National Robotics Engineering Center on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The National Robotics Engineering Center (NREC) is an operating unit within the


Lassen Canyon Nursery
and other growers, representing approximately 85% of California's strawberry plant nursery market, supported this project and plan to use the technology in their operations. ''Orchard Spraying'': NREC developed a retrofit kit that allows a tractor to operate without a driver. Its software accurately estimated the vehicle’s location and enabled it to autonomously follow a predetermined path. The autonomous tractor sprayed water while following a seven-kilometer-long path through an orange orchard without any human intervention. To achieve the path teach/playback capability, NREC developed a positioning system that uses an
Oshkosh Defense official web site
Journal of Petroleum Technology, October 2012
Robotics Institute
The Robotics Institute (RI) is a division of the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. A June 2014 article in ''Robotics Business Review'' magazine calls it "the world's best robo ...
(RI) of Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institu ...
. NREC works closely with government and industry clients to apply robotic technologies to real-world processes and products, including unmanned vehicle and platform design, autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be ...
, sensing and image processing, machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, manipulation, and human–robot interaction
Human–robot interaction (HRI) is the study of interactions between humans and robots. Human–robot interaction is a multidisciplinary field with contributions from human–computer interaction, artificial intelligence, robotics, natural languag ...
.
NREC research objectives and approach
NREC applies roboticstechnologies
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
to build functional prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
systems from concept to commercialization
Commercialisation or commercialization is the process of introducing a new product or production method into commerce—making it available on the market. The term often connotes especially entry into the mass market (as opposed to entry into e ...
. A typical NREC project includes a rapid proof-of-concept
A proof of concept (POC or PoC), also known as proof of principle, is an inchoate realization of a certain idea or method in order to demonstrate its feasibility or viability. A proof of concept is usually small and may or may not be complete ...
demonstration followed by an in-depth development and testing phase that produces a robust prototype with intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
for licensing
A license (American English) or licence ( Commonwealth English) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another par ...
and commercialization. Throughout this process, NREC applies best practices for software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
, system integration
System integration is defined in engineering as the process of bringing together the component sub-systems into one system (an aggregation of subsystems cooperating so that the system is able to deliver the overarching functionality) and ensuring ...
, and field testing. Sponsors and partners include industrial companies, technology startups
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an Entrepreneurship, entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses tha ...
, and federal agencies such as DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
, the Department of Transportation, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
, the Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research and development detachment of the United States Air Force Air Force Materiel Command, Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of direct- ...
, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wor ...
.
NREC's research model is based on
* Creative design and engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
on all levels and across all disciplines
* Rapid prototyping using in-house fabrication capabilities
* Collaboration with sponsors to commercialize technology
NREC history
In 1994, theCarnegie Mellon
Carnegie may refer to:
People
*Carnegie (surname), including a list of people with the name
**Andrew Carnegie, Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist
* Clan Carnegie, a lowland Scottish clan
Institutions Named for Andrew Carnegie
* ...
Field Robotics Center scientists realized that the mobile robotics field was mature enough for commercial application in agriculture, construction, mining, utilities, and other markets. Consequently, the National Robotics Engineering Consortium (NREC) was chartered with a mission to develop and transition robotic technology to industry and federal agencies. Original funding for the center included $2.5 million seed funding from NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
.
In 1996, the organization moved to its current facility in Pittsburgh’s Lawrenceville neighborhood and was renamed the National Robotics Engineering Center. The NREC is housed in a renovated, 100,000-square-foot foundry building on a reclaimed industrial brownfield site.



NREC timeline
Project case studies
DARPA robotics challenge
CHIMP is a human-sized robot that, when standing, is 5-foot-2-inches tall and weighs about 400 pounds. Tartan Rescue Team engineers designed CHIMP to work in dangerous, degraded environments that were built for people, not robots. CHIMP operates semi-autonomously and can plan and carry out high-level instructions given by its operator. Its near-human form, strength, precision, and dexterity enable it to perform complex, human-level tasks. CHIMP is not a dynamically balanced walking robot. Instead, it is designed to move on stable, tank-like treads incorporated into its four limbs. When it needs to operate power tools, turn valves, or otherwise use its arms, CHIMP can stand and roll on its leg treads. The robot’s long front arms (almost 5 feet) give it an ape-like appearance. CHIMP ranked third in the DARPA Robotics Challenge Trials in December 2013. Scoring 18 out of a possible 32 points during the two-day trials, the team demonstrated the system's ability to perform such tasks as removing debris, opening doors, cutting a hole in a wall, and closing a series of valves. The system was selected as one of nine eligible for DARPA funding to prepare for the DARPA Robotics Challenge Finals in 2015.Urban challenge
Carnegie Mellon University's Tartan Racing team and General Motors built an autonomous SUV that won first place in the 2007 DARPA Urban Challenge. The Urban Challenge race was held on November 3, 2007, at the Victorville training facility in California. Eleven teams competed against each other to finish a 60-mile city course in less than six hours. Their vehicles had to execute simulated missions in a mock urban area while obeying traffic laws, safely merging into moving traffic, navigating traffic circles, negotiating busy intersections, and avoiding other vehicles – all without human intervention.Automation and machine learning for agriculture
''Vehicle safeguarding'': Being able to detect obstacles and terrain hazards significantly increases the safety of both manned and unmanned agricultural vehicles. The project uses machine learning techniques to build a robust obstacle detection system that can be easily adapted to different environments and operating conditions. NREC integrated its add-on perception packages onto a team of three computer-controlled tractors developed byJohn Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
. These autonomous tractors were used in harvesting operations in a peat bog. The robotic peat harvesting team was tested for a full season, completing over 100 harvesting missions in a working peat bog. Their behavior imitated manual peat harvesting operations while maintaining a safe operating environment.
''Strawberry Plant Sorter'': Building upon expertise in vision, mechanisms, and manipulation, NREC built an automated strawberry plant sorter that streamlines the harvesting process, improves efficiency, and ensures consistent plant quality. The machine vision system is trained to sort strawberry plants using samples harvested by a human, sorting plants of different varieties and levels of maturity while operating under realistic conditions, where rain and frost change plants' appearance and roots may contain mud and debrisLassen Canyon Nursery
and other growers, representing approximately 85% of California's strawberry plant nursery market, supported this project and plan to use the technology in their operations. ''Orchard Spraying'': NREC developed a retrofit kit that allows a tractor to operate without a driver. Its software accurately estimated the vehicle’s location and enabled it to autonomously follow a predetermined path. The autonomous tractor sprayed water while following a seven-kilometer-long path through an orange orchard without any human intervention. To achieve the path teach/playback capability, NREC developed a positioning system that uses an
extended Kalman filter
In estimation theory, the extended Kalman filter (EKF) is the nonlinear version of the Kalman filter which linearizes about an estimate of the current mean and covariance. In the case of well defined transition models, the EKF has been considered t ...
for fusing the odometry, the GPS information, and the IMU measurements. The path following system is based on the Pure Pursuit algorithm.
Defense robotics for convoy safety
NREC and Oshkosh Defense are developing autonomous unmanned ground vehicle technologies for logistics tactical wheeled vehicles used by the US Marine Corps. ''CARGO Unmanned Ground Vehicles'' (CARGO UGVs or CUGVs) are designed for autonomous use in convoys that combine manned and unmanned vehicles. An operator in another vehicle supervises one or more unmanned vehicles, which drive autonomously in convoy formation day and night, in all weather, and when dust and smoke limit visibility. Technologies developed under this project are part of Oshkosh Defense’s TerraMax™ UGV kit, which supports unmanned convoy operations.Unmanned Ground VehicleOshkosh Defense official web site
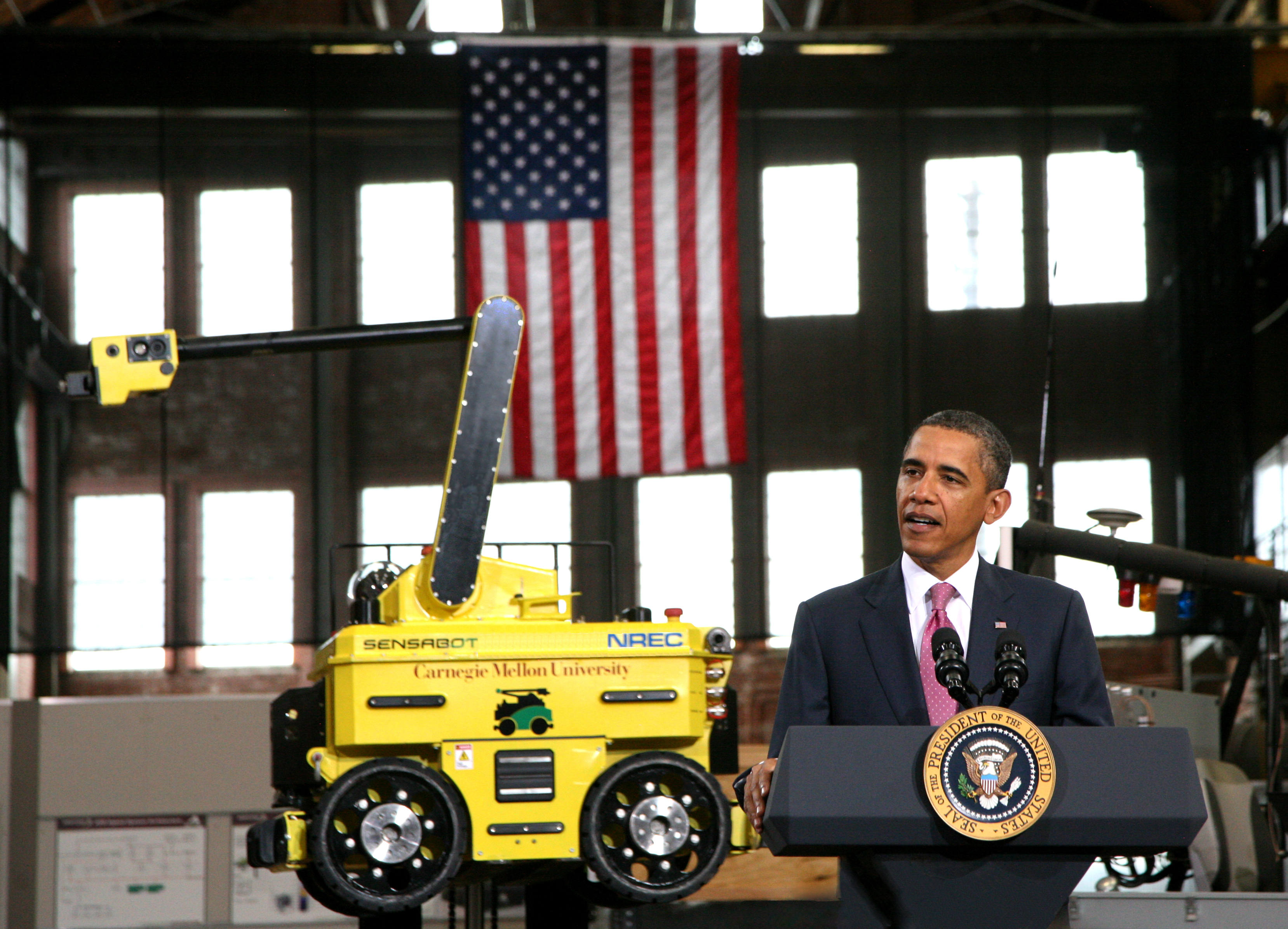
Sensabot
Sensabot is a rugged robot designed to safely carry out on-site inspections in hazardous environments, isolated facilities, and other places that are difficult or dangerous for personnel to access. Benefits include reduced risk and improved efficiency of operation. The system consists of a mobile robotic base equipped with a sensor boom that is fitted with inspection sensors. It is capable of operating in extreme temperatures, as well as explosive and toxic atmospheres. The robot is remotely controlled by a human operator who utilizes the sensors to conduct inspections on pipes, fittings, and valves. Sensabot has been designed to conform to the IECEx Zone 1 standards for explosive environments, as well as the ANSI safety standards for guided industrial vehicles.Sensabot: A Safe and Cost-Effective Inspection SolutionJournal of Petroleum Technology, October 2012
Advanced Robotic Laser Coating Removal System (ARLCRS)
TheAir Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research and development detachment of the United States Air Force Air Force Materiel Command, Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of direct- ...
(AFRL), Concurrent Technologies Corporation (CTC), and NREC are developing an environmentally friendly system to remove coatings from U.S. Air Force aircraft through funding from Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC).
The Advanced Robotic Laser Coating Removal System (ARLCRS) uses a powerful laser stripping tool and state-of-the-art mobile robots to automatically remove paint and coatings from aircraft. The complete system is scalable for use from fighters to cargo and tanker aircraft. ARLCRS will reduce hazardous waste, air emissions, maintenance costs, and processing time. CTC is developing the laser coatings removal and particle capture systems. NREC is developing the mobile robots, sensors, and autonomy system.
Operator assistance for underground coal mining
NREC has worked with coal mining industry partners to develop operator assistance technology forlongwall mining
Longwall mining is a form of underground coal mining where a long wall of coal is mined in a single slice (typically thick). The section of rock that is being mined, known as the longwall panel, is typically long, but can be up to long and wi ...
. This includes a complete navigation system for a continuous mining machine, laser rangefinder-based perception for robot localization
Robot localization denotes the robot's ability to establish its own position and orientation within the frame of reference. Path planning is effectively an extension of localization, in that it requires the determination of the robot's current pos ...
, planning for cluttered spaces, and integration and simulation tools. This system was successfully demonstrated in a working mine in West Virginia. Related research and objectives include automated mine surveying, haulage, and multiple-machine interaction.
ARMOR 1: mat sinking system
ARMOR 1 is an automated robotic system for the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to performrevetment
A revetment in stream restoration, river engineering or coastal engineering is a facing of impact-resistant material (such as stone, concrete, sandbags, or wooden piles) applied to a bank or wall in order to absorb the energy of incoming water an ...
operations along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
. Once deployed, ARMOR 1 will replace the old Mat Sinking Unit, originally built in 1948. The goal is to increase the speed of revetment operations and improve the safety and working conditions of the employees who perform this vital work.
When completed, ARMOR 1 will include six, independent robotic cranes. These cranes will pick up the large concrete squares from the supply barge and place them on the "mat deck" of ARMOR 1's manufacturing barge. There, the individual squares will be tied together into one 140 ft wide (and up to 900 ft long) flexible "mat" by an automated tie system. The completed mat will be launched from the barge and will be submerged along the banks of the Mississippi River, while more mats are continuously being assembled on the deck.
Contribution to education
The Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy (CMRA) is an educational outreach of Carnegie Mellon University and part of the university's world-renowned Robotics Institute. In 2000, CMRA's administrative staff and development team became housed at NREC's facilities. The Computer Science STEM Network (CS2N) is a collaborative research project between Carnegie Mellon University, including the Robotics Academy, and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) designed to increase the number of students pursuing advanced Computer Science and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (CS-STEM) degrees.See also
*Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
References
* {{authority control Software engineering organizations Carnegie Mellon University Computer science institutes in the United States Robotics in the United States Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh) Research institutes in Pennsylvania Organizations based in Pittsburgh de:Software Engineering Institute es:Software Engineering Institute kk:Бағдарламалық Жасақтама Инжинирингі Институты pl:Software Engineering Institute pt:Software Engineering Institute