Peripheral Administration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
Citing: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000
 Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by gastric feeding tube or
Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by gastric feeding tube or  The
The
 The parenteral route is any route that is not
The parenteral route is any route that is not  * Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical
* Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical  * Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for
* Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for
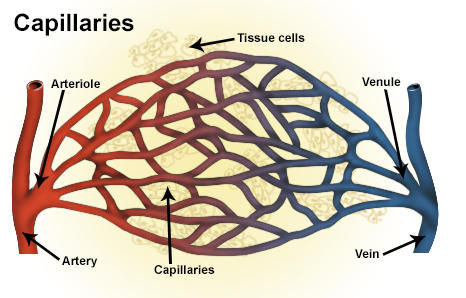

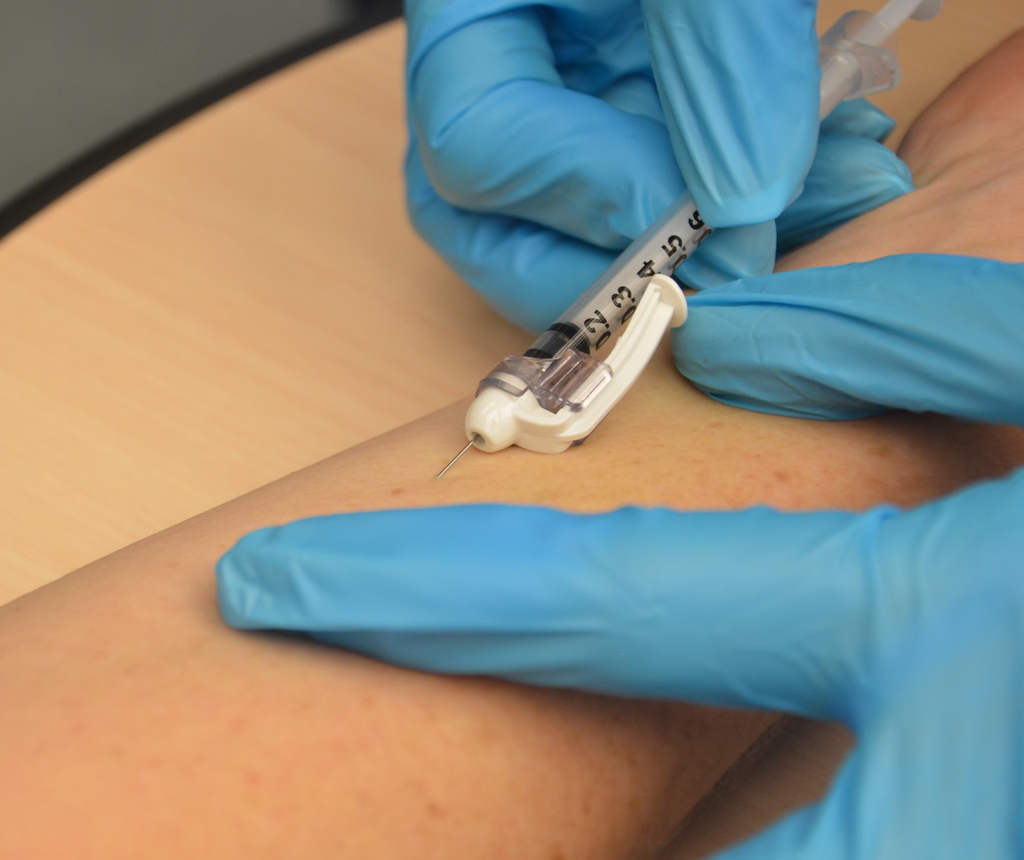 The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous (SC) and Intradermal injection, intradermal (ID) administration.
Parenteral administration generally acts more rapidly than topical or enteral administration, with onset of action often occurring in 15–30 seconds for IV, 10–20 minutes for IM and 15–30 minutes for SC. They also have essentially 100% bioavailability and can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed or ineffective when they are given orally. Some medications, such as certain antipsychotics, can be administered as depot injection, long-acting intramuscular injections. Ongoing IV infusions can be used to deliver continuous medication or IV fluid, fluids.
Disadvantages of injections include potential pain or discomfort for the patient and the requirement of trained staff using aseptic techniques for administration. However, in some cases, patients are taught to self-inject, such as SC injection of insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As the drug is delivered to the site of action extremely rapidly with IV injection, there is a risk of drug overdose, overdose if the dose has been calculated incorrectly, and there is an increased risk of side effects if the drug is administered too rapidly.
The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous (SC) and Intradermal injection, intradermal (ID) administration.
Parenteral administration generally acts more rapidly than topical or enteral administration, with onset of action often occurring in 15–30 seconds for IV, 10–20 minutes for IM and 15–30 minutes for SC. They also have essentially 100% bioavailability and can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed or ineffective when they are given orally. Some medications, such as certain antipsychotics, can be administered as depot injection, long-acting intramuscular injections. Ongoing IV infusions can be used to deliver continuous medication or IV fluid, fluids.
Disadvantages of injections include potential pain or discomfort for the patient and the requirement of trained staff using aseptic techniques for administration. However, in some cases, patients are taught to self-inject, such as SC injection of insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As the drug is delivered to the site of action extremely rapidly with IV injection, there is a risk of drug overdose, overdose if the dose has been calculated incorrectly, and there is an increased risk of side effects if the drug is administered too rapidly.
 Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with inhaler devices is necessary to achieve the correct dose. Some medications can have an unpleasant taste or irritate the mouth.
In general, only 20–50% of the pulmonary-delivered dose rendered in powdery particles will be deposited in the lung upon mouth inhalation. The remainder of 50-70% undeposited aerosolized particles are cleared out of lung as soon as exhalation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is >8 μm is structurally predisposed to depositing in the central and conducting airways (conducting zone) by inertial impaction.
An inhaled powdery particle that is between 3 and 8 μm in diameter tend to largely deposit in the Transitional zone (lung), transitional zones of the lung by sedimentation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is <3 μm in diameter is structurally predisposed to depositing primarily in the respiratory regions of the peripheral lung via diffusion.
Particles that deposit in the upper and central airways are generally absorbed systemically to great extent because they are only partially removed by mucociliary clearance, which results in orally mediated absorption when the transported mucus is swallowed, and first pass metabolism or incomplete absorption through loss at the fecal route can sometimes reduce the bioavailability. This should in no way suggest to clinicians or researchers that inhaled particles are not a greater threat than swallowed particles, it merely signifies that a combination of both methods may occur with some particles, no matter the size of or lipo/hydrophilicity of the different particle surfaces.
Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with inhaler devices is necessary to achieve the correct dose. Some medications can have an unpleasant taste or irritate the mouth.
In general, only 20–50% of the pulmonary-delivered dose rendered in powdery particles will be deposited in the lung upon mouth inhalation. The remainder of 50-70% undeposited aerosolized particles are cleared out of lung as soon as exhalation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is >8 μm is structurally predisposed to depositing in the central and conducting airways (conducting zone) by inertial impaction.
An inhaled powdery particle that is between 3 and 8 μm in diameter tend to largely deposit in the Transitional zone (lung), transitional zones of the lung by sedimentation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is <3 μm in diameter is structurally predisposed to depositing primarily in the respiratory regions of the peripheral lung via diffusion.
Particles that deposit in the upper and central airways are generally absorbed systemically to great extent because they are only partially removed by mucociliary clearance, which results in orally mediated absorption when the transported mucus is swallowed, and first pass metabolism or incomplete absorption through loss at the fecal route can sometimes reduce the bioavailability. This should in no way suggest to clinicians or researchers that inhaled particles are not a greater threat than swallowed particles, it merely signifies that a combination of both methods may occur with some particles, no matter the size of or lipo/hydrophilicity of the different particle surfaces.
The 10th US-Japan Symposium on Drug Delivery Systems
* [https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/FormsSubmissionRequirements/ElectronicSubmissions/DataStandardsManualmonographs/ucm071666.htm FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Dosage Form.]
A.S.P.E.N. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Route Of Administration Drugs Pharmacokinetics Routes of administration,
pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
and toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating ex ...
, a route of administration is the way by which a drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
and intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
(local), enteral
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
(system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
), or parenteral
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
(systemic action, but is delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products presented in a specific form for use. They contain a mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients), configured in a particular way (such as a capsule she ...
are aspects of drug delivery
Drug delivery involves various methods and technologies designed to transport pharmaceutical compounds to their target sites helping therapeutic effect. It involves principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specif ...
.
Classification
Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather a matter ofpharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific su ...
(concerning the processes of uptake, distribution, and elimination of drugs). Exceptions include the transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointm ...
or transmucosal routes, which are still commonly referred to as ''routes of administration''.
The location of the target effect of active substances is usually rather a matter of pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or comb ...
(concerning, for example, the physiological effects of drugs). An exception is topical administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
, which generally means that both the application location and the effect thereof is local.
Topical administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
is sometimes defined as both a local application location and local pharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or comb ...
effect, and sometimes merely as a local application location regardless of location of the effects.thefreedictionary.com > topicalCiting: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000
By application location
Enteral/gastrointestinal route
Through thegastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
is sometimes termed ''enteral or enteric administration'' (literally meaning 'through the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
'). ''Enteral/enteric administration'' usually includes ''oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
'' (through the mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
) and ''rectal
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces te ...
'' (into the rectum
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces temporarily. The adult ...
) administration, in the sense that these are taken up by the intestines. However, uptake of drugs administered orally may also occur already in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, and as such ''gastrointestinal'' (along the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
) may be a more fitting term for this route of administration. Furthermore, some application locations often classified as ''enteral'', such as sublingual
Sublingual (List of abbreviations used in medical prescriptions, abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through Tissue (biology), t ...
(under the tongue) and sublabial or buccal (between the cheek and gums/gingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the ...
), are taken up in the proximal part of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
without reaching the intestines. Strictly enteral administration (directly into the intestines) can be used for systemic administration, as well as local (sometimes termed topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
), such as in a contrast enema
An enema, also known as a clyster, is the rectal administration of a fluid by injection into the Large intestine, lower bowel via the anus.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word ''enema'' can also refer to the ...
, whereby contrast media are infused into the intestines for imaging. However, for the purposes of classification based on location of effects, the term enteral is reserved for substances with systemic effects.
 Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by gastric feeding tube or
Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by gastric feeding tube or gastrostomy
A gastrostomy is the creation of an artificial external opening into the stomach for nutritional support or gastric decompression.
Typically this would include an incision in the patient's epigastrium as part of a formal operation. When originall ...
. Substances may also be placed into the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
s, as with a duodenal feeding tube and enteral nutrition
Enteral administration is food or pharmaceutical drug#Administration, drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occu ...
. Enteric coated tablets are designed to dissolve in the intestine, not the stomach, because the drug present in the tablet causes irritation in the stomach.
 The
The rectal
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces te ...
route is an effective route of administration for many medications, especially those used at the end of life. The walls of the rectum absorb many medications quickly and effectively. Medications delivered to the distal one-third of the rectum at least partially avoid the "first pass effect
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism at a specific location in the body which leads to a reduction in the concentration of the active drug before it reaches the ...
" through the liver, which allows for greater bio-availability of many medications than that of the oral route. Rectal mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
is highly vascularized
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting an ...
tissue that allows for rapid and effective absorption of medications. A suppository
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver pharmaceutical drug, medications by insertion into a body orifice (any opening in the body), where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, eac ...
is a solid dosage form
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products presented in a specific form for use. They contain a mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients), configured in a particular way (such as a capsule she ...
that fits for rectal administration
Rectal administration (colloquially known as boofing or plugging) uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum's blood vessels,The rectum has numerous blood vessels available to a ...
. In hospice care
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life b ...
, a specialized rectal catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
, designed to provide comfortable and discreet administration of ongoing medications provides a practical way to deliver and retain liquid formulations in the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
rectum, giving health practitioners a way to leverage the established benefits of rectal administration. The Murphy drip is an example of rectal infusion.
Parenteral route
 The parenteral route is any route that is not
The parenteral route is any route that is not enteral
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
('' par-'' + ''enteral'').
Parenteral administration can be performed by injection
Injection or injected may refer to:
Science and technology
* Injective function, a mathematical function mapping distinct arguments to distinct values
* Injection (medicine), insertion of liquid into the body with a syringe
* Injection, in broadca ...
, that is, using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug admini ...
) and a syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
, or by the insertion of an indwelling catheter.
Locations of application of parenteral administration include:
* Central nervous system:
:* Epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, "upon" + '' dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians ...
(synonym: peridural) (injection or infusion into the epidural space
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae ( spine).
The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "e ...
), e.g. epidural anesthesia.
:* Intracerebral (into the cerebrum) administration by direct injection into the brain. Used in experimental research of chemicals and as a treatment for malignancies of the brain. The intracerebral route can also interrupt the blood brain barrier from holding up against subsequent routes.
:* Intracerebroventricular (into the cerebral ventricles) administration into the ventricular system of the brain. One use is as a last line of opioid treatment for terminal cancer patients with intractable cancer pain
Pain in cancer may arise from a tumor compressing or infiltrating nearby body parts; from treatments and diagnostic procedures; or from skin, nerve and other changes caused by a hormone imbalance or immune response. Most chronic (long-lasting) pai ...
.
 * Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical
* Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sense, sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. ...
, as well as systemic effects when the active substance diffuses through skin in a transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointm ...
route.
*Sublingual and buccal medication administration is a way of giving someone medicine orally (by mouth). Sublingual administration
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
Many drugs are absorbed through sublingual a ...
is when medication is placed under the tongue to be absorbed by the body. The word "sublingual" means "under the tongue." Buccal administration involves placement of the drug between the gums and the cheek. These medications can come in the form of tablets, films, or sprays. Many drugs are designed for sublingual administration, including cardiovascular drugs, steroids, barbiturates, opioid analgesics with poor gastrointestinal bioavailability, enzymes and, increasingly, vitamins and minerals.
* Extra-amniotic administration Extra-amniotic administration is a route of administration to the space between the fetal membranes and endometrium inside the uterus of a pregnant woman.
It can be used to administer drugs affecting uterus motility, such as oxytocin and prostagl ...
, between the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ...
and fetal membranes
The fetal membranes are the four extraembryonic membranes, associated with the developing embryo, and fetus in humans and other mammals. They are the amnion, chorion, allantois, and yolk sac. The amnion and the chorion are the chorioamniotic ...
.
* Nasal administration
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs thus locally delivered ...
(through the nose) can be used for topically acting substances, as well as for insufflation
In religious and magical practice, insufflation and exsufflation are ritual acts of blowing, breathing, hissing, or puffing that signify variously expulsion or renunciation of evil or of the devil (the Evil One), or infilling or blessing with go ...
of e.g. decongestant
A decongestant, or nasal decongestant, is a type of pharmaceutical drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion in the upper respiratory tract. The active ingredient in most decongestants is either pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine (the latter o ...
nasal sprays to be taken up along the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
. Such substances are also called ''inhalational'', e.g. inhalational anesthetics.
* Intra-arterial (into an artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
), e.g. vasodilator
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wal ...
drugs in the treatment of vasospasm
Vasospasm refers to a condition in which an arterial spasm leads to vasoconstriction. This can lead to tissue ischemia (insufficient blood flow) and tissue death (necrosis).
Along with physical resistance, vasospasm is a main cause of ischemi ...
and thrombolytic drug
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism (massive pu ...
s for treatment of embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (air embolism, gas embolism), amniotic ...
.
* Intra-articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two o ...
, into a joint space. It is generally performed by joint injection. It is mainly used for symptomatic relief in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
.
* Intracardiac (into the heart), e.g. adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure used during Cardiac arrest, cardiac or Respiratory arrest, respiratory arrest that involves chest compressions, often combined with artificial ventilation, to preserve brain function ...
(no longer commonly performed).
* Intracavernous injection
An intracavernous (or intracavernosal) injection is an injection into the base of the penis. This injection site is often used to administer medications to check for or treat erectile dysfunction in adult men (in, for example, a combined intrac ...
, an injection into the base of the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
.
* Intradermal
Intradermal injection (also intracutaneous or intradermic, abbreviated as ID) is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. For certain substances, administration ...
, (into the skin itself) is used for skin testing some allergens
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
, and also for mantoux test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening (medicine), screening for tuberculosis, tuberculo ...
for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
.
* Intralesional (into a skin lesion), is used for local skin lesions, e.g. acne medication.
* Intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles hav ...
(into a muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
), e.g. many vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s, antibiotics, and long-term psychoactive agents. Recreationally the colloquial term 'muscling' is used.
 * Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for
* Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
or eye neoplasm
An eye neoplasm is a tumor of the eye. A rare type of tumor, eye neoplasms can affect all parts of the eye, and can either be benign or malignant (cancerous), in which case it is known as eye cancer. Eye cancers can be primary (starts within the e ...
s.
* Intraosseous infusion (into the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
marrow) is, in effect, an indirect intravenous access because the bone marrow drains directly into the venous system. This route is occasionally used for drugs and fluids in emergency medicine and pediatrics when intravenous access is difficult.
* Intraperitoneal
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothe ...
, (infusion or injection into the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
) e.g. peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of kidney dialysis, dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct e ...
.
* Intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space (sin. ''intrathecal space'') so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is useful in several applic ...
(into the spinal canal) is most commonly used for spinal anesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
and chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
.
* Intrauterine.
* Intravaginal administration
Intravaginal administration is a route of administration where the substance is applied inside the vagina. Pharmacologically, it has the potential advantage to result in effects primarily in the vagina or nearby structures (such as the vaginal po ...
, in the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
.
* Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
(into a vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
), e.g. many drugs, total parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN), or intravenous feeding, is the feeding of nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by pharmaceutical compounding entities or standard pha ...
.
* Intravesical
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensi ...
infusion is into the urinary bladder.
* Intravitreal, through the eye.
* Subcutaneous (under the skin). This generally takes the form of subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and ...
, e.g. with insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
. Skin popping
Skin popping is a route of administration of street drugs where they are injected or deposited under the skin. It is usually a depot injection, either subcutaneous or intradermal, and not an intramuscular injection. After deposition, the drug t ...
is a slang term that includes subcutaneous injection, and is usually used in association with recreational drugs
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or plea ...
. In addition to injection, it is also possible to slowly infuse fluids subcutaneously in the form of hypodermoclysis.
* Transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointm ...
(diffusion through the intact skin for systemic rather than topical distribution), e.g. transdermal patch
A transdermal patch is a medicated adhesive patch that is placed on the skin to deliver a specific Dose (biochemistry), dose of medication through the skin and into the bloodstream. An advantage of a transdermal drug delivery route over ot ...
es such as fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
in pain therapy, nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
patches for treatment of Substance use disorder, addiction and Glyceryl trinitrate (pharmacology), nitroglycerine for treatment of angina pectoris.
* Perivascular administration (perivascular medical devices and perivascular drug delivery systems are conceived for local application around a blood vessel during open vascular surgery).
* Transmucosal (diffusion through a mucous membrane), e.g. insufflation
In religious and magical practice, insufflation and exsufflation are ritual acts of blowing, breathing, hissing, or puffing that signify variously expulsion or renunciation of evil or of the devil (the Evil One), or infilling or blessing with go ...
(snorting) of cocaine, sublingual, i.e. under the tongue, Sublabial route of administration, sublabial, i.e. between the lips and gingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the ...
, and oral spray or vaginal suppository for nitroglycerine.
Topical route
The definition of the topical route of administration sometimes states that both the application location and thepharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or comb ...
effect thereof is local.
In other cases, ''topical'' is defined as applied to a localized area of the body or to the surface of a body part regardless of the location of the effect. By this definition, topical administration also includes transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointm ...
application, where the substance is administered onto the skin but is absorption (skin), absorbed into the body to attain systemic administration, systemic distribution.
If defined strictly as having local effect, the topical route of administration can also include enteral administration of medications that are poorly absorbable by the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
. One such medication is the antibiotic vancomycin, which cannot be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and is used orally only as a treatment for Clostridioides difficile colitis, ''Clostridioides difficile'' colitis.
Choice of routes
The reason for choice of routes of drug administration are governing by various factors: * Physical and chemical properties of the drug. The physical properties are solid, liquid and gas. The chemical properties are solubility, stability, pH, irritancy etc. * Site of desired action: the action may be localised and approachable or generalised and not approachable. * Rate of extent of absorption of the drug from different routes. * Effect of digestive juices and the first pass metabolism of drugs. * Condition of the patient. In acute situations, in emergency medicine and intensive care medicine, drugs are most often given intravenously. This is the most reliable route, as in acutely ill patients the absorption of substances from the tissues and from the digestive tract can often be unpredictable due to altered blood flow or bowel motility.Convenience
Enteral routes are generally the most convenient for the patient, as no punctures or sterile technique, sterile procedures are necessary. Enteral medications are therefore often preferred in the treatment of chronic disease. However, some drugs can not be used enterally because their absorption in the digestive tract is low or unpredictable. Transdermal administration is a comfortable alternative; there are, however, only a few drug preparations that are suitable for transdermal administration.Desired target effect
Identical drugs can produce different results depending on the route of administration. For example, some drugs are not significantly absorbed into the bloodstream from the gastrointestinal tract and their action after enteral administration is therefore different from that after parenteral administration. This can be illustrated by the action of naloxone (Narcan), an antagonist of opiates such as morphine. Naloxone counteracts opiate action in the central nervous system when given intravenously and is therefore used in the treatment of opiate overdose. The same drug, when swallowed, acts exclusively on the bowels; it is here used to treat constipation under opiate pain therapy and does not affect the pain-reducing effect of the opiate.Oral
The oral route is generally the most convenient and costs the least. However, some drugs can causegastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
irritation. For drugs that come in delayed release (pharmacology), delayed release or Time Release Capsule, time-release formulations, breaking the tablets or capsules can lead to more rapid delivery of the drug than intended. The oral route is limited to Formulation#Pharmacy, formulations containing small molecules only while biopharmaceuticals (usually proteins) would be digested in the stomach and thereby become ineffective. Biopharmaceuticals have to be given by injection or infusion. However, recent research found various ways to improve oral bioavailability of these drugs. In particular permeation enhancers, ionic liquids, lipid-based nanocarriers, enzyme inhibitors and microneedles have shown potential.
Oral administration is often denoted "PO" from "per os", the Latin for "by mouth".
The bioavailability of oral administration is affected by the amount of drug that is absorbed across the intestinal epithelium and first-pass metabolism.
Oral mucosal
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth.Buccal
Buccal administration, Buccally administered medication is achieved by placing the drug between gums and the inner lining of the cheek. In comparison with sublingual tissue, buccal tissue is less permeable resulting in slower Absorption (pharmacology), absorption.Sublabial
Sublingual
Sublingual administration
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
Many drugs are absorbed through sublingual a ...
is fulfilled by placing the drug between the tongue and the lower surface of the mouth. The sublingual mucosa is highly permeable and thereby provides access to the underlying expansive network composed of capillaries, leading to rapid drug absorption.
Intranasal
Drug administration via the nasal cavity yields rapid drug absorption and therapeutic effects. This is because drug absorption through the nasal passages does not go through the gut before entering capillaries situated at tissue cells and then systemic circulation and such absorption route allows transport of drugs into the central nervous system via the pathways of olfactory and trigeminal nerve. Intranasal absorption features low lipophilicity, enzymatic degradation within the nasal cavity, large molecular size, and rapid mucociliary clearance from the nasal passages, which explains the low bioavailability, risk of systemic exposure of the administered drug absorbed via intranasal.
Local
By delivering drugs almost directly to the site of action, the risk of systemic adverse effect, side effects is reduced. Skin absorption (dermal absorption), for example, is to directly deliver drug to the skin and, hopefully, to the systemic circulation. However, skin irritation may result, and for some forms such as creams or lotions, the dosage is difficult to control. Upon contact with the skin, the drug penetrates into the dead stratum corneum and can afterwards reach the viable epidermis, the dermis, and the blood vessels.Parenteral
The term parenteral is from para-1 'beside' + Greek enteron 'intestine' + -al. This name is due to the fact that it encompasses a route of administration that is not intestinal. However, in common English the term has mostly been used to describe the four most well-known routes of injection. The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous (SC) and Intradermal injection, intradermal (ID) administration.
Parenteral administration generally acts more rapidly than topical or enteral administration, with onset of action often occurring in 15–30 seconds for IV, 10–20 minutes for IM and 15–30 minutes for SC. They also have essentially 100% bioavailability and can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed or ineffective when they are given orally. Some medications, such as certain antipsychotics, can be administered as depot injection, long-acting intramuscular injections. Ongoing IV infusions can be used to deliver continuous medication or IV fluid, fluids.
Disadvantages of injections include potential pain or discomfort for the patient and the requirement of trained staff using aseptic techniques for administration. However, in some cases, patients are taught to self-inject, such as SC injection of insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As the drug is delivered to the site of action extremely rapidly with IV injection, there is a risk of drug overdose, overdose if the dose has been calculated incorrectly, and there is an increased risk of side effects if the drug is administered too rapidly.
The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous (SC) and Intradermal injection, intradermal (ID) administration.
Parenteral administration generally acts more rapidly than topical or enteral administration, with onset of action often occurring in 15–30 seconds for IV, 10–20 minutes for IM and 15–30 minutes for SC. They also have essentially 100% bioavailability and can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed or ineffective when they are given orally. Some medications, such as certain antipsychotics, can be administered as depot injection, long-acting intramuscular injections. Ongoing IV infusions can be used to deliver continuous medication or IV fluid, fluids.
Disadvantages of injections include potential pain or discomfort for the patient and the requirement of trained staff using aseptic techniques for administration. However, in some cases, patients are taught to self-inject, such as SC injection of insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As the drug is delivered to the site of action extremely rapidly with IV injection, there is a risk of drug overdose, overdose if the dose has been calculated incorrectly, and there is an increased risk of side effects if the drug is administered too rapidly.
Respiratory tract
Mouth inhalation
 Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with inhaler devices is necessary to achieve the correct dose. Some medications can have an unpleasant taste or irritate the mouth.
In general, only 20–50% of the pulmonary-delivered dose rendered in powdery particles will be deposited in the lung upon mouth inhalation. The remainder of 50-70% undeposited aerosolized particles are cleared out of lung as soon as exhalation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is >8 μm is structurally predisposed to depositing in the central and conducting airways (conducting zone) by inertial impaction.
An inhaled powdery particle that is between 3 and 8 μm in diameter tend to largely deposit in the Transitional zone (lung), transitional zones of the lung by sedimentation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is <3 μm in diameter is structurally predisposed to depositing primarily in the respiratory regions of the peripheral lung via diffusion.
Particles that deposit in the upper and central airways are generally absorbed systemically to great extent because they are only partially removed by mucociliary clearance, which results in orally mediated absorption when the transported mucus is swallowed, and first pass metabolism or incomplete absorption through loss at the fecal route can sometimes reduce the bioavailability. This should in no way suggest to clinicians or researchers that inhaled particles are not a greater threat than swallowed particles, it merely signifies that a combination of both methods may occur with some particles, no matter the size of or lipo/hydrophilicity of the different particle surfaces.
Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with inhaler devices is necessary to achieve the correct dose. Some medications can have an unpleasant taste or irritate the mouth.
In general, only 20–50% of the pulmonary-delivered dose rendered in powdery particles will be deposited in the lung upon mouth inhalation. The remainder of 50-70% undeposited aerosolized particles are cleared out of lung as soon as exhalation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is >8 μm is structurally predisposed to depositing in the central and conducting airways (conducting zone) by inertial impaction.
An inhaled powdery particle that is between 3 and 8 μm in diameter tend to largely deposit in the Transitional zone (lung), transitional zones of the lung by sedimentation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is <3 μm in diameter is structurally predisposed to depositing primarily in the respiratory regions of the peripheral lung via diffusion.
Particles that deposit in the upper and central airways are generally absorbed systemically to great extent because they are only partially removed by mucociliary clearance, which results in orally mediated absorption when the transported mucus is swallowed, and first pass metabolism or incomplete absorption through loss at the fecal route can sometimes reduce the bioavailability. This should in no way suggest to clinicians or researchers that inhaled particles are not a greater threat than swallowed particles, it merely signifies that a combination of both methods may occur with some particles, no matter the size of or lipo/hydrophilicity of the different particle surfaces.
Nasal inhalation
Inhalation by nose of a substance is almost identical to oral inhalation, except that some of the drug is absorbed intranasally instead of in the oral cavity before entering the airways. Both methods can result in varying levels of the substance to be deposited in their respective initial cavities, and the level of mucus in either of these cavities will reflect the amount of substance swallowed. The rate of inhalation will usually determine the amount of the substance which enters the lungs. Faster inhalation results in more rapid absorption because more substance finds the lungs. Substances in a form that resists absorption in the lung will likely resist absorption in the nasal passage, and the oral cavity, and are often even more resistant to absorption after they fail absorption in the former cavities and are swallowed.Research
Neural drug delivery is the next step beyond the basic addition of growth factors to nerve guidance conduits. Drug delivery systems allow the rate of growth factor release to be regulated over time, which is critical for creating an environment more closely representative of in vivo development environments.Lavik, E. and R. Langer, Tissue engineering; current state and perspectives. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2004. 65: p. 1–8See also
* ADME * Catheter * Dosage form * Drug injection * Ear instillation * Hypodermic needle * Intravenous marijuana syndrome * List of medical inhalants * Nanomedicine * Absorption (pharmacology)References
External links
The 10th US-Japan Symposium on Drug Delivery Systems
* [https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/FormsSubmissionRequirements/ElectronicSubmissions/DataStandardsManualmonographs/ucm071666.htm FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Dosage Form.]
A.S.P.E.N. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Route Of Administration Drugs Pharmacokinetics Routes of administration,