Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of
PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of
 In 1996, an international group of 30 clinical epidemiologists, clinicians, statisticians, editors, and researchers convened The Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) conference to address standards for improving the quality of reporting of meta-analyses of clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This conference resulted in the QUOROM checklist and a flow diagram that described the preferred way to present the abstract, introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections of a report of a
In 1996, an international group of 30 clinical epidemiologists, clinicians, statisticians, editors, and researchers convened The Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) conference to address standards for improving the quality of reporting of meta-analyses of clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This conference resulted in the QUOROM checklist and a flow diagram that described the preferred way to present the abstract, introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections of a report of a
PRISMA Statement
EQUATOR Network
(Enhancing the Quality and Transparency of Health Care Research Epidemiology Meta-analysis Quality assurance Systematic review Reporting guidelines Standards
 PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of
PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of systematic reviews
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
and meta-analyses
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
, primarily used to assess the benefits and harms of a health care intervention. PRISMA focuses on ways in which authors can ensure a transparent and complete reporting of this type of research. The PRISMA standard superseded the earlier QUOROM standard. It offers the replicability of a systematic literature review. Researchers have to figure out research objectives that answer the research question, states the keywords, a set of exclusion and inclusion criteria. In the review stage, relevant articles were searched, irrelevant ones are removed. Articles are analyzed according to some pre-defined categories.
The PRISMA statement
The aim of the PRISMA statement is to help authors improve the reporting ofsystematic reviews
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
and meta-analyses
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
. PRISMA has mainly focused on systematic reviews and meta-analysis of randomized trials, but it can also be used as a basis for reporting reviews of other types of research (e.g., diagnostic
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
studies, observational studies
In fields such as epidemiology, social sciences, psychology and statistics, an observational study draws inferences from a sample to a population where the independent variable is not under the control of the researcher because of ethical conc ...
).
History
In 1987, Cynthia Mulrow examined for the first time the methodological quality of a sample of 50 review articles published in four leading medical journals between 1985 and 1986. She found that none met a set of eight explicit scientific criteria, and that the lack of quality assessment of primary studies was a major pitfall in these reviews. In 1987, Sacks and colleagues evaluated the quality of 83 meta-analyses, using a scoring method that considered 23 items in six major areas: study design, combinability, control of bias, statistical analysis, sensitivity analysis, and application of results. Results of this research showed that reporting was generally poor; and pointed out an urgent need for improved methods in literature searching, quality evaluation of trials, and synthesizing of the results. In 1996, an international group of 30 clinical epidemiologists, clinicians, statisticians, editors, and researchers convened The Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) conference to address standards for improving the quality of reporting of meta-analyses of clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This conference resulted in the QUOROM checklist and a flow diagram that described the preferred way to present the abstract, introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections of a report of a
In 1996, an international group of 30 clinical epidemiologists, clinicians, statisticians, editors, and researchers convened The Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) conference to address standards for improving the quality of reporting of meta-analyses of clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This conference resulted in the QUOROM checklist and a flow diagram that described the preferred way to present the abstract, introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections of a report of a systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
or a meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
. Eight of the original 18 items formed the basis of the QUOROM reporting. Evaluation of reporting was organized into headings and subheadings regarding searches, selection, validity assessment, data abstraction, study characteristics, and quantitative data synthesis. The rationale behind the inclusion of such a diagram is to increase the transparency of decisions made by the researcher for including or excluding certain studies, which may subsequently introduce biases
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is inaccurate, closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individ ...
in the overall measure of effect An outcome measure, endpoint, effect measure or measure of effect is a measure within medical practice or research, (primarily clinical trials) which is used to assess the effect, both positive and negative, of an intervention or treatment. Measures ...
. It subsequently became a required element in a number of medical
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
and life science
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, respon ...
journals when submitting review papers.
In 2009, the QUOROM was updated to address several conceptual and practical advances in the science of systematic reviews
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
, and was renamed PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses). This was then updated by the PRISMA 2020 which includes new reporting guidance.
In 2021, a 'PRISMA for Searching' (PRISMA-S) guidance was added and published, to improve the literature searches of systematic reviews, which are accentuated to "underlie the foundations of systematic review".
Components
Checklist
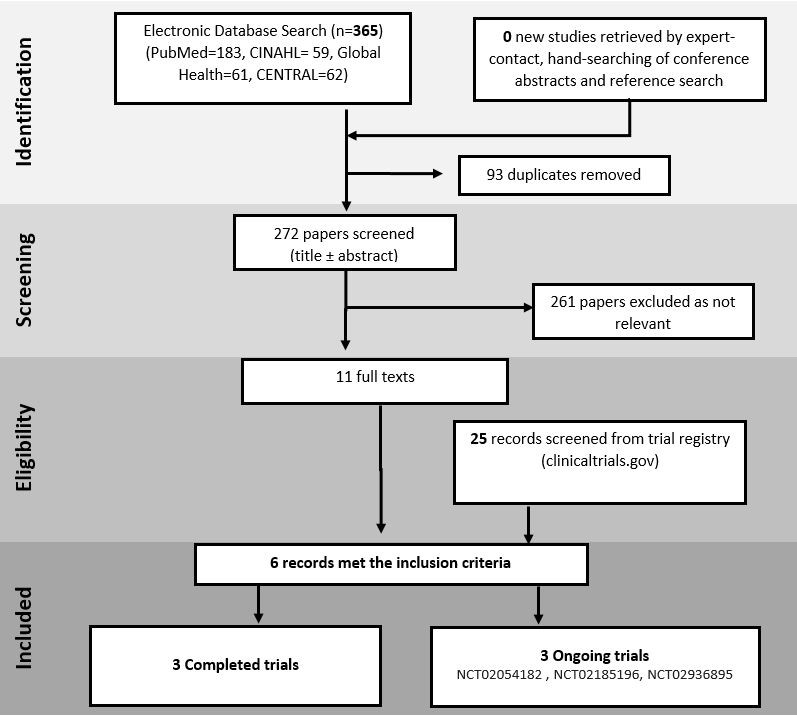
The checklist includes 27 items pertaining to the content of a systematic review and meta-analysis, which include the title, abstract, methods, results, discussion and funding.Flow diagram
The following is an example of a PRISMA flow diagram:
Impact
The use of checklists like PRISMA is likely to improve the reporting quality of a systematic review and provides substantial transparency in the selection process of papers in a systematic review. The PRISMA Statement has been published in several journals. Many journals publishing health research refer to PRISMA in their Instructions to Authors and some require authors to adhere to them. The PRISMA Group advised that PRISMA should replace QUOROM for those journals that endorsed QUOROM in the past. Recent surveys of leading medical journals evaluated the extent to which the PRISMA Statement has been incorporated into their Instructions to Authors. In a sample of 146 journals publishing systematic reviews, the PRISMA Statement was referred to in the instructions to authors for 27% of journals; more often in general and internal medicine journals (50%) than in specialty medicine journals (25%). These results showed that the uptake of PRISMA guidelines by journals is still inadequate although there has been some improvement over time. Approximately 174 journals in the health sciences endorse the PRISMA Statement for the reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analysis published in their collections.PRISMA Endorsers. http://www.prisma-statement.org/Endorsement/PRISMAEndorsers PRISMA has been also included as one of the tools for assessing the reporting of research within theEQUATOR Network
The Enhancing the Quality and Transparency of health research Network (EQUATOR Network) is an international initiative aimed at promoting transparent and accurate reporting of health research studies to enhance the value and reliability of medic ...
(Enhancing the Quality and Transparency of Health Care Research), an international initiative that seeks to enhance reliability and value of medical research literature by promoting transparent and accurate reporting of research studies.
See also
*Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology #REDIRECT Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology {{R from other capitalisation ...
References
{{reflist, 30emExternal links
PRISMA Statement
EQUATOR Network
(Enhancing the Quality and Transparency of Health Care Research Epidemiology Meta-analysis Quality assurance Systematic review Reporting guidelines Standards