Non-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Non-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (N-OFDM) is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies with non-orthogonal intervals between frequency of sub-carriers.RU2054684 (C1) G01R 23/16. Amplitude-frequency response measurement technique// Slyusar V. – Appl. Number SU 19925055759, Priority Data: 19920722. – Official Publication Data: 1996-02-2
/ref>Slyusar, V. I. Smolyar, V. G. Multifrequency operation of communication channels based on super-Rayleigh resolution of signals// Radio electronics and communications systems c/c of Izvestiia- vysshie uchebnye zavedeniia radioelektronika.. – 2003, volume 46; part 7, pages 22–27. – Allerton press Inc. (US
/ref>Slyusar, V. I. Smolyar, V. G. The method of nonorthogonal frequency-discrete modulation of signals for narrow-band communication channels// Radio electronics and communications systems c/c of Izvestiia- vysshie uchebnye zavedeniia radioelektronika. – 2004, volume 47; part 4, pages 40–44. – Allerton press Inc. (US
/ref> N-OFDM signals can be used in communication and
 The low-pass equivalent N-OFDM signal is expressed as:
:
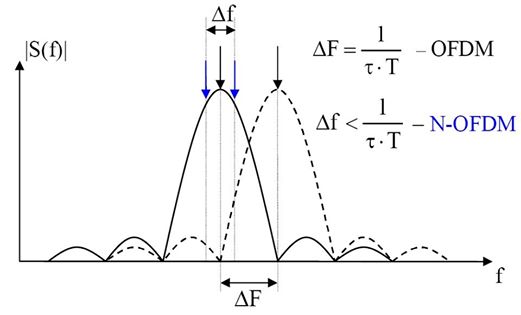
where are the data symbols, is the number of sub-carriers, and is the N-OFDM symbol time. The sub-carrier spacing for makes them non-orthogonal over each symbol period.
The low-pass equivalent N-OFDM signal is expressed as:
:
where are the data symbols, is the number of sub-carriers, and is the N-OFDM symbol time. The sub-carrier spacing for makes them non-orthogonal over each symbol period.
 An N-OFDM carrier signal is the sum of a number of not-orthogonal subcarriers, with
An N-OFDM carrier signal is the sum of a number of not-orthogonal subcarriers, with
/ref>Slyusar, V. I. Smolyar, V. G. Multifrequency operation of communication channels based on super-Rayleigh resolution of signals// Radio electronics and communications systems c/c of Izvestiia- vysshie uchebnye zavedeniia radioelektronika.. – 2003, volume 46; part 7, pages 22–27. – Allerton press Inc. (US
/ref>Slyusar, V. I. Smolyar, V. G. The method of nonorthogonal frequency-discrete modulation of signals for narrow-band communication channels// Radio electronics and communications systems c/c of Izvestiia- vysshie uchebnye zavedeniia radioelektronika. – 2004, volume 47; part 4, pages 40–44. – Allerton press Inc. (US
/ref> N-OFDM signals can be used in communication and
radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
systems.
Subcarriers system
 The low-pass equivalent N-OFDM signal is expressed as:
:
where are the data symbols, is the number of sub-carriers, and is the N-OFDM symbol time. The sub-carrier spacing for makes them non-orthogonal over each symbol period.
The low-pass equivalent N-OFDM signal is expressed as:
:
where are the data symbols, is the number of sub-carriers, and is the N-OFDM symbol time. The sub-carrier spacing for makes them non-orthogonal over each symbol period.
History
The history of N-OFDM signals theory was started in 1992 from the Patent of Russian Federation No. 2054684. In this patent, Vadym Slyusar proposed the 1st method of optimal processing for N-OFDM signals afterFast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in ...
(FFT).
In this regard need to say that W. Kozek and A. F. Molisch wrote in 1998 about N-OFDM signals with that "it is not possible to recover the information from the received signal, even in the case of an ideal channel."
In 2001, V. Slyusar proposed non-orthogonal frequency digital modulation (N-OFDM) as an alternative of OFDM for communications systems.
The next publication about this method has priority in July 2002 before the conference paper regarding SEFDM of I. Darwazeh and M.R.D. Rodrigues (September, 2003).M. R. D. Rodrigues and I. Darwazeh. A Spectrally Efficient Frequency Division Multiplexing Based Communications System.// InOWo'03, 8th International OFDM-Workshop, Proceedings, Hamburg, DE, September 24–25, 2003. - https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309373002
Advantages of N-OFDM
Despite the increased complexity of demodulating N-OFDM signals compared toOFDM
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission used in digital modulation for encoding digital (binary) data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for ...
, the transition to non-orthogonal subcarrier frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
arrangement provides several advantages:
# higher spectral efficiency, which allows to reduce the frequency band occupied by the signal and improve the electromagnetic compatibility of many terminals;
# adaptive detuning from interference concentrated in frequency by changing the nominal frequencies of the subcarriers;
# an ability to take into account Doppler frequency shifts of subcarriers when working with subscribers moving at high speeds;
# reduction of the peak factor of the multi-frequency signal mixture.
Idealized system model
This section describes a simple idealized N-OFDM system model suitable for a time-invariantAWGN
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is a basic noise model used in information theory to mimic the effect of many random processes that occur in nature. The modifiers denote specific characteristics:
* ''Additive'' because it is added to any nois ...
channel.
Transmitter N-OFDM signals
 An N-OFDM carrier signal is the sum of a number of not-orthogonal subcarriers, with
An N-OFDM carrier signal is the sum of a number of not-orthogonal subcarriers, with baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into ...
data on each subcarrier being independently modulated commonly using some type of quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signa ...
(QAM) or phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency carrier wave. The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. I ...
(PSK). This composite baseband signal is typically used to modulate a main RF carrier.