantic Collegiate Athletic Association conference of the Canadian Collegiate Athletic Association.
Sister province
Hainan
Hainan is an island provinces of China, province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally mean ...
, China, has been the sister province of Prince Edward Island since 2001. This came about after Vice-Governor Lin Fanglue stayed for two days to hold discussions about partnership opportunities and trade.
See also
* Outline of Prince Edward Island * Index of Canada-related articles * List of people from Prince Edward IslandNotes
References
Further reading
* * * Also under * * * A very broad look at the historical geography of P.E.I. * * * * * * * * *External links
*University of Prince Edward Island Digital Historical Archives
The Government Prince Edward Island Visitor's Guide
PEI info
Mi'kmaq Confederacy home page
{{Authority control 1873 establishments in Canada Atlantic Canada British North America Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas The Maritimes States and territories established in 1873 Provinces and territories of Canada
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...