Nico Pérez Terrane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The geology of Uruguay combines areas of
 The
The
Paraná flood basalts: Rapid extrusion hypothesis confirmed by new 40Ar/39Ar results
''Geology'' vol 38.
National Mining and Geology Office
by
Geological evolution of Uruguay
by Agronomy Faculty,
Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
-aged shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles suc ...
unit
Unit may refer to:
General measurement
* Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law
**International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system
**English units, histo ...
s with a region of volcanic rock
Volcanic rocks (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) are rocks formed from lava erupted from a volcano. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and me ...
erupted during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
and copious sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with distinctive characteristics. The characteristics can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or con ...
the oldest of which date from the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
. Big events that have shaped the geology of Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
include the Transamazonian orogeny The Transamazonian orogeny was a mountain building event in the Paleoproterozoic, affecting what is now the São Francisco Craton and Guyana Shield. During the orogeny from 2.14 to 1.94 billion years ago two small Archean proto-continents—inclu ...
(2000 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
(mya)), the breakup of Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). wer ...
(700–500 mya) and the opening of the South Atlantic (~145 mya).
Shield region
 The
The Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles suc ...
in Uruguay includes part of Río de la Plata craton
The Rio de la Plata Craton (RPC) is a medium-sized continental block found in Uruguay, eastern Argentina and southern Brazil. During its complex and protracted history it interacted with a series other blocks and is therefore considered importan ...
, an extensive area of stable crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
basement rock
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The baseme ...
underlying Uruguay and large areas of eastern Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and southern Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. The shield in Uruguay goes under the name of Rio Grande do Sul—Uruguay Shield and includes parts of Southern Brazil
The South Region of Brazil ( ) is one of the five regions of Brazil. It includes the states of Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, and Santa Catarina, and covers , being the smallest region of the country, occupying only about 6.76% of the territory of ...
. Though the Río de la Plata Craton underlies practically all of Uruguay, it only shows up in the south and east of the country since in other parts of the country, it is covered by younger volcanic rocks or sediments. The shield was formed during two orogenic
Orogeny () is a mountain-building process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involv ...
events; one 2000 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
(mya) for the western part and another 700–500 mya for the eastern part. The later orogenic event is the result of the accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
of blocks and terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its d ...
s in the aftermath of the breakup of Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). wer ...
when São Francisco and Río de la Plata cratons formed one plate in the west of the Adamastor Ocean
The Adamastor Ocean was a "proto-Atlantic" ocean that formed with the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent 780–750 . It separated the Río de la Plata Craton from the Congo Craton. The inversion of the Adamastor Ocean began about 640&nb ...
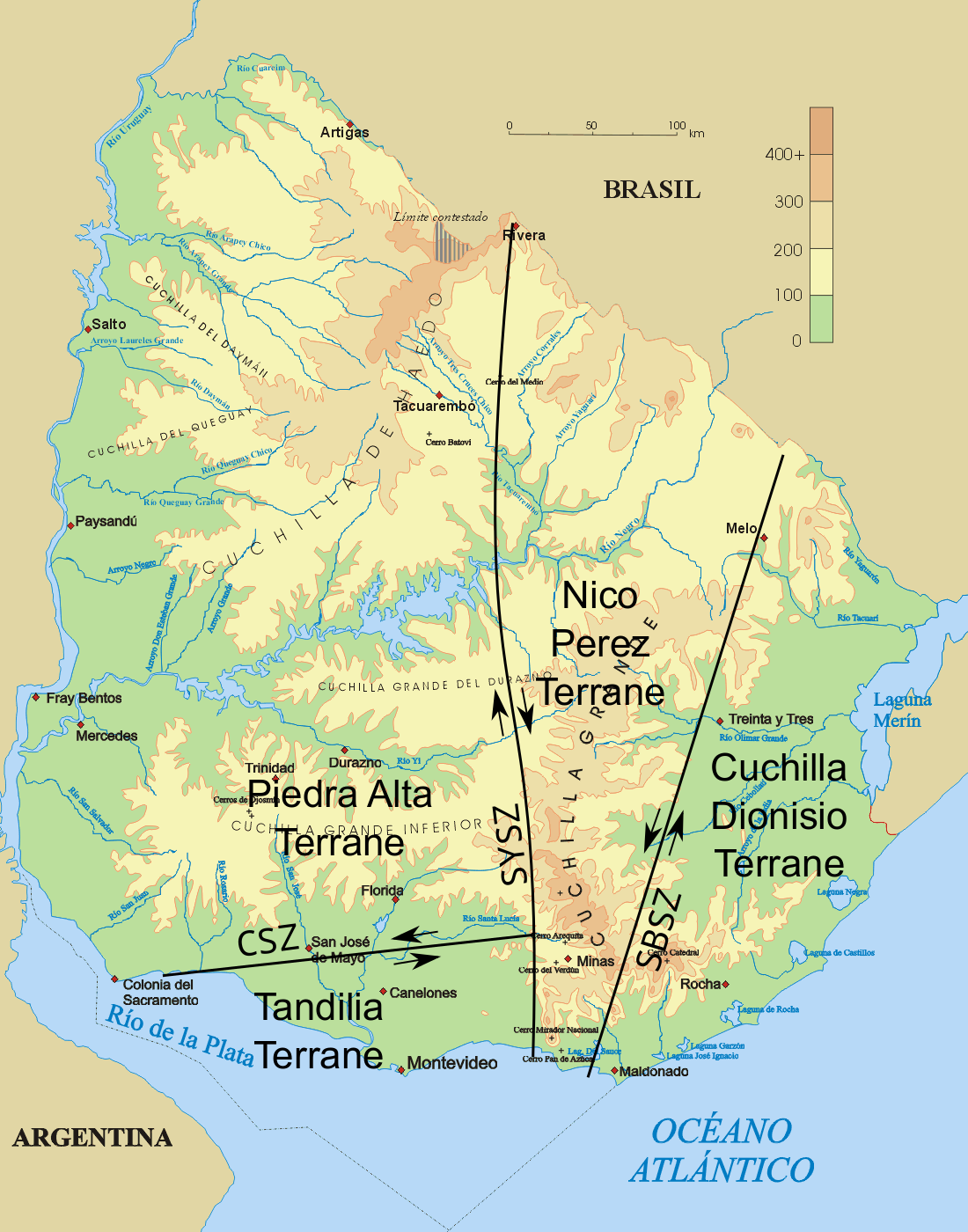
. The eastern part of the Uruguayan shield region is crossed by two major shear zone
In geology, a shear zone is a thin zone within the Earth's crust or upper mantle that has been strongly deformed, due to the walls of rock on either side of the zone slipping past each other. In the upper crust, where rock is brittle, the shear ...
s both running roughly in north-south direction the dextral
Sinistral and dextral, in some scientific fields, are the two types of chirality ("handedness") or relative direction. The terms are derived from the Latin words for "left" (''sinister'') and "right" (''dexter''). Other disciplines use different ...
Sarandí del Yí-Piriápolis Shear Zone and the sinistral
Sinistral and dextral, in some scientific fields, are the two types of chirality ("handedness") or relative direction. The terms are derived from the Latin words for "left" (''sinister'') and "right" (''dexter''). Other disciplines use different ...
Sierra Ballena Shear Zone. West of Sarandí del Yí Shear Zone the Río de la Plata Craton is intruded by the Late Paleoproterozoic Florida dyke swarm.
The area between Sarandí del Yí and Sierra Ballena shear zone
In geology, a shear zone is a thin zone within the Earth's crust or upper mantle that has been strongly deformed, due to the walls of rock on either side of the zone slipping past each other. In the upper crust, where rock is brittle, the shear ...
s –that is the Nico Pérez Terrane– is made of metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
and granitoid
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
rocks which are the oldest rocks in Uruguay. It has not been established to which degree this terrane belongs to or has affinity with the Río de la Plata Craton. The rocks of Nico Pérez Terrane formed originally in the Archean
The Archean ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan), in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history of Earth, history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic and t ...
eon and Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further sub ...
era and much were later affected by the Brasiliano orogeny
Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle ( and ''Ciclo Brasiliano'') refers to a series of orogenies from the Neoproterozoic era, exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a regional name for the l ...
in Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
era.
Sedimentary formations
After the assembly of the finalshield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles suc ...
configuration the territory of Uruguay have been covered by several sedimentary formations ranging from Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
s to Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
loess
A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits.
A loess ...
. All of the sedimentary formations covers only patches of the country since deposition have not been uniform and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
have cleaned surfaces, creeks and shores.
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s of Lower Devonian
The Early Devonian is the first of three epochs comprising the Devonian period, corresponding to the Lower Devonian series. It lasted from and began with the Lochkovian Stage , which was followed by the Pragian from and then by the Emsian, whic ...
age are found in the central part of Uruguay being exposed as a narrow east-west to northeast oriented band. The upper and better known part of this sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
is made up of sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
. The lower sandstones of this sequence have characteristics similar to the ''Furnas Formation'' of São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. During the Late Paleozoic the territory of Uruguay was affected by the Karoo Glaciation
The late Paleozoic icehouse, also known as the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA) and formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was an ice age that began in the Late Devonian and ended in the Late Permian, occurring from 360 to 255 million years ago (Mya), ...
and was subsequently covered by ice lobes of the great ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
that covered large parts of Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
. Glacial striae on shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny f ...
s and varve
A varve is an annual layer of sediment or sedimentary rock.
The word 'varve' derives from the Swedish word ''varv'' whose meanings and connotations include 'revolution', 'in layers', and 'circle'.
Of the many rhythmites in the geological record ...
-like sediments found in Uruguay have been associated with this glaciation.
During the early rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
ing stages of the South Atlantic the area of southern Paraná Basin
The Paraná Basin (, ) is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distribu ...
suffered a gentle uplifting that deviated sediments into the Tacuarembó region of Uruguay. These changes led to the formation of the Itacuanbú and Tacuarembó formations during the Mid Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
to Early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
. Parts of the Tacuarembó formation
The Tacuarembó Formation is a Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 154.8 ±0.8 Ma and 149.2 ±0.7 Ma ...
came to be preserved thanks to a unit of the Paraná traps, the Arapey basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
s, that erupted 132 mya and covered the sediments.
Paraná traps
In the north of Uruguay, volcanic materials from the Paraná continental flood basalt province form a majorlithological
The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lith ...
unit extending beyond Uruguay's borders into Argentina and Brazil, with parts of it now lying in Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
on the other side of the Atlantic due to plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
. This volcanic material erupted in the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period during the opening of the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
and has been linked to the Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha (), colloquially Tristan, is a remote group of volcano, volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascensi ...
plume. The bulk of this volcanic material is basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
but there are rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
s as well. Associated with this volcanism are also syenite
Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a general composition similar to that of granite, but deficient in quartz, which, if present at all, occurs in relatively small concentrations (< 5%). It is considered a granitoid
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s exposed as outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth and other terrestrial planets.
Features
Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most p ...
s in small areas of Southeastern Uruguay. Although volcanic rocks of the Paraná volcanism underlies more than half of Uruguay, they have in many areas been covered by younger sediments so that the lavas only crop out as a geological province in the Uruguayan northwest.David S. Thiede and Paulo M. Vasconcelos. 2010Paraná flood basalts: Rapid extrusion hypothesis confirmed by new 40Ar/39Ar results
''Geology'' vol 38.
References
External links
National Mining and Geology Office
by
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
Geological evolution of Uruguay
by Agronomy Faculty,
Universidad de la República
The University of the Republic (, sometimes ''UdelaR'') is a public research university in Montevideo, Uruguay. It is the country's oldest and largest university, as well as one of the largest public universities in South America in terms of en ...
, Uruguay
{{Uruguay topics