NB Class on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Commonwealth Railways NB class originated in a shipment of four
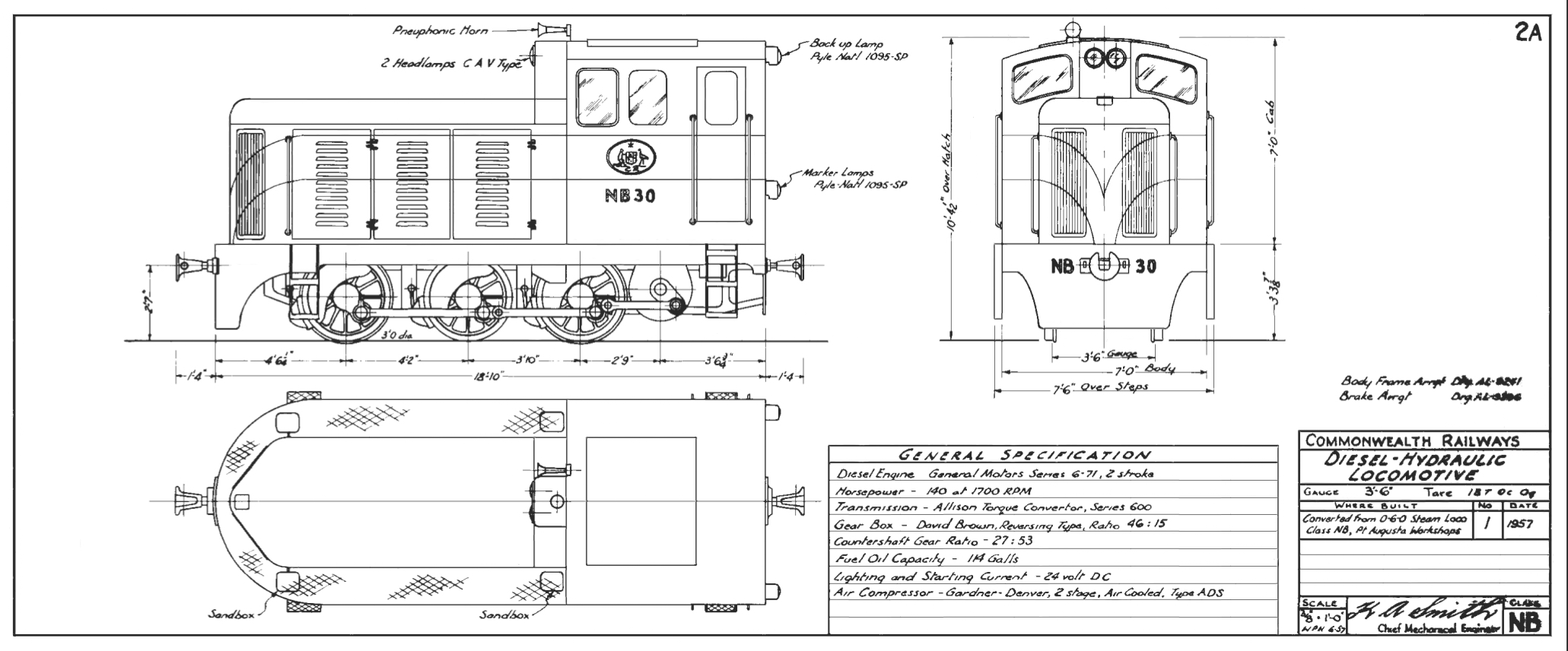 In 1957, the frame and wheels of NB30 were used as the basis of a small
In 1957, the frame and wheels of NB30 were used as the basis of a small
0-6-0
is the Whyte notation designation for steam locomotives with a wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. Historically, this was the most common wheel arrangement used o ...
, gauge, saddle tank steam locomotives built by the Vulcan Iron Works
Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several Ironworks, iron foundries in both England and the United States during the Industrial Revolution and, in one case, lasting until the mid-20th century. Vulcan (mythology), Vulcan, the Roman god of fir ...
of Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. They were imported to Australia in 1916 for construction work at the naval base at Henderson, Western Australia. Their tractive effort was 9500 pounds.
In 1925 two of them (builder's numbers 2532 and 2533) were acquired by the Commonwealth Railways
The Commonwealth Railways were established in 1917 by the Government of Australia with the Commonwealth Railways Act to administer the Trans-Australian Railway, Trans-Australia and Adelaide-Darwin railway, Port Augusta to Darwin railways. In 1 ...
and placed in service on the Central Australia Railway
The former Central Australia Railway, which was built between 1878 and 1929 and dismantled in 1980, was a Narrow-gauge railway, 1067 mm narrow gauge railway between Port Augusta railway station, Port Augusta and Alice Springs. A standard gau ...
as NB29 and NB30 respectively. After shunting for two decades at Quorn, where they were nicknamed "pugs", the two locomotives were set aside. NB29 was written off in 1946 and scrapped in 1958. NB30 was written off in 1950.
Conversion to diesel – NB30
 In 1957, the frame and wheels of NB30 were used as the basis of a small
In 1957, the frame and wheels of NB30 were used as the basis of a small diesel-hydraulic
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is con ...
locomotive designed and built at Commonwealth Railways' Port Augusta
Port Augusta (''Goordnada'' in the revived indigenous Barngarla language) is a coastal city in South Australia about by road from the state capital, Adelaide. Most of the city is on the eastern shores of Spencer Gulf, immediately south of the ...
workshops.Specifications included power output of – from a General Motors model 6/71, bore x in stroke, 6-in-line, 2-stroke diesel engine – at 1700 rpm; maximum speed limit ; and a maximum axle load of 6 tons (6.1 tonnes). Other specifications are in the general arrangement diagram. Retaining its number, NB30 was initially used in recovering rails from the closed Brachina–Hawker section of the Central Australia Railway
The former Central Australia Railway, which was built between 1878 and 1929 and dismantled in 1980, was a Narrow-gauge railway, 1067 mm narrow gauge railway between Port Augusta railway station, Port Augusta and Alice Springs. A standard gau ...
, after which it was assigned to Quorn for shunting work. It was then transferred to Port Augusta for use as a workshops shunter, where it was withdrawn from service in 1972.
In 1979, NB30 was donated to the Pichi Richi Railway by the successor to the Commonwealth Railways, the Australian National Railways Commission
The Australian National Railways Commission was an agency of the Government of Australia that was a railway operator between 1975 and 1998. It traded as Australian National Railways (ANR) in its early years, before being rebranded as Australia ...
, whose chairman, Keith Smith, had been the Chief Mechanical Engineer who had overseen its design. , the heritage railway employed the locomotive on shunting duties.
Notes
References