okapi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe and zebra giraffe, is an
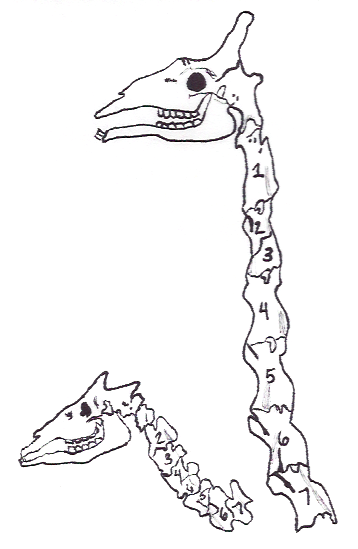 The earliest members of the Giraffidae first appeared in the early
The earliest members of the Giraffidae first appeared in the early
 Okapis are
Okapis are
 The IUCN classifies the okapi as endangered. It is fully protected under Congolese law. The Okapi Wildlife Reserve and Maiko National Park support significant populations of the okapi, though a steady decline in numbers has occurred due to several threats. Other areas of occurrence are the Rubi Tele Hunting Reserve, the Abumombanzi Reserve, the
Sankuru Nature Reserve, the Lomami National Park. Major threats include habitat loss due to
The IUCN classifies the okapi as endangered. It is fully protected under Congolese law. The Okapi Wildlife Reserve and Maiko National Park support significant populations of the okapi, though a steady decline in numbers has occurred due to several threats. Other areas of occurrence are the Rubi Tele Hunting Reserve, the Abumombanzi Reserve, the
Sankuru Nature Reserve, the Lomami National Park. Major threats include habitat loss due to
Searching for the okapi (Okapia johnstoni) in Semuliki National Park, Uganda
. ''Afr. J. Ecol.'' Vol. 59, issue 1: 1–7. .
The okapi management site
''Monograph of the Okapi''
(1910) by E. Ray Lankester and William George Ridewood * * * {{Authority control Endangered fauna of Africa Endemic fauna of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Fauna of Central Africa Giraffes Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1901 Mammals of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Northeastern Congolian lowland forests Taxa named by Philip Sclater Articles containing video clips
artiodactyl
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof). The other t ...
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
that is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
in central Africa. However, non-invasive genetic identification has suggested that a population has occurred south-west of the Congo River as well. It is the only species in the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Okapia''. Although the okapi has striped markings reminiscent of zebras, it is most closely related to the giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
. The okapi and the giraffe are the only living members of the family Giraffidae.
The okapi stands about tall at the shoulder and has a typical body length around . Its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large, flexible ears. Its coat is a chocolate to reddish brown, much in contrast with the white horizontal stripes and rings on the legs, and white ankles. Male okapis have short, distinct horn-like protuberances on their heads called ossicones, less than in length. Females possess hair whorls, and ossicones are absent.
Okapis are primarily diurnal, but may be active for a few hours in darkness. They are essentially solitary, coming together only to breed. Okapis are herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
s, feeding on tree leaves and buds, grasses, ferns, fruits, and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. Rut in males and estrus in females does not depend on the season. In captivity, estrus cycles recur every 15 days. The gestational period is around 440 to 450 days long, following which usually a single calf is born. The juveniles are kept in hiding, and nursing takes place infrequently. Juveniles start taking solid food from three months, and weaning takes place at six months.
Okapis inhabit canopy forests at altitudes of . The International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources classifies the okapi as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
. Major threats include habitat loss due to logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidder, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or trunk (botany), logs onto logging truck, trucksIllegal mining
Illegal mining is mining activity that is undertaken without state permission. Illegal mining is the extraction of precious metals/rocks without following the proper procedures to participate in legal mining activity. These procedures include pe ...
and extensive hunting for bushmeat and skin have also led to a decline in populations. The Okapi Conservation Project was established in 1987 to protect okapi populations.
Etymology and taxonomy
Although the okapi was unknown to the Western world until the 20th century, it may have been depicted since the early fifth century BCE on thefaçade
A façade or facade (; ) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a loanword from the French language, French (), which means "frontage" or "face".
In architecture, the façade of a building is often the most important asp ...
of the Apadana
Apadana (, or ) is a large hypostyle hall in Persepolis, Iran. It belongs to the oldest building phase of the city of Persepolis, in the first half of the 5th century BC, as part of the original design by Darius I, Darius the Great. Its cons ...
at Persepolis, a gift from the Ethiopian procession to the Achaemenid kingdom.
For years, Europeans in Africa had heard of an animal that they came to call the African unicorn
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since Classical antiquity, antiquity as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn (anatomy), horn projecting from its forehead.
In European literature and art, the unico ...
. The animal was brought to prominent European attention by speculation on its existence found in press reports covering Henry Morton Stanley
Sir Henry Morton Stanley (born John Rowlands; 28 January 1841 – 10 May 1904) was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author, and politician famous for his exploration of Central Africa and search for missi ...
's journeys in 1887. In his travelogue of exploring the Congo, Stanley mentioned a kind of donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
that the natives called the ''atti'', which scholars later identified as the okapi.
When the British special commissioner in Uganda, Sir Harry Johnston, discovered some Pygmy
In anthropology, pygmy peoples are ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. The term pygmyism is used to describe the phenotype of endemic short stature (as opposed to disproportionate dwarfism occurring in isolated cases in a po ...
inhabitants of the Congo being abducted by a showman for exhibition, he rescued them and promised to return them to their homes. The Pygmies fed Johnston's curiosity about the animal mentioned in Stanley's book. Johnston was puzzled by the okapi tracks the natives showed him; while he had expected to be on the trail of some sort of forest-dwelling horse, the tracks were of a cloven-hoofed beast.
Though Johnston did not see an okapi himself, he did manage to obtain pieces of striped skin and eventually a skull. From this skull, the okapi was correctly classified as a relative of the giraffe; in 1901, the species was formally recognized as ''Okapia johnstoni''.
''Okapia johnstoni'' was first described as ''Equus johnstoni'' by English zoologist Philip Lutley Sclater in 1901. The generic name ''Okapia'' derives either from the Mbuba name or the related Lese Karo name , while the specific name (''johnstoni'') is in recognition of Johnston, who first acquired an okapi specimen for science from the Ituri Forest.Nowak, Ronald M. (1999) ''Walker's Mammals of the World.'' 6th ed. p. 1085.
In 1901, Sclater presented a painting of the okapi before the Zoological Society of London that depicted its physical features with some clarity. Much confusion arose regarding the taxonomical status of this newly discovered animal. Sir Harry Johnston himself called it a '' Helladotherium'', or a relative of other extinct giraffids. Based on the description of the okapi by Pygmies, who referred to it as a "horse", Sclater named the species '' Equus johnstoni''. Subsequently, zoologist Ray Lankester declared that the okapi represented an unknown genus of the Giraffidae, which he placed in its own genus, ''Okapia'', and assigned the name ''Okapia johnstoni'' to the species.
In 1902, Swiss zoologist Charles Immanuel Forsyth Major suggested the inclusion of ''O. johnstoni'' in the extinct giraffid subfamily Palaeotraginae. However, the species was placed in its own subfamily Okapiinae, by Swedish palaeontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
Birger Bohlin in 1926, mainly due to the lack of a cingulum, a major feature of the palaeotragids. In 1986, ''Okapia'' was finally established as a sister genus of '' Giraffa'' on the basis of cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
analysis. The two genera together with '' Palaeotragus'' constitute the tribe Giraffini.
Evolution
 The earliest members of the Giraffidae first appeared in the early
The earliest members of the Giraffidae first appeared in the early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
in Africa, having diverged from the superficially deer-like climacoceratids. Giraffids spread into Europe and Asia by the middle Miocene in a first radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
. Another radiation began in the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
. Several important primitive giraffids existed more or less contemporaneously in the Miocene (23–10 million years ago), including '' Canthumeryx'', '' Giraffokeryx'', '' Palaeotragus'', and '' Samotherium''. According to palaeontologist and author Kathleen Hunt, ''Samotherium'' split into ''Okapia'' (18 million years ago) and ''Giraffa'' (12 million years ago). However, J. D. Skinner argued that ''Canthumeryx'' gave rise to the okapi and giraffe through the latter three genera and that the okapi is the extant form of ''Palaeotragus''. The okapi is sometimes referred to as a living fossil
A living fossil is a Deprecation, deprecated term for an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of or ...
, as it has existed as a species over a long geological time period, and morphologically resembles more primitive forms (e.g. ''Samotherium'').
In 2016, a genetic study found that the common ancestor of giraffe and okapi lived about 11.5 million years ago.
Description
The okapi is a medium-sized giraffid, standing tall at the shoulder. Its average body length is about and its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large and flexible ears. In sharp contrast to the white horizontal stripes on the legs and white ankles, the okapi's coat is a chocolate to reddish brown. The distinctive stripes resemble those of a zebra. These features serve as an effective camouflage amidst dense vegetation. The face, throat, and chest are greyish white. Interdigital glands are present on all four feet, and are slightly larger on the front feet. Male okapis have short, hair-covered horn-like structures called ossicones, less than in length, which are similar in form and function to the ossicones of agiraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
. The okapi exhibits sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
, with females taller on average, slightly redder, and lacking prominent ossicones, instead possessing hair whorls.
The okapi shows several adaptations to its tropical habitat. The large number of rod cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in ...
s in the retina facilitate night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night v ...
, and an efficient olfactory system
The olfactory system, is the sensory nervous system, sensory system used for the sense of smell (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses directly associated with specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system ...
is present. The large auditory bullae of the temporal bone allow a strong sense of hearing. The dental formula of the okapi is . Teeth are low- crowned and finely cusped, and efficiently cut tender foliage. The large cecum and colon help in microbial digestion, and a quick rate of food passage allows for lower cell wall digestion than in other ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
s.
The okapi is easily distinguished from its nearest extant relative, the giraffe. It is much smaller than the giraffe and shares more external similarities with bovids and cervids. Ossicones are present only in the male okapi, while both sexes of giraffe possess this feature. The okapi has large palatine sinuses (hollow cavities in the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ...
), unique among the giraffids. Morphological features shared between the giraffe and the okapi include a similar gait – both use a pacing gait, stepping simultaneously with the front and the hind leg on the same side of the body, unlike other ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
s that walk by moving alternate legs on either side of the body – and a long, black tongue (longer in the okapi) useful for plucking buds and leaves, as well as for grooming.
Ecology and behaviour
Okapis are primarily diurnal, but may be active for a few hours in darkness. They are essentially solitary, coming together only to breed. They have overlapping home ranges and typically occur at densities around 0.6 animals per square kilometre. Male home ranges average , while female home ranges average . Males migrate continuously, while females are sedentary. Males often mark territories and bushes with their urine, while females use common defecation sites. Grooming is a common practice, focused at the earlobes and the neck. Okapis often rub their necks against trees, leaving a brown exudate. The male is protective of his territory, but allows females to pass through the domain to forage. Males visit female home ranges at breeding time. Although generally tranquil, the okapi can kick and butt with its head to show aggression. As the vocal cords are poorly developed, vocal communication is mainly restricted to three sounds — "chuff" (contact calls used by both sexes), "moan" (by females during courtship) and "bleat" (by infants under stress). Individuals may engage in Flehmen response, a visual expression in which the animal curls back its upper lips, displays the teeth, and inhales through the mouth for a few seconds. The leopard is the main natural predator of the okapi.Diet
 Okapis are
Okapis are herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
s, feeding on tree leaves and buds, branches, grasses, fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s, fruits, and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. They are unique in the Ituri Forest as they are the only known mammal that feeds solely on understory vegetation, where they use their tongues to selectively browse for suitable plants. The tongue is also used to groom their ears and eyes. They prefer to feed in treefall gaps. The okapi has been known to feed on over 100 species of plants, some of which are known to be poisonous to humans and other animals. Fecal analysis shows that none of those 100 species dominates the diet of the okapi. Staple foods comprise shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
s and liana
A liana is a long-Plant stem, stemmed Woody plant, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the Canopy (biology), canopy in search of direct sunlight. T ...
s. The main constituents of the diet are woody, dicotyledonous species; monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but ...
yledonous plants are not eaten regularly. In the Ituri forest, the okapi feeds mainly upon the plant families Acanthaceae
Acanthaceae () is a Family (biology), family (the acanthus family) of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing almost 250 genera and about 2500 species. Most are Tropics, tropical Herbaceous plant, herbs, shrubs, or twining vines; some are epip ...
, Ebenaceae, Euphorbiaceae
Euphorbiaceae (), the spurge family, is a large family of flowering plants. In English, they are also commonly called euphorbias, which is also the name of Euphorbia, the type genus of the family. Most spurges, such as ''Euphorbia paralias'', ar ...
, Flacourtiaceae, Loganiaceae, Rubiaceae
Rubiaceae () is a family (biology), family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with Petiole ( ...
, and Violaceae
Violaceae is a family of flowering plants established in 1802, consisting of about 1000 species in about 25 genera. It takes its name from the genus '' Viola'', the violets and pansies.
Older classifications such as the Cronquist system plac ...
.
Reproduction
Female okapis become sexually mature at about one-and-a-half years old, while males reach maturity after two years. Rut in males andestrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is a set of recurring physiological changes induced by reproductive hormones in females of mammalian subclass Theria. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phas ...
in females does not depend on the season. In captivity, estrous cycles recur every 15 days. The male and the female begin courtship by circling, smelling, and licking each other. The male shows his interest by extending his neck, tossing his head, and protruding one leg forward. This is followed by mounting and copulation.
The gestational period is around 440 to 450 days long, following which usually a single calf is born, weighing . The udder of the pregnant female starts swelling 2 months before parturition, and vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
l discharges may occur. Parturition takes 3–4 hours, and the female stands throughout this period, though she may rest during brief intervals. The mother consumes the afterbirth and extensively grooms the infant. Her milk is very rich in proteins and low in fat.
As in other ruminants, the infant can stand within 30 minutes of birth. Although generally similar to adults, newborn calves have long hairs around the eye (resembling false eyelashes), a long dorsal mane, and long white hairs in the stripes. These features gradually disappear and give way to the general appearance within a year. The juveniles are kept in hiding, and nursing takes place infrequently. Calves are known not to defecate for the first month or two of life, which is hypothesized to help avoid predator detection in their most vulnerable phase of life. The growth rate of calves is appreciably high in the first few months of life, after which it gradually declines. Juveniles start taking solid food from 3 months, and weaning takes place at 6 months. Ossicone development in males takes 1 year after birth. The okapi's typical lifespan is 20–30 years.
Distribution and habitat
The okapi isendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it occurs north and east of the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
. It ranges from the Maiko National Park northward to the Ituri rainforest, then through the river basins of the Rubi, Lake Tele, and Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after in ...
to the west and the Ubangi River further north. Smaller populations exist west and south of the Congo River. It is also common in the Wamba and Epulu areas. It is extinct in Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
.
The okapi inhabits canopy forests at elevations of . It occasionally uses seasonally inundated areas, but does not occur in gallery forests, swamp forests, and habitats disturbed by human settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community of people living in a particular location, place. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of Dwelling, dwellings gro ...
s. In the wet season, it visits rocky inselbergs that offer forage uncommon elsewhere. Results of research conducted in the late 1980s in a mixed '' Cynometra'' forest indicated that the okapi population density averaged 0.53 animals per square kilometre. In 2008, it was recorded in Virunga National Park. There is also evidence that okapis were also observed in the Semuliki Valley in Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
by Europeans, but later became extinct in the late 1970s. The Semuliki Valley provides a similar habitat to the Congo Basin.
Status
Threats and conservation
 The IUCN classifies the okapi as endangered. It is fully protected under Congolese law. The Okapi Wildlife Reserve and Maiko National Park support significant populations of the okapi, though a steady decline in numbers has occurred due to several threats. Other areas of occurrence are the Rubi Tele Hunting Reserve, the Abumombanzi Reserve, the
Sankuru Nature Reserve, the Lomami National Park. Major threats include habitat loss due to
The IUCN classifies the okapi as endangered. It is fully protected under Congolese law. The Okapi Wildlife Reserve and Maiko National Park support significant populations of the okapi, though a steady decline in numbers has occurred due to several threats. Other areas of occurrence are the Rubi Tele Hunting Reserve, the Abumombanzi Reserve, the
Sankuru Nature Reserve, the Lomami National Park. Major threats include habitat loss due to logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidder, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or trunk (botany), logs onto logging truck, trucksbushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are Hunting, hunted for human consumption. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity in poor and rural communities of humid tropical forest regions of the worl ...
and skin and illegal mining have also led to population declines. A threat that has emerged quite recently is the presence of illegal armed groups around protected areas, inhibiting conservation and monitoring actions. A small population occurs north of the Virunga National Park, but lacks protection due to the presence of armed groups in the vicinity. In June 2012, a gang of poachers attacked the headquarters of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve, killing six guards and other staff as well as all 14 okapis at their breeding center.
The Okapi Conservation Project, established in 1987, works towards the conservation of the okapi, as well as the growth of the indigenous Mbuti people. In November 2011, the White Oak Conservation center and Jacksonville Zoo and Gardens hosted an international meeting of the Okapi Species Survival Plan and the Okapi European Endangered Species Programme The EAZA Ex-situ Programme (EEP) is a population management and Ex situ conservation, conservation programme by European Association of Zoos and Aquaria, European Association of Zoos and Aquaria (EAZA) for wild animals living in European zoos. The p ...
at Jacksonville, which was attended by representatives from zoos from the US, Europe, and Japan. The aim was to discuss the management of captive okapis and arrange support for okapi conservation. Many zoos in North America and Europe currently have okapis in captivity.
Okapis in zoos
Around 100 okapis are in accredited Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) zoos. The okapi population is managed in America by the AZA's Species Survival Plan, a breeding program that works to ensure genetic diversity in the captive population of endangered animals, while the EEP (European studbook) and ISB (Global studbook) are managed by Antwerp Zoo in Belgium, which was the first zoo to have an Okapi on display (in 1919), as well as one of the most successful in breeding them. In 1937, the Bronx Zoo became the first in North America to acquire an okapi. With one of the most successful breeding programs, 13 calves have been born there between 1991 and 2011. TheSan Diego Zoo
The San Diego Zoo is a zoo in San Diego, California, United States, located in Balboa Park (San Diego), Balboa Park. It began with a collection of animals left over from the 1915 Panama–California Exposition that were brought together by its ...
has exhibited okapis since 1956, and their first okapi calf was born in 1962. Since then, there have been more than 60 okapis born at the zoo and the nearby San Diego Zoo Safari Park, the most recent being Mosi, a male calf born on 21 July 2017 at the zoo. The Brookfield Zoo in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
has also greatly contributed to the captive population of okapis in accredited zoos. The zoo has had 28 okapi births since 1959.
Other North American zoos that exhibit and breed okapis include: Denver Zoo and Cheyenne Mountain Zoo (Colorado); Houston Zoo, Dallas Zoo, and San Antonio Zoo (Texas); Disney's Animal Kingdom, White Oak Conservation, Zoo Miami, and ZooTampa at Lowry Park (Florida); Los Angeles Zoo
The Los Angeles Zoo and Botanical Gardens is a zoo founded in 1966 and located in Los Angeles, California, United States. The city of Los Angeles owns the zoo, its land and facilities, and the animals.
History
Eastlake Zoo, opened in Eastlak ...
, Sacramento Zoo, and San Diego Zoo
The San Diego Zoo is a zoo in San Diego, California, United States, located in Balboa Park (San Diego), Balboa Park. It began with a collection of animals left over from the 1915 Panama–California Exposition that were brought together by its ...
(California); Saint Louis Zoo (Missouri); Cincinnati Zoo and Botanical Garden and Columbus Zoo and Aquarium (Ohio); Memphis Zoo and Nashville Zoo (Tennessee); The Maryland Zoo in Baltimore (Maryland); Sedgwick County Zoo and Tanganyika Wildlife Park (Kansas); Roosevelt Park Zoo (North Dakota); Henry Doorly Zoo and Aquarium (Nebraska); Philadelphia Zoo (Pennsylvania); Potawatomi Zoo (Indiana); Oklahoma City Zoo and Botanical Garden
The Oklahoma City Zoo and Botanical Garden is a zoo and botanical garden located in Oklahoma City's Adventure District in northeast Oklahoma City, Oklahoma.
The zoo covers and is home to more than 2,000 animals of more than 500 species. It is ...
(Oklahoma); Blank Park Zoo (Iowa); and Potter Park Zoo (Michigan).
In Europe, zoos that exhibit and breed okapis include: Chester Zoo, London Zoo, Marwell Zoo, The Wild Place, and Yorkshire Wildlife Park (United Kingdom); Dublin Zoo (Ireland); Berlin Zoo, Frankfurt Zoo, Wilhelma Zoo, Wuppertal Zoo, Cologne Zoo, and Leipzig Zoo (Germany); Zoo Basel (Switzerland); Copenhagen Zoo (Denmark); Rotterdam Zoo and Safaripark Beekse Bergen (Netherlands); Antwerp Zoo (Belgium); Dvůr Králové Zoo (Czech Republic); Wrocław Zoo (Poland); Bioparc Zoo de Doué and ZooParc de Beauval (France); and Lisbon Zoo (Portugal).
In Asia, three Japanese zoos exhibit okapis: Ueno Zoo in Tokyo; Kanazawa Zoo and Zoorasia in Yokohama.
See also
* *References
Further reading
* Bell, Wolfram (Nov. 2009). ''Okapis: geheimnisvolle Urwaldgiraffen; Entdeckungsgeschichte, Biologie, Haltung und Medizin einer seltenen Tierart''. Schüling Verlag Münster, Germany. . * Sever, Zvi (March 2021).Searching for the okapi (Okapia johnstoni) in Semuliki National Park, Uganda
. ''Afr. J. Ecol.'' Vol. 59, issue 1: 1–7. .
External links
The okapi management site
''Monograph of the Okapi''
(1910) by E. Ray Lankester and William George Ridewood * * * {{Authority control Endangered fauna of Africa Endemic fauna of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Fauna of Central Africa Giraffes Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1901 Mammals of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Northeastern Congolian lowland forests Taxa named by Philip Sclater Articles containing video clips