Old Church Of St Nidan, Llanidan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Old Church of St Nidan, Llanidan is a
 Parish worship transferred to the new church, along with some of the fittings. The old church was thereafter used as a
Parish worship transferred to the new church, along with some of the fittings. The old church was thereafter used as a
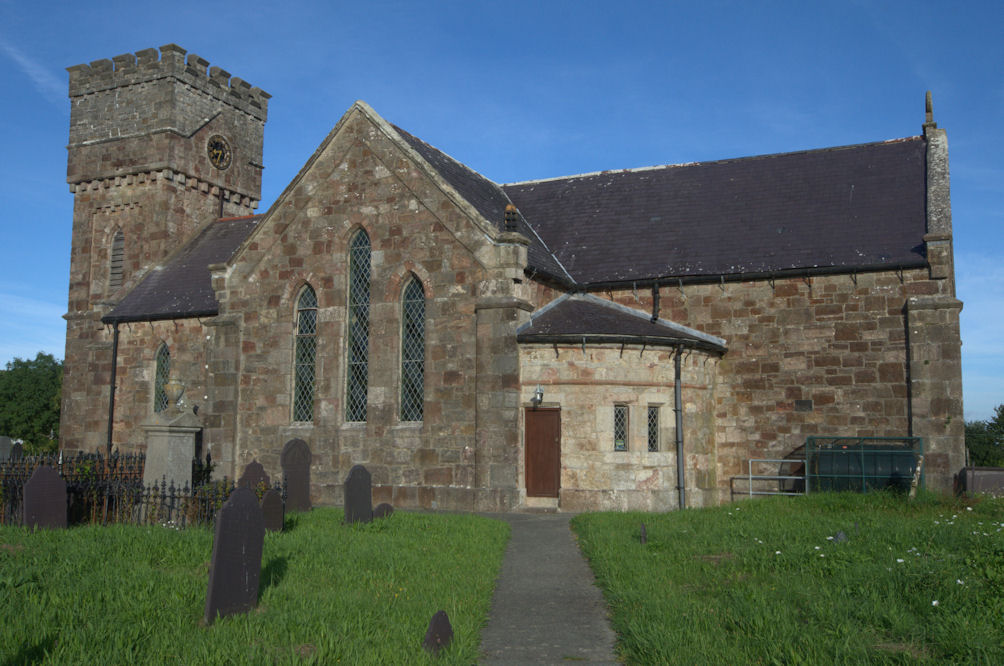
 St Nidan's has two naves or aisles divided by a central arcade, and a porch in the south-west corner. It is wide, the northern nave being about wider than the other. Before the church's partial demolition, the church was long and had a chapel, , on the south side. The walls, about thick, are built from local
St Nidan's has two naves or aisles divided by a central arcade, and a porch in the south-west corner. It is wide, the northern nave being about wider than the other. Before the church's partial demolition, the church was long and had a chapel, , on the south side. The walls, about thick, are built from local  Two of the six arches in the arcade are inside the church; the other four project beyond the east wall, which has been built around one of the octagonal piers that support the arches. The roof dates from the 15th century, although the visible beams are not original; the roof's exposed wooden trusses rest on sandstone
Two of the six arches in the arcade are inside the church; the other four project beyond the east wall, which has been built around one of the octagonal piers that support the arches. The roof dates from the 15th century, although the visible beams are not original; the roof's exposed wooden trusses rest on sandstone
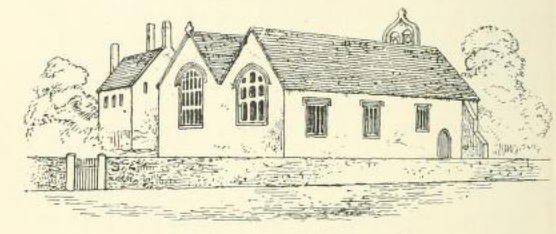 In 1802 the clergyman and antiquarian
In 1802 the clergyman and antiquarian
 The Welsh politician and church historian Sir Stephen Glynne visited the church in 1850. He said that St Nidan's, which he described as "now abandoned and in great measure ruinated", was "a larger and better structure than most of the Anglesey churches." At the time he saw it, the walls were still largely in place but the only roofed section was the western end; he commented that most of the church was "open to the skies."
The historian and clergyman Edmund Tyrrell Green, writing a survey of Anglesey church architecture and contents in 1929, described the arcade as "good" and some of the tracery in the windows as "very good". His view was that the "excellence of the work" at St Nidan's was because of its link with Beddgelert Priory.
The authors of a 1990 book about the lost churches of Wales said that St Nidan's was "now an evocative shell decorously mantled with ivy and enclosed by an overgrown graveyard". They described it as "a dark, dusty and empty place", but said that the "elegant" arcade "rises from the graveyard like an abstract sculpture." The quality of the stone carving of the doors and windows, they said, was evidence of "the vanished splendour of Llanidan."
A 2002 book about Welsh churchyards comments that "a pilgrimage undertaken to this churchyard is rewarding", since there is "little to distract and much to suggest the quiet years of Nidan's ministry in this secluded spot." Noting how the site can be reached from the Menai Strait yet remains hidden from it, the author added that "some stillness still remains in secret places like Llanidan." A 2005 guide to Wales said that "the romantic yew-encircled ruin" of St Nidan's "should not be missed."
The Welsh politician and church historian Sir Stephen Glynne visited the church in 1850. He said that St Nidan's, which he described as "now abandoned and in great measure ruinated", was "a larger and better structure than most of the Anglesey churches." At the time he saw it, the walls were still largely in place but the only roofed section was the western end; he commented that most of the church was "open to the skies."
The historian and clergyman Edmund Tyrrell Green, writing a survey of Anglesey church architecture and contents in 1929, described the arcade as "good" and some of the tracery in the windows as "very good". His view was that the "excellence of the work" at St Nidan's was because of its link with Beddgelert Priory.
The authors of a 1990 book about the lost churches of Wales said that St Nidan's was "now an evocative shell decorously mantled with ivy and enclosed by an overgrown graveyard". They described it as "a dark, dusty and empty place", but said that the "elegant" arcade "rises from the graveyard like an abstract sculpture." The quality of the stone carving of the doors and windows, they said, was evidence of "the vanished splendour of Llanidan."
A 2002 book about Welsh churchyards comments that "a pilgrimage undertaken to this churchyard is rewarding", since there is "little to distract and much to suggest the quiet years of Nidan's ministry in this secluded spot." Noting how the site can be reached from the Menai Strait yet remains hidden from it, the author added that "some stillness still remains in secret places like Llanidan." A 2005 guide to Wales said that "the romantic yew-encircled ruin" of St Nidan's "should not be missed."
medieval church
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
in the community of Llanidan
Llanidan is a community in the south of Anglesey, Wales which includes the village of Brynsiencyn (). The parish is along the Menai Strait, about 4 miles north-east of Caernarfon (across the strait). The parish church of St Nidan is near the A ...
, in Anglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
, North Wales
North Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdon ...
, close to the Menai Strait
The Menai Strait () is a strait which separates the island of Anglesey from Gwynedd, on the mainland of Wales. It is situated between Caernarfon Bay in the south-west and Conwy Bay in the north-east, which are both inlets of the Irish Sea. The s ...
. The first church on the site was established in the 7th century by St Nidan, the confessor
In a number of Christian traditions, including Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism, a confessor is a priest who hears the confessions of penitents and pronounces absolution.
History
During the Diocletianic Persecut ...
of the monastery at Penmon
Penmon is a promontory, village and ecclesiastical parish on the eastern tip of the Isle of Anglesey in Wales, about east of the town of Beaumaris. It is in the community of Llangoed. The name comes from (which can mean "head", "end" or "pro ...
, Anglesey, but the oldest parts of the present structure, now closed and partly ruined, date from the 14th century. In about 1500 the church was enlarged by the addition of a second nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
on the north side, separated from the earlier nave by an arcade
Arcade most often refers to:
* Arcade game, a coin-operated video, pinball, electro-mechanical, redemption, etc., game
** Arcade video game, a coin-operated video game
** Arcade cabinet, housing which holds an arcade video game's hardware
** Arcad ...
of six arches. During 1839 till 1843 a new church was built nearby to serve the local community, partly due to the cost of repairing the old church. Much of the building was subsequently demolished, leaving only part of the western end and the central arcade. The decision was condemned at the time by Harry Longueville Jones
Harry Longueville Jones (1806–1870) was a Welsh archæologist, artist, Inspector of Schools for Wales and leading founding member of the Cambrian Archaeological Association.
Ancestry and early life
Harry Longueville Jones was the great-gran ...
, a clergyman and antiquarian, who lamented the "melancholy fate" of what he called "one of the largest and most important hurchesin the island of Anglesey". Other appreciative comments have been made about the church both before and after its partial demolition.
After that a new church was opened, the old church was used as a chapel for funerals for a period of time. It has been restored by the owners of the adjoining house, Plas Llanidan, and is occasionally open to the public. The remaining parts of the church are a Grade II* listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
, a national designation given to "particularly important buildings of more than special interest", in particular because St Nidan's is regarded as "a good example of a simple medieval rural church, enriched by 15th-century additions".
In the 12th century, Gerald of Wales
Gerald of Wales (; ; ; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He ...
said that the church possessed a curious stone carving similar to a thigh that would always return by the next day no matter how far away it was taken. A Norman earl, he recounted, had chained it to a large rock and thrown it into the sea, only for the stone to return to the church by the following morning. A sandstone chest containing bone fragments, possibly are relics of a saint, were found buried beneath the altar. The chest and the church's 13th-century font were relocated to the new church.
History and location
Foundation and construction
St Nidan's Church is in the south ofAnglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
, Wales, near the village of Brynsiencyn. It is about a quarter of a mile (400 m) from the Menai Strait
The Menai Strait () is a strait which separates the island of Anglesey from Gwynedd, on the mainland of Wales. It is situated between Caernarfon Bay in the south-west and Conwy Bay in the north-east, which are both inlets of the Irish Sea. The s ...
, which divides the mainland of Wales from the island of Anglesey. The authors of a 2009 guide to the buildings of north-west Wales record the tradition that a church was first established at this site in 616. St Nidan, who founded the church, was associated with St Seiriol's monastery at Penmon
Penmon is a promontory, village and ecclesiastical parish on the eastern tip of the Isle of Anglesey in Wales, about east of the town of Beaumaris. It is in the community of Llangoed. The name comes from (which can mean "head", "end" or "pro ...
, on the eastern tip of Anglesey, and was the monastery's confessor
In a number of Christian traditions, including Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism, a confessor is a priest who hears the confessions of penitents and pronounces absolution.
History
During the Diocletianic Persecut ...
. The area takes its name from the church: the Welsh word originally meant "enclosure" and then "church", and "‑idan" is a modified form of the saint's name.
The church and rectory are mentioned in a charter of 1360 as being owned by the priory at Beddgelert
Beddgelert () is a village and community (Wales), community in the Snowdonia area of Gwynedd, Wales. The population of the community taken at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census was 460 (rounded to the nearest 10). This includes Nan ...
, Gwynedd; earlier records have been lost and therefore the date of the priory's acquisition is unknown. As a result, writes the historian Antony Carr, the reason for the "distant community" of Augustinians
Augustinians are members of several religious orders that follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, written about 400 A.D. by Augustine of Hippo. There are two distinct types of Augustinians in Catholic religious orders dating back to the 12th–13 ...
in Beddgelert possessing Llanidan and three other churches in Anglesey cannot now be discovered. Carr notes that the priory also controlled two churches on the other side of the Menai Strait from Llanidan. Ownership of the church was passed down to Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement wit ...
at the dissolution of the monasteries in 1535. His successor, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history ...
, granted the advowson
Advowson () or patronage is the right in English law of a patron (avowee) to present to the diocesan bishop (or in some cases the ordinary if not the same person) a nominee for appointment to a vacant ecclesiastical benefice or church living, a ...
(the right of a patron to choose the parish priest) and the grounds surrounding St Nidan's, including the estate house called Plas Llanidan, to an Edward Downam and a Peter Ashton; thereafter, in the following centuries, the right and the land passed on through sale, on marriage and by bequest into the hands of the Boston family.
The remaining part of the south nave, the oldest section of the present structure, dates from medieval times
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and t ...
; the north doorway and tracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support th ...
(patterns of stonework in the windows) point to the 14th century. In about 1500, the church was enlarged by the addition of a south porch and a second nave to the north. An arcade
Arcade most often refers to:
* Arcade game, a coin-operated video, pinball, electro-mechanical, redemption, etc., game
** Arcade video game, a coin-operated video game
** Arcade cabinet, housing which holds an arcade video game's hardware
** Arcad ...
(row of arches) was constructed between the two naves. Enlargement by adding a second nave was not as common in Anglesey as elsewhere in Wales. Llanidan is one of three examples on the island; the others are St Beuno's, Aberffraw and St Cwyfan's, Llangwyfan. It is uncertain whether St Nidan's was enlarged because of a growth in the numbers attending the church or because of the generosity of a benefactor.
Replacement and demolition
A new church, also dedicated to St Nidan, was built to replace the old one between 1839 and 1843. This was because the old church required considerable repair and the growing population in Brynsiencyn needed a church closer to their village. Much of the structure of the old church was demolished in 1844, leaving only the western end (enclosed by a new wall at the east) and the arcade. Some walling was constructed at the east end of the arcade to help support the arches, but it sank because it was apparently built over a grave. In 1913, the tops of the external arches were covered with asphalt and turf in an attempt to make them more weather-proof. One of thevoussoir
A voussoir ( UK: ; US: ) is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault.“Voussoir, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Acces ...
s in the easternmost arch was replaced at the same time due to its poor condition.
 Parish worship transferred to the new church, along with some of the fittings. The old church was thereafter used as a
Parish worship transferred to the new church, along with some of the fittings. The old church was thereafter used as a mortuary
A morgue or mortuary (in a hospital or elsewhere) is a place used for the storage of human corpses awaiting identification (ID), removal for autopsy, respectful burial, cremation or other methods of disposal. In modern times, corpses have cus ...
chapel for a time. The churchyard continued to be used for burials until 1902. In modern times, the owners of Plas Llanidan have restored the church, and it is used by them as a private chapel. The churchyard is kept locked, but the church and the gardens of Plas Llanidan are occasionally opened to the public.
The 19th-century clergyman and antiquarian Harry Longueville Jones
Harry Longueville Jones (1806–1870) was a Welsh archæologist, artist, Inspector of Schools for Wales and leading founding member of the Cambrian Archaeological Association.
Ancestry and early life
Harry Longueville Jones was the great-gran ...
disputed the need to replace the old church and condemned its "melancholy fate", describing the reasons for its demise as "pretexts". In his view the only part of the church that needed repair was the "ruinous" western end (which had been "badly constructed in the first instance"), yet this part was saved while the "good portions of the building" were destroyed. Furthermore, the cost of the new church was more than double the cost of repairs to the medieval church, which could have "endure for ages to come". He added that it might have been thought to be safe, as it was so close to Lord Boston's house and thus "under the shadow of the lord of the domain", and he condemned the "evil hour" in which "the ruthless hand of the destroyer was allowed to be lifted against it by those whose first duty it was to see that it took no harm". He stated that "when buildings, dedicated to God's service by the piety of former ages, are allowed to be treated in this manner by the constituted authorities of the land ... the institutions to which they are attached cannot be expected to find greater favour at the hands of the fickle and ignorant multitude." He also noted that the new church was only a little larger than its predecessor.
People associated with the church
The cleric and antiquarianHenry Rowlands
Henry Rowlands (1655–1723) was rector of Llanidan on Anglesey, and the author of ''Mona Antiqua Restaurata: An Archaeological Discourse on the Antiquities, Natural and Historical, of the Isle of Anglesey, the Antient Seat of the British Druids' ...
, who wrote a history of Anglesey entitled ''Mona Antiqua Restaurata'', was the vicar of St Nidan's from 1696 until his death in 1723. Thomas Williams, a politician and businessman who became wealthy through copper mining in Anglesey, was buried in the churchyard in 1802, but was reburied at St Tegfan's, Llandegfan, in the 1830s. Isaac Jones, a cleric and translator of theological texts, was a curate of Llanidan and other churches in the vicinity from 1840 until his death in 1850. He is buried in the churchyard of St Nidan's. The sculptor John Gibson (1790–1866) was the son of William Gibson, the fourth of his family to serve as the parish clerk at St Nidan's. The Gibson family was associated with the church from the early 18th century onwards; the baptism of Grace, daughter of George Gibson, is recorded in the registers in 1708.
Architecture and fittings
Structure
 St Nidan's has two naves or aisles divided by a central arcade, and a porch in the south-west corner. It is wide, the northern nave being about wider than the other. Before the church's partial demolition, the church was long and had a chapel, , on the south side. The walls, about thick, are built from local
St Nidan's has two naves or aisles divided by a central arcade, and a porch in the south-west corner. It is wide, the northern nave being about wider than the other. Before the church's partial demolition, the church was long and had a chapel, , on the south side. The walls, about thick, are built from local rubble masonry
Rubble masonry or rubble stone is rough, uneven building stone not laid in regular courses. It may fill the core of a wall which is faced with unit masonry such as brick or ashlar. Some medieval cathedral walls have outer shells of ashlar wi ...
with a covering of sandstone. The present wall at the east end was added after the rest of the church was demolished. The western wall has been rebuilt and buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient (typically Gothic) buildings, as a means of providing support to act ...
es added to the south side and north-west corner to help support the structure; Jones thought that they dated from the 16th century. The roof above the remaining western section is made from slates. At the top of the west end of the roof above the south aisle, there is a stone bellcote
A bellcote, bell-cote or bell-cot is a small framework and shelter for one or more bells. Bellcotes are most common in church architecture but are also seen on institutions such as schools. The bellcote may be carried on brackets projecting from ...
with two bells.
The south porch contains a water stoup
A holy water font or stoup is a vessel containing holy water which is generally placed near the entrance of a church. It is often placed at the base of a crucifix or other Christian art. It is used in Catholic, as well as many Lutheran and Anglica ...
that was said miraculously never to dry up; the water was traditionally regarded as having healing powers. There is a second entrance on the north side through a 15th-century arched doorway decorated with carved human heads. Two verses from Psalm 84
Psalm 84 is the 84th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in the English of the King James Version: "How amiable are thy tabernacles, O Lord of hosts!". The Book of Psalms forms part of the ''Ketuvim'' section of the Hebrew Bible and part of ...
(in Welsh) are written on the wall above the doorway: "For one day in thy Courts is better than a thousand. I had rather be a door-keeper in the house of my God than to dwell in the tents of ungodliness." These are the only surviving portions of the Biblical texts that once decorated the internal walls.
The north wall has a window with two lights (sections of window separated by mullion
A mullion is a vertical element that forms a division between units of a window or screen, or is used decoratively. It is also often used as a division between double doors. When dividing adjacent window units its primary purpose is a rigid sup ...
s) topped with trefoil
A trefoil () is a graphic form composed of the outline of three overlapping rings, used in architecture, Pagan and Christian symbolism, among other areas. The term is also applied to other symbols with a threefold shape. A similar shape with f ...
s (a pattern of three overlapping circles). The two arched east windows, one in each aisle, are decorated with tracery; the southern window reuses some tracery from the 15th century. The demolished southern chapel had a two-light window similar to that at St Peter's, Newborough, which Jones considered to be of "very rude workmanship", and three-light square-headed windows in the east and west walls. Jones also noted the loss of the original window at the end of the northern aisle, which was from the 14th century in his view, and some windows in the north wall "of excellent workmanship". The southern aisle, he said, had had "a small circular headed window, filled up from a pointed one" at the eastern end; the east window "was of a design more remarkable for its singularity than its beauty."
 Two of the six arches in the arcade are inside the church; the other four project beyond the east wall, which has been built around one of the octagonal piers that support the arches. The roof dates from the 15th century, although the visible beams are not original; the roof's exposed wooden trusses rest on sandstone
Two of the six arches in the arcade are inside the church; the other four project beyond the east wall, which has been built around one of the octagonal piers that support the arches. The roof dates from the 15th century, although the visible beams are not original; the roof's exposed wooden trusses rest on sandstone corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal keyed into and projecting from a wall to carry a wikt:superincumbent, bearing weight, a type of bracket (architecture), bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in t ...
s. A 1937 survey by the Royal Commission on Ancient and Historical Monuments in Wales and Monmouthshire
The Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales (RCAHMW; ; ), established in 1908, is a Welsh Government sponsored body concerned with some aspects of the archaeological, architectural and historic environment of Wales. I ...
noted 20 memorials from the 17th and 18th centuries. It also recorded the presence of a sundial on a pedestal, dated 1768, and some stone shields that were not attached to the building, bearing dates of 1561 and 1563. Most of the fittings now in St Nidan's are not original, and come from other churches in north-west Wales; the granite altar is modern.
Thigh stone and reliquary
The 19th-century antiquarianAngharad Llwyd
Angharad Llwyd (15 April 1780 – 16 October 1866) was a Welsh antiquary and a prizewinner at the National Eisteddfod of Wales. She is generally considered one of the most important collectors and copiers of manuscripts of the period.
Biography ...
, who wrote a history of Anglesey in 1833, recorded the story noted by Gerald of Wales
Gerald of Wales (; ; ; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He ...
in the late 12th century that the church once possessed a stone "resembling a human thigh" which would return "of its own accord" however far away it was carried. It was sometimes known as the "homing stone". Gerald said that Hugh d'Avranches, 1st Earl of Chester
Hugh d'Avranches ( 1047 – 27 July 1101), nicknamed ''le Gros'' (the Large) or ''Lupus'' (the Wolf), was from 1071 the second Norman Earl of Chester and one of the great magnates of early Norman England.
Early life and career
Hugh d'A ...
(who died in 1101) had tested this story by throwing the stone into the sea, chained to a large rock, only to discover that the stone had returned by the next morning. As a result, the Norman earl issued an order that no-one was to attempt to move it. It was popularly believed that if a couple had sexual intercourse near the stone (something that Gerald said happened "frequently"), it would "sweat large drops of water" and the woman would not become pregnant. Henry Rowlands wrote that the stone had been stolen from the wall of the churchyard (into which it had been set) during his time at St Nidan's.
When Rowlands was vicar of St Nidan's, a small chest was found buried about under the altar, containing some bone pieces. His view was that it contained the relics of a saint from St Nidan's or another church in the region ( St Beuno's Church, Clynnog Fawr or St Dwynwen's Church, Llanddwyn), and that the chest had placed in St Nidan's during the time of Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. The only surviving son of Henry VIII by his third wife, Jane Se ...
for safe keeping. The sandstone reliquary
A reliquary (also referred to as a ''shrine'', ''Chasse (casket), chasse'', or ''phylactery'') is a container for relics. A portable reliquary, or the room in which one is stored, may also be called a ''feretory''.
Relics may be the purported ...
is now kept at the new church, where local tradition maintains that it holds the remains of St Nidan. Jones said that it was "unique, as far as Wales is concerned." The 13th-century font, which Jones described as "a singularly beautiful specimen", was moved to the new church in about 1860.
Assessment
Listing
St Nidan's has national recognition and statutory protection from alteration as it is a Grade II*listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
, the second-highest of the three grades of listing, designating "particularly important buildings of more than special interest". It was given this status on 30 January 1968 and has been listed because it is regarded as "a good example of a simple medieval rural church, enriched by 15th-century additions." Cadw
(, a Welsh verbal noun meaning "keeping/preserving") is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government and part of the Tourism and Culture group. works to protect the historic buildings and structures, the landscapes and heritage ...
, the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of Cabinet secretary, cabinet secretaries and Minister of State, ministers. It is led by the F ...
body responsible for the built heritage of Wales and the inclusion of Welsh buildings on the statutory lists, also notes that although it was partly demolished in the middle of the 19th century, "what remains can be considered a well preserved and important survival of a double-naved church, retaining many 15th-century features such as the central arcade."
The wall around the churchyard is also a listed building, at Grade II – the lowest of the three grades of listing, designating "buildings of special interest, which warrant every effort being made to preserve them". According to Cadw, the wall probably dates from the 15th century, from around the time that the church was extended.
Pre-demolition comments
 In 1802 the clergyman and antiquarian
In 1802 the clergyman and antiquarian John Skinner John Skinner may refer to:
Politicians
* John Skinner (MP for Maldon), 1391–1393, MP for Maldon 1391 and 1393
* John Skinner (fl.1395-99), MP for Reigate 1395, 1397 and 1399
* John Skinner (fl.1414-20), MP for Reigate 1414, 1415 and 1420
*John Sk ...
visited Anglesey to see the island's Celtic remains, beginning his tour by rowing across the Menai Strait to land at Llanidan. His view was that the church "seems superior to the generality of Welsh buildings of the kind", with its double roof and two bells, but he also said that "the interior of the building has little to attract notice". Angharad Llwyd described it in 1833 as "a spacious structure, containing several good monuments".
Commenting in 1846 on the church as it had been before demolition started, Harry Longueville Jones said that St Nidan's was "one of the largest and most important hurchesin the island of Anglesey" for its varied architecture, fittings and traditions. He noted the "rather curious" position of the church, in a "nearly circular enclosure" with tall trees around it, and said that "the effect of the western end with the porch, overgrown by an enormous quantity of ivy, was picturesque in the extreme".
Post-demolition comments
 The Welsh politician and church historian Sir Stephen Glynne visited the church in 1850. He said that St Nidan's, which he described as "now abandoned and in great measure ruinated", was "a larger and better structure than most of the Anglesey churches." At the time he saw it, the walls were still largely in place but the only roofed section was the western end; he commented that most of the church was "open to the skies."
The historian and clergyman Edmund Tyrrell Green, writing a survey of Anglesey church architecture and contents in 1929, described the arcade as "good" and some of the tracery in the windows as "very good". His view was that the "excellence of the work" at St Nidan's was because of its link with Beddgelert Priory.
The authors of a 1990 book about the lost churches of Wales said that St Nidan's was "now an evocative shell decorously mantled with ivy and enclosed by an overgrown graveyard". They described it as "a dark, dusty and empty place", but said that the "elegant" arcade "rises from the graveyard like an abstract sculpture." The quality of the stone carving of the doors and windows, they said, was evidence of "the vanished splendour of Llanidan."
A 2002 book about Welsh churchyards comments that "a pilgrimage undertaken to this churchyard is rewarding", since there is "little to distract and much to suggest the quiet years of Nidan's ministry in this secluded spot." Noting how the site can be reached from the Menai Strait yet remains hidden from it, the author added that "some stillness still remains in secret places like Llanidan." A 2005 guide to Wales said that "the romantic yew-encircled ruin" of St Nidan's "should not be missed."
The Welsh politician and church historian Sir Stephen Glynne visited the church in 1850. He said that St Nidan's, which he described as "now abandoned and in great measure ruinated", was "a larger and better structure than most of the Anglesey churches." At the time he saw it, the walls were still largely in place but the only roofed section was the western end; he commented that most of the church was "open to the skies."
The historian and clergyman Edmund Tyrrell Green, writing a survey of Anglesey church architecture and contents in 1929, described the arcade as "good" and some of the tracery in the windows as "very good". His view was that the "excellence of the work" at St Nidan's was because of its link with Beddgelert Priory.
The authors of a 1990 book about the lost churches of Wales said that St Nidan's was "now an evocative shell decorously mantled with ivy and enclosed by an overgrown graveyard". They described it as "a dark, dusty and empty place", but said that the "elegant" arcade "rises from the graveyard like an abstract sculpture." The quality of the stone carving of the doors and windows, they said, was evidence of "the vanished splendour of Llanidan."
A 2002 book about Welsh churchyards comments that "a pilgrimage undertaken to this churchyard is rewarding", since there is "little to distract and much to suggest the quiet years of Nidan's ministry in this secluded spot." Noting how the site can be reached from the Menai Strait yet remains hidden from it, the author added that "some stillness still remains in secret places like Llanidan." A 2005 guide to Wales said that "the romantic yew-encircled ruin" of St Nidan's "should not be missed."
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Llanidan, Old Saint Nidan Grade II* listed churches in Anglesey Church in Wales church buildings in Anglesey Church ruins in Wales 14th-century church buildings in Wales Old Saint Nidan Grade II* listed ruins in Wales Scheduled monuments in Anglesey