Osgood–Schlatter Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Osgood–Schlatter disease (OSD) is
 Osgood–Schlatter disease causes pain in the front lower part of the knee. This is usually at the ligament-bone junction of the patellar ligament and the tibial tuberosity.Çakmak, S., Tekin, L., & Akarsu, S. (2014). Long-term outcome of Osgood-Schlatter disease: not always favorable. Rheumatology International, 34(1), 135–136. The tibial tuberosity is a slight elevation of bone on the
Osgood–Schlatter disease causes pain in the front lower part of the knee. This is usually at the ligament-bone junction of the patellar ligament and the tibial tuberosity.Çakmak, S., Tekin, L., & Akarsu, S. (2014). Long-term outcome of Osgood-Schlatter disease: not always favorable. Rheumatology International, 34(1), 135–136. The tibial tuberosity is a slight elevation of bone on the
 OSD may result in an
OSD may result in an
 One of the main ways to prevent OSD is to check the participant's flexibility in their quadriceps and hamstrings. Lack of flexibility in these muscles can be a direct risk indicator for OSD. Muscles can shorten, which can cause pain but this is not permanent. Stretches can help reduce shortening of the muscles. The main stretches for prevention of OSD focus on the
One of the main ways to prevent OSD is to check the participant's flexibility in their quadriceps and hamstrings. Lack of flexibility in these muscles can be a direct risk indicator for OSD. Muscles can shorten, which can cause pain but this is not permanent. Stretches can help reduce shortening of the muscles. The main stretches for prevention of OSD focus on the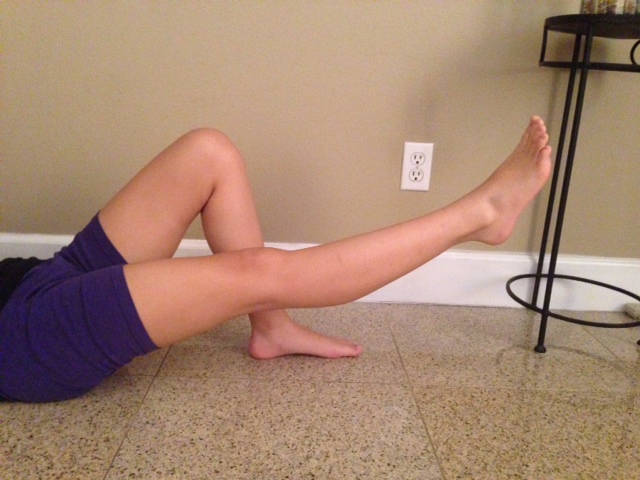 
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the patellar ligament
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when ...
at the tibial tuberosity (apophysitis
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a Tubercle, protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue bet ...
) usually affecting adolescents during growth spurts. It is characterized by a painful bump just below the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
that is worse with activity and better with rest. Episodes of pain typically last a few weeks to months. One or both knees may be affected and flares may recur.
Risk factors include overuse, especially sports which involve frequent running or jumping. The underlying mechanism is repeated tension on the growth plate
The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with ma ...
of the upper tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms. A plain X-ray may be either normal or show fragmentation in the attachment area.
Pain typically resolves with time. Applying cold to the affected area, rest, stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately expanded and flexed in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feelin ...
, and strengthening exercises may help. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
may be used. Slightly less stressful activities such as swimming or walking may be recommended. Casting the leg for a period of time may help. After growth slows, typically age 16 in boys and 14 in girls, the pain will no longer occur despite a bump potentially remaining.
About 4% of people are affected at some point in time. Males between the ages of 10 and 15 are most often affected. The condition is named after Robert Bayley Osgood (18731956), an American orthopedic surgeon, and Carl B. Schlatter (18641934), a Swiss surgeon, who described the condition independently in 1903.
Signs and symptoms
 Osgood–Schlatter disease causes pain in the front lower part of the knee. This is usually at the ligament-bone junction of the patellar ligament and the tibial tuberosity.Çakmak, S., Tekin, L., & Akarsu, S. (2014). Long-term outcome of Osgood-Schlatter disease: not always favorable. Rheumatology International, 34(1), 135–136. The tibial tuberosity is a slight elevation of bone on the
Osgood–Schlatter disease causes pain in the front lower part of the knee. This is usually at the ligament-bone junction of the patellar ligament and the tibial tuberosity.Çakmak, S., Tekin, L., & Akarsu, S. (2014). Long-term outcome of Osgood-Schlatter disease: not always favorable. Rheumatology International, 34(1), 135–136. The tibial tuberosity is a slight elevation of bone on the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
portion of the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
. The patellar tendon
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection whe ...
attaches the anterior quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
muscles to the tibia via the knee cap.
Intense knee pain is usually the presenting symptom that occurs during activities such as running, jumping, lifting things, squatting, and especially ascending or descending stairs and during kneeling. The pain is worse with acute knee impact. The pain can be reproduced by extending the knee against resistance, stressing the quadriceps, or striking the knee. Pain is initially mild and intermittent. In the acute phase, the pain is severe and continuous in nature. Impact of the affected area can be very painful. Bilateral symptoms are observed in 20–30% of people.
Risk factors
Risk factors include overuse, especially sports which involve running or jumping. The underlying mechanism is repeated tension on thegrowth plate
The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with ma ...
of the upper tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
. It also occurs frequently in male pole vaulters aged 14–22.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made based on signs and symptoms.Ultrasonography
This test can see various warning signs that predict if OSD might occur.Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, ...
can detect if there is any tissue swelling and cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
swelling. Ultrasonography's main goal is to identify OSD in the early stage rather than later on. It has unique features such as detection of an increase of swelling within the tibia or the cartilage surrounding the area and can also see if there is any new bone starting to build up around the tibial tuberosity.
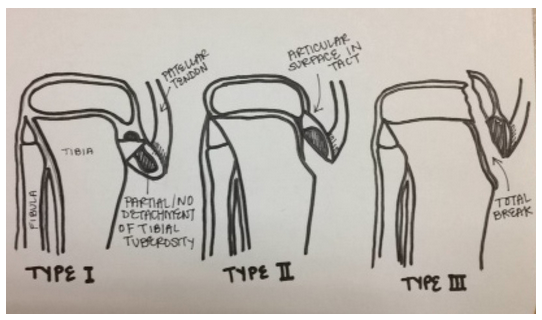
Types
 OSD may result in an
OSD may result in an avulsion fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall ...
, with the tibial tuberosity separating from the tibia (usually remaining connected to a tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tensi ...
or ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
). This injury is uncommon because there are mechanisms that prevent strong muscles from doing damage. The fracture on the tibial tuberosity can be a complete or incomplete break.
Type I: A small fragment is displaced proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
ly and does not require surgery.
Type II: The articular surface
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
of the tibia remains intact and the fracture occurs at the junction where the secondary center of ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
and the proximal tibial epiphysis
An epiphysis (; : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from one or more secondary centers of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, inc ...
come together (may or may not require surgery).
Type III: Complete fracture (through articular surface) including high chance of meniscal damage. This type of fracture usually requires surgery.
Differential diagnosis
Sinding-Larsen and Johansson syndrome, is an analogous condition involving thepatellar tendon
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection whe ...
and the lower margin of the patella
The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in m ...
bone, instead of the upper margin of the tibia. Sever's disease is an analogous condition affecting the Achilles tendon attachment to the heel
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg.
Structure
To distribute the compressive forces exerted ...
.
Prevention
 One of the main ways to prevent OSD is to check the participant's flexibility in their quadriceps and hamstrings. Lack of flexibility in these muscles can be a direct risk indicator for OSD. Muscles can shorten, which can cause pain but this is not permanent. Stretches can help reduce shortening of the muscles. The main stretches for prevention of OSD focus on the
One of the main ways to prevent OSD is to check the participant's flexibility in their quadriceps and hamstrings. Lack of flexibility in these muscles can be a direct risk indicator for OSD. Muscles can shorten, which can cause pain but this is not permanent. Stretches can help reduce shortening of the muscles. The main stretches for prevention of OSD focus on the hamstrings
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from anatomical_terms_of_location#Medial_and_lateral, medial to anatomical_terms_of_location#Medial_and_lateral, lateral, the semimembra ...
and quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
.
Direct stretching of the quadriceps can be painful so the use of foam rolling for self myofascial release can help gently restore flexibility and range of movement

Treatment
Treatment is generally conservative with rest, ice, and specific exercises being recommended. Simple pain medication may be used such as acetaminophen (paracetamol), or NSAIDs such asibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
. Saline injections have also been proposed for pain reduction. Typically symptoms resolve as the growth plate closes. Physiotherapy is generally recommended once the initial symptoms have improved to prevent recurrence. Surgery may rarely be used in those who have stopped growing yet still have symptoms.
Physiotherapy
Recommended efforts include exercises to improve the strength of the gluteals,quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
, hamstring
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.
Etymology
The word " ham" is derived from the Old ...
and gastrocnemius muscles.
Bracing or use of an orthopedic cast
An orthopedic cast, commonly referred to simply as a cast, is a form of medical treatment used to immobilize and support bones and soft tissues during the healing process after fractures, surgeries, or severe injuries. By restricting movement, ...
to enforce joint immobilization is rarely required and does not necessarily encourage a quicker resolution. However, bracing may give comfort and help reduce pain as it reduces strain on the tibial tubercle.
Surgery
Surgical excision may rarely be required in people who have stopped growing. Surgical removal of the ossicles generally results in good outcomes, with symptoms improvement after several weeks.Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation focuses on muscle strengthening, gait training, and pain control to restore knee function. Nonsurgical treatments for less severe symptoms include: exercises for strength, stretches to increase range of motion, ice packs, knee tape, knee braces, anti-inflammatory agents, and electrical stimulation to control inflammation and pain.Quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
and hamstring
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.
Etymology
The word " ham" is derived from the Old ...
exercises are commonly prescribed by rehabilitation experts restore flexibility and muscle strength.
Isometric exercise
An isometric exercise is an exercise involving the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement in the angle of the joint. The term "isometric" combines the Greek words ''isos'' (equal) and ''-metria'' (measuring), meaning that i ...
s, such as isometric leg extension
The leg extension is a resistance weight training exercise that targets the quadriceps muscle (m. quadriceps femoris) in the legs. The exercise is done using a machine called the Leg Extension Machine. There are various manufacturers of these mach ...
s, have been shown to strengthen the knee, reduce pain and inhibition, and help the tissue repair through Mechanotransduction
In cellular biology, mechanotransduction ('' mechano'' + '' transduction'') is any of various mechanisms by which cells convert mechanical stimulus into electrochemical activity. This form of sensory transduction is responsible for a number o ...
.
Other exercises can include leg raises, squats, and wall stretches to increase quadriceps and hamstring strength. This helps to avoid pain, stress, and tight muscles that lead to further injury that oppose healing.
Education and knowledge on stretches and exercises are important. Exercises should lack pain and increase gradually with intensity. The patient is given strict guidelines on how to perform exercises at home to avoid more injury. Exercises can include leg raises, squats and wall stretches to increase quadriceps and hamstring strength. This helps to avoid pain, stress, and tight muscles that lead to further injury that oppose healing. Knee orthotics
Orthotics () is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, sometimes known as braces, calipers, or splints. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of ...
such as patella straps and knee sleeves help decrease force traction and prevent painful tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
contact by restricting unnecessary movement, providing support, and also adding compression to the area of pain.
Prognosis
The condition is usually self-limiting and is caused by stress on thepatellar tendon
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection whe ...
that attaches the quadriceps muscle
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
at the front of the thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissu ...
to the tibial tuberosity. Following an adolescent growth spurt, repeated stress from contraction of the quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
is transmitted through the patellar tendon to the immature tibial tuberosity. This can cause multiple subacute avulsion fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall ...
s along with inflammation of the tendon, leading to excess bone growth in the tuberosity and producing a visible lump which can be very painful, especially when hit. Activities such as kneeling may also irritate the tendon.
The syndrome may develop without trauma or other apparent cause; however, some studies report up to 50% of patients relate a history of precipitating trauma. Several authors have tried to identify the actual underlying etiology and risk factors that predispose Osgood–Schlatter disease and postulated various theories. However, currently, it is widely accepted that Osgood–Schlatter disease is a traction apophysitis of the proximal tibial tubercle at the insertion of the patellar tendon caused by repetitive micro-trauma. In other
words, Osgood–Schlatter disease is an overuse injury and closely related to the physical activity of the child. It was shown that children
who actively participate in sports are affected more frequently as compared with non-participants. In a retrospective study of adolescents, old athletes actively participating in sports showed a frequency of 21% reporting the syndrome compared with only 4.5% of age-matched nonathletic controls.
The symptoms usually resolve with treatment but may recur for 12–24 months before complete resolution at skeletal maturity, when the tibial epiphysis fuses. In some cases the symptoms do not resolve until the patient is fully grown. In approximately 10% of patients the symptoms continue unabated into adulthood, despite all conservative measures.
Long-term implications
OSD occurs from the combined effects of tibial tuberosity immaturity and quadriceps tightness. There is a possibility of migration of theossicle
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossicu ...
or fragmentation in Osgood-Schlatter patients. The implications of OSD and the ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
of the tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
can lead to functional limitations and pain for patients into adulthood.
Of people admitted with OSD, about half were children who were between the ages of 1 and 17. In addition, in 2014, a case study of 261 patients was observed over 12 to 24 months. 237 of these people responded well to sport restriction and non-steroid anti-inflammatory agents, which resulted in recovery to normal athletic activity.
Epidemiology
Osgood–Schlatter disease generally occurs in boys and girls aged 9–16 coinciding with periods of growth spurts. It occurs more frequently in boys than in girls, with reports of a male-to-female ratio ranging from 3:1 to as high as 7:1. It has been suggested that difference is related to a greater participation by boys in sports and risk activities than by girls. Osgood–Schlatter disease resolves or becomes asymptomatic in the majority of cases. One study showed that 90% of reported patients had symptom resolution in 12–24 months. Because of this short symptomatic period with most patients, the number of people who become diagnosed is a fraction of the true number. For adolescents between the ages of 12–15, there is a disease prevalence of 9.8% with a greater 11.4% in males and 8.3% in females. Osgood-Schlatter's disease presents bilaterally in a range of about 20%-30% of patients. It was found that the leading cause for the incidence of the disease was regular sport practicing and shortening of the rectus femoris muscle in adolescents that were in the pubertal phase. There is a 76% prevalence of patients with a shortened rectus femoris in those who have the Osgood-Schlatter's disease. This risk ratio shows the anatomical relationship between the tibial tuberosity and the quadriceps muscle group, which connect through the patella and its ligamentous structures. In a survey of patients with the diagnosis, 97% reported to have pain during palpation over the tibial tuberosity. The high risk ratio with people with the disease and palpatory pain is likely the reason that the number one diagnosis method is with physical examination, rather than imaging as most bone pathologies are diagnosed. Research suggests that Osgood–Schlatter disease also increases the risk of tibial fractures. It's possible that the rapid tuberosity bone development and other changes to the proximal aspect of the knee with those who have the disease is the culprit to the increased risk. Because increased activity is a risk factor for developing Osgood–Schlatter disease there is also research that may suggest children and adolescents withADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple ...
are at higher risk. Increased activity and stress on the tibial tuberosity would be greater in a more active population in the 9-16 age bracket, but this study was still not conclusive as to which aspect of ADHD was the cause of the higher incidence.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Osgood-Schlatter Disease Chondropathies Inflammations Knee injuries and disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate