non-destructive evaluation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive, and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery.
Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologists were able to direct interventional instruments through the body by way of
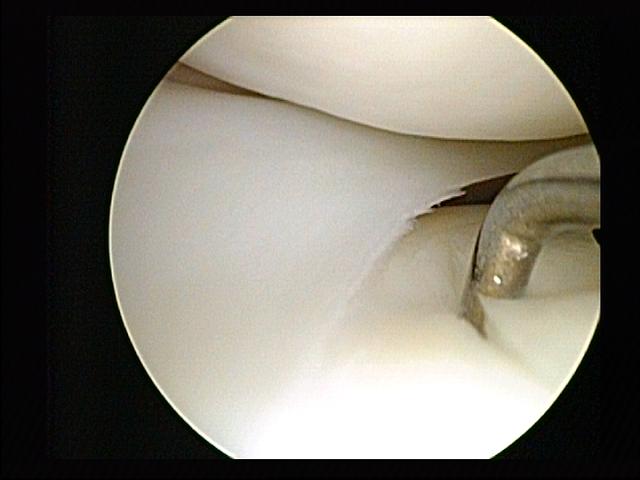 Minimally invasive procedures were pioneered by interventional radiologists who had first introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Many other minimally invasive procedures have followed where images of all parts of the body can be obtained and used to direct interventional instruments by way of
Minimally invasive procedures were pioneered by interventional radiologists who had first introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Many other minimally invasive procedures have followed where images of all parts of the body can be obtained and used to direct interventional instruments by way of
 Many medical procedures are called minimally invasive; those that involve small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in the suffix ''-oscopy'', such as
Many medical procedures are called minimally invasive; those that involve small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in the suffix ''-oscopy'', such as
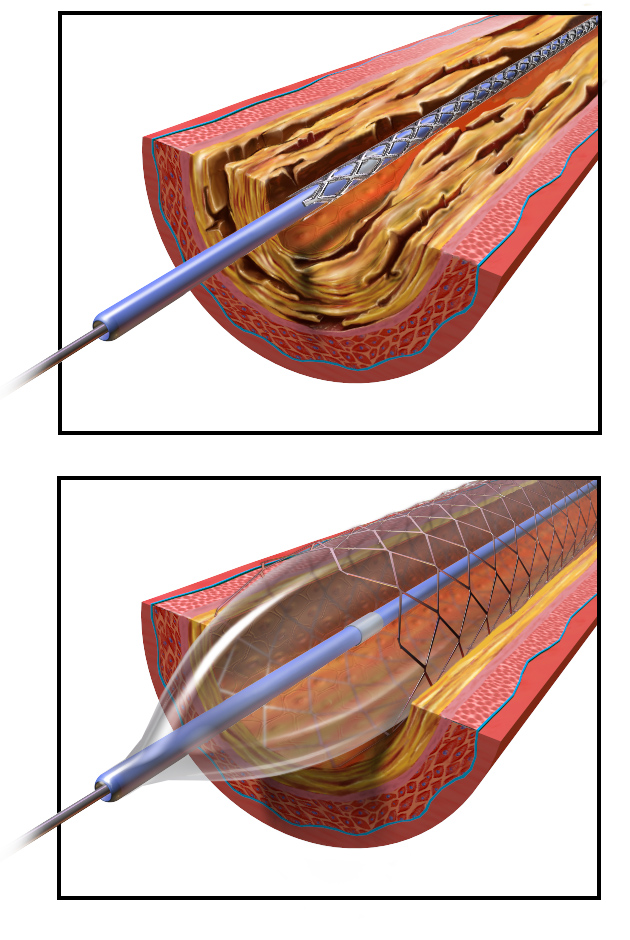 Sometimes the use of non-invasive methods is not an option, so that the next level of minimally invasive techniques are looked to. These include the use of hypodermic injection (using the syringe), an
Sometimes the use of non-invasive methods is not an option, so that the next level of minimally invasive techniques are looked to. These include the use of hypodermic injection (using the syringe), an
Minimally invasive heart surgery
Medical Encyclopedia, MedlinePlus. {{Authority control Medical terminology
catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
s instead of the large incisions needed in traditional surgery. As a result, many conditions once requiring surgery can now be treated non-surgically.
Diagnostic techniques that do not involve incisions, puncturing the skin, or the introduction of foreign objects or materials into the body are known as non-invasive procedures. Several treatment procedures are classified as non-invasive. A major example of a non-invasive alternative treatment to surgery is radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
, also called radiotherapy.
Medical uses
 Minimally invasive procedures were pioneered by interventional radiologists who had first introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Many other minimally invasive procedures have followed where images of all parts of the body can be obtained and used to direct interventional instruments by way of
Minimally invasive procedures were pioneered by interventional radiologists who had first introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Many other minimally invasive procedures have followed where images of all parts of the body can be obtained and used to direct interventional instruments by way of catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
s (needles and fine tubes), so that many conditions once requiring open surgery can now be treated non-surgically. A minimally invasive procedure typically involves the use of arthroscopic (for joints and the spine) or laparoscopic devices and remote-control manipulation of instruments with indirect observation of the surgical field through an endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern ...
or large scale display panel, and is carried out through the skin or through a body cavity or anatomical opening. Interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
now offers many techniques that avoid the need for surgery.
By use of a minimally invasive procedure, a patient may require only an adhesive bandage on the incision, rather than multiple stitches or staples to close a large incision. This usually results in less infection, a quicker recovery time and shorter hospital stays, or allow outpatient treatment. However, the safety and effectiveness of each procedure must be demonstrated with randomized controlled trials. The term was coined by John E. A. Wickham in 1984, who wrote of it in '' British Medical Journal'' in 1987.
Specific procedures
 Many medical procedures are called minimally invasive; those that involve small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in the suffix ''-oscopy'', such as
Many medical procedures are called minimally invasive; those that involve small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in the suffix ''-oscopy'', such as endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
, laparoscopy, arthroscopy. Other examples of minimally invasive procedures include the use of hypodermic injection, and air-pressure injection, subdermal implants, refractive surgery, percutaneous surgery, cryosurgery, microsurgery, keyhole surgery, endovascular surgery using interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
(such as angioplasty or embolization), coronary catheterization, permanent placement of spinal and brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
electrodes, stereotactic surgery, the Nuss procedure, radioactivity-based medical imaging methods, such as gamma camera, positron emission tomography and SPECT (single photon emission tomography). Related procedures are image-guided surgery, and robot-assisted surgery.
Equipment
Special medical equipment may be used, such as fiber optic cables, miniature video cameras and special surgical instruments handled via tubes inserted into the body through small openings in its surface. The images of the interior of the body are transmitted to an external video monitor and the surgeon has the possibility of making a diagnosis, visually identifying internal features and acting surgically on them.Benefits
Minimally invasivesurgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
should have less operative trauma, other complications and adverse effects than an equivalent open surgery. It may be more or less expensive (for dental implants, a minimally invasive method reduces the cost of installed implants and shortens the implant-prosthetic rehabilitation time with four–six months). Operative time is longer, but hospitalization time is shorter. It causes less pain and scarring, speeds recovery, and reduces the incidence of post-surgical complications, such as adhesions and wound rupture. Some studies have compared heart surgery.
Risks
Risks and complications of minimally invasive procedures are the same as for any other surgical operation, among the risks are: death, bleeding,infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, organ injury, and thromboembolic disease.
There may be an increased risk of hypothermia and peritoneal trauma due to increased exposure to cold, dry gases during insufflation. The use of surgical humidification therapy, which is the use of heated and humidified CO2 for insufflation, may reduce this risk.
Invasive procedures
 Sometimes the use of non-invasive methods is not an option, so that the next level of minimally invasive techniques are looked to. These include the use of hypodermic injection (using the syringe), an
Sometimes the use of non-invasive methods is not an option, so that the next level of minimally invasive techniques are looked to. These include the use of hypodermic injection (using the syringe), an endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern ...
, percutaneous surgery which involves needle puncture of the skin, laparoscopic surgery commonly called ''keyhole surgery'', a coronary catheter, angioplasty and stereotactic surgery.
Open surgery
"Open surgery" is any surgical procedure where the incision made is enough to allow the surgery to take place. With tissues and structures exposed to the air, the procedure can be performed either with the unaided vision of the surgeon or with the use of loupes or microscopes. Some examples of open surgery used are for herniated disc commonly called a "slipped disc", and most types of cardiac surgery and neurosurgery.Associations
Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) for adults. International Pediatric Endosurgery Group (IPEG) for pediatrics.See also
* Anesthesia * ASA physical status classification system *Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
* Natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery
* Traumatology
* Biomedical engineering
* Molecular imaging
* Venipuncture
References
Further reading
External links
Minimally invasive heart surgery
Medical Encyclopedia, MedlinePlus. {{Authority control Medical terminology