Peuci on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the
LI.24.4
"For not only were they hindered by their waggons, which were in the rear, but their desire to save their wives and their children was also instrumental in their defeat." It has also been suggested that the name is linked with the Germanic word ''bastard'', meaning illegitimate or mongrel, and this name is sometimes contrasted to proposed Germanic etymologies for the name of the
 The earliest classical mentions of the Bastarnae locate them north of the Lower Danube, although they apparently made frequent crossings impacting upon the peoples living south of the Danube.
Strabo (about 20 AD) made several remarks about the location of the Bastarnae. In one place he described the lands beyond the Rhine and Danube as the home of the Galatian (Celtic) and the Germanic peoples, and beyond these (to the east) were the Bastarnae and their neighbours the Tyregetans "and the River Borysthenes" (Dnieper). However, in another similar passage he says only that "most writers suspect" the Bastarnae to be next beyond the Germanic Peoples, but he indicates that it is also possible that "others lie in between, either the Iazyges, or the Roxolani, or certain other of the wagon-dwellers — it is not easy to say". In yet another similar passage he describes the Bastarnae as the most inland (northerly) of the peoples living between the Borysthenes (Dnieper) and the Ister (Lower Danube), and indicates that their neighbours the Tyregetans are closer to the Black Sea.
Strabo also mentioned their interactions with other peoples near the Danube, specifying that in his time, "wagon-dwelling" Scythians and Sarmatians, "as well as the Bastarnian tribes, are mingled with the Thracians (more indeed with those outside the Ister orth of the Danube but also with those inside). And mingled with them are also the Celtic tribes — the Boii, the Scordisci, and the Taurisci". He confirmed that historically "the Scythians and Bastarnians and Sauromatians on the far side of the river he Lower Danubeoften prevail to the extent that they actually cross over to attack those whom they have already driven out, and some of them remain there, either in the islands or in Thrace". In particular, Near the outlets of the Ister River ower Danubeis a great island called Peuce; and when the Bastarnians took possession of it they received the appellation of Peucini."
In one passage Pliny the Elder located the Bastarnae "and other Germanic peoples" in the lands beyond the Iazyges and Dacians (''aversa Basternae tenent aliique inde Germani''). In another he describes "the Peucini, the Basternae", as neighbours of the
The earliest classical mentions of the Bastarnae locate them north of the Lower Danube, although they apparently made frequent crossings impacting upon the peoples living south of the Danube.
Strabo (about 20 AD) made several remarks about the location of the Bastarnae. In one place he described the lands beyond the Rhine and Danube as the home of the Galatian (Celtic) and the Germanic peoples, and beyond these (to the east) were the Bastarnae and their neighbours the Tyregetans "and the River Borysthenes" (Dnieper). However, in another similar passage he says only that "most writers suspect" the Bastarnae to be next beyond the Germanic Peoples, but he indicates that it is also possible that "others lie in between, either the Iazyges, or the Roxolani, or certain other of the wagon-dwellers — it is not easy to say". In yet another similar passage he describes the Bastarnae as the most inland (northerly) of the peoples living between the Borysthenes (Dnieper) and the Ister (Lower Danube), and indicates that their neighbours the Tyregetans are closer to the Black Sea.
Strabo also mentioned their interactions with other peoples near the Danube, specifying that in his time, "wagon-dwelling" Scythians and Sarmatians, "as well as the Bastarnian tribes, are mingled with the Thracians (more indeed with those outside the Ister orth of the Danube but also with those inside). And mingled with them are also the Celtic tribes — the Boii, the Scordisci, and the Taurisci". He confirmed that historically "the Scythians and Bastarnians and Sauromatians on the far side of the river he Lower Danubeoften prevail to the extent that they actually cross over to attack those whom they have already driven out, and some of them remain there, either in the islands or in Thrace". In particular, Near the outlets of the Ister River ower Danubeis a great island called Peuce; and when the Bastarnians took possession of it they received the appellation of Peucini."
In one passage Pliny the Elder located the Bastarnae "and other Germanic peoples" in the lands beyond the Iazyges and Dacians (''aversa Basternae tenent aliique inde Germani''). In another he describes "the Peucini, the Basternae", as neighbours of the
G.46
/ref> :As to the tribes of the Peucini, Veneti, and Fenni I am in doubt whether I should class them with the Germans or the Sarmatæ, although indeed the Peucini called by some Bastarnæ, are like Germans in their language, mode of life, and in the permanence of their settlements. They all live in filth and sloth, and by the intermarriages of the chiefs they are becoming in some degree debased into a resemblance to the Sarmatæ.
 The Bastarnae first appear in the historical record in 179 BC, when they crossed the Danube in a massive force. They did so at the invitation of their long-time ally, King
The Bastarnae first appear in the historical record in 179 BC, when they crossed the Danube in a massive force. They did so at the invitation of their long-time ally, King
 The Bastarnae first came into direct conflict with Rome as a result of expansion into the lower Danube region by the
The Bastarnae first came into direct conflict with Rome as a result of expansion into the lower Danube region by the
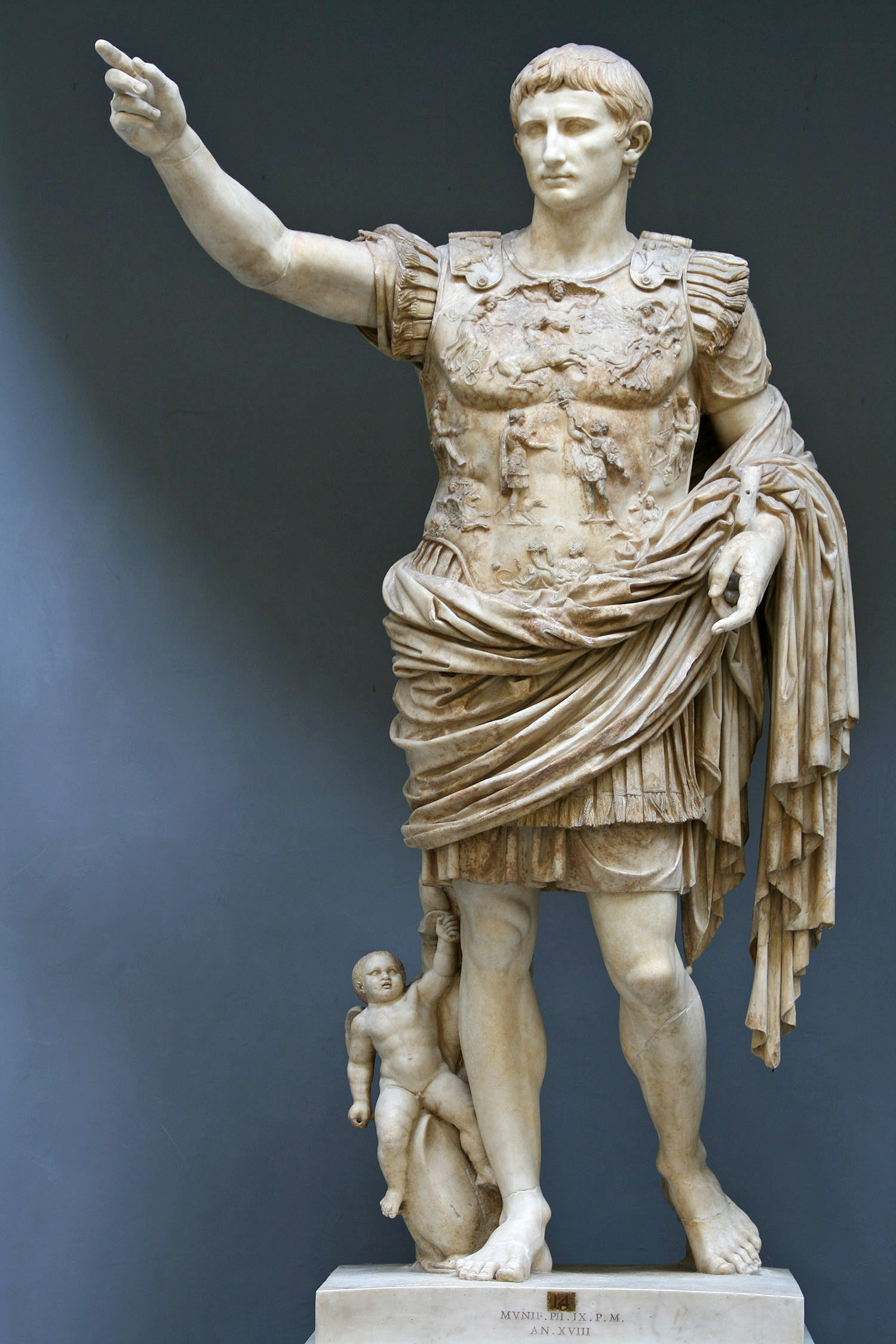 Once he had established himself as sole ruler of the Roman state in 30 BC, Caesar's grand-nephew and adopted son
Once he had established himself as sole ruler of the Roman state in 30 BC, Caesar's grand-nephew and adopted son
 It appears that in the final years of Augustus' rule, the Bastarnae made their peace with Rome. The ''
It appears that in the final years of Augustus' rule, the Bastarnae made their peace with Rome. The ''
 The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
between about 300 BC and about 300 AD, stretching in an ark from the sources of the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
in present-day Poland and Slovakia, to the Lower Danube, and including all or most of present-day Moldava. The Peucini were sometimes described as a subtribe, who settled the Peuke Island in the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (, ; , ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. Occurring where the Danube, Danube River empties into the Black Sea, most of the Danube Delta lies in Romania ...
, but apparently due to their importance their name was sometimes used for the Bastarnae as a whole. Near the sources of the Vistula another part of the Bastarnae were the Sidones, while the Atmoni, another tribe of the Bastarnae are only mentioned in one listing by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
.
The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they were culturally Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
. Also consistent with connections to the cultures to their west, later Roman-era sources state directly that they spoke Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoke ...
, and could be considered Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
. In contrast, like other peoples who lived in this geographical region, Graeco-Roman writers also sometimes referred to the Bastarnae as a "Scythian" or "Sarmatian" people, but this was a reference to their location, and customs, rather than a linguistic category. Although largely sedentary, at least one Roman writer, Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
, stated that the Bastarnae had adopted some Sarmatian customs. So far, no archaeological sites have been conclusively attributed to the Bastarnae. The archaeological horizon most often associated by scholars with the Bastarnae is the Poieneşti-Lucașeuca culture.
From the first records which mention them, the Bastarnae were active in the region of the Danube estuary on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
coast. The Bastarnae first came into conflict with the Romans during the first century BC when, in alliance with Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
and Sarmatians, they unsuccessfully resisted Roman expansion into Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
, south of the Danube. Later, they appear to have maintained friendly relations with the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
during the first two centuries AD. This changed around 180 AD, when the Bastarnae are recorded as participants in an invasion of Roman territory, once again in alliance with Sarmatians and Dacians. In the mid-3rd century AD, the Bastarnae were part of a Gothic-led grand coalition of lower Danube tribes that repeatedly invaded the Balkan provinces of the Roman Empire.
Many Bastarnae were resettled within the Roman Empire in the late third century.
Etymology
The origin of the tribal name is uncertain. It is not even clear whether it was an exonym (a name ascribed to them by outsiders) or an endonym (a name by which the Bastarnae described themselves). A related question is whether the groups denoted "Bastarnae" by the Romans considered themselves a distinct ethnic group at all (endonym) or whether it was a generic exonym used by the Greco-Romans to denote a disparate group of tribes of the Carpathian region that could not be classified as Dacians or Sarmatians. One possible derivation is from theproto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
word ''*bastjan'' (from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
root *''bʰas-''), meaning "binding" or "tie". In this case, ''Bastarnae'' may have had the original meaning of a coalition or ''bund'' of tribes.
It is possible that the Roman term ''basterna
A basterna was a kind of vehicle, or litter (vehicle), litter, in which Ancient Roman women were carried. It appears to have resembled the lectica; and the only difference apparently was, that the lectica was carried on the shoulders of slaves, and ...
'', denoting a type of wagon or litter, is derived from the name of this people (or, if it is an exonym, that the name of the people is derived from it) who were known, like many Germanic tribes, to travel with a wagon train for their families.DiLI.24.4
"For not only were they hindered by their waggons, which were in the rear, but their desire to save their wives and their children was also instrumental in their defeat." It has also been suggested that the name is linked with the Germanic word ''bastard'', meaning illegitimate or mongrel, and this name is sometimes contrasted to proposed Germanic etymologies for the name of the
Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the ...
who lived in the same general region. However, Roger Batty considers this Germanic derivation unlikely. If the name is an endonym, then this derivation is unlikely, as most endonyms have flattering meanings (e.g. "brave", "strong", "noble").
TrubačevTrubačev INDOARICA в Северном Причерноморье, pp. 212–3 proposes a derivation from Old Persian
Old Persian is one of two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of the Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (I ...
, Avestan
Avestan ( ) is the liturgical language of Zoroastrianism. It belongs to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and was First language, originally spoken during the Avestan period, Old ...
''bast-'' "bound, tied; slave" (cf. Ossetic
Ossetian ( , , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete, is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Russian-Georgian border in the Greater Caucasus region. ...
bættən "bind", bast "bound") and Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
''*arna-'' "offspring", equating it with the ''δουλόσποροι'' "slave Sporoi" mentioned by Nonnus
Nonnus of Panopolis (, ''Nónnos ho Panopolítēs'', 5th century AD) was the most notable Greek epic poet of the Imperial Roman era. He was a native of Panopolis (Akhmim) in the Egyptian Thebaid and probably lived in the 5th century AD. He i ...
and Cosmas
Cosmas or Kosmas is a Greek language, Greek name (), from Ancient Greek Κοσμᾶς (Kosmâs), associated with the noun κόσμος (kósmos), meaning "Cosmos, universe", and the verb κοσμέω (to order, govern, adorn) linked to propr ...
, where the Sporoi are the people Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
mentions as the ancestors of the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
.
Location
 The earliest classical mentions of the Bastarnae locate them north of the Lower Danube, although they apparently made frequent crossings impacting upon the peoples living south of the Danube.
Strabo (about 20 AD) made several remarks about the location of the Bastarnae. In one place he described the lands beyond the Rhine and Danube as the home of the Galatian (Celtic) and the Germanic peoples, and beyond these (to the east) were the Bastarnae and their neighbours the Tyregetans "and the River Borysthenes" (Dnieper). However, in another similar passage he says only that "most writers suspect" the Bastarnae to be next beyond the Germanic Peoples, but he indicates that it is also possible that "others lie in between, either the Iazyges, or the Roxolani, or certain other of the wagon-dwellers — it is not easy to say". In yet another similar passage he describes the Bastarnae as the most inland (northerly) of the peoples living between the Borysthenes (Dnieper) and the Ister (Lower Danube), and indicates that their neighbours the Tyregetans are closer to the Black Sea.
Strabo also mentioned their interactions with other peoples near the Danube, specifying that in his time, "wagon-dwelling" Scythians and Sarmatians, "as well as the Bastarnian tribes, are mingled with the Thracians (more indeed with those outside the Ister orth of the Danube but also with those inside). And mingled with them are also the Celtic tribes — the Boii, the Scordisci, and the Taurisci". He confirmed that historically "the Scythians and Bastarnians and Sauromatians on the far side of the river he Lower Danubeoften prevail to the extent that they actually cross over to attack those whom they have already driven out, and some of them remain there, either in the islands or in Thrace". In particular, Near the outlets of the Ister River ower Danubeis a great island called Peuce; and when the Bastarnians took possession of it they received the appellation of Peucini."
In one passage Pliny the Elder located the Bastarnae "and other Germanic peoples" in the lands beyond the Iazyges and Dacians (''aversa Basternae tenent aliique inde Germani''). In another he describes "the Peucini, the Basternae", as neighbours of the
The earliest classical mentions of the Bastarnae locate them north of the Lower Danube, although they apparently made frequent crossings impacting upon the peoples living south of the Danube.
Strabo (about 20 AD) made several remarks about the location of the Bastarnae. In one place he described the lands beyond the Rhine and Danube as the home of the Galatian (Celtic) and the Germanic peoples, and beyond these (to the east) were the Bastarnae and their neighbours the Tyregetans "and the River Borysthenes" (Dnieper). However, in another similar passage he says only that "most writers suspect" the Bastarnae to be next beyond the Germanic Peoples, but he indicates that it is also possible that "others lie in between, either the Iazyges, or the Roxolani, or certain other of the wagon-dwellers — it is not easy to say". In yet another similar passage he describes the Bastarnae as the most inland (northerly) of the peoples living between the Borysthenes (Dnieper) and the Ister (Lower Danube), and indicates that their neighbours the Tyregetans are closer to the Black Sea.
Strabo also mentioned their interactions with other peoples near the Danube, specifying that in his time, "wagon-dwelling" Scythians and Sarmatians, "as well as the Bastarnian tribes, are mingled with the Thracians (more indeed with those outside the Ister orth of the Danube but also with those inside). And mingled with them are also the Celtic tribes — the Boii, the Scordisci, and the Taurisci". He confirmed that historically "the Scythians and Bastarnians and Sauromatians on the far side of the river he Lower Danubeoften prevail to the extent that they actually cross over to attack those whom they have already driven out, and some of them remain there, either in the islands or in Thrace". In particular, Near the outlets of the Ister River ower Danubeis a great island called Peuce; and when the Bastarnians took possession of it they received the appellation of Peucini."
In one passage Pliny the Elder located the Bastarnae "and other Germanic peoples" in the lands beyond the Iazyges and Dacians (''aversa Basternae tenent aliique inde Germani''). In another he describes "the Peucini, the Basternae", as neighbours of the Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
.
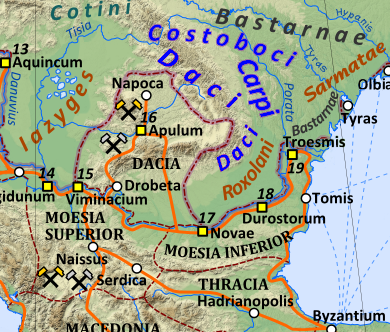
In the second century AD, the texts attached to Ptolemy's ''Geography'' say that "above Dacia are the Peucini and the Basternae"; "between the Peucini and the Basternae are the Carpiani"; "between the Basternae and the Rhoxolani" who he places on the Black Sea coast, "are the Chuni" (otherwise unknown); and "below the Basternae near Dacia are the Tigri and below these are the Tyrangitae" whose names are linked to the Tyras or Dniester river. Possibly relevant, he also mentioned a mountainous region called the "Peuca" mountains south of the Costoboci
The Costoboci (; , or Κιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dniester river, Dniester. During the Marcomannic Wars the Costoboci invaded the Roman Empire i ...
and Transmontani. The Sidones, named as one part of the Bastarnae by Strabo, are described by Ptolemy as one of the peoples east of the Vistula, although the location is not clear. It thus appears that the Bastarnae were settled in a vast arc stretching around the northern and eastern flanks of the Carpathians from western Ukraine to the Danube Delta.
The Peutinger Map (produced ca. 400 AD, but including material from as early as the first century) shows the Bastarnae (mis-spelt ''Blastarni'') north of the Carpathian mountains and appears to name the Galician Carpathians as the ''Alpes Bastarnicae''.
Because of their apparent cultural and linguistic connections to the west, the Bastarnae are generally believed to have moved originally from that direction, but this remains uncertain. Babeş and Shchukin argue in favour of an origin in eastern Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
on the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
coast of today's north-west Poland, on the grounds of correspondences in archaeological material, e.g. a Pomeranian-style fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
found in a Poieneşti site in Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
, although Batty considers the evidence insufficient. Babeş identifies the Sidoni, a branch of the Bastarnae which Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
mentionedStrabo VII.3.17 with the ''Sidini'' located by Ptolemy in Pomerania.
Batty argues that Greco-Roman sources of the first century AD locate the Bastarnae homeland on the northern side of the Northern Carpathian mountain range, encompassing south-east Poland and south-west Ukraine (i.e. the region traditionally known as Galicia).Batty (2008) 238
Ethno-linguistic affiliation
Scholars hold divergent theories about the ethnicity of the Bastarnae. One view, implied by some of the earliest reports, is that they spoke aCeltic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
. The only explicit description of their language, was a much later remark by Tacitus, who said they spoke a language like the Germanic peoples. However others hold that they were Scythian/Germanic, or mixed Germanic/Sarmatian. A fringe theory is that they were Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th ...
. Shchukin argues that the ethnicity of the Bastarnae was unique and rather than trying to label them as Celtic, Germanic or Sarmatian, it should be accepted that the "Basternae were the Basternae".Shchukin (1990), p. 10. Batty argues that assigning an "ethnicity" to the Bastarnae is meaningless; as in the context of the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
Pontic-Danubian region, with its multiple overlapping peoples and languages, ethnicity was a very fluid concept, which changed rapidly and frequently, according to socio-political vicissitudes. That was especially true of the Bastarnae, who are attested over a relatively-vast area. The Bastarnae maintained a separate name until ca. 300 AD, probably implying retention of their distinctive ethno-linguistic heritage up to that time.
Celtic
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
(200–118 BC) writing about the time of Perseus of Macedon
Perseus (; – 166 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 179 until 168BC. He is widely regarded as the last List of kings of Macedonia, king of Macedonia and the last ruler from th ...
(d. 166 BCE) explained how the Dardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
ans sought help from the Romans against the Bastarnae, who were allied with the Macedonian and Celtic (Galatian) enemies of Rome, which can be taken as implying that they were not Galatian. He described them as numerous, physically large, and valorous warriors.
On the other hand, a much later report of these events by Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
(64 BC – 17 AD), writing about 10 AD, is sometimes understood to imply that the Bastarnae spoke a Celtic language (or a related language) because when comparing them to the Scordisci
The Scordisci (; ) were an Iron Age cultural group who emerged after the Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe, and who were centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morav ...
, a major Galatian tribe of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
, it specifies that the Bastarnae were "neither in speech nor habits were they dissimilar". The Scordisci are described as Celtic by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, although he adds that they had mingled with Illyrians and Thracians).
Much later still, the Greek historian Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
(about 46-120 AD), also talking the time of Perseus of Macedon, went further, writing that the Roman consul Hostilius "secretly stirred up the Gauls settled along the Danube, who are called Basternae".
Another reason to consider the Bastarnae as Celtic is that the regions they are documented to have occupied (the northern and eastern slopes of the Carpathians) overlapped to a great extent with the locations of Celtic tribes attested in the northern Carpathians. (The modern name of this region, Galicia, is generally regarded as having a later origin, in either a Slavic or Turkic language. However, some scholars have instead suggested that the name Galicia may derive from its former Celtic inhabitants the Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici.
Et ...
, Osi, Cotini The Cotini, sometimes spelled Gotini (because it is found in some manuscript copies of Tacitus), were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland, and Slovakia.
The ...
and Anartes of Slovakia and northern Romania and the Britogalli of the Danube Delta region.) In addition, archaeological cultures which some scholars have linked to the Bastarnae (Poieneşti-Lukashevka and Zarubintsy) display pronounced Celtic affinities. Finally, the arrival of the Bastarnae in the Pontic-Danubian region, which can be dated to 233–216 BC according to two ancient sources,Batty (2008), 237. coincides with the latter phase of Celtic migration into the region (400–200 BC).
In addition, inscription AE (1905) 14, recording a campaign on the Hungarian Plain by the Augustan-era general Marcus Vinucius (10 BC or 8 BC), also appears to distinguish the Bastarnae from neighbouring Celtic tribes: "Marcus Vinucius... governor of Illyricum, the first oman general
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
to advance across the river Danube, defeated in battle and routed an army of Dacians and Basternae, and subjugated the Cotini, Osi,... issing tribal nameand Anartii to the power of the emperor Augustus and of the people of Rome."
The three names of Bastarnae leaders found in ancient sources are of Celtic origin: Cotto,Livy XL.57 ClondicusLivy XL.58 and Teutagonus.
Germanic
Three Greco-Roman geographers of the first century AD associated the Bastarnae and Peucini with theGermanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
, and one source, Tacitus, specifies that they spoke a language like the Germanic peoples. The Greek geographer Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
(64 BC – 24 AD) writing c. 5–20 AD, made several remarks about the location of the Bastarnae in his own time. In one passage he says that their country borders on that of the Tyregetans towards the Black Sea and Danube, and Germanic peoples to the west, and that they "one might say", were of "Germanic stock".
The Roman geographer Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
(c. 77 AD), classified the Bastarnae or Peucini as being one of the five main subdivisions of Germanic peoples, the other subdivisions as the three West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germ ...
groups, the ''Inguaeones'', ''Istuaeones'' and ''Hermiones'', and the East Germanic
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that eas ...
'' Vandili''.
Notably, the Roman historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
(56–120 AD), writing about 100 AD, described the Bastarnae as probably being a Germanic people, but with substantial Sarmatian cultural influence and intermarriage:TacituG.46
/ref> :As to the tribes of the Peucini, Veneti, and Fenni I am in doubt whether I should class them with the Germans or the Sarmatæ, although indeed the Peucini called by some Bastarnæ, are like Germans in their language, mode of life, and in the permanence of their settlements. They all live in filth and sloth, and by the intermarriages of the chiefs they are becoming in some degree debased into a resemblance to the Sarmatæ.
Scytho-Sarmatian
Strabo includes theRoxolani
The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( , ; ) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders of Roman Daci ...
, generally considered by scholars to have been a Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
tribe, in a list of Bastarnae subgroups. However, this may simply be an error due to the close proximity of the two peoples north of the Danube Delta.
In the third century, the Greek historian Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
(155–235 AD) stated that the "Bastarnae are properly classed as Scythians" and "members of the Scythian race".
:"During the same period in which these events occurred Marcus Crassus was sent into Macedonia and Greece and carried on war with the Dacians and Bastarnae. I have already stated who the former were and why they had become hostile; the Bastarnae, on the other hand, who are properly classed as Scythians, had at this time crossed the Ister and subdued the part of Moesia opposite them, and afterwards subdued the Triballi who adjoin this district and the Dardani who inhabit the Triballian country."
Likewise, the sixth-century historian Zosismus (490s–510 AD), reporting events around 280 AD, refers to "the Bastarnae, a Scythian people".Zosimus I.34
However, late Greco-Roman chroniclers used the term "Scythian" without regard to language. The earliest Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
were steppe nomads associated with Iranic languages, as were their successors the Sarmatians, who were also called Scythians, while classical authors such as Zosimus also routinely refers to the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
, who were undoubtedly Germanic-speakers, as "Scythians". On the other hand, it is likely that Bastarnae were influenced the surrounding Sarmatians, as reflected in Tacitus' comment that "mixed marriages" debasing them to appear more like the Sarmatians.
Material culture
According toMalcolm Todd
Malcolm Todd (27 November 19396 June 2013) was an English archaeologist. Born in Durham, England, the son of a miner, Todd was educated in classics and classical archaeology at St David's College, Lampeter and Brasenose College, Oxford. He s ...
, traditional archaeology has not been able to construct a typology of Bastarnae material culture, and thus to ascribe particular archaeological sites to the Bastarnae.Todd (2004) 23-4 A complicating factor is that the regions where Bastarnae are attested contained a patchwork of peoples and cultures (Sarmatians, Scythians, Dacians, Thracians, Celts, Germans and others), some sedentary, some nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic. In any event, post-1960s archaeological theory has questioned the validity of equating material "cultures", as defined by archaeologists, with distinct ethnic groups. In this view, it is impossible to attribute a "culture" to a particular ethnic group: it is likely that the material cultures discerned in the region belonged to several, if not all, of the groups inhabiting it. These cultures probably represent relatively large-scale socio-economic interactions between disparate communities of the broad region, possibly including mutually antagonistic groups.
It is not even certain whether the Bastarnae were sedentary, nomadic or semi-nomadic. Tacitus' statement that they were "German in their way of life and types of dwelling" implies a sedentary bias, but their close relations with the Sarmatians, who were nomadic, may indicate a more nomadic lifestyle for some Bastarnae, as does their attested wide geographical range.Todd (2004) 23 If the Bastarnae were nomadic, then the sedentary "cultures" identified by archaeologists in their ''lebensraum'' would not represent them. Nomadic peoples generally leave scant traces, due to the impermanent materials and foundations used in the construction of their dwellings.
Scholars have identified two closely related sedentary "cultures" as possible candidates to represent the Bastarnae (among other peoples) as their locations broadly correspond to where ancient sources placed the Basternae: the Zarubintsy culture lying in the forest-steppe zone in northern Ukraine and southern Belarus, and the Poieneşti-Lukashevka culture ( Lucăşeuca) in northern Moldavia. These cultures were characterised by agriculture, documented by numerous finds of sickles. Dwellings were either of surface or semi-subterranean types, with posts supporting the walls, a hearth in the middle and large conical pits located nearby. Some sites were defended by ditches and banks, structures thought to have been built to defend against nomadic tribes from the steppe. Inhabitants practiced cremation. Cremated remains were either placed in large, hand-made ceramic urns, or were placed in a large pit and surrounded by food and ornaments such as spiral bracelets and Middle to Late La Tène-type ''fibulae'' (attesting the continuing strength of Celtic influence in this region).
A major problem with associating the Poieneşti-Lukashevka and Zarubintsy cultures with the Bastarnae is that both cultures had disappeared by the early first century AD, while the Bastarnae continue to be attested in those regions throughout the Roman Principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
. Another issue is that the Poieneşti-Lukashevka culture has also been attributed to the Costoboci
The Costoboci (; , or Κιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dniester river, Dniester. During the Marcomannic Wars the Costoboci invaded the Roman Empire i ...
, a people considered ethnically Dacian by mainstream scholarship, who inhabited northern Moldavia, according to Ptolemy (ca. 140 AD). Indeed, Mircea Babeş and Silvia Theodor, the two Romanian archaeologists who identified Lukashevka as Bastarnic, nevertheless insisted that the majority of the population in the Lukashevka sphere (in northern Moldavia) was "Geto-Dacian". A further problem is that neither of these cultures were present in the Danube Delta region, where a major concentration of Bastarnae are attested by the ancient sources.
Starting in about 200 AD, the Chernyakhov culture became established in the modern-day western Ukraine and Moldova region inhabited by the Bastarnae. The culture is characterised by a high degree of sophistication in the production of metal and ceramic artefacts, as well as of uniformity over a vast area. Although this culture has conventionally been identified with the migration of the Gothic ''ethnos'' into the region from the northwest, Todd argues that its most important origin is Scytho-Sarmatian. Although the Goths certainly contributed to it, so probably did other peoples of the region such as the Dacians, proto-Slavs
The early Slavs were speakers of Indo-European languages, Indo-European dialects
who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Ea ...
, Carpi and possibly the Bastarnae.
Relations with Rome
Roman Republican era (to 30 BC)
Allies of Philip of Macedon (179–8 BC)
 The Bastarnae first appear in the historical record in 179 BC, when they crossed the Danube in a massive force. They did so at the invitation of their long-time ally, King
The Bastarnae first appear in the historical record in 179 BC, when they crossed the Danube in a massive force. They did so at the invitation of their long-time ally, King Philip V of Macedon
Philip V (; 238–179 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War (220–217 BC), Social War in Greece (220-217 BC) ...
, a direct descendant of Antigonus, one of the Diadochi
The Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterran ...
, the generals of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
who had shared his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Macedonian king had suffered a disastrous defeat at the hands of the Romans in the Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. ...
(200–197 BC), which had reduced him from a powerful Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
monarch to the status of a petty client-king with a much-reduced territory and a tiny army. After nearly 20 years of slavish adherence to the Roman Senate's dictats, Philip had been goaded by the incessant and devastating raiding of the Dardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
, a warlike Illyrian tribe on his northern border, which his treaty-limited army was too small to counter effectively. Counting on the Bastarnae, with whom he had forged friendly relations, he plotted a strategy to deal with the Dardani and then to regain his lost territories in Greece and his political independence. First, he would unleash the Bastarnae against the Dardani. After the latter had been crushed, Philip planned to settle Bastarnae families in Dardania (southern Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
/Skopje
Skopje ( , ; ; , sq-definite, Shkupi) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It lies in the northern part of the country, in the Skopje Basin, Skopje Valley along the Vardar River, and is the political, economic, and cultura ...
region) to ensure that the region was permanently subdued. In a second phase, Philip aimed to launch the Bastarnae on an invasion of Italy via the Adriatic coast. Although he was aware that the Bastarnae were likely to be defeated, Philip hoped that the Romans would be distracted long enough to allow him to reoccupy his former possessions in Greece.
However, Philip, now 60 years of age, died before the Bastarnae could arrive. The Bastarnae host was still ''en route'' through Thrace, where it became embroiled in hostilities with the locals, who had not provided them with sufficient food at affordable prices as they marched through. Probably in the vicinity of Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv, Bulgaria), the Bastarnae broke out of their marching columns and pillaged the land far and wide. The terrified local Thracians took refuge with their families and animal herds on the slopes of ''Mons Donuca'' ( Mount Musala), the highest mountain in Thrace. A large force of Bastarnae chased them up the mountain, but were driven back and scattered by a massive hailstorm. Then the Thracians ambushed them, turning their descent into a panic-stricken rout. Back at their wagon fort in the plain, around half of the demoralised Bastarnae decided to return home, leaving c. 30,000 to press on to Macedonia.
Philip's son and successor Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
, while protesting his loyalty to Rome, deployed his Bastarnae guests in winter quarters in a valley in Dardania, presumably as a prelude to a campaign against the Dardani the following summer. However, in the depths of winter their camp was attacked by the Dardani. The Bastarnae easily beat off the attackers, chased them back to their chief town and besieged them, but they were surprised in the rear by a second force of Dardani, which had approached their camp stealthily by mountain paths, and proceeded to storm and ransack it. Having lost their entire baggage and supplies, the Bastarnae were obliged to withdraw from Dardania and to return home. Most perished as they crossed the frozen Danube on foot, only for the ice to give way. Despite the failure of Philip's Bastarnae strategy, the suspicion aroused by these events in the Roman Senate, which had been warned by the Dardani of the Bastarnae invasion, ensured the demise of Macedonia as an independent state. Rome declared war on Perseus in 171 BC and after the Macedonian army was crushed at the Battle of Pydna
The Battle of Pydna took place in 168 BC between Rome and Macedon during the Third Macedonian War. The battle saw the further ascendancy of Rome in the Hellenistic world and the end of the Antigonid line of kings, whose power traced back ...
(168 BC), Macedonia was split up into four Roman puppet-cantons (167 BC). Twenty-one years later, these were in turn abolished and annexed to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
as the province of Macedonia (146 BC).
Allies of Getan high king Burebista (62 BC)
 The Bastarnae first came into direct conflict with Rome as a result of expansion into the lower Danube region by the
The Bastarnae first came into direct conflict with Rome as a result of expansion into the lower Danube region by the proconsuls
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military command, or ' ...
(governors) of Macedonia in 75–72 BC. Gaius Scribonius Curio (proconsul 75–73 BC) campaigned successfully against the Dardani and the Moesi
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; , ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the Timok River to the south of the Danube. The Moesi do ...
, becoming the first Roman general to reach the Danube with his army. His successor, Marcus Licinius Lucullus (brother of the famous Lucius Lucullus), campaigned against the Thracian Bessi tribe and the Moesi, ravaging the whole of Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
, the region between the Haemus (Balkan
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
) mountain range and the Danube. In 72 BC, his troops occupied the Greek coastal cities of Scythia Minor (modern Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
region, Romania/Bulgaria), which had sided with Rome's Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
arch-enemy, King Mithridates VI of Pontus, in the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies, dragging the entire east of th ...
(73–63 BC).
The presence of Roman forces in the Danube Delta was seen as a major threat by all the neighbouring transdanubian peoples: the Peucini Bastarnae, the Sarmatians and, most importantly, by Burebista (ruled 82–44 BC), king of the Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of informa ...
. The Getae occupied the region today called Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
as well as Scythia Minor and were either a Dacian- or Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
- speaking people. Burebista had unified the Getae tribes into a single kingdom, for which the Greek cities were vital trade outlets. In addition, he had established his hegemony over neighbouring Sarmatian and Bastarnae tribes. At its peak, the Getae kingdom reportedly was able to muster 200,000 warriors. Burebista led his transdanubian coalition in a struggle against Roman encroachment, conducting many raids against Roman allies in Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
and Thrace, penetrating as far as Macedonia and Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
.
The coalition's main chance came in 62 BC, when the Greek cities rebelled against Roman rule. In 61 BC, the notoriously oppressive and militarily incompetent proconsul of Macedonia, Gaius Antonius, nicknamed ''Hybrida'' ("The Monster"), an uncle of the famous Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
, led an army against the Greek cities. As his army approached Histria, Antonius detached his entire mounted force from the marching column and led it away on a lengthy excursion, leaving his infantry without cavalry cover, a tactic he had already used with disastrous results against the Dardani. Dio implies that he did so out of cowardice, in order to avoid the imminent clash with the opposition, but it is more likely that he was pursuing a large enemy cavalry force, probably Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
. A Bastarnae host, which had crossed the Danube to assist the Histrians, promptly attacked, surrounded and massacred the Roman infantry, capturing several of their '' vexilla'' (military standards). This battle resulted in the collapse of the Roman position on the lower Danube. Burebista apparently annexed the Greek cities (55–48 BC). At the same time, the subjugated "allied" tribes of Moesia and Thrace evidently repudiated their treaties with Rome, as they had to be reconquered by Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
in 29–8 BC (see below).
In 44 BC, Roman dictator-for-life Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
planned to lead a major campaign to crush Burebista and his allies once and for all, but he was assassinated before it could start. However, the campaign was made redundant by Burebista's overthrow and death in the same year, after which his Getae empire fragmented into four, later five, independent petty kingdoms. These were militarily far weaker, as Strabo assessed their combined military potential at just 40,000 armed men, and were often involved in internecine warfare. The Geto-Dacians did not again become a threat to Roman hegemony in the lower Danube until the rise of Decebal 130 years later (86 AD).
Roman Principate (30 BC – 284 AD)
Augustan era (30 BC – 14 AD)
 Once he had established himself as sole ruler of the Roman state in 30 BC, Caesar's grand-nephew and adopted son
Once he had established himself as sole ruler of the Roman state in 30 BC, Caesar's grand-nephew and adopted son Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
inaugurated a strategy of advancing the empire's south-eastern European border to the line of the Danube from the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern Europe, Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia ...
and Macedonia. The primary objective was to increase strategic depth between the border and Italy and also to provide a major fluvial supply route between the Roman armies in the region.
On the lower Danube, which was given priority over the upper Danube, this required the annexation of Moesia. The Romans' target was thus the tribes which inhabited Moesia, namely (from west to east) the Triballi, Moesi and those Getae who dwelt south of the Danube. The Bastarnae were also a target because they had recently subjugated the Triballi, whose territory lay on the southern bank of the Danube between the tributary rivers '' Utus'' (Vit) and '' Ciabrus'' (Tsibritsa), with their chief town at Oescus (Gigen, Bulgaria). In addition, Augustus wanted to avenge the defeat of Gaius Antonius at Histria 32 years before and to recover the lost military standards. These were held in a powerful fortress called Genucla (Isaccea, near modern Tulcea, Romania, in the Danube Delta region), controlled by Zyraxes, the local Getan king.Dio LI.26.5 The man selected for the task was Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a ancient Rome, Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome".Wallechinsky, Da ...
, grandson of Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome". Wallechinsky, David & Walla ...
the triumvir
In the Roman Republic, or were commissions of three men appointed for specific tasks. There were many tasks that commissions could be established to conduct, such as administer justice, mint coins, support religious tasks, or found colonies.
M ...
and an experienced general at 33 years of age, who was appointed proconsul of Macedonia in 29 BC.
The Bastarnae provided the ''casus belli'' by crossing the Haemus and attacking the Dentheletae
The Dentheletae (), also Danthaletae (Δανθαλῆται) or Denseletae, were a Thracian tribe that in antiquity lived near the sources of the River Strymon, and are mentioned in texts by Polybius, Cassius Dio, Tacitus and by Livy. They li ...
, a Thracian tribe who were Roman allies. Crassus marched to the Dentheletae's assistance, but the Bastarnae host hastily withdrew over the Haemus at his approach. Crassus followed them closely into Moesia but they would not be drawn into battle, withdrawing beyond the Tsibritsa. Crassus now turned his attention to the Moesi, his prime target. After a successful campaign which resulted in the submission of a substantial section of the Moesi, Crassus again sought out the Bastarnae. Discovering their location from some peace envoys they had sent to him, he lured them into battle near the Tsibritsa by a stratagem. Hiding his main body of troops in a wood, he stationed as bait a smaller vanguard in open ground before the wood. As expected, the Bastarnae attacked the vanguard in force, only to find themselves entangled in the full-scale pitched battle with the Romans that they had tried to avoid. The Bastarnae tried to retreat into the forest but were hampered by the wagon train carrying their women and children, as these could not move through the trees. Trapped into fighting to save their families, the Bastarnae were routed. Crassus personally killed their king, Deldo, in combat, a feat which qualified him for Rome's highest military honour, '' spolia opima'', but Augustus refused to award it on a technicality. Thousands of fleeing Bastarnae perished, many asphyxiated in nearby woods by encircling fires set by the Romans, others drowned trying to swim across the Danube. Nevertheless, a substantial force dug themselves into a powerful hillfort. Crassus laid siege to fort, but had to enlist the assistance of Rholes, a Getan petty king, to dislodge them, for which service Rholes was granted the title of ''socius et amicus populi Romani'' ("ally and friend of the Roman people").
The following year (28 BC), Crassus marched on Genucla. Zyraxes escaped with his treasure and fled over the Danube into Scythia to seek aid from the Bastarnae. Before he was able to bring reinforcements, Genucla fell to a combined land and fluvial assault by the Romans. The strategic result of Crassus' campaigns was the permanent annexation of Moesia by Rome.
About a decade later, in 10 BC, the Bastarnae again clashed with Rome during Augustus' conquest of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
(the ''bellum Pannonicum'' 14–9 BC). Inscription AE (1905) 14 records a campaign on the Hungarian Plain by the Augustan-era general Marcus Vinucius: Marcus Vinucius... atronymic Consul n 19 BC.. arious official titles governor of Illyricum, the firstMost likely, the Bastarnae, in alliance with Dacians, were attempting to assist the hard-pressed Illyrian/Celtic tribes of Pannonia in their resistance to Rome.oman general Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...to advance across the river Danube, defeated in battle and routed an army of Dacians and Basternae, and subjugated theCotini The Cotini, sometimes spelled Gotini (because it is found in some manuscript copies of Tacitus), were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland, and Slovakia. The ..., Osi,... issing tribal nameand Anartii to the power of the emperor Augustus and of the people of Rome.
First and second centuries
 It appears that in the final years of Augustus' rule, the Bastarnae made their peace with Rome. The ''
It appears that in the final years of Augustus' rule, the Bastarnae made their peace with Rome. The ''Res Gestae Divi Augusti
''Res Gestae Divi Augusti'' (Eng. ''The Deeds of the Divine Augustus'') is a monumental inscription composed by the first Roman emperor, Augustus, giving a first-person record of his life and accomplishments. The ''Res Gestae'' is especially sig ...
'' ("Acts of the divine Augustus", 14 AD), an inscription commissioned by Augustus to list his achievements, states that he received an embassy from the Bastarnae seeking a treaty of friendship. It appears that a treaty was concluded and apparently proved remarkably effective, as no hostilities with the Bastarnae are recorded in surviving ancient sources until c. 175, some 160 years after Augustus' inscription was carved. But surviving evidence for the history of this period is so thin that it cannot be excluded that the Bastarnae clashed with Rome during it. The Bastarnae participated in the Dacian Wars of Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a r ...
(86–88) and Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
(101–102 and 105–106), fighting on both wars on the Dacian side
In the late second century, the ''Historia Augusta'' mentions that in the rule of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
(161–180), an alliance of lower Danube tribes including the Bastarnae, the Sarmatian Roxolani and the Costoboci
The Costoboci (; , or Κιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dniester river, Dniester. During the Marcomannic Wars the Costoboci invaded the Roman Empire i ...
took advantage of the emperor's difficulties on the upper Danube (the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars () were a series of wars lasting from about AD 166 until 180. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against principally the Germanic peoples, Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts ...
) to invade Roman territory.
Third century
During the late second century, the main ethnic change in the northern Black Sea region was the immigration, from the Vistula valley in the North, of theGoths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
and accompanying Germanic tribes such as the Taifali
The Taifals or Tayfals ( or ''Theifali''; ) were a people of Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fragmented history, for the most part in associ ...
and the Hasdingi
The Hasdingi were one of the Vandal peoples of the Roman era. The Vandals were Germanic peoples, who are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language, and were first reported during the first centuries of the Roman empire in the area which i ...
, a branch of the Vandal
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal ...
people. This migration was part of a series of major population movements in the European ''barbaricum'' (the Roman term for regions outside their empire). The Goths appear to have established a loose political hegemony over the existing tribes in the region.
Under the leadership of the Goths, a series of major invasions of the Roman empire were launched by a grand coalition of lower Danubian tribes from c. 238 onwards. The participation of the Bastarnae in these is likely but largely unspecified, due to Zosimus' and other chroniclers' tendency to lump all these tribes under the general term "Scythians" – meaning all the inhabitants of Scythia, rather than the specific Iranic
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European langu ...
-speaking people called the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
. Thus, in 250–251, the Bastarnae were probably involved in the Gothic and Sarmatian invasions which culminated in the Roman defeat at the Battle of Abrittus and the slaying of Emperor Decius
Gaius Messius Quintus Trajanus Decius ( 201June 251), known as Trajan Decius or simply Decius (), was Roman emperor from 249 to 251.
A distinguished politician during the reign of Philip the Arab, Decius was proclaimed emperor by his troops a ...
(251). This disaster was the start of the Third Century Crisis of the Roman Empire, a period of military and economic chaos. At this critical moment, the Roman army was crippled by the outbreak of a second smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
pandemic, the plague of Cyprian
The Plague of Cyprian was a pandemic which afflicted the Roman Empire from about AD 249 to 262, or 251/2 to 270. The plague is thought to have caused widespread manpower shortages for food production and the Roman army, severely weakening the em ...
(251–70). The effects are described by Zosimus as even worse than the earlier Antonine plague (166–180), which probably killed 15–30% of the empire's inhabitants.
Taking advantage of Roman military disarray, a vast number of barbarian peoples overran much of the empire. The Sarmato-Gothic alliance of the lower Danube carried out major invasions of the Balkans region in 252, and in the periods 253–258 and 260–268. The Peucini Bastarnae are specifically mentioned in the 267/268 invasion, when the coalition built a fleet in the estuary of the river ''Tyras'' (Dniester
The Dniester ( ) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and then through Moldova (from which it more or less separates the breakaway territory of Transnistria), finally discharging into the Black Sea on Uk ...
). The Peucini Bastarnae would have been critical to this venture since, as coastal and delta dwellers, they would have had seafaring experience that the nomadic Sarmatians and Goths lacked. The barbarians sailed along the Black Sea coast to Tomis in Moesia Inferior, which they tried to take by assault without success. They then attacked the provincial capital Marcianopolis (Devnya, Bulgaria), also in vain. Sailing on through the Bosporus
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait ( ; , colloquially ) is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental bo ...
, the expedition laid siege to Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
in Macedonia. Driven off by Roman forces, the coalition host moved overland into Thracia, where finally it was crushed by Emperor Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – August/September 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Batt ...
(r. 268–270) at Naissus (269).
Claudius II was the first of a sequence of military emperors (the so-called " Illyrian emperors" from their main ethnic origin) who restored order in the empire in the late third century. These emperors followed a policy of large-scale resettlement within the empire of defeated barbarian tribes, granting them land in return for an obligation of military service much heavier than the usual conscription quota. The policy had the triple benefit, from the Roman point of view, of weakening the hostile tribe, repopulating the plague-ravaged frontier provinces (bringing their abandoned fields back into cultivation) and providing a pool of first-rate recruits for the army. It could also be popular with the barbarian prisoners, who were often delighted by the prospect of a land grant within the empire. In the fourth century, such communities were known as '' laeti''.
The emperor Probus Probus may refer to:
People
* Marcus Valerius Probus (c. 20/30–105 AD), Roman grammarian
* Marcus Pomponius Maecius Probus, consul in 228
* Probus (emperor), Roman Emperor (276–282)
* Probus of Byzantium (–306), Bishop of Byzantium from 293 t ...
(r. 276–282) is recorded as resettling 100,000 Bastarnae in Moesia, in addition to other peoples, including Goths, Gepids and Vandals. The Bastarnae are reported to have honoured their oath of allegiance to the emperor, while the other resettled peoples mutinied while Probus was distracted by usurpation attempts and ravaged the Danubian provinces far and wide. A further massive transfer of Bastarnae was carried out by Emperor Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
(ruled 284–305) after he and his colleague Galerius
Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; Greek: Γαλέριος; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. He participated in the system of government later known as the Tetrarchy, first acting as '' caesar'' under Emperor Diocletian. In th ...
defeated a coalition of Bastarnae and Carpi in 299.
Later Roman empire (305 onwards)
The remaining transdanubian Bastarnae disappear into historical obscurity in the late empire. Neither of the main ancient sources for this period,Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
and Zosimus Zosimus, Zosimos, Zosima or Zosimas may refer to:
People
*
* Rufus and Zosimus (died 107), Christian saints
* Zosimus (martyr) (died 110), Christian martyr who was executed in Umbria, Italy
* Zosimos of Panopolis, also known as ''Zosimus Alch ...
, mention the Bastarnae in their accounts of the fourth century, possibly implying the loss of their separate identity, presumably assimilated by the regional hegemons, the Goths. Such assimilation would have been facilitated if, as is possible, the Bastarnae spoke an East Germanic
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that eas ...
language closely related to Gothic. If the Bastarnae remained an identifiable group, it is highly likely that they participated in the vast Gothic-led migration, driven by Hunnic pressure, that was admitted into Moesia by Emperor Valens
Valens (; ; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the Byzantine Empire, eastern half of the Roman Em ...
in 376 and eventually defeated and killed Valens at Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
in 378. Although Ammianus refers to the migrants collectively as "Goths", he states that, in addition, "Taifali and other tribes" were involved.
However, after a gap of 150 years, there is a final mention of Bastarnae in the mid-5th century. In 451, the Hunnic leader Attila
Attila ( or ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central Europe, C ...
invaded Gaul with a large army which was ultimately routed at the Battle of Châlons by a Roman-led coalition under the general Aetius. Attila's host, according to Jordanes
Jordanes (; Greek language, Greek: Ιορδάνης), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat, claimed to be of Goths, Gothic descent, who became a historian later in life.
He wrote two works, one on R ...
, included contingents from the "innumerable tribes that had been brought under his sway". This included the Bastarnae, according to the Gallic nobleman Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Born into the Gallo-Roman aristocracy, he was son-in-law to Emperor Avitus and was appointed Urb ...
.Sidonius ''Carmina'' 7.341 However, E.A. Thompson argues that Sidonius' mention of Bastarnae at Chalons is probably false: his purpose was to write a panegyric
A panegyric ( or ) is a formal public speech or written verse, delivered in high praise of a person or thing. The original panegyrics were speeches delivered at public events in ancient Athens.
Etymology
The word originated as a compound of - ' ...
and not a history, and Sidonius added some spurious names to the list of real participants (e.g. Burgundians
The Burgundians were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Roman Gaul, Gaul. In the first and seco ...
, Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the ...
and Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
) for dramatic effect.Thompson (1996) 149
See also
* Carpathian Tumuli culture * Tiberius Plautius Silvanus Aelianus *List of Germanic tribes
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* List of Celtic tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a la ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
Modern
* * Babeş, Mircea: ''Noi date privind arheologia şi istoria bastarnilor'' in SCIV 20 (1969) 195–218 * Barrington (2000): ''Atlas of the Greek and Roman World'' * Batty, Roger (2008): ''Rome and the Nomads: the Pontic-Danubian region in Antiquity'' * * Crişan, Ion (1978): ''Burebista and his Time'' * Faliyeyev, Alexander (2007): ''Dictionary of Continental Celtic Placenames'' (online) * Goldsworthy, Adrian (2000): ''Roman Warfare'' * * * Heather, Peter (2009): ''Empires and Barbarians'' * * Jones, A.H.M. (1964): ''Later Roman Empire'' * Köbler, Gerhard (2000): ''Indo-Germanisches Wörterbuch'' (online) * Müllenhoff, Karl (1887): ''Deutsche altertumskunde'' (vol. II) * * * Thompson, E.A. (1996): ''The Huns'' * Todd, Malcolm (2004): ''The early Germans'' * O. N. Trubačev (1999): ''INDOARICA в Северном Причерноморье'' * * * Wolfram, Herwig (1988): ''History of the Goths''Ancient
* ''Res Gestae Divi Augusti
''Res Gestae Divi Augusti'' (Eng. ''The Deeds of the Divine Augustus'') is a monumental inscription composed by the first Roman emperor, Augustus, giving a first-person record of his life and accomplishments. The ''Res Gestae'' is especially sig ...
'' (c. 14 AD)
* Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
''Res Gestae'' (c. 395 AD)
* Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
''Roman History'' (c. 230 AD)
* Eutropius ''Historiae Romanae Breviarium'' (c. 360 AD)
* Anonymous ''Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, Caesar (title), designated heirs and Roman usurper, usurpers from 117 to 284. S ...
'' (c. 400 AD)
* Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' (; 'from the founding of Rome, founding of the City'), or (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is ...
'' (c. 20 BC)
* Jordanes
Jordanes (; Greek language, Greek: Ιορδάνης), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat, claimed to be of Goths, Gothic descent, who became a historian later in life.
He wrote two works, one on R ...
''Getica
''De origine actibusque Getarum'' (''The Origin and Deeds of the Getae''), commonly abbreviated ''Getica'' (), written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the ori ...
'' (c. 550 AD)
* Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
''Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work' ...
'' (c. 70 AD)
* Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
'' Geographia'' (c. 140)
* Sextus Aurelius Victor ''De Caesaribus'' (c. 380 AD)
* Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Born into the Gallo-Roman aristocracy, he was son-in-law to Emperor Avitus and was appointed Urb ...
''Carmina'' (late fifth century AD)
* Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st cen ...
'' (c. 10 AD)
* Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
''Annales
Annals are a concise form of historical writing which record events chronologically, year by year. The equivalent word in Latin and French is ''annales'', which is used untranslated in English in various contexts.
List of works with titles contai ...
'' (c. 100 AD)
* Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
'' (c. 100 AD)
* Zosimus Zosimus, Zosimos, Zosima or Zosimas may refer to:
People
*
* Rufus and Zosimus (died 107), Christian saints
* Zosimus (martyr) (died 110), Christian martyr who was executed in Umbria, Italy
* Zosimos of Panopolis, also known as ''Zosimus Alch ...
''Historia Nova'' (c. 500 AD)
{{EB1911 poster, Bastarnae
Historical Celtic peoples
Early Germanic peoples
Wars involving the Roman Republic
Wars involving the Roman Empire
Hellenistic-era tribes in the Balkans
Ancient tribes in Dacia
Hellenistic Thrace
Antigonid Macedonia