Nicolaides–Baraitser Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nicolaides–Baraitser syndrome (NCBRS) is a rare genetic condition caused by

Nicolaides Baraitser Syndrome (NCBRS) Website
Nicolaides Baraitser Syndrome Website (Spanish)
Facebook Support Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome Syndromes
de novo
De novo (Latin, , used in English to mean 'from the beginning', 'anew') may refer to:
Science and computers
* ''De novo'' mutation, a new germline mutation not inherited from either parent
* ''De novo'' protein design, the creation of a protei ...
missense
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Missense mutations change amino acids, which in turn al ...
mutations in the SMARCA2
Probable global transcription activator SNF2L2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCA2'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins and is highly similar to the brahma protein ...
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
and has only been reported in fewer than 200 cases worldwide. NCBRS is a distinct condition and well recognizable once the symptoms have been identified.
The differential includes Coffin–Siris syndrome
Coffin–Siris syndrome (CSS), first described in 1970 by Dr Grange S. Coffin and Dr E. Siris, is a rare genetic disorder that causes developmental delays and absent fifth finger and toe nails.
There had been 31 reported cases by 1991. The numbe ...
.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of Nicolaides–Baraitser syndrome are mild to severedevelopmental delays
Global developmental delay is an umbrella term used when children are significantly delayed in two or more areas of development. It can be diagnosed when a child is delayed in one or more milestones, categorised into motor skills, speech, cognitive ...
with absent or limited speech, seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, short stature
Short stature refers to a height of a human which is below typical. Whether a person is considered short depends on the context. Because of the lack of preciseness, there is often disagreement about the degree of shortness that should be called ...
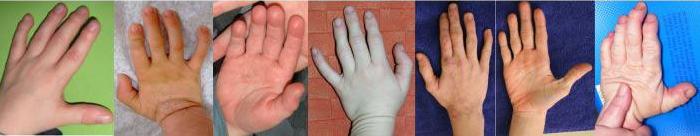
, sparse hair, typical facial characteristics, brachydactyly
Brachydactyly () is a medical term denoting the presence of abnormally short digits (fingers or toes) at birth. The shortness is relative to the length of other long bones and other parts of the body. Brachydactyly is an inherited, dominant t ...
, and prominent finger joints and broad distal phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
Structu ...
.
Major Features of NCBRS
* Mild prenatal growth retardation * Moderate postnatal growth retardation * Mild to severe developmental delay * Severely impaired speech * Seizures *Microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
* Sparse hair
* Progressive skin wrinkling
* Thick, anteverted alae nasi
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, wh ...
* Long and broad philtrum
The philtrum (, from Ancient Greek , lit. 'love charm') or medial cleft is a vertical indentation in the middle area of the upper lip, common to therian mammals, extending in humans from the nasal septum to the tubercle of the upper lip. Toget ...
* Large mouth
* Thin upper and thick lower vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color family and pigment most often used between antiquity and the 19th century from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide). It is synonymous with red orange, which often takes a moder ...
* Progressive prominence of distal phalanges
* Progressive prominence of inter-phalangeal joints
* Scoliosis
* Short metacarpals
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular skeleton, appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones (wrist, wris ...
–metatarsals
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are nu ...
Cause
This condition occurs via mutations in the SMARCA2 gene. In rare instances this condition can occur via a mutation in theARID1B
AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARID1B'' gene. ARID1B is a component of the human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex.
Clinical significance
Germline mutations in ARID1B are as ...
gene.
History
Paola Nicolaides was a pediatric neurologist and Michael Baraitser a clinical geneticist, both working inGreat Ormond Street Hospital for Children
Great Ormond Street Hospital (informally GOSH, formerly the Hospital for Sick Children) is a children's hospital located in the Bloomsbury area of the London Borough of Camden, and a part of Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foun ...
in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
. They saw a young girl with an unusual combination of signs and symptoms, and thought this to be a recognizable entity. They published this in a medical journal in 1993. Other authors later suggested to name the entity after the authors who had first described it.
References
External links
Nicolaides Baraitser Syndrome (NCBRS) Website
Nicolaides Baraitser Syndrome Website (Spanish)
Facebook Support Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome Syndromes