Nanotube(10,10)Armchair on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
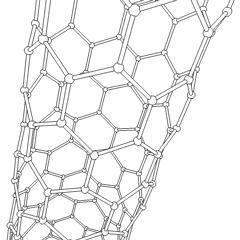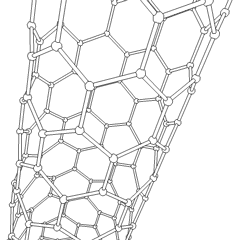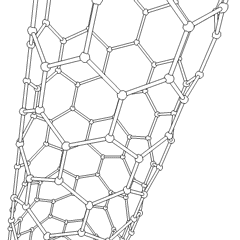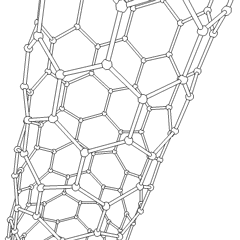 A nanotube is a
A nanotube is a
 A nanotube is a
A nanotube is a nanoscale
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
cylindrical structure with a hollow core, typically composed of carbon atoms, though other materials can also form nanotubes. Carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''S ...
s (CNTs) are the most well-known and widely studied type, consisting of rolled-up sheets of graphene
Graphene () is a carbon allotrope consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, honeycomb planar nanostructure. The name "graphene" is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, indicating ...
with diameters ranging from about 1 to tens of nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling
Despite the va ...
s and lengths up to millimeter
330px, Different lengths as in respect of the electromagnetic spectrum, measured by the metre and its derived scales. The microwave is between 1 metre to 1 millimetre.
The millimetre (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, i ...
s. These structures exhibit remarkable physical, chemical, and electrical properties, including high tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate ...
, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity in ...
, and unique quantum effects
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of a ...
due to their one-dimensional nature. Nanotubes can be classified into two main categories: single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs), each with distinct characteristics and potential applications. Since their discovery in 1991, nanotubes have been the subject of intense research and development, with promising applications in fields such as electronics, materials science, energy storage, and medicine.
Types
* BCN nanotube, composed of comparable amounts ofboron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
, carbon, and nitrogen atoms
* Boron nitride nanotube
Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) are a polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of boron nitride. They were predicted in 1994 and experimentally discovered in 1995. Structurally they are similar to carbon nanotubes, which are cylinders with sub- ...
, a polymorph of boron nitride
* Carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''S ...
, includes general nanotube terminology and diagrams
* DNA nanotube, a two-dimensional lattice which curves back upon itself, somewhat similar in size and shape to a carbon nanotube
* Gallium nitride nanotube, a nanotube of gallium nitride
* Silicon nanotube, made of silicon atoms
* Non-carbon nanotube
A non-carbon nanotube is a cylindrical molecule often composed of metal oxides, or group 13-Nitrides, such as BN, AlN, GaN and morphologically similar to a carbon nanotube. Non-carbon nanotubes have been observed to occur naturally in some m ...
, especially tungsten(IV) sulfide nanotubes
* Tunneling nanotube, a tubular membrane connection between cells
* Titanium nanotubes, created by the conversion of the mineral anatase by hydrothermal synthesis
Nanotubes builders
* Chiraltube. Atomistic builder for any nanotubes with any chirality from any 2D material. * TubeASP. For carbon nanotubes. * Nanotuve Modeler. For carbon nanotubes only.References
{{chemistry index