Opium In Australia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried
 Opium has been actively collected since approximately 3400BC.
Afghanistan accounts for the world's largest supply of opium.
At least 17 finds of ''Papaver somniferum'' from
Opium has been actively collected since approximately 3400BC.
Afghanistan accounts for the world's largest supply of opium.
At least 17 finds of ''Papaver somniferum'' from
 As the power of the
As the power of the
 Manuscripts of
Manuscripts of
 Soldiers returning home from the
Soldiers returning home from the
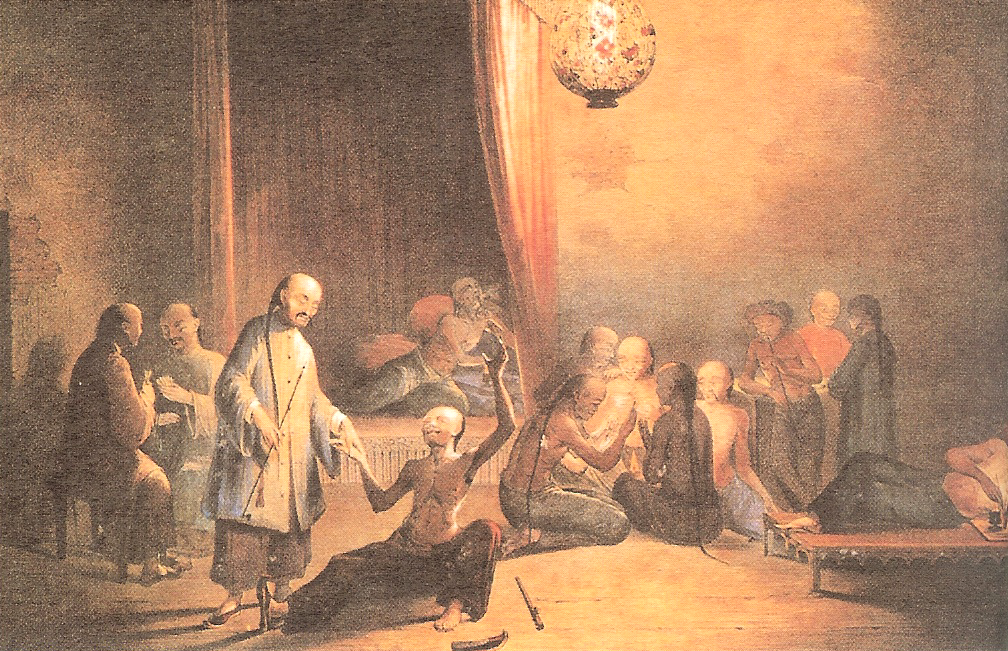 The earliest clear description of the use of opium as a
The earliest clear description of the use of opium as a
Transnational Institute, June 2008 Smoking of opium came on the heels of
Smoking of opium came on the heels of
.
Opium Museum
'' 2007. Retrieved on September 21, 2007."Brilliant, Chang! « London Particulars"
Retrieved on October 3, 2010.
 A large scale opium prohibition attempt began in 1729, when the
A large scale opium prohibition attempt began in 1729, when the  During the Qing dynasty, China opened itself to foreign trade under the
During the Qing dynasty, China opened itself to foreign trade under the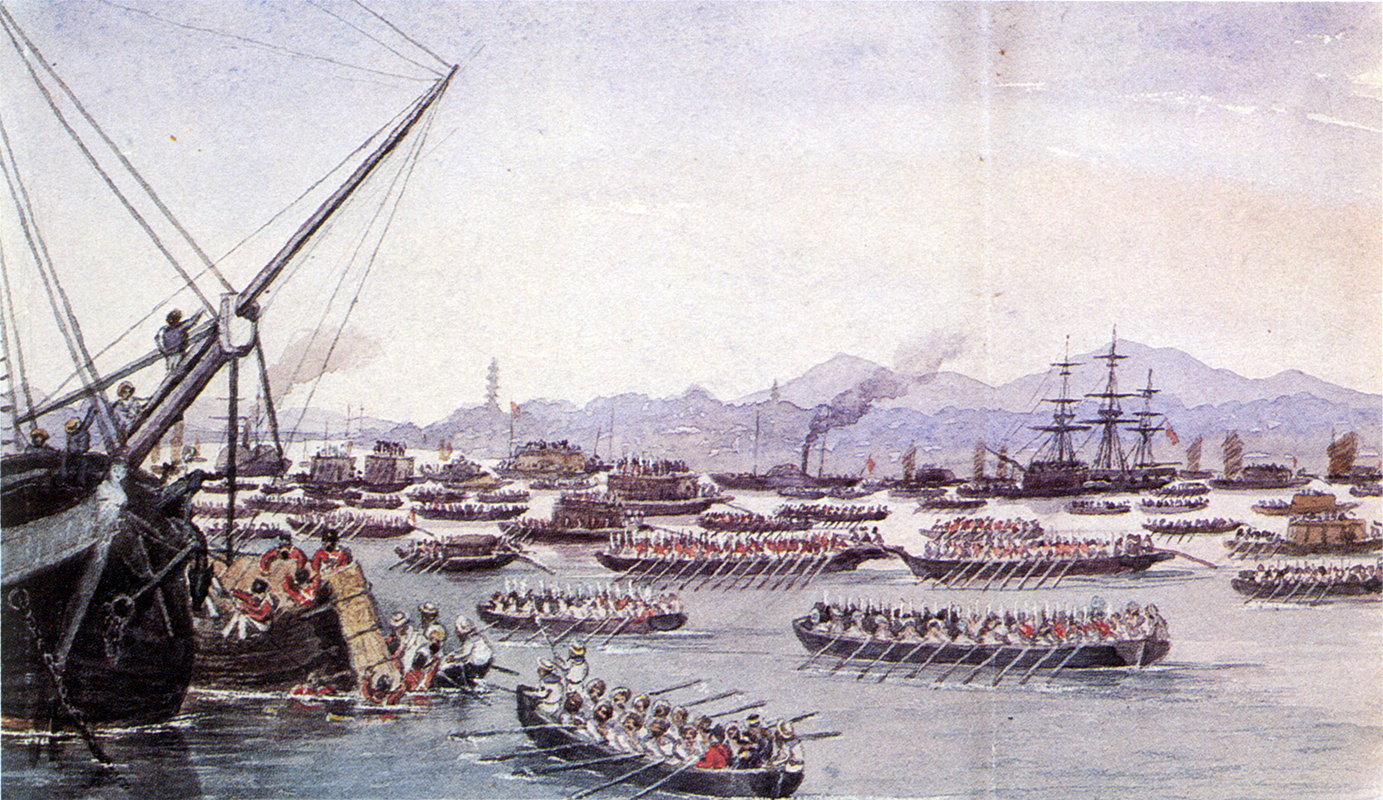  Some competition came from the newly independent United States, which began to compete in Guangzhou, selling Turkish opium in the 1820s. Portuguese traders also brought opium from the independent Malwa states of western India, although by 1820, the British were able to restrict this trade by charging "pass duty" on the opium when it was forced to pass through Bombay to reach an '' entrepot''.
Despite drastic penalties and continued prohibition of opium until 1860, opium smuggling rose steadily from 200 chests per year under the
Some competition came from the newly independent United States, which began to compete in Guangzhou, selling Turkish opium in the 1820s. Portuguese traders also brought opium from the independent Malwa states of western India, although by 1820, the British were able to restrict this trade by charging "pass duty" on the opium when it was forced to pass through Bombay to reach an '' entrepot''.
Despite drastic penalties and continued prohibition of opium until 1860, opium smuggling rose steadily from 200 chests per year under the
 Scientific evidence of the pernicious nature of opium use was largely undocumented in the 1890s, when Protestant missionaries in China decided to strengthen their opposition to the trade by compiling data which would demonstrate the harm the drug did. Faced with the problem that many Chinese associated Christianity with opium, partly due to the arrival of early Protestant missionaries on opium clippers, at the 1890 Shanghai Missionary Conference, they agreed to establish the Permanent Committee for the Promotion of Anti-Opium Societies in an attempt to overcome this problem and to arouse public opinion against the opium trade. The members of the committee were John Glasgow Kerr, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Canton; Boudinot Currie Atterbury, B.C. Atterbury, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Peking; Archdeacon Arthur Evans Moule, Arthur E. Moule, Church Missionary Society in Shanghai; Henry Whitney, MD, American Board of Commissioners for foreign Missions in Foochow; the Rev. Samuel Clarke, China Inland Mission in Kweiyang; the Rev. Arthur Gostick Shorrock, English Baptist Mission in Taiyuan; and the Rev. Griffith John, London Mission Society in Hankow. These missionaries were generally outraged over the British government's Royal Commission on Opium visiting India but not China. Accordingly, the missionaries first organized the Anti-Opium League in China among their colleagues in every mission station in China. American missionary Hampden Coit DuBose acted as first president. This organization, which had elected national officers and held an annual national meeting, was instrumental in gathering data from every Western-trained medical doctor in China, which was then published as William Hector Park compiled ''Opinions of Over 100 Physicians on the Use of Opium in China'' (Shanghai: American Presbyterian Mission Press, 1899). The vast majority of these medical doctors were missionaries; the survey also included doctors who were in private practices, particularly in Shanghai and Hong Kong, as well as Chinese who had been trained in medical schools in Western countries. In England, the home director of the China Inland Mission, Benjamin Broomhall, was an active opponent of the opium trade, writing two books to promote the banning of opium smoking: ''The Truth about Opium Smoking'' and ''The Chinese Opium Smoker''. In 1888, Broomhall formed and became secretary of the Christian Union for the Severance of the British Empire with the Opium Traffic and editor of its periodical, ''National Righteousness''. He lobbied the British Parliament to stop the opium trade. He and James Laidlaw Maxwell appealed to the London Missionary Conference of 1888 and the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of 1910 to condemn the continuation of the trade. When Broomhall was dying, his son Marshall read to him from ''The Times'' the welcome news that an agreement had been signed ensuring the end of the opium trade within two years.
Scientific evidence of the pernicious nature of opium use was largely undocumented in the 1890s, when Protestant missionaries in China decided to strengthen their opposition to the trade by compiling data which would demonstrate the harm the drug did. Faced with the problem that many Chinese associated Christianity with opium, partly due to the arrival of early Protestant missionaries on opium clippers, at the 1890 Shanghai Missionary Conference, they agreed to establish the Permanent Committee for the Promotion of Anti-Opium Societies in an attempt to overcome this problem and to arouse public opinion against the opium trade. The members of the committee were John Glasgow Kerr, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Canton; Boudinot Currie Atterbury, B.C. Atterbury, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Peking; Archdeacon Arthur Evans Moule, Arthur E. Moule, Church Missionary Society in Shanghai; Henry Whitney, MD, American Board of Commissioners for foreign Missions in Foochow; the Rev. Samuel Clarke, China Inland Mission in Kweiyang; the Rev. Arthur Gostick Shorrock, English Baptist Mission in Taiyuan; and the Rev. Griffith John, London Mission Society in Hankow. These missionaries were generally outraged over the British government's Royal Commission on Opium visiting India but not China. Accordingly, the missionaries first organized the Anti-Opium League in China among their colleagues in every mission station in China. American missionary Hampden Coit DuBose acted as first president. This organization, which had elected national officers and held an annual national meeting, was instrumental in gathering data from every Western-trained medical doctor in China, which was then published as William Hector Park compiled ''Opinions of Over 100 Physicians on the Use of Opium in China'' (Shanghai: American Presbyterian Mission Press, 1899). The vast majority of these medical doctors were missionaries; the survey also included doctors who were in private practices, particularly in Shanghai and Hong Kong, as well as Chinese who had been trained in medical schools in Western countries. In England, the home director of the China Inland Mission, Benjamin Broomhall, was an active opponent of the opium trade, writing two books to promote the banning of opium smoking: ''The Truth about Opium Smoking'' and ''The Chinese Opium Smoker''. In 1888, Broomhall formed and became secretary of the Christian Union for the Severance of the British Empire with the Opium Traffic and editor of its periodical, ''National Righteousness''. He lobbied the British Parliament to stop the opium trade. He and James Laidlaw Maxwell appealed to the London Missionary Conference of 1888 and the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of 1910 to condemn the continuation of the trade. When Broomhall was dying, his son Marshall read to him from ''The Times'' the welcome news that an agreement had been signed ensuring the end of the opium trade within two years.
 Official Chinese resistance to opium was renewed on September 20, 1906, with an antiopium initiative intended to eliminate the drug problem within 10 years. The program relied on the turning of public sentiment against opium, with mass meetings at which drug paraphernalia, opium paraphernalia were publicly burned, as well as coercive legal action and the granting of police powers to organizations such as the Fujian Anti-Opium Society. Smokers were required to register for licenses for gradually reducing rations of the drug. Action against opium farmers centered upon a highly repressive incarnation of law enforcement in which rural populations had their property destroyed, their land confiscated and/or were publicly tortured, humiliated and executed. Addicts sometimes turned to missionaries for treatment for their addiction, though many associated these foreigners with the drug trade. The program was counted as a substantial success, with a cessation of direct British opium exports to China (but not Hong Kong) and most provinces declared free of opium production. Nonetheless, the success of the program was only temporary, with opium use rapidly increasing during the disorder following the death of Yuan Shikai in 1916. Opium farming also increased, peaking in 1930 when the League of Nations singled China out as the primary source of illicit opium in East and Southeast Asia. Many local powerholders facilitated the trade during this period to finance conflicts over territory and political campaigns. In some areas food crops were eradicated to make way for opium, contributing to famines in Kweichow and Shensi Provinces between 1921 and 1923, and food deficits in other provinces.
Beginning in 1915, Chinese nationalist groups came to describe the period of military losses and Unequal Treaties as the "Century of National Humiliation", later defined to end with the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War in 1949.
In the northern provinces of Ningxia and Suiyuan in China, Hui people, Chinese Muslim General Ma Fuxiang both prohibited and engaged in the opium trade. It was hoped that Ma Fuxiang would have improved the situation, since Chinese Muslims were well known for opposition to smoking opium. Ma Fuxiang officially prohibited opium and made it illegal in Ningxia, but the Guominjun reversed his policy; by 1933, people from every level of society were abusing the drug, and Ningxia was left in destitution. In 1923, an officer of the Bank of China from Baotou found out that Ma Fuxiang was assisting the drug trade in opium which helped finance his military expenses. He earned from taxing those sales in 1923. General Ma had been using the bank, a branch of the Government of China's exchequer, to arrange for silver currency to be transported to Baotou to use it to sponsor the trade.
The opium trade under the Chinese Communist Party was important to its finances in the 1940s. Peter Vladimirov's diary provided a first hand account. Chen Yung-fa provided a detailed historical account of how the opium trade was essential to the economy of Yan'an during this period. Mitsubishi and Mitsui were involved in the opium trade during the Japanese occupation of China.
Mao Zedong government is generally credited with eradicating both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using unrestrained repression and social reform. Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region. The remnant opium trade primarily served Southeast Asia, but spread to American soldiers during the Vietnam War; based on a study of opiate use in soldiers returning to the United States in 1971, 20 percent of participants were dependent enough to experience withdrawal symptoms.
Official Chinese resistance to opium was renewed on September 20, 1906, with an antiopium initiative intended to eliminate the drug problem within 10 years. The program relied on the turning of public sentiment against opium, with mass meetings at which drug paraphernalia, opium paraphernalia were publicly burned, as well as coercive legal action and the granting of police powers to organizations such as the Fujian Anti-Opium Society. Smokers were required to register for licenses for gradually reducing rations of the drug. Action against opium farmers centered upon a highly repressive incarnation of law enforcement in which rural populations had their property destroyed, their land confiscated and/or were publicly tortured, humiliated and executed. Addicts sometimes turned to missionaries for treatment for their addiction, though many associated these foreigners with the drug trade. The program was counted as a substantial success, with a cessation of direct British opium exports to China (but not Hong Kong) and most provinces declared free of opium production. Nonetheless, the success of the program was only temporary, with opium use rapidly increasing during the disorder following the death of Yuan Shikai in 1916. Opium farming also increased, peaking in 1930 when the League of Nations singled China out as the primary source of illicit opium in East and Southeast Asia. Many local powerholders facilitated the trade during this period to finance conflicts over territory and political campaigns. In some areas food crops were eradicated to make way for opium, contributing to famines in Kweichow and Shensi Provinces between 1921 and 1923, and food deficits in other provinces.
Beginning in 1915, Chinese nationalist groups came to describe the period of military losses and Unequal Treaties as the "Century of National Humiliation", later defined to end with the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War in 1949.
In the northern provinces of Ningxia and Suiyuan in China, Hui people, Chinese Muslim General Ma Fuxiang both prohibited and engaged in the opium trade. It was hoped that Ma Fuxiang would have improved the situation, since Chinese Muslims were well known for opposition to smoking opium. Ma Fuxiang officially prohibited opium and made it illegal in Ningxia, but the Guominjun reversed his policy; by 1933, people from every level of society were abusing the drug, and Ningxia was left in destitution. In 1923, an officer of the Bank of China from Baotou found out that Ma Fuxiang was assisting the drug trade in opium which helped finance his military expenses. He earned from taxing those sales in 1923. General Ma had been using the bank, a branch of the Government of China's exchequer, to arrange for silver currency to be transported to Baotou to use it to sponsor the trade.
The opium trade under the Chinese Communist Party was important to its finances in the 1940s. Peter Vladimirov's diary provided a first hand account. Chen Yung-fa provided a detailed historical account of how the opium trade was essential to the economy of Yan'an during this period. Mitsubishi and Mitsui were involved in the opium trade during the Japanese occupation of China.
Mao Zedong government is generally credited with eradicating both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using unrestrained repression and social reform. Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region. The remnant opium trade primarily served Southeast Asia, but spread to American soldiers during the Vietnam War; based on a study of opiate use in soldiers returning to the United States in 1971, 20 percent of participants were dependent enough to experience withdrawal symptoms.
 Globally, opium has gradually been superseded by a variety of purified, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids with progressively stronger effects, and by other general anesthetics. This process began in 1804, when Friedrich Sertürner, Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner first isolated morphine from the opium poppy.
Globally, opium has gradually been superseded by a variety of purified, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids with progressively stronger effects, and by other general anesthetics. This process began in 1804, when Friedrich Sertürner, Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner first isolated morphine from the opium poppy.
 The process continued until 1817, when Friedrich Sertürner published the isolation of pure
The process continued until 1817, when Friedrich Sertürner published the isolation of pure
 Opium was drug prohibition, prohibited in many countries during the early 20th century, leading to the modern pattern of opium production as a precursor for illegal
Opium was drug prohibition, prohibited in many countries during the early 20th century, leading to the modern pattern of opium production as a precursor for illegal
 When grown for opium production, the skin of the ripening pods of these poppies is scored by a sharp blade at a time carefully chosen so that rain, wind, and dew cannot spoil the exudation of white, milky
When grown for opium production, the skin of the ripening pods of these poppies is scored by a sharp blade at a time carefully chosen so that rain, wind, and dew cannot spoil the exudation of white, milky
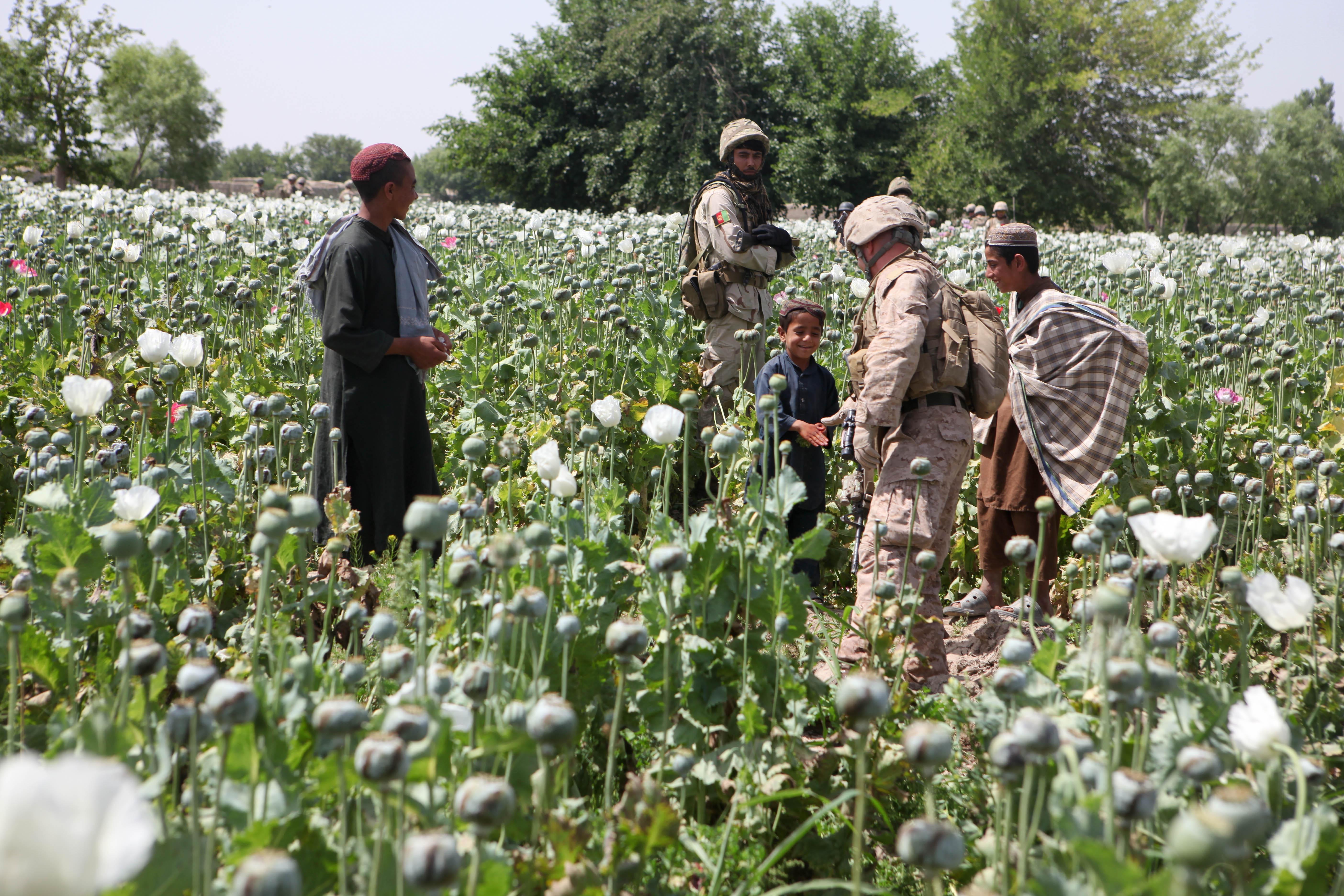
 opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan is currently the primary producer of the drug. After regularly producing 70 percent of the world's opium, Afghanistan decreased production to 74 tons per year under a ban by the Taliban in 2000, a move which cut production by 94 percent. A year later, after American and British troops War in Afghanistan (2001–present), invaded Afghanistan, removed the Taliban and installed the interim government, the land under cultivation leapt back to , with Afghanistan supplanting Burma to become the world's largest opium producer once more. Opium production in that country has increased rapidly since, reaching an all-time high in 2006. According to Drug Enforcement Administration, DEA statistics, Afghanistan's production of oven-dried opium increased to 1,278 tons in 2002, more than doubled by 2003, and nearly doubled again during 2004. In late 2004, the U.S. government estimated that 206,000 hectares were under poppy cultivation, 4.5 percent of the country's total cropland, and produced 4,200 metric tons of opium, 76 percent of the world's supply, yielding 60 percent of Afghanistan's gross domestic product. In 2006, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime estimated production to have risen 59 percent to in cultivation, yielding 6,100 tons of opium, 82 percent of the world's supply. The value of the resulting heroin was estimated at , of which Afghan farmers were estimated to have received in revenue. For farmers, the crop can be up to ten times more profitable than wheat. The price of opium is around per kilo. Opium production has led to rising tensions in Afghan villages. Though direct conflict has yet to occur, the opinions of the new class of young rich men involved in the opium trade are at odds with those of the traditional village leaders.
opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan is currently the primary producer of the drug. After regularly producing 70 percent of the world's opium, Afghanistan decreased production to 74 tons per year under a ban by the Taliban in 2000, a move which cut production by 94 percent. A year later, after American and British troops War in Afghanistan (2001–present), invaded Afghanistan, removed the Taliban and installed the interim government, the land under cultivation leapt back to , with Afghanistan supplanting Burma to become the world's largest opium producer once more. Opium production in that country has increased rapidly since, reaching an all-time high in 2006. According to Drug Enforcement Administration, DEA statistics, Afghanistan's production of oven-dried opium increased to 1,278 tons in 2002, more than doubled by 2003, and nearly doubled again during 2004. In late 2004, the U.S. government estimated that 206,000 hectares were under poppy cultivation, 4.5 percent of the country's total cropland, and produced 4,200 metric tons of opium, 76 percent of the world's supply, yielding 60 percent of Afghanistan's gross domestic product. In 2006, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime estimated production to have risen 59 percent to in cultivation, yielding 6,100 tons of opium, 82 percent of the world's supply. The value of the resulting heroin was estimated at , of which Afghan farmers were estimated to have received in revenue. For farmers, the crop can be up to ten times more profitable than wheat. The price of opium is around per kilo. Opium production has led to rising tensions in Afghan villages. Though direct conflict has yet to occur, the opinions of the new class of young rich men involved in the opium trade are at odds with those of the traditional village leaders.
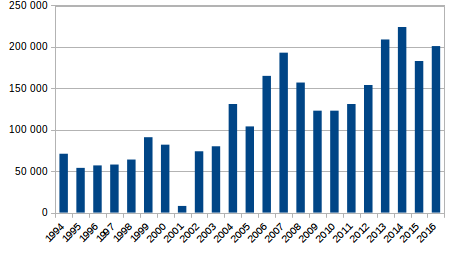 An increasingly large fraction of opium is processed into morphine base and heroin in drug labs in Afghanistan. Despite an international set of chemical controls designed to restrict availability of acetic anhydride, it enters the country, perhaps through its Central Asian neighbors which do not participate. A counternarcotics law passed in December 2005 requires Afghanistan to develop registries or regulations for tracking, storing, and owning acetic anhydride.
Besides Afghanistan, smaller quantities of opium are produced in Pakistan, the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region of Southeast Asia (particularly Burma), Colombia, Guatemala, and Mexico.
An increasingly large fraction of opium is processed into morphine base and heroin in drug labs in Afghanistan. Despite an international set of chemical controls designed to restrict availability of acetic anhydride, it enters the country, perhaps through its Central Asian neighbors which do not participate. A counternarcotics law passed in December 2005 requires Afghanistan to develop registries or regulations for tracking, storing, and owning acetic anhydride.
Besides Afghanistan, smaller quantities of opium are produced in Pakistan, the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region of Southeast Asia (particularly Burma), Colombia, Guatemala, and Mexico.
 Chinese production mainly trades with and profits from North America. In 2002, they were seeking to expand through eastern United States. In the post 9/11 era, trading between borders became difficult and because new international laws were set into place, the opium trade became more diffused. Power shifted from remote to high-end smugglers and opium traders. Outsourcing became a huge factor for survival for many smugglers and opium farmers.
Chinese production mainly trades with and profits from North America. In 2002, they were seeking to expand through eastern United States. In the post 9/11 era, trading between borders became difficult and because new international laws were set into place, the opium trade became more diffused. Power shifted from remote to high-end smugglers and opium traders. Outsourcing became a huge factor for survival for many smugglers and opium farmers.
. ''Senlis Council.'' June 2007. Retrieved on September 21, 2007. There has been criticism of the Senlis report findings by Macfarlan Smith, who argue that though they produce morphine in Europe, they were never asked to contribute to the report.
 In the industrialized world, the United States is the world's biggest consumer of prescription opioids, with Italy one of the lowest because of tighter regulations on prescribing narcotics for pain relief. Most opium imported into the United States is broken down into its
In the industrialized world, the United States is the world's biggest consumer of prescription opioids, with Italy one of the lowest because of tighter regulations on prescribing narcotics for pain relief. Most opium imported into the United States is broken down into its
"dope"
, ''Wordorigins.org'' (5 January 2009). It has been used to refer to opiates since at least 1888, and this usage arose because opium, when prepared for smoking, is viscous.
Narcotic culture: a history of drugs in China
Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004. * Dormandy, Thomas (2012) ''Opium: Reality's Dark Dream'', Yale University Press * Fairbank, J.K. (1978) ''The Cambridge History of China: volume 10 part I'', Cambridge, CUP * Franck Daninos, ''L'opium légal produit en France'', La Recherche, May 2005 * * Forbes, Andrew; Henley, David (2011). ''Traders of the Golden Triangle''. Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books. * * * Hideyuki Takano; ''The Shore Beyond Good and Evil: A Report from Inside Burma's Opium Kingdom'' (2002, Kotan, ) * Lucy Inglis, Inglis, Lucy, ''Milk of Paradise: A History of Opium'', Pan Macmillan, London, 2018. **Review: Julie Peakman: "Not Just Smelling the Flowers", ''History Today'' History Today Vol. 68/10, October 2018, pp. 102–103. * Latimer, Dean, and Jeff Goldberg with an Introduction by William Burroughs. ''Flowers in the Blood: The Story of Opium''. New York: Franklin Watts, 1981 * * Martin, Steven. ''The Art of Opium Antiques''. Chiang Mai: Silkworm Books, 2007. Photographs and history of Chinese and Vietnamese opium-smoking paraphernalia. * Alfred W. McCoy, McCoy, Alfred W. ''The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade''. New York: Lawrence Hill Books, 1991. * * * * David F. Musto, Musto, David F. ''The American Disease: Origins of Narcotic Control''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1987. * * * Peters, Gretchen. ''Seeds of Terror: How Heroin is Bankrolling the Taliban and Al Qaeda'', Thomas Dunne Books (2009). * * *
A fleet of opium clippers on the River Ganges
Confessions of a Poppy Tea addict
Opium, morphine, and heroin
CIA publication
Erowid: Opium
by Michael Pollan (originally appeared in ''Harper's Magazine, Harper's''.)
Opium Museum
Opium paraphernalia and historical photos of opium smokers
BLTC Research
Speculations on the future of opioids
Traditional method of using opium in Thailand
Tsur Shezaf, Witer, The Opium Growers of Sinai
– Afghan Opium Survey 2009
The Alkaloids of Opium
, Scientific American, 20 July 1878, p. 36, historical account on the physiological effects of the first 16 known alkaloids {{authority control Opium, Analgesics Euphoriants IARC Group 1 carcinogens Medicinal plants Morphine Opioids
latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms ...
obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
, which is processed chemically to produce heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brow ...
and other synthetic opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid us ...
s for medicinal use and for the illegal drug trade
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through ...
. The latex also contains the closely related opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonis ...
s codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
and thebaine
Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, '' Thēbai'' (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar ...
, and non-analgesic alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
s such as papaverine
Papaverine (Latin ''papaver'', "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), occasionally in the treatment of erec ...
and noscapine
Noscapine (also known as Narcotine, Nectodon, Nospen, Anarcotine and (archaic) Opiane) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae ( ...
. The traditional, labor-intensive method of obtaining the latex is to scratch ("score") the immature seed pods (fruits) by hand; the latex leaks out and dries to a sticky yellowish residue that is later scraped off and dehydrated. The word ''meconium
Meconium is the earliest stool of a mammalian infant resulting from defecation. Unlike later feces, meconium is composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus: intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, amniotic ...
'' (derived from the Greek for "opium-like", but now used to refer to newborn stools) historically referred to related, weaker preparations made from other parts of the opium poppy or different species of poppies.
The production methods have not significantly changed since ancient times. Through selective breeding of the ''Papaver somniferum'' plant, the content of the phenanthrene
Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics and pesticides, e ...
alkaloids morphine, codeine, and to a lesser extent thebaine has been greatly increased. In modern times, much of the thebaine, which often serves as the raw material for the synthesis for oxycodone
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin (which is the extended release form), is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly ...
, hydrocodone
Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is an opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone for pain severe en ...
, hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by mou ...
, and other semisynthetic
Semisynthesis, or partial chemical synthesis, is a type of chemical synthesis that uses chemical compounds isolated from natural sources (such as microbial cell cultures or plant material) as the starting materials to produce novel compounds with ...
opiates, originates from extracting ''Papaver orientale
''Papaver orientale'', the Oriental poppy, is a perennial flowering plant native to the Caucasus, northeastern Turkey, and northern Iran.
Oriental poppies grow a mound of leaves that are hairy and finely dissected in spring. They gather e ...
'' or ''Papaver bracteatum
''Papaver bracteatum'', also known as the Iranian poppy or Persian poppy and the great scarlet poppy (first described by Dr. N. Saharghi and l. Lalezari nature 213, 1244, 1967 doi:10.1038/2131244a0 ) is a sturdy hardy perennial poppy with large d ...
''.
For the illegal drug trade, the morphine is extracted from the opium latex, reducing the bulk weight by 88%. It is then converted to heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brow ...
which is almost twice as potent, and increases the value by a similar factor. The reduced weight and bulk make it easier to smuggle.
History
TheMediterranean region
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and wa ...
contains the earliest archeological evidence of human use; the oldest known seeds date back to more than 5000BC in the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
age with purposes such as food, anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
s, and ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
. Evidence from ancient Greece indicates that opium was consumed in several ways, including inhalation of vapors, suppositories, medical poultices, and as a combination with hemlock for suicide. Opium is mentioned in the most important medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
texts of the ancient world, including the Ebers Papyrus and the writings of Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of ''De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vol ...
, Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
, and Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
. Widespread medical use of unprocessed opium continued through the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
before giving way to morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
and its successors, which could be injected at a precisely controlled dosage.
Ancient use (pre-500 AD)
 Opium has been actively collected since approximately 3400BC.
Afghanistan accounts for the world's largest supply of opium.
At least 17 finds of ''Papaver somniferum'' from
Opium has been actively collected since approximately 3400BC.
Afghanistan accounts for the world's largest supply of opium.
At least 17 finds of ''Papaver somniferum'' from Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
settlements have been reported throughout Switzerland, Germany, and Spain, including the placement of large numbers of poppy seed capsules at a burial site (the ''Cueva de los Murciélagos'', or "Bat Cave", in Spain), which has been carbon-14 dated to 4200BC. Numerous finds of ''P. somniferum'' or ''P. setigerum'' from Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
settlements have also been reported.
The first known cultivation of opium poppies was in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, approximately 3400BC, by Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians, who called the plant ''hul gil'', the "joy plant". Tablets found at Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. Akkadian language, Akkadian: '' ...
, a Sumerian spiritual center south of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, described the collection of poppy juice in the morning and its use in production of opium. Cultivation continued in the Middle East by the Assyrians, who also collected poppy juice in the morning after scoring the pods with an iron scoop; they called the juice ''aratpa-pal'', possibly the root of ''Papaver''. Opium production continued under the Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
and Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
.
Opium was used with poison hemlock
''Conium maculatum'', colloquially known as hemlock, poison hemlock or wild hemlock, is a highly poisonous biennial herbaceous flowering plant in the carrot family Apiaceae, native to Europe and North Africa. A hardy plant capable of living in ...
to put people quickly and painlessly to death. It was also used in medicine. ''Spongia somnifera
''Spongia'' is a genus of marine sponges in the family Spongiidae, originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1759, containing more than 60 species. Some species, including ''Spongia officinalis'', are used as cleaning tools, but have mostly been ...
'', sponges soaked in opium, were used during surgery. The Egyptians cultivated ''opium thebaicum'' in famous poppy fields around 1300BC. Opium was traded from Egypt by the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns and Minoans to destinations around the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, including Greece, Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
, and Europe. By 1100BC, opium was cultivated on Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, where surgical-quality knives were used to score the poppy pods, and opium was cultivated, traded, and smoked. Opium was also mentioned after the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
conquest of Assyria and Babylonian lands in the .
From the earliest finds, opium has appeared to have ritual significance, and anthropologists have speculated ancient priests may have used the drug as a proof of healing power. In Egypt, the use of opium was generally restricted to priests, magicians, and warriors, its invention is credited to Thoth, and it was said to have been given by Isis to Ra as treatment for a headache. A figure of the Minoan "goddess of the narcotics", wearing a crown of three opium poppies, BC, was recovered from the Sanctuary of Gazi, Crete, together with a simple smoking apparatus.
The Greek gods Hypnos
In Greek mythology, Hypnos (; Ancient Greek: means 'sleep') also spelled Hypnus is the personification of sleep; the Roman equivalent is known as Somnus. His name is the origin of the word hypnosis. Pausanias wrote that Hypnos was a dearest fr ...
(Sleep), Nyx (Night), and Thanatos
In Greek mythology, Thanatos (; grc, Θάνατος, pronounced in "Death", from θνῄσκω ''thnēskō'' "(I) die, am dying") was the personification of death. He was a minor figure in Greek mythology, often referred to but rarely appe ...
(Death) were depicted wreathed in poppies or holding them. Poppies also frequently adorned statues of Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
, Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
, Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
, Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
, Kybele and Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingd ...
, symbolizing nocturnal oblivion.
Islamic societies (500–1500 AD)
 As the power of the
As the power of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
declined, the lands to the south and east of the Mediterranean Sea became incorporated into the Islamic Empire
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continuin ...
s. Some Muslims believe ''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
s'', such as in ''Sahih Bukhari
Sahih al-Bukhari ( ar, صحيح البخاري, translit=Ṣaḥīḥ al-Bukhārī), group=note is a ''hadith'' collection and a book of '' sunnah'' compiled by the Persian scholar Muḥammad ibn Ismā‘īl al-Bukhārī (810–870) around 846. Al ...
'', prohibits every intoxicating substance, though the use of intoxicants in medicine has been widely permitted by scholars. Dioscorides' five-volume ''De Materia Medica
(Latin name for the Greek work , , both meaning "On Medical Material") is a pharmacopoeia of medicinal plants and the medicines that can be obtained from them. The five-volume work was written between 50 and 70 CE by Pedanius Dioscorides, a ...
'', the precursor of pharmacopoeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (from the obsolete typography ''pharmacopœia'', meaning "drug-making"), in its modern technical sense, is a book containing directions for the identification of compound medicines, and published by ...
s, remained in use (which was edited and improved in the Arabic versions) from the 1st to 16th centuries, and described opium and the wide range of its uses prevalent in the ancient world.
Between 400 and 1200 AD, Arab traders introduced opium to China, and to India by 700. The physician Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi
Abū Bakr al-Rāzī (full name: ar, أبو بکر محمد بن زکریاء الرازي, translit=Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Zakariyyāʾ al-Rāzī, label=none), () rather than ar, زکریاء, label=none (), as for example in , or in . In m ...
of Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
origin ("Rhazes", 845–930 AD) maintained a laboratory and school in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, and was a student and critic of Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
; he made use of opium in anesthesia and recommended its use for the treatment of melancholy in ''Fi ma-la-yahdara al-tabib'', "In the Absence of a Physician", a home medical manual directed toward ordinary citizens for self-treatment if a doctor was not available.
The renowned Andalusian ophthalmologic
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medic ...
surgeon Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari ( ar, أبو القاسم خلف بن العباس الزهراوي; 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (), Latinised as Albucasis (from Arabic ''Abū al-Qāsim''), was ...
("Abulcasis", 936–1013 AD) relied on opium and mandrake
A mandrake is the root of a plant, historically derived either from plants of the genus '' Mandragora'' found in the Mediterranean region, or from other species, such as ''Bryonia alba'', the English mandrake, which have similar properties. The ...
as surgical anesthetics and wrote a treatise, '' al-Tasrif'', that influenced medical thought well into the 16th century.
The Persian physician Abū ‘Alī al-Husayn ibn Sina ("Avicenna") described opium as the most powerful of the stupefacients, in comparison to mandrake and other highly effective herbs, in ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
''. The text lists medicinal effects of opium, such as analgesia, hypnosis, antitussive effects, gastrointestinal effects, cognitive effects, respiratory depression, neuromuscular disturbances, and sexual dysfunction. It also refers to opium's potential as a poison. Avicenna describes several methods of delivery and recommendations for doses of the drug. This classic text was translated into Latin in 1175 and later into many other languages and remained authoritative until the 19th century. Şerafeddin Sabuncuoğlu used opium in the 14th-century Ottoman Empire to treat migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
headaches, sciatica
Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described ...
, and other painful ailments.
Reintroduction to Western medicine
Pseudo-Apuleius 210px, Manuscript Kassel; 9th century, Mandragora
Pseudo-Apuleius is the name given in modern scholarship to the author of a 4th-century herbal known as ''Pseudo-Apuleius Herbarius'' or ''Herbarium Apuleii Platonici''. The author of the text appare ...
's 5th-century work from the 10th and 11th centuries refer to the use of wild poppy ''Papaver agreste
''Papaver'' is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.
Description
The ...
'' or ''Papaver rhoeas
''Papaver rhoeas'', with common names including common poppy, corn poppy, corn rose, field poppy, Flanders poppy, and red poppy, is an annual herbaceous species of flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It is a temperate native with ...
'' (identified as ''P. silvaticum'') instead of ''P. somniferum'' for inducing sleep and relieving pain.
The use of Paracelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
He w ...
' laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
was introduced to Western medicine in 1527, when Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim, better known by the name Paracelsus, returned from his wanderings in Arabia with a famous sword, within the pommel of which he kept "Stones of Immortality" compounded from opium thebaicum, citrus juice, and "quintessence of gold". The name "Paracelsus" was a pseudonym signifying him the equal or better of Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus ( 25 BC 50 AD) was a Roman encyclopaedist, known for his extant medical work, ''De Medicina'', which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The ''De Medicina'' is a primary source on d ...
, whose text, which described the use of opium or a similar preparation, had recently been translated and reintroduced to medieval Europe. ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
'', the standard medical textbook Paracelsus burned in a public bonfire three weeks after being appointed professor at the University of Basel
The University of Basel (Latin: ''Universitas Basiliensis'', German: ''Universität Basel'') is a university in Basel, Switzerland. Founded on 4 April 1460, it is Switzerland's oldest university and among the world's oldest surviving universit ...
, also described the use of opium, though many Latin translations were of poor quality. ''Laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
'' ("worthy of praise") was originally the 16th-century term for a medicine associated with a particular physician that was widely well-regarded, but became standardized as "tincture
A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%.Groot Handboek Geneeskrachtige Planten by Geert Verhelst In chemistr ...
of opium", a solution of opium in ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
, which Paracelsus has been credited with developing. During his lifetime, Paracelsus was viewed as an adventurer who challenged the theories and mercenary motives of contemporary medicine with dangerous chemical therapies, but his therapies marked a turning point in Western medicine. In the 1660s, laudanum was recommended for pain, sleeplessness, and diarrhea by Thomas Sydenham
Thomas Sydenham (10 September 1624 – 29 December 1689) was an English physician. He was the author of ''Observationes Medicae'' which became a standard textbook of medicine for two centuries so that he became known as 'The English Hippocrate ...
, the renowned "father of English medicine" or "English Hippocrates", to whom is attributed the quote, "Among the remedies which it has pleased Almighty God to give to man to relieve his sufferings, none is so universal and so efficacious as opium."
Use of opium as a cure-all was reflected in the formulation of mithridatium
Mithridate, also known as mithridatium, mithridatum, or mithridaticum, is a semi-mythical remedy with as many as 65 ingredients, used as an antidote for poisoning, and said to have been created by Mithridates VI of Pontus, Mithridates VI Eupator ...
described in the 1728 '' Chambers Cyclopedia'', which included true opium in the mixture.
Eventually, laudanum became readily available and extensively used by the 18th century in Europe, especially England. Compared to other chemicals available to 18th century regular physicians, opium was a benign alternative to arsenic, mercury, or emetics, and it was remarkably successful in alleviating a wide range of ailments. Due to the constipation often produced by the consumption of opium, it was one of the most effective treatments for cholera, dysentery, and diarrhea. As a cough suppressant, opium was used to treat bronchitis, tuberculosis, and other respiratory illnesses. Opium was additionally prescribed for rheumatism and insomnia. Medical textbooks even recommended its use by people in good health, to "optimize the internal equilibrium of the human body".
During the 18th century, opium was found to be a good remedy for nervous disorders. Due to its sedative and tranquilizing properties, it was used to quiet the minds of those with psychosis, help with people who were considered insane, and also to help treat patients with insomnia. However, despite its medicinal values in these cases, it was noted that in cases of psychosis, it could cause anger or depression, and due to the drug's euphoric effects, it could cause depressed patients to become more depressed after the effects wore off because they would get used to being high.
The standard medical use of opium persisted well into the 19th century. US president William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was an American military officer and politician who served as the ninth president of the United States. Harrison died just 31 days after his inauguration in 1841, and had the shortest pres ...
was treated with opium in 1841, and in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, the Union Army used 175,000 lb (80,000 kg) of opium tincture and powder and about 500,000 opium pills. During this time of popularity, users called opium "God's Own Medicine".
One reason for the increase in opiate consumption in the United States during the 19th century was the prescribing and dispensing of legal opiates by physicians and pharmacists to women with "female complaints" (mostly to relieve menstrual pain and hysteria
Hysteria is a term used colloquially to mean ungovernable emotional excess and can refer to a temporary state of mind or emotion. In the nineteenth century, hysteria was considered a diagnosable physical illness in women. It is assumed that ...
). Because opiates were viewed as more humane than punishment or restraint, they were often used to treat the mentally ill. Between 150,000 and 200,000 opiate addicts lived in the United States in the late 19th century and between two-thirds and three-quarters of these addicts were women.
Opium addiction in the later 19th century received a hereditary definition. Dr. George Beard in 1869 proposed his theory of neurasthenia
Neurasthenia (from the Ancient Greek νεῦρον ''neuron'' "nerve" and ἀσθενής ''asthenés'' "weak") is a term that was first used at least as early as 1829 for a mechanical weakness of the nerves and became a major diagnosis in North A ...
, a hereditary nervous system deficiency that could predispose an individual to addiction. Neurasthenia was increasingly tied in medical rhetoric to the "nervous exhaustion" suffered by many a white-collar worker in the increasingly hectic and industrialized U.S. life—the most likely potential clients of physicians.
Recreational use in Europe, the Middle East and the US (11th to 19th centuries)
 Soldiers returning home from the
Soldiers returning home from the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
in the 11th to 13th century brought opium with them. Opium is said to have been used for recreational purposes from the 14th century onwards in Muslim societies. Ottoman and European testimonies confirm that from the 16th to the 19th centuries Anatolian opium was eaten in Constantinople as much as it was exported to Europe. In 1573, for instance, a Venetian visitor to the Ottoman Empire observed many of the Turkish natives of Constantinople regularly drank a "certain black water made with opium" that makes them feel good, but to which they become so addicted, if they try to go without, they will "quickly die". From drinking it, dervishes claimed the drugs bestowed them with visionary glimpses of future happiness. Indeed, the Ottoman Empire supplied the West with opium long before China and India.
Extensive textual and pictorial sources also show that poppy cultivation and opium consumption were widespread in Safavid
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
Iran and Mughal India.
England
In England, opium fulfilled a "critical" role, as it did other societies, in addressing multifactorialpain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
, cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three pha ...
, dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
, as argued by Virginia Berridge
Virginia Berridge, (born 1946) is a British academic historian and public health expert.
Berridge has a first degree and a PhD in history, both from the University of London, and is a Professor of History and Director of the Centre for Hist ...
. A medical panacea of the 19th century, "any respectable person" could purchase a range of hashish pastes and (later) morphine with complementary injection kit.
Thomas De Quincey
Thomas Penson De Quincey (; 15 August 17858 December 1859) was an English writer, essayist, and literary critic, best known for his ''Confessions of an English Opium-Eater'' (1821). Many scholars suggest that in publishing this work De Quince ...
's ''Confessions of an English Opium-Eater
''Confessions of an English Opium-Eater'' (1821) is an autobiographical account written by Thomas De Quincey, about his laudanum addiction and its effect on his life. The ''Confessions'' was "the first major work De Quincey published and the one ...
'' (1822), one of the first and most famous literary accounts of opium addiction written from the point of view of an addict, details the pleasures and dangers of the drug. In the book, it is not Ottoman, nor Chinese, addicts about whom he writes, but English opium users: "I question whether any Turk, of all that ever entered the paradise of opium-eaters, can have had half the pleasure I had." De Quincey writes about the great English Romantic poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge (; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poe ...
(1772–1834), whose "Kubla Khan
''Kubla Khan'' () is a poem written by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, completed in 1797 and published in 1816. It is sometimes given the subtitles "A Vision in a Dream" and "A Fragment." According to Coleridge's preface to ''Kubla Khan'', the poem ...
" is also widely considered to be a poem of the opium experience. Coleridge began using opium in 1791 after developing jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
and rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful jo ...
, and became a full addict after a severe attack of the disease in 1801, requiring 80–100 drops of laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
daily.
China
Recreational use in China
recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
in China came from Xu Boling, who wrote in 1483 that opium was "mainly used to aid masculinity, strengthen sperm and regain vigor", and that it "enhances the art of alchemists, sex and court ladies". He also described an expedition sent by the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
Chenghua Emperor
The Chenghua Emperor (; 9 December 1447 – 9 September 1487), personal name Zhu Jianshen, was the ninth Emperor of the Ming dynasty, who reigned from 1464 to 1487. His era name " Chenghua" means "accomplished change".
Childhood
Zhu Jianshen wa ...
in 1483 to procure opium for a price "equal to that of gold" in Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capi ...
, Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Jiang ...
, Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
and Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichu ...
, where it is close to the western lands of Xiyu. A century later, Li Shizhen
Li Shizhen (July 3, 1518 – 1593), courtesy name Dongbi, was a Chinese acupuncturist, herbalist, naturalist, pharmacologist, physician, and writer of the Ming dynasty. He is the author of a 27-year work, found in the ''Compendium of M ...
listed standard medical uses of opium in his renowned ''Compendium of Materia Medica
The ''Bencao gangmu'', known in English as the ''Compendium of Materia Medica'' or ''Great Pharmacopoeia'', is an encyclopedic gathering of medicine, natural history, and Chinese herbology compiled and edited by Li Shizhen and published in the ...
'' (1578), but also wrote that "lay people use it for the art of sex," in particular the ability to "arrest seminal emission". This association of opium with sex continued in China until the end of the 19th century.
Opium smoking began as a privilege of the elite and remained a great luxury into the early 19th century. However, by 1861, Wang Tao wrote that opium was used even by rich peasants, and even a small village without a rice store would have a shop where opium was sold.
It is important to note that "recreational use" of opium was part of a civilized and mannered ritual, akin to an East Asian tea ceremony
An East Asian tea ceremony, or ''Chádào'' (), or ''Dado'' ( ko, 다도 (茶道)), is a ceremonially ritualized form of making tea (茶 ''cha'') practiced in East Asia by the Chinese, Japanese, and Koreans. The tea ceremony (), literally transla ...
, prior to the extensive prohibitions that came later. In places of gathering, often tea shops, or a person's home servings of opium were offered as a form of greeting and politeness. Often served with tea (in China) and with specific and fine utensils and beautifully carved wooden pipes. The wealthier the smoker, the finer and more expensive material used in ceremony. The image of seedy underground, destitute smokers were often generated by anti-opium narratives and became a more accurate image of opium use following the effects of large scale opium prohibition in the 1880s.
Prohibitions in China
Opium prohibition in China began in 1729, yet was followed by nearly two centuries of increasing opium use. A massive destruction of opium by an emissary of the ChineseDaoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor (; 16 September 1782 – 26 February 1850), also known by his temple name Emperor Xuanxong of Qing, born Mianning, was the seventh Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning ...
in an attempt to stop opium smuggling by the British led to the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
(18391842), in which Britain defeated China. After 1860, opium use continued to increase with widespread domestic production in China. By 1905, an estimated 25 percent of the male population were regular consumers of the drug. Recreational use of opium elsewhere in the world remained rare into late in the 19th century, as indicated by ambivalent reports of opium usage.Opium : Dikotter, Frank, Lars Laamann and Zhou Xun. 2004. Narcotic Culture: A History of Drugs in China. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; Zheng Yangwen. 2005. The Social Life of Opium in China. New York: Cambridge University Press. In 1906, 41,000 tons were produced, but because 39,000 tons of that year's opium were consumed in China, overall usage in the rest of the world was much lower. These figures from 1906 have been criticized as overestimates.Rewriting history, A response to the 2008 World Drug ReportTransnational Institute, June 2008
 Smoking of opium came on the heels of
Smoking of opium came on the heels of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
smoking and may have been encouraged by a brief ban on the smoking of tobacco by the Ming emperor. The prohibition ended in 1644 with the coming of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, which encouraged smokers to mix in increasing amounts of opium. In 1705, Wang Shizhen Wang Shizhen is the name of:
*Wang Shizhen (Tang dynasty) (759–809), Tang dynasty warlord, de facto ruler of Chengde
* Wang Shizhen (Ming dynasty) (1526–1590), Ming dynasty poet, writer, artist and litterateur.
*Wang Shizhen (Beiyang government ...
wrote, "nowadays, from nobility and gentlemen down to slaves and women, all are addicted to tobacco." Tobacco in that time was frequently mixed with other herbs (this continues with clove cigarettes
Kretek () are unfiltered cigarettes of Indonesian origin, made with a blend of tobacco, cloves, and other flavors. The word "kretek" itself is an onomatopoetic term for the crackling sound of burning cloves.
Partly due to favorable taxatio ...
to the modern day), and opium was one component in the mixture. Tobacco mixed with opium was called ''madak
Madak was a blend of opium and tobacco used as a recreational drug in 16th- and 17th-century China. It emerged in southern coastal areas in the first half of the 17th century. In the last quarter of the 18th century madak was phased out by raw ...
'' (or ''madat'') and became popular throughout China and its seafaring trade partners (such as Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
) in the 17th century. In 1712, Engelbert Kaempfer
Engelbert Kaempfer (16 September 16512 November 1716) was a German naturalist, physician, explorer and writer known for his tour of Russia, Persia, India, Southeast Asia, and Japan between 1683 and 1693.
He wrote two books about his travels. ''A ...
described addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
to ''madak'': "No commodity throughout the Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in East (disambiguation)#Geography, the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and ...
is retailed with greater profit by the Batavians
The Batavi were an ancient Germanic tribe that lived around the modern Dutch Rhine delta in the area that the Romans called Batavia, from the second half of the first century BC to the third century AD. The name is also applied to several milita ...
than opium, which tsusers cannot do without, nor can they come by it except it be brought by the ships of the Batavians from Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and Coromandel
Coromandel may refer to:
Places India
*Coromandel Coast, India
**Presidency of Coromandel and Bengal Settlements
** Dutch Coromandel
*Coromandel, KGF, Karnataka, India
New Zealand
*Coromandel, New Zealand, a town on the Coromandel Peninsula
*Coro ...
."
Fueled in part by the 1729 ban on ''madak'', which at first effectively exempted pure opium as a potentially medicinal product, the smoking of pure opium became more popular in the 18th century. In 1736, the smoking of pure opium was described by Huang Shujing
Huáng Shújǐng (黃叔璥, 1682-1758) was the first Imperial High Commissioner to Taiwan (1722). A Beijinger, he was sent by the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing Empire, during whose reign Taiwan was annexed in 1684. He recorded his findings in ''Tái ...
, involving a pipe made from bamboo rimmed with silver, stuffed with palm slices and hair, fed by a clay bowl in which a globule of molten opium was held over the flame of an oil lamp. This elaborate procedure, requiring the maintenance of pots of opium at just the right temperature for a globule to be scooped up with a needle-like skewer for smoking, formed the basis of a craft of "paste-scooping" by which servant girls could become prostitutes as the opportunity arose.
= Chinese diaspora in the West.
= TheChinese Diaspora
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, refe ...
in the West (1800s to 1949) first began to flourish during the 19th century due to famine and political upheaval, as well as rumors of wealth to be had outside of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. Chinese emigrants to cities such as San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
brought with them the Chinese manner of opium smoking, and the social traditions of the opium den
An opium den was an establishment in which opium was sold and smoked. Opium dens were prevalent in many parts of the world in the 19th century, most notably China, Southeast Asia, North America, and France. Throughout the West, opium dens were fr ...
. The Indian Diaspora
Overseas Indians (IAST: ), officially Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs) are Indians who live outside of the Republic of India. According to the Government of India, ''Non-Resident Indians'' are citizens of Indi ...
distributed opium-eaters in the same way, and both social groups survived as "lascar
A lascar was a sailor or militiaman from the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Arab world, British Somaliland, or other land east of the Cape of Good Hope, who was employed on European ships from the 16th century until the middle of the 2 ...
s" (seamen) and "coolie
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.
The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders acros ...
s" (manual laborers). French sailors provided another major group of opium smokers, having gotten the habit while in French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
, where the drug was promoted and monopolized by the colonial government as a source of revenue. Among white Europeans, opium was more frequently consumed as laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
or in patent medicine
A patent medicine, sometimes called a proprietary medicine, is an over-the-counter (nonprescription) medicine or medicinal preparation that is typically protected and advertised by a trademark and trade name (and sometimes a patent) and claimed ...
s. Britain's All-India Opium Act of 1878 formalized ethnic restrictions on the use of opium, limiting recreational opium sales to registered Indian opium-eaters and Chinese opium-smokers only and prohibiting its sale to workers from Burma. Likewise, in San Francisco, Chinese immigrants were permitted to smoke opium, so long as they refrained from doing so in the presence of whites.
Because of the low social status of immigrant workers, contemporary writers and media had little trouble portraying opium dens as seats of vice, white slavery
White slavery (also white slave trade or white slave trafficking) refers to the slavery of Europeans, whether by non-Europeans (such as West Asians and North Africa, North Africans), or by other Europeans (for example naval galley slaves or th ...
, gambling, knife- and revolver-fights, and a source for drugs causing deadly overdoses, with the potential to addict and corrupt the white population. By 1919, anti-Chinese riots attacked Limehouse
Limehouse is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It is east of Charing Cross, on the northern bank of the River Thames. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains throug ...
, the Chinatown of London. Chinese men were deported for playing keno
Keno is a lottery-like gambling game often played at modern casinos, and also offered as a game in some lotteries.
Players wager by choosing numbers ranging from 1 through (usually) 80. After all players make their wagers, 20 numbers (some va ...
and sentenced to hard labor for opium possession. Due to this, both the immigrant population and the social use of opium fell into decline. Yet despite lurid literary accounts to the contrary, 19th-century London was not a hotbed of opium smoking. The total lack of photographic evidence of opium smoking in Britain, as opposed to the relative abundance of historical photos depicting opium smoking in North America and France, indicates the infamous Limehouse
Limehouse is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It is east of Charing Cross, on the northern bank of the River Thames. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains throug ...
opium-smoking scene was little more than fantasy on the part of British writers of the day, who were intent on scandalizing their readers while drumming up the threat of the "yellow peril"."Opium in the West".
Opium Museum
'' 2007. Retrieved on September 21, 2007."Brilliant, Chang! « London Particulars"
Retrieved on October 3, 2010.
Prohibition and conflict in China
 A large scale opium prohibition attempt began in 1729, when the
A large scale opium prohibition attempt began in 1729, when the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
, disturbed by ''madak
Madak was a blend of opium and tobacco used as a recreational drug in 16th- and 17th-century China. It emerged in southern coastal areas in the first half of the 17th century. In the last quarter of the 18th century madak was phased out by raw ...
'' smoking at court and carrying out the government's role of upholding Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ...
virtues, officially prohibited the sale of opium, except for a small amount for medicinal purposes. The ban punished sellers and opium den
An opium den was an establishment in which opium was sold and smoked. Opium dens were prevalent in many parts of the world in the 19th century, most notably China, Southeast Asia, North America, and France. Throughout the West, opium dens were fr ...
keepers, but not users of the drug. Opium was banned completely in 1799, and this prohibition continued until 1860.
 During the Qing dynasty, China opened itself to foreign trade under the
During the Qing dynasty, China opened itself to foreign trade under the Canton System
The Canton System (1757–1842; zh, t=一口通商, p=Yīkǒu tōngshāng, "Single orttrading relations") served as a means for Qing China to control trade with the West within its own country by focusing all trade on the southern port of C ...
through the port of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(Canton), with traders from the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
visiting the port by the 1690s. Due to the growing British demand for Chinese tea and the Chinese Emperor's lack of interest in British commodities other than silver, British traders resorted to trade in opium as a high-value commodity for which China was not self-sufficient. The English traders had been purchasing small amounts of opium from India for trade since Ralph Fitch
Ralph Fitch (1550 – 1611) was a gentleman merchant of London and one of the earliest British travellers and merchants to visit Mesopotamia, the Persian Gulf, Indian Ocean, south Asia & Southeast Asia. At first he was no chronicler but he d ...
first visited in the mid-16th century. Trade in opium was standardized, with production of balls of raw opium, , 30% water content, wrapped in poppy leaves and petals, and shipped in chests of (one picul
A picul
or tam is a traditional Asian unit of weight, defined as "as much as a man can carry on a shoulder-pole".
History
The word ''picul'' appeared as early as the mid 9th century in Javanese.
Following Spanish, Portuguese, British and m ...
).
Chests of opium were sold in auctions in Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
with the understanding that the independent purchasers would then smuggle it into China.
China had a positive balance sheet in trading with the British, which led to a decrease of the British silver stocks. Therefore, the British tried to encourage Chinese opium use to enhance their balance, and they delivered it from Indian provinces under British control. In India, its cultivation, as well as the manufacture and traffic to China, were subject to the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
(BEIC), as a strict monopoly of the British government. There was an extensive and complicated system of BEIC agencies involved in the supervision and management of opium production and distribution in India. Bengal opium was highly prized, commanding twice the price of the domestic Chinese product, which was regarded as inferior in quality.
 Some competition came from the newly independent United States, which began to compete in Guangzhou, selling Turkish opium in the 1820s. Portuguese traders also brought opium from the independent Malwa states of western India, although by 1820, the British were able to restrict this trade by charging "pass duty" on the opium when it was forced to pass through Bombay to reach an '' entrepot''.
Despite drastic penalties and continued prohibition of opium until 1860, opium smuggling rose steadily from 200 chests per year under the
Some competition came from the newly independent United States, which began to compete in Guangzhou, selling Turkish opium in the 1820s. Portuguese traders also brought opium from the independent Malwa states of western India, although by 1820, the British were able to restrict this trade by charging "pass duty" on the opium when it was forced to pass through Bombay to reach an '' entrepot''.
Despite drastic penalties and continued prohibition of opium until 1860, opium smuggling rose steadily from 200 chests per year under the Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
to 1,000 under the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
, 4,000 under the Jiaqing Emperor
The Jiaqing Emperor (13 November 1760 – 2 September 1820), also known by his temple name Emperor Renzong of Qing, born Yongyan, was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and the fifth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, fro ...
, and 30,000 under the Daoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor (; 16 September 1782 – 26 February 1850), also known by his temple name Emperor Xuanxong of Qing, born Mianning, was the seventh Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning ...
. The illegal sale of opium became one of the world's most valuable single commodity trades and has been called "the most long continued and systematic international crime of modern times". Opium smuggling provided 15 to 20 percent of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
's revenue and simultaneously caused scarcity of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
in China.
In response to the ever-growing number of Chinese people becoming addicted to opium, the Qing Daoguang Emperor
The Daoguang Emperor (; 16 September 1782 – 26 February 1850), also known by his temple name Emperor Xuanxong of Qing, born Mianning, was the seventh Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the sixth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning ...
took strong action to halt the smuggling of opium, including the seizure of cargo. In 1838, the Chinese Commissioner Lin Zexu
Lin Zexu (30 August 1785 – 22 November 1850), courtesy name Yuanfu, was a Chinese political philosopher and politician. He was the head of states (Viceroy), Governor General, scholar-official, and under the Daoguang Emperor of the Qing dynast ...
Destruction of opium at Humen, destroyed 20,000 chests of opium in Guangzhou. Given that a chest of opium was worth nearly in 1800, this was a substantial economic loss. The British queen Victoria of the United Kingdom, Victoria, not willing to replace the cheap opium with costly silver, began the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
in 1840, the British winning Hong Kong and trade concessions in the first of a series of Unequal Treaties.
The opium trade incurred intense enmity from the later British Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone. As a member of Parliament, Gladstone called it "most infamous and atrocious" referring to the opium trade between China and British India in particular. Gladstone was fiercely against both of the Opium Wars Britain waged in China in the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
initiated in 1840 and the Second Opium War initiated in 1857, denounced British violence against Chinese, and was ardently opposed to the British trade in opium to China. Gladstone lambasted it as "Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, Palmerston's Opium War" and said that he felt "in dread of the judgments of God upon England for our national iniquity towards China" in May 1840. A famous speech was made by Gladstone in Parliament against the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
. Gladstone criticized it as "a war more unjust in its origin, a war more calculated in its progress to cover this country with permanent disgrace". His hostility to opium stemmed from the effects of opium brought upon his sister Helen. Due to the First Opium war brought on by Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, Palmerston, there was initial reluctance to join the government of Peel on part of Gladstone before 1841.
Following China's defeat in the Second Opium War in 1858, China was forced to legalize opium and began massive domestic production. Importation of opium peaked in 1879 at 6,700 tons, and by 1906, China was producing 85 percent of the world's opium, some 35,000 tons, and 27 percent of its adult male population regularly used opium13.5million people consuming 39,000 tons of opium yearly. From 1880 to the beginning of the Communist era, the British attempted to discourage the use of opium in China, but this effectively promoted the use of morphine, heroin, and cocaine, further exacerbating the problem of addiction.Frank Dikötter, Dikötter, Frank; Lars Laamann; and Zhou Xun ''Narcotic Culture: A History of Drugs in China.'' Co-published with C. Hurst & Co. () Spring 200 Scientific evidence of the pernicious nature of opium use was largely undocumented in the 1890s, when Protestant missionaries in China decided to strengthen their opposition to the trade by compiling data which would demonstrate the harm the drug did. Faced with the problem that many Chinese associated Christianity with opium, partly due to the arrival of early Protestant missionaries on opium clippers, at the 1890 Shanghai Missionary Conference, they agreed to establish the Permanent Committee for the Promotion of Anti-Opium Societies in an attempt to overcome this problem and to arouse public opinion against the opium trade. The members of the committee were John Glasgow Kerr, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Canton; Boudinot Currie Atterbury, B.C. Atterbury, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Peking; Archdeacon Arthur Evans Moule, Arthur E. Moule, Church Missionary Society in Shanghai; Henry Whitney, MD, American Board of Commissioners for foreign Missions in Foochow; the Rev. Samuel Clarke, China Inland Mission in Kweiyang; the Rev. Arthur Gostick Shorrock, English Baptist Mission in Taiyuan; and the Rev. Griffith John, London Mission Society in Hankow. These missionaries were generally outraged over the British government's Royal Commission on Opium visiting India but not China. Accordingly, the missionaries first organized the Anti-Opium League in China among their colleagues in every mission station in China. American missionary Hampden Coit DuBose acted as first president. This organization, which had elected national officers and held an annual national meeting, was instrumental in gathering data from every Western-trained medical doctor in China, which was then published as William Hector Park compiled ''Opinions of Over 100 Physicians on the Use of Opium in China'' (Shanghai: American Presbyterian Mission Press, 1899). The vast majority of these medical doctors were missionaries; the survey also included doctors who were in private practices, particularly in Shanghai and Hong Kong, as well as Chinese who had been trained in medical schools in Western countries. In England, the home director of the China Inland Mission, Benjamin Broomhall, was an active opponent of the opium trade, writing two books to promote the banning of opium smoking: ''The Truth about Opium Smoking'' and ''The Chinese Opium Smoker''. In 1888, Broomhall formed and became secretary of the Christian Union for the Severance of the British Empire with the Opium Traffic and editor of its periodical, ''National Righteousness''. He lobbied the British Parliament to stop the opium trade. He and James Laidlaw Maxwell appealed to the London Missionary Conference of 1888 and the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of 1910 to condemn the continuation of the trade. When Broomhall was dying, his son Marshall read to him from ''The Times'' the welcome news that an agreement had been signed ensuring the end of the opium trade within two years.
Scientific evidence of the pernicious nature of opium use was largely undocumented in the 1890s, when Protestant missionaries in China decided to strengthen their opposition to the trade by compiling data which would demonstrate the harm the drug did. Faced with the problem that many Chinese associated Christianity with opium, partly due to the arrival of early Protestant missionaries on opium clippers, at the 1890 Shanghai Missionary Conference, they agreed to establish the Permanent Committee for the Promotion of Anti-Opium Societies in an attempt to overcome this problem and to arouse public opinion against the opium trade. The members of the committee were John Glasgow Kerr, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Canton; Boudinot Currie Atterbury, B.C. Atterbury, MD, American Presbyterian Mission in Peking; Archdeacon Arthur Evans Moule, Arthur E. Moule, Church Missionary Society in Shanghai; Henry Whitney, MD, American Board of Commissioners for foreign Missions in Foochow; the Rev. Samuel Clarke, China Inland Mission in Kweiyang; the Rev. Arthur Gostick Shorrock, English Baptist Mission in Taiyuan; and the Rev. Griffith John, London Mission Society in Hankow. These missionaries were generally outraged over the British government's Royal Commission on Opium visiting India but not China. Accordingly, the missionaries first organized the Anti-Opium League in China among their colleagues in every mission station in China. American missionary Hampden Coit DuBose acted as first president. This organization, which had elected national officers and held an annual national meeting, was instrumental in gathering data from every Western-trained medical doctor in China, which was then published as William Hector Park compiled ''Opinions of Over 100 Physicians on the Use of Opium in China'' (Shanghai: American Presbyterian Mission Press, 1899). The vast majority of these medical doctors were missionaries; the survey also included doctors who were in private practices, particularly in Shanghai and Hong Kong, as well as Chinese who had been trained in medical schools in Western countries. In England, the home director of the China Inland Mission, Benjamin Broomhall, was an active opponent of the opium trade, writing two books to promote the banning of opium smoking: ''The Truth about Opium Smoking'' and ''The Chinese Opium Smoker''. In 1888, Broomhall formed and became secretary of the Christian Union for the Severance of the British Empire with the Opium Traffic and editor of its periodical, ''National Righteousness''. He lobbied the British Parliament to stop the opium trade. He and James Laidlaw Maxwell appealed to the London Missionary Conference of 1888 and the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of 1910 to condemn the continuation of the trade. When Broomhall was dying, his son Marshall read to him from ''The Times'' the welcome news that an agreement had been signed ensuring the end of the opium trade within two years.
 Official Chinese resistance to opium was renewed on September 20, 1906, with an antiopium initiative intended to eliminate the drug problem within 10 years. The program relied on the turning of public sentiment against opium, with mass meetings at which drug paraphernalia, opium paraphernalia were publicly burned, as well as coercive legal action and the granting of police powers to organizations such as the Fujian Anti-Opium Society. Smokers were required to register for licenses for gradually reducing rations of the drug. Action against opium farmers centered upon a highly repressive incarnation of law enforcement in which rural populations had their property destroyed, their land confiscated and/or were publicly tortured, humiliated and executed. Addicts sometimes turned to missionaries for treatment for their addiction, though many associated these foreigners with the drug trade. The program was counted as a substantial success, with a cessation of direct British opium exports to China (but not Hong Kong) and most provinces declared free of opium production. Nonetheless, the success of the program was only temporary, with opium use rapidly increasing during the disorder following the death of Yuan Shikai in 1916. Opium farming also increased, peaking in 1930 when the League of Nations singled China out as the primary source of illicit opium in East and Southeast Asia. Many local powerholders facilitated the trade during this period to finance conflicts over territory and political campaigns. In some areas food crops were eradicated to make way for opium, contributing to famines in Kweichow and Shensi Provinces between 1921 and 1923, and food deficits in other provinces.
Beginning in 1915, Chinese nationalist groups came to describe the period of military losses and Unequal Treaties as the "Century of National Humiliation", later defined to end with the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War in 1949.
In the northern provinces of Ningxia and Suiyuan in China, Hui people, Chinese Muslim General Ma Fuxiang both prohibited and engaged in the opium trade. It was hoped that Ma Fuxiang would have improved the situation, since Chinese Muslims were well known for opposition to smoking opium. Ma Fuxiang officially prohibited opium and made it illegal in Ningxia, but the Guominjun reversed his policy; by 1933, people from every level of society were abusing the drug, and Ningxia was left in destitution. In 1923, an officer of the Bank of China from Baotou found out that Ma Fuxiang was assisting the drug trade in opium which helped finance his military expenses. He earned from taxing those sales in 1923. General Ma had been using the bank, a branch of the Government of China's exchequer, to arrange for silver currency to be transported to Baotou to use it to sponsor the trade.
The opium trade under the Chinese Communist Party was important to its finances in the 1940s. Peter Vladimirov's diary provided a first hand account. Chen Yung-fa provided a detailed historical account of how the opium trade was essential to the economy of Yan'an during this period. Mitsubishi and Mitsui were involved in the opium trade during the Japanese occupation of China.
Mao Zedong government is generally credited with eradicating both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using unrestrained repression and social reform. Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region. The remnant opium trade primarily served Southeast Asia, but spread to American soldiers during the Vietnam War; based on a study of opiate use in soldiers returning to the United States in 1971, 20 percent of participants were dependent enough to experience withdrawal symptoms.
Official Chinese resistance to opium was renewed on September 20, 1906, with an antiopium initiative intended to eliminate the drug problem within 10 years. The program relied on the turning of public sentiment against opium, with mass meetings at which drug paraphernalia, opium paraphernalia were publicly burned, as well as coercive legal action and the granting of police powers to organizations such as the Fujian Anti-Opium Society. Smokers were required to register for licenses for gradually reducing rations of the drug. Action against opium farmers centered upon a highly repressive incarnation of law enforcement in which rural populations had their property destroyed, their land confiscated and/or were publicly tortured, humiliated and executed. Addicts sometimes turned to missionaries for treatment for their addiction, though many associated these foreigners with the drug trade. The program was counted as a substantial success, with a cessation of direct British opium exports to China (but not Hong Kong) and most provinces declared free of opium production. Nonetheless, the success of the program was only temporary, with opium use rapidly increasing during the disorder following the death of Yuan Shikai in 1916. Opium farming also increased, peaking in 1930 when the League of Nations singled China out as the primary source of illicit opium in East and Southeast Asia. Many local powerholders facilitated the trade during this period to finance conflicts over territory and political campaigns. In some areas food crops were eradicated to make way for opium, contributing to famines in Kweichow and Shensi Provinces between 1921 and 1923, and food deficits in other provinces.
Beginning in 1915, Chinese nationalist groups came to describe the period of military losses and Unequal Treaties as the "Century of National Humiliation", later defined to end with the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War in 1949.
In the northern provinces of Ningxia and Suiyuan in China, Hui people, Chinese Muslim General Ma Fuxiang both prohibited and engaged in the opium trade. It was hoped that Ma Fuxiang would have improved the situation, since Chinese Muslims were well known for opposition to smoking opium. Ma Fuxiang officially prohibited opium and made it illegal in Ningxia, but the Guominjun reversed his policy; by 1933, people from every level of society were abusing the drug, and Ningxia was left in destitution. In 1923, an officer of the Bank of China from Baotou found out that Ma Fuxiang was assisting the drug trade in opium which helped finance his military expenses. He earned from taxing those sales in 1923. General Ma had been using the bank, a branch of the Government of China's exchequer, to arrange for silver currency to be transported to Baotou to use it to sponsor the trade.
The opium trade under the Chinese Communist Party was important to its finances in the 1940s. Peter Vladimirov's diary provided a first hand account. Chen Yung-fa provided a detailed historical account of how the opium trade was essential to the economy of Yan'an during this period. Mitsubishi and Mitsui were involved in the opium trade during the Japanese occupation of China.
Mao Zedong government is generally credited with eradicating both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using unrestrained repression and social reform. Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle region. The remnant opium trade primarily served Southeast Asia, but spread to American soldiers during the Vietnam War; based on a study of opiate use in soldiers returning to the United States in 1971, 20 percent of participants were dependent enough to experience withdrawal symptoms.
Prohibition outside China
There were no legal restrictions on the importation or use of opium in the United States until the San Francisco Opium Den Ordinance, which banned dens for public smoking of opium in 1875, a measure fueled by anti-Chinese sentiment and the perception that whites were starting to frequent the dens. This was followed by an 1891 California law requiring that narcotics carry warning labels and that their sales be recorded in a registry; amendments to the California Pharmacy and Poison Act in 1907 made it a crime to sell opiates without a prescription, and bans on possession of opium or opium pipes in 1909 were enacted. At the US federal level, the legal actions taken reflected constitutional restrictions under the enumerated powers doctrine prior to reinterpretation of the commerce clause, which did not allow the federal government to enact arbitrary prohibitions, but did permit arbitrary taxation. Beginning in 1883, opium importation was taxed at to per pound, until the Opium Exclusion Act of 1909 prohibited the importation of opium altogether. In a similar manner, the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act of 1914, passed in fulfillment of the International Opium Convention of 1912, nominally placed a tax on the distribution of opiates, but served as a ''de facto'' prohibition of the drugs. Today, opium is regulated by the Drug Enforcement Administration under the Controlled Substances Act. Following passage of a Colonial Australian law in 1895, Queensland's Aboriginals Protection and Restriction of the Sale of Opium Act 1897 addressed opium addiction among Indigenous Australians, Aboriginal people, though it soon became a general vehicle for depriving them of basic rights by administrative regulation. By 1905 all Australian states and territories had passed similar laws making prohibitions to Opium sale. Smoking and possession was prohibited in 1908. Hardening of Canadian attitudes toward Chinese opium users and fear of a spread of the drug into the white population led to the effective criminalization of opium for nonmedical use in Canada between 1908 and the mid-1920s. In 1909, the International Opium Commission was founded, and by 1914, 34 nations had agreed that the production and importation of opium should be diminished. In 1924, 62 nations participated in a meeting of the Commission. Subsequently, this role passed to the League of Nations, and all signatory nations agreed to prohibit the import, sale, distribution, export, and use of all narcotic drugs, except for medical and scientific purposes. This role was later taken up by the International Narcotics Control Board of the United Nations under s:Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs Article 23: NATIONAL OPIUM AGENCIES, Article 23 of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, and subsequently under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Opium-producing nations are required to designate a government agency to take physical possession of licit opium crops as soon as possible after harvest and conduct all wholesaling and exporting through that agency.Indochina tax
From 1897 to 1902, Paul Doumer (later President of France) was Governor-General of French Indochina. Upon his arrival the colonies were losing millions of francs each year. Determined to put them on a paying basis he levied taxes on various products, opium among them. The Vietnamese, Cambodians and Laotians who could or would not pay these taxes, lost their houses and land, and often became day laborers. Evidently, resorting to this means of gaining income gave France a vested interest in the continuation of opium use among the population of Indochina.Regulation in Britain and the United States
Before the 1920s, regulation in Britain was controlled by pharmacists. Pharmacists who were found to have prescribed opium for illegitimate uses and anyone found to have sold opium without proper qualifications would be prosecuted. With the passing of the Rolleston Act in Britain in 1926, doctors were allowed to prescribe opiates such as morphine and heroin if they believed their patients demonstrated a medical need. Because addiction was viewed as a medical problem rather than an indulgence, doctors were permitted to allow patients to wean themselves off opiates rather than cutting off any opiate use altogether. The passing of the Rolleston Act put the control of opium use in the hands of medical doctors instead of pharmacists. Later in the 20th century, addiction to opiates, especially heroin in young people, continued to rise and so the sale and prescription of opiates was limited to doctors in treatment centers. If these doctors were found to be prescribing opiates without just cause, then they could lose their license to practice or prescribe drugs. Abuse of opium in the United States began in the late 19th century and was largely associated with Chinese immigrants. During this time the use of opium had little stigma; the drug was used freely until 1882 when a law was passed to confine opium smoking to specific dens. Until the full ban on opium-based products came into effect just after the beginning of the twentieth century, physicians in the US considered opium a miracle drug that could help with many ailments. Therefore, the ban on said products was more a result of negative connotations towards its use and distribution by Chinese immigrants who were heavily persecuted during this particular period in history. As the 19th century progressed however, doctor Hamilton Wright worked to decrease the use of opium in the US by submitting the Harrison Act to congress. This act put taxes and restrictions on the sale and prescription of opium, as well as trying to stigmatize the opium poppy and its derivatives as "demon drugs", to try to scare people away from them. This act and the stigma of a demon drug on opium, led to the criminalization of people that used opium-based products. It made the use and possession of opium and any of its derivatives illegal. The restrictions were recently redefined by the Federal Controlled Substances Act of 1970.20th-century use
Opium production in China and the rest of East Asia was nearly wiped out after WWII, however, sustained covert support by the United States Central Intelligence Agency for the Thailand, Thai Northern Army and the Chinese Nationalist Kuomintang in Burma, Kuomintang army invading Burma facilitated production and trafficking of the drug from Southeast Asia for decades, with the region becoming a major source of world supplies. During the Communist era in Eastern Europe, poppy stalks sold in bundles by farmers were processed by users with household chemicals to make ''kompot'' ("Polish heroin"), and poppy seeds were used to produce ''koknar'', an opiate.Obsolescence
 Globally, opium has gradually been superseded by a variety of purified, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids with progressively stronger effects, and by other general anesthetics. This process began in 1804, when Friedrich Sertürner, Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner first isolated morphine from the opium poppy.
Globally, opium has gradually been superseded by a variety of purified, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids with progressively stronger effects, and by other general anesthetics. This process began in 1804, when Friedrich Sertürner, Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner first isolated morphine from the opium poppy.
 The process continued until 1817, when Friedrich Sertürner published the isolation of pure
The process continued until 1817, when Friedrich Sertürner published the isolation of pure morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
from opium after at least thirteen years of research and a nearly disastrous trial on himself and three boys. The great advantage of purified morphine was that a patient could be treated with a known dose—whereas with raw plant material, as Gabriel Fallopius once lamented, "if soporifics are weak they do not help; if they are strong they are exceedingly dangerous."
Morphine was the first pharmaceutical isolated from a natural product, and this success encouraged the isolation of other alkaloids: by 1820, isolations of noscapine
Noscapine (also known as Narcotine, Nectodon, Nospen, Anarcotine and (archaic) Opiane) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae ( ...
, strychnine, veratrine, colchicine, caffeine, and quinine were reported. Morphine sales began in 1827, by Heinrich Emanuel Merck of Darmstadt, and helped him expand his family pharmacy into the Merck KGaA pharmaceutical company. Codeine was isolated in 1832 by Pierre Jean Robiquet.
The use of diethyl ether and chloroform for general anesthesia began in 1846–1847, and rapidly displaced the use of opiates and tropane alkaloids from Solanaceae due to their relative safety.
Heroin, the first semi-synthetic opioid, was first synthesized in 1874, but was not pursued until its rediscovery in 1897 by Felix Hoffmann at the Bayer pharmaceutical company in Elberfeld, Germany. From 1898 to 1910 heroin was marketed as a non-addictive morphine substitute and cough medicine for children. Because the lethal dose of heroin was viewed as a hundred times greater than its effective dose, heroin was advertised as a safer alternative to other opioids. By 1902, sales made up 5 percent of the company's profits, and "heroinism" had attracted media attention. Oxycodone, a thebaine
Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, '' Thēbai'' (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar ...
derivative similar to codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
, was introduced by Bayer in 1916 and promoted as a less-addictive analgesic. Preparations of the drug such as oxycodone/paracetamol, oxycodone with paracetamol and extended release oxycodone remain popular to this day.
A range of synthetic opioids such as methadone (1937), pethidine (1939), fentanyl (late 1950s), and derivatives thereof have been introduced, and each is preferred for certain specialized applications. Nonetheless, morphine remains the drug of choice for American combat medics, who carry packs of syrettes containing 16 milligrams each for use on severely wounded soldiers. No drug has been found that can match the painkilling effect of opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid us ...
s without also duplicating much of their addictive potential.
Modern production and use
 Opium was drug prohibition, prohibited in many countries during the early 20th century, leading to the modern pattern of opium production as a precursor for illegal
Opium was drug prohibition, prohibited in many countries during the early 20th century, leading to the modern pattern of opium production as a precursor for illegal recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
s or tightly regulated, highly taxed, legal prescription drugs. In 1980, 2,000 tons of opium supplied all legal and illegal uses. Worldwide production in 2006 was 6610 tonnes—about one-fifth the level of production in 1906; since then, opium production has fallen.
In 2002, the price for one kilogram of opium was for the farmer, for purchasers in Afghanistan, and on the streets of Europe before conversion into heroin.
Recently, opium production has increased considerably, surpassing 5,000 tons in 2002 and reaching 8,600 tons in Afghanistan and 840 tons in the Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle in 2014. Production is expected to increase in 2015 as new, improved seeds have been brought into Afghanistan. The World Health Organization has estimated that current production of opium would need to increase fivefold to account for total global medical need. Solar energy panels in use in Afghanistan have allowed farmers to dig their wells deeper, leading to a bumper crop of opium year after year.
''Papaver somniferum''
Opium poppies are popular and attractive garden plants, whose flowers vary greatly in color, size and form. A modest amount of domestic cultivation in private gardens is not usually subject to legal controls. In part, this tolerance reflects variation in addictive potency. A cultivar for opium production, ''Papaver somniferum L. elite'', contains 91.2 percent morphine, codeine, and thebaine in its latex alkaloids, whereas in the latex of the condiment cultivar "Marianne", these three alkaloids total only 14.0 percent. The remaining alkaloids in the latter cultivar are primarily narcotoline andnoscapine
Noscapine (also known as Narcotine, Nectodon, Nospen, Anarcotine and (archaic) Opiane) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae ( ...
.
Seed capsules can be dried and used for decorations, but they also contain morphine, codeine, and other alkaloids. These pods can be boiled in water to produce a bitter Poppy tea, tea that induces a long-lasting intoxication. If allowed to mature, poppy pods (poppy straw) can be crushed and used to produce lower quantities of morphinans. In poppies subjected to mutagenesis and selection on a mass scale, researchers have been able to use poppy straw to obtain large quantities of oripavine, a precursor to opioids and antagonists such as naltrexone. Although millennia older, the production of poppy head decoctions can be seen as a quick-and-dirty variant of the Kábáy poppy straw process, which since its publication in 1930 has become the major method of obtaining licit opium alkaloids worldwide, as discussed in Morphine.
Poppy seeds are a common and flavorsome topping for breads and cakes. One gram of poppy seeds contains up to 33 micrograms of morphine and 14 micrograms of codeine, and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration in the United States formerly mandated that all drug screening laboratories use a standard cutoff of 300 nanograms per milliliter in urine samples. A single poppy seed roll (0.76 grams of seeds) usually did not produce a positive drug test, but a positive result was observed from eating two rolls. A slice of poppy seed cake containing nearly five grams of seeds per slice produced positive results for 24 hours. Such results are viewed as false positive indications of drug use and were the basis of Poppy seed defence, a legal defense. On November 30, 1998, the standard cutoff was increased to 2000 nanograms (two micrograms) per milliliter. Confirmation by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry will distinguish amongst opium and variants including poppy seeds, heroin, and morphine and codeine pharmaceuticals by measuring the morphine:codeine ratio and looking for the presence of noscapine and acetylcodeine, the latter of which is only found in illicitly produced heroin, and heroin metabolites such as 6-monoacetylmorphine.
Harvesting and processing
 When grown for opium production, the skin of the ripening pods of these poppies is scored by a sharp blade at a time carefully chosen so that rain, wind, and dew cannot spoil the exudation of white, milky
When grown for opium production, the skin of the ripening pods of these poppies is scored by a sharp blade at a time carefully chosen so that rain, wind, and dew cannot spoil the exudation of white, milky latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms ...
, usually in the afternoon. Incisions are made while the pods are still raw, with no more than a slight yellow tint, and must be shallow to avoid penetrating hollow inner chambers or ''loculi'' while cutting into the lactiferous vessels. In the Indian Subcontinent, Afghanistan, Central Asia and Iran, the special tool used to make the incisions is called a ''nushtar'' or "nishtar" (from Persian language, Persian, meaning a lancet) and carries three or four blades three millimeters apart, which are scored upward along the pod. Incisions are made three or four times at intervals of two to three days, and each time the "poppy tears", which dry to a sticky brown resin, are collected the following morning. One acre harvested in this way can produce three to five kilograms of raw opium. In the Soviet Union, pods were typically scored horizontally, and opium was collected three times, or else one or two collections were followed by isolation of opiates from the ripe capsules. Oil poppies, an alternative strain of ''P. somniferum'', were also used for production of opiates from their capsules and stems. A traditional Chinese method of harvesting opium latex involved cutting off the heads and piercing them with a coarse needle then collecting the dried opium 24 to 48 hours later.
Raw opium may be sold to a merchant or broker on the black market, but it usually does not travel far from the field before it is refined into morphine base, because pungent, jelly-like raw opium is bulkier and harder to smuggle. Crude laboratories in the field are capable of refining opium into morphine base by a simple acid-base extraction. A sticky, brown paste, morphine base is pressed into bricks and sun-dried, and can either be smoked, prepared into other forms or processed into heroin.
Other methods of preparation (besides smoking), include processing into regular opium tincture
A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%.Groot Handboek Geneeskrachtige Planten by Geert Verhelst In chemistr ...
(''tinctura opii''), laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
, paregoric (''tinctura opii camphorata''), herbal wine (e.g., ''vinum opii''), opium powder (''pulvis opii''), opium sirup (''sirupus opii'') and opium extract (''extractum opii'').Belgische Farmacopee, 5de uitgave, 1966; part 3 Vinum opii is made by combining sugar, white wine, cinnamon, and cloves. Opium syrup is made by combining 97.5 part sugar syrup with 2.5 parts opium extract. Opium extract (''extractum opii'') finally can be made by macerating raw opium with water. To make opium extract, 20 parts water are combined with 1 part raw opium which has been boiled for 5 minutes (the latter to ease mixing).
Heroin is widely preferred because of increased potency. One study in postaddicts found heroin to be approximately 2.2 times more potent than morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
by weight with a similar duration; at these relative quantities, they could distinguish the drugs subjectively but had no preference. Heroin was also found to be twice as potent as morphine in surgical anesthesia. Morphine is converted into heroin by a simple chemical reaction with acetic anhydride, followed by purification. Especially in Mexican production, opium may be converted directly to "black tar heroin" in a simplified procedure. This form predominates in the U.S. west of the Mississippi. Relative to other preparations of heroin, it has been associated with a dramatically decreased rate of HIV transmission among intravenous drug users (4 percent in Los Angeles vs. 40 percent in New York) due to technical requirements of injection, although it is also associated with greater risk of venous Sclerosis (medicine), sclerosis and necrotizing fasciitis.
Illegal production

 opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan is currently the primary producer of the drug. After regularly producing 70 percent of the world's opium, Afghanistan decreased production to 74 tons per year under a ban by the Taliban in 2000, a move which cut production by 94 percent. A year later, after American and British troops War in Afghanistan (2001–present), invaded Afghanistan, removed the Taliban and installed the interim government, the land under cultivation leapt back to , with Afghanistan supplanting Burma to become the world's largest opium producer once more. Opium production in that country has increased rapidly since, reaching an all-time high in 2006. According to Drug Enforcement Administration, DEA statistics, Afghanistan's production of oven-dried opium increased to 1,278 tons in 2002, more than doubled by 2003, and nearly doubled again during 2004. In late 2004, the U.S. government estimated that 206,000 hectares were under poppy cultivation, 4.5 percent of the country's total cropland, and produced 4,200 metric tons of opium, 76 percent of the world's supply, yielding 60 percent of Afghanistan's gross domestic product. In 2006, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime estimated production to have risen 59 percent to in cultivation, yielding 6,100 tons of opium, 82 percent of the world's supply. The value of the resulting heroin was estimated at , of which Afghan farmers were estimated to have received in revenue. For farmers, the crop can be up to ten times more profitable than wheat. The price of opium is around per kilo. Opium production has led to rising tensions in Afghan villages. Though direct conflict has yet to occur, the opinions of the new class of young rich men involved in the opium trade are at odds with those of the traditional village leaders.
opium production in Afghanistan, Afghanistan is currently the primary producer of the drug. After regularly producing 70 percent of the world's opium, Afghanistan decreased production to 74 tons per year under a ban by the Taliban in 2000, a move which cut production by 94 percent. A year later, after American and British troops War in Afghanistan (2001–present), invaded Afghanistan, removed the Taliban and installed the interim government, the land under cultivation leapt back to , with Afghanistan supplanting Burma to become the world's largest opium producer once more. Opium production in that country has increased rapidly since, reaching an all-time high in 2006. According to Drug Enforcement Administration, DEA statistics, Afghanistan's production of oven-dried opium increased to 1,278 tons in 2002, more than doubled by 2003, and nearly doubled again during 2004. In late 2004, the U.S. government estimated that 206,000 hectares were under poppy cultivation, 4.5 percent of the country's total cropland, and produced 4,200 metric tons of opium, 76 percent of the world's supply, yielding 60 percent of Afghanistan's gross domestic product. In 2006, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime estimated production to have risen 59 percent to in cultivation, yielding 6,100 tons of opium, 82 percent of the world's supply. The value of the resulting heroin was estimated at , of which Afghan farmers were estimated to have received in revenue. For farmers, the crop can be up to ten times more profitable than wheat. The price of opium is around per kilo. Opium production has led to rising tensions in Afghan villages. Though direct conflict has yet to occur, the opinions of the new class of young rich men involved in the opium trade are at odds with those of the traditional village leaders.
 Chinese production mainly trades with and profits from North America. In 2002, they were seeking to expand through eastern United States. In the post 9/11 era, trading between borders became difficult and because new international laws were set into place, the opium trade became more diffused. Power shifted from remote to high-end smugglers and opium traders. Outsourcing became a huge factor for survival for many smugglers and opium farmers.
Chinese production mainly trades with and profits from North America. In 2002, they were seeking to expand through eastern United States. In the post 9/11 era, trading between borders became difficult and because new international laws were set into place, the opium trade became more diffused. Power shifted from remote to high-end smugglers and opium traders. Outsourcing became a huge factor for survival for many smugglers and opium farmers.
Legal production
Legal opium production is allowed under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs and other international drug treaties, subject to strict supervision by the law enforcement agency, law enforcement agencies of individual countries. The leading legal production method is the Robertson-Gregory process, whereby the entire poppy, excluding roots and leaves, is mashed and stewed in dilute acid solutions. The alkaloids are then recovered via acid-base extraction and purified. The exact date of its discovery is unknown, but it was described by Wurtz in his ''Dictionnaire de chimie pure et appliquée'' published in 1868. Legal opium production in India is much more traditional. As of 2008, opium was collected by farmers who were licensed to grow of opium poppies, who to maintain their licences needed to sell 56 kilograms of unadulterated raw opium paste. The price of opium paste is fixed by the government according to the quality and quantity tendered. The average is around 1500 rupees () per kilogram. Some additional money is made by drying the poppy heads and collecting poppy seeds, and a small fraction of opium beyond the quota may be consumed locally or diverted to the black market. The opium paste is dried and processed into government opium and alkaloid factories before it is packed into cases of 60 kilograms for export. Purification of chemical constituents is done in India for domestic production, but typically done abroad by foreign importers. Legal opium importation from India and Turkey is conducted by Mallinckrodt, Noramco, Abbott Laboratories, Purdue Pharma, and Cody Laboratories Inc. in the United States, and legal opium production is conducted by GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, Johnson Matthey, and Mayne Pharma, Mayne in Tasmania, Australia; Sanofi Aventis in France; Shionogi Pharmaceutical in Japan; and MacFarlan Smith in the United Kingdom. The UN treaty requires that every country submit annual reports to the International Narcotics Control Board, stating that year's actual consumption of many classes of controlled drugs as well as opioids and projecting required quantities for the next year. This is to allow trends in consumption to be monitored and production quotas allotted. In 2005, the European Senlis Council began developing a programme which hopes to solve the problems caused by the large quantity of Opium production in Afghanistan, opium produced illegally in Afghanistan, most of which is converted to heroin and smuggled for sale in Europe and the United States. This proposal is to opium licensing, license Afghan farmers to produce opium for the world pharmaceutical market, and thereby solve another problem, that of chronic underuse of potent analgesics where required within developing country, developing nations. Part of the proposal is to overcome the "80–20 rule" that requires the U.S. to purchase 80 percent of its legal opium from India and Turkey to include Afghanistan, by establishing a second-tier system of supply control that complements the current INCB regulated supply and demand system by providing poppy-based medicines to countries who cannot meet their demand under the current regulations. Senlis arranged a conference in Kabul that brought drug policy experts from around the world to meet with Afghan government officials to discuss internal security, corruption issues, and legal issues within Afghanistan. In June 2007, the Council launched a "Poppy for Medicines" project that provides a technical blueprint for the implementation of an integrated control system within Afghan village-based poppy for medicine projects: the idea promotes the economic diversification by redirecting proceeds from the legal cultivation of poppy and production of poppy-based medicines.Poppy for Medicine: "Licensing poppy for the production of essential medicines: an integrated counter-narcotics, development, and counter-insurgency model for Afghanistan". ''Senlis Council.'' June 2007. Retrieved on September 21, 2007. There has been criticism of the Senlis report findings by Macfarlan Smith, who argue that though they produce morphine in Europe, they were never asked to contribute to the report.
Cultivation in the UK
In late 2006, the British government permitted the pharmaceutical company MacFarlan Smith (a Johnson Matthey company) to cultivate opium poppies in England for medicinal reasons, after Macfarlan Smith's primary source, India, decided to increase the price of export opium latex. This move is well received by British farmers, with a major opium poppy field located in Didcot, England. The British government has contradicted the Home Office's suggestion that opium cultivation can be legalized in Afghanistan for exports to the United Kingdom, helping lower poverty and internal fighting while helping the National Health Service, NHS to meet the high demand formorphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
and heroin. Opium poppy cultivation in the United Kingdom does not need a licence, but a licence is required for those wishing to extract opium for medicinal products.
Consumption
 In the industrialized world, the United States is the world's biggest consumer of prescription opioids, with Italy one of the lowest because of tighter regulations on prescribing narcotics for pain relief. Most opium imported into the United States is broken down into its
In the industrialized world, the United States is the world's biggest consumer of prescription opioids, with Italy one of the lowest because of tighter regulations on prescribing narcotics for pain relief. Most opium imported into the United States is broken down into its alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
constituents, and whether legal or illegal, most current drug use occurs with processed derivatives such as heroin rather than with unrefined opium.
Intravenous injection of opiates is most used: by comparison with injection, "dragon chasing" (heating of heroin on a piece of foil), and madak
Madak was a blend of opium and tobacco used as a recreational drug in 16th- and 17th-century China. It emerged in southern coastal areas in the first half of the 17th century. In the last quarter of the 18th century madak was phased out by raw ...
and "ack ack" (smoking of cigarettes containing tobacco mixed with heroin powder) are only 40 percent and 20 percent efficient, respectively. One study of British heroin addicts found a 12-fold excess mortality ratio (1.8 percent of the group dying per year). Most heroin deaths result not from overdose ''per se'', but combination with other depressant drugs such as alcohol or benzodiazepines.
The smoking of opium does not involve the pyrolysis, burning of the material as might be imagined. Rather, the prepared opium is indirectly heated to temperatures at which the active alkaloids, chiefly morphine, are vaporized. In the past, smokers would use a specially designed opium pipe which had a removable knob-like pipe-bowl of fired earthenware attached by a metal fitting to a long, cylindrical stem. A small "pill" of opium about the size of a pea would be placed on the pipe-bowl, which was then heated by holding it over an opium lamp, a special oil lamp with a distinct funnel-like chimney to channel heat into a small area. The smoker would lie on his or her side in order to guide the pipe-bowl and the tiny pill of opium over the stream of heat rising from the chimney of the oil lamp and inhale the vaporized opium fumes as needed. Several pills of opium were smoked at a single session depending on the smoker's tolerance to the drug. The effects could last up to twelve hours.
In Eastern world, Eastern culture, opium is more commonly used in the form of paregoric to treat diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
. This is a weaker solution than laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
, an alcoholic tincture which was prevalently used as a pain medication and sleeping aid. Tincture of opium has been prescribed for, among other things, severe diarrhea. Taken thirty minutes prior to meals, it significantly slows intestinal motility, giving the intestines greater time to absorb fluid in the stool.
Despite the historically negative view of opium as a cause of addiction, the use of morphine and other derivatives isolated from opium in the treatment of chronic pain has been reestablished. If given in controlled doses, modern opiates can be an effective treatment for neuropathic pain and other forms of chronic pain.Ballantyne, Jane C., and Jianren Mao. "Opioid Therapy For Chronic Pain". ''New England Journal of Medicine'' 349.20 (n.d.): 1943–1953. SocINDEX with Full Text. Web. November 3, 2011.
Chemical and physiological properties
Opium contains two main groups ofalkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
s. Phenanthrenes such as morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
, codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
, and thebaine
Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, '' Thēbai'' (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar ...
are the main psychoactive constituents. Isoquinolines such as papaverine
Papaverine (Latin ''papaver'', "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), occasionally in the treatment of erec ...
and noscapine
Noscapine (also known as Narcotine, Nectodon, Nospen, Anarcotine and (archaic) Opiane) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae ( ...
have no significant central nervous system effects. Morphine is the most prevalent and important alkaloid in opium, consisting of 10–16 percent of the total, and is responsible for most of its harmful effects such as lung edema, respiratory difficulties, coma, or cardiac or respiratory collapse. Morphine binds to and activates mu opioid receptors in the brain, spinal cord, stomach and intestine. Regular use can lead to drug tolerance or physical dependence. Chronic opium addicts in 1906 China or modern-day Iran consume an average of eight grams of opium daily.
Both analgesia and drug addiction are functions of the mu opioid receptor, the class of opioid receptor first identified as responsive to morphine. Tolerance is associated with the superactivation of the receptor, which may be affected by the degree of endocytosis caused by the opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid us ...
administered, and leads to a superactivation of cyclic AMP signaling. Long-term use of morphine in palliative care and the management of chronic pain always entails a risk that the patient develops tolerance or physical dependence. There are many kinds of Drug rehabilitation, rehabilitation treatment, including pharmacologically based treatments with naltrexone, methadone, or ibogaine.
In 2021, the International Agency for Research on Cancer concluded that opium is a Group 1 (sufficient evidence) human carcinogen, causing cancers of the larynx, lung, and urinary bladder.
Slang terms
Some slang terms for opium include: "Big O", "Shanghai Sally", "dope", "hop", "midnight oil", "O.P.", and "tar". "Dope" and "tar" can also refer to heroin. The traditional opium pipe is known as a "dream stick." The term ''dope'' entered the English language in the early nineteenth century, originally referring to viscous liquids, particularly sauces or gravy.Dave Wilton"dope"
, ''Wordorigins.org'' (5 January 2009). It has been used to refer to opiates since at least 1888, and this usage arose because opium, when prepared for smoking, is viscous.
See also
* Golden Crescent * Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Golden Triangle * History of Jardine, Matheson & Co. * Illegal drug trade in Colombia * Mexican Drug War * Nabidh * Opium replacement * Protocol for Limiting and Regulating the Cultivation of the Poppy Plant, the Production of, International and Wholesale Trade in, and Use of Opium * Psychoactive drug * Society for the Suppression of the Opium Trade * Morphine * HeroinReferences
Further reading
* Ahmad, Diana L. ''The Opium Debate and Chinese Exclusion Laws in the Nineteenth-century American West'' (University of Nevada Press, 2007). Drugs and Racism in the Old West. * Armero and Rapaport. ''The Arts of an Addiction. Qing Dynasty Opium Pipes and Accessories'' (privately printed, 2005) * Auerbach, Sascha. ''Race, Law and 'The Chinese Puzzle' in Imperial Britain.'' New York: Palgrave-Macmillan Press, 2009. * Booth, Martin. ''Opium: A History''. London: Simon & Schuster, Ltd., 1996. * * * * * Derks, Hans: ''History of the Opium Problem: The Assault on the East, ca. 1600–1950.'' Sinica Leidensia, 105. Leiden: Brill, 2012. . * Dikötter, Frank, Lars Laamann, and Zhou XunNarcotic culture: a history of drugs in China
Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004. * Dormandy, Thomas (2012) ''Opium: Reality's Dark Dream'', Yale University Press * Fairbank, J.K. (1978) ''The Cambridge History of China: volume 10 part I'', Cambridge, CUP * Franck Daninos, ''L'opium légal produit en France'', La Recherche, May 2005 * * Forbes, Andrew; Henley, David (2011). ''Traders of the Golden Triangle''. Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books. * * * Hideyuki Takano; ''The Shore Beyond Good and Evil: A Report from Inside Burma's Opium Kingdom'' (2002, Kotan, ) * Lucy Inglis, Inglis, Lucy, ''Milk of Paradise: A History of Opium'', Pan Macmillan, London, 2018. **Review: Julie Peakman: "Not Just Smelling the Flowers", ''History Today'' History Today Vol. 68/10, October 2018, pp. 102–103. * Latimer, Dean, and Jeff Goldberg with an Introduction by William Burroughs. ''Flowers in the Blood: The Story of Opium''. New York: Franklin Watts, 1981 * * Martin, Steven. ''The Art of Opium Antiques''. Chiang Mai: Silkworm Books, 2007. Photographs and history of Chinese and Vietnamese opium-smoking paraphernalia. * Alfred W. McCoy, McCoy, Alfred W. ''The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade''. New York: Lawrence Hill Books, 1991. * * * * David F. Musto, Musto, David F. ''The American Disease: Origins of Narcotic Control''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1987. * * * Peters, Gretchen. ''Seeds of Terror: How Heroin is Bankrolling the Taliban and Al Qaeda'', Thomas Dunne Books (2009). * * *
External links
A fleet of opium clippers on the River Ganges
Confessions of a Poppy Tea addict
Opium, morphine, and heroin
CIA publication
Erowid: Opium
by Michael Pollan (originally appeared in ''Harper's Magazine, Harper's''.)
Opium Museum
Opium paraphernalia and historical photos of opium smokers
BLTC Research
Speculations on the future of opioids
Traditional method of using opium in Thailand
Tsur Shezaf, Witer, The Opium Growers of Sinai
– Afghan Opium Survey 2009
The Alkaloids of Opium
, Scientific American, 20 July 1878, p. 36, historical account on the physiological effects of the first 16 known alkaloids {{authority control Opium, Analgesics Euphoriants IARC Group 1 carcinogens Medicinal plants Morphine Opioids