Multiethnic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A multinational state or a multinational
union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
is a sovereign entity
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person ...
that comprises two or more nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by those ...
s or states. This contrasts with a nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of "nation" (which touches on ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, language, and political identity), a multinational state is usually multicultural
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for "Pluralism (political theory), ethnic pluralism", with the tw ...
or multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all E ...
, and is geographically composed of more than one country, eg Countries of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK), since 1922, comprises three constituent countries and a region: England, Scotland, and Wales (which collectively make up the region of Great Britain), as well as Nor ...
.
Historical multinational states that have since split into multiple sovereign states include the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
(a dual monarchy of two multinational states). Some analysts have described the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
as a multinational state or a potential one.Kelemen, R. Daniel. (2007). In ''Making History: State of the European Union'', Vol. 8, edited by Sophie Meunier Sophie Meunier (born 1967 in Paris, France) is a senior research scholar in Public and International Affairs at Princeton University'School of Public and International Affairs(formerly known as the Woodrow Wilson School). She is the Director of Pri ...
and Kate McNamara, Oxford University Press, p. 52.
Countries
Definition
Many attempts have been made to define what a multinational state is. One complicating factor is that it is possible for members of a group that could be considered a nation to identify with two different nationalities simultaneously. AsIlan Peleg Ilan may refer to:
Organization
*ILAN, Israeli umbrella organization for the treatment of disabled children
Given name
*Ilan (name), a Hebrew/Israeli name
* Ilan Bakhar, a retired Israeli footballer
* Ilan Araújo Dall'Igna, a Brazilian footballe ...
wrote in ''Democratizing the Hegemonic State'':
A state may also be a society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Socie ...
, and a multiethnic society has people belonging to more than one ethnic group, in contrast to societies that are ethnically homogeneous. By some definitions of "society" and "homogeneous", virtually all contemporary national societies are multiethnic. The scholar David Welsh argued in 1993 that fewer than 20 of the 180 sovereign states then in existence were ethnically and nationally homogeneous, if a homogeneous state was defined as one in which minorities made up less than 5 percent of the population. Sujit Choudhry
Sujit Choudhry is a lawyer, legal scholar, and expert in comparative constitutional law.
He is also an internationally recognized authority on comparative constitutional law. For over 20 years, he has been an advisor for constitution building, g ...
therefore argues that " e age of the agriculturally homogeneous state, if ever there was one, is over".
Modern multinational states
Africa
Most countries inSub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
are former colonies and, as such, are not drawn along national lines, making them truly multinational states.
Ghana
There is no ethnic majority in Ghana. The plurality group, theAkan people
The Akan () people live primarily in present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language (also known as ''Twi/Fante'') are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo ...
, are a meta-ethnicity
Meta-ethnicity is a relatively recent term (or neologism) occasionally used in academic literature or public discourse on ethnic studies. It describes a level of commonality that is wider ("meta-") and more general (i.e., might differ on specifics) ...
(that is, a collection of similar but distinct ethnicities). While Akan is the most-widely spoken language in Ghana, English is the official language of government
Kenya
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
is home to more than 70 ethnic groups, the most populous of which are the Kikuyu Kikuyu or Gikuyu (Gĩkũyũ) mostly refers to an ethnic group in Kenya or its associated language.
It may also refer to:
* Kikuyu people, a majority ethnic group in Kenya
*Kikuyu language, the language of Kikuyu people
*Kikuyu, Kenya, a town in Cent ...
, at about 20 percent of the population. Together, the five largest groups—the Kikuyu, Luo Luo may refer to:
Luo peoples and languages
*Luo peoples, an ethno-linguistic group of eastern and central Africa
**Luo people of Kenya and Tanzania or Joluo, an ethnic group in western Kenya, eastern Uganda, and northern Tanzania.
*** Luoland, th ...
, Luhya Luhya or Abaluyia may refer to:
* Luhya people
* Luhya language
Luhya (; also Luyia, Luhia or Luhiya) is a Bantu language of western Kenya.
Dialects
The various Luhya tribes speak several related languages and dialects, though some of them are ...
, Kamba
Kamba may refer to:
*Kamba people
The Kamba or Akamba (sometimes called Wakamba) people are a Bantu ethnic group who predominantly live in the area of Kenya stretching from Nairobi to Tsavo and north to Embu, in the southern part of the f ...
, and Kalenjin Kalenjin may refer to:
* Kalenjin people
The Kalenjin are a group of tribes designated as Highland Nilotes and are descended from Maliri people ''(thus related to Daasanach of Ethiopia.)'' The Kalenjin are cousins with Datooga people of Tan ...
—account for 70 percent of Kenyans.
Nigeria
The largest nation inNigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
is the Hausa-Fulani, which accounts for 29 percent of the country's population. However, the group actually encompasses two distinct ethnicities: the Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
* ...
and the Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
(or Fulbe). While both ethnicities are found in large areas of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
, it is only in Nigeria that they are classified as a single ethnic group for political expediency. Nigeria is also made up of many other ethnic groups like the Yoruba, Igbo and Ibibio. Prior to colonialism, they were not self identified as one ethnic nationality but are so today along with the three Hausa-Fulani, Yoruba, and Igbo which classification does carry between each group of who is part of and not part of the group aside from them Nigeria as about 250–500 other ethnic nationalities considered minorities with some large enough to control the outcomes of elections in states such as the Igala and Urhobo. While some are so small that they only show up in one local Government area
South Africa
Present-daySouth Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
is the successor state to the Union of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Trans ...
, which was formed from four British colonies in 1910.
South Africa has eleven official languages (Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gra ...
, English, Ndebele
Ndebele may refer to:
*Southern Ndebele people, located in South Africa
*Northern Ndebele people, located in Zimbabwe and Botswana
Languages
* Southern Ndebele language, the language of the South Ndebele
*Northern Ndebele language
Northern ...
, Pedi, Sotho Sotho may refer to:
*Sotho people (or ''Basotho''), an African ethnic group principally resident in South Africa, Lesotho and southern Botswana
* Sotho language (''Sesotho'' or ''Southern Sotho''), a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa, an off ...
, Swazi Swazi may refer to:
* Swazi people, a people of southeastern Africa
* Swazi language
* Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked coun ...
, Tsonga
Tsonga may refer to:
* Tsonga language, a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa
* Tsonga people, a large group of people living mainly in southern Mozambique and South Africa.
* Jo-Wilfried Tsonga
Jo-Wilfried Tsonga (; born 17 April 1985) i ...
, Tswana
Tswana may refer to:
* Tswana people, the Bantu speaking people in Botswana, South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Zambia, and other Southern Africa regions
* Tswana language, the language spoken by the (Ba)Tswana people
* Bophuthatswana, the former ba ...
, Venda
Venda () was a Bantustan in northern South Africa, which is fairly close to the South African border with Zimbabwe to the north, while to the south and east, it shared a long border with another black homeland, Gazankulu. It is now part of the ...
, Xhosa
Xhosa may refer to:
* Xhosa people, a nation, and ethnic group, who live in south-central and southeasterly region of South Africa
* Xhosa language, one of the 11 official languages of South Africa, principally spoken by the Xhosa people
See als ...
, and Zulu) and formally recognises several other languages spoken by minority nations. Speakers of each language may be of a different nationality—for example, some members of the Ndebele
Ndebele may refer to:
*Southern Ndebele people, located in South Africa
*Northern Ndebele people, located in Zimbabwe and Botswana
Languages
* Southern Ndebele language, the language of the South Ndebele
*Northern Ndebele language
Northern ...
and Tswana
Tswana may refer to:
* Tswana people, the Bantu speaking people in Botswana, South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Zambia, and other Southern Africa regions
* Tswana language, the language spoken by the (Ba)Tswana people
* Bophuthatswana, the former ba ...
nations speak Zulu, and groups such as the Thembu
The Thembu Kingdom (''abaThembu ababhuzu-bhuzu, abanisi bemvula ilanga libalele'') was a Xhosa-state in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa.
According to Xhosa oral tradition, the AbaThembu migrated along the east coast of Southern Africa ...
and Hlubi
The Hlubi people or AmaHlubi are an Nguni ethnic group native to Southern Africa, with the majority of population found in KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.
List of AmaHlubi kings
Origins
The Hlubi, similar to o ...
speak Xhosa.
As is the case throughout Africa, the nations of South Africa mostly correspond to specific regions. However, large cities such as Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Demo ...
are home to a mixture of national groups, leading to a "melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
" of cultures. The government has continuously attempted to unify the country's various nationalities and to foster a South African identity.
Many of the nationalities found in South Africa are also found in bordering countries, and in some cases, more members live in South Africa than in the country where the group originated. For example, there are more Sotho Sotho may refer to:
*Sotho people (or ''Basotho''), an African ethnic group principally resident in South Africa, Lesotho and southern Botswana
* Sotho language (''Sesotho'' or ''Southern Sotho''), a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa, an off ...
, Tswana, and Swazi Swazi may refer to:
* Swazi people, a people of southeastern Africa
* Swazi language
* Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked coun ...
people living in South Africa than in the bordering nation states of Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
, Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
, and Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
, respectively. In the past, this has led to conflict. Lesotho still claims large swathes of South Africa, and attempts have been made to cede some South African territory to Botswana and Eswatini. All three states were intended to be incorporated in the Union of South Africa, but those plans never came to fruition because of power struggles within their apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
governments.
Americas
Bolivia
Since 2010, under the presidency of Evo Morales,Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
has been officially defined as a plurinational state, which recognizes the national distinctiveness of various indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
.
Canada
WhetherCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
should be described as "multinational" is an ongoing topic in academia and popular discourse. The current policy of the federal government is that Canada is bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all E ...
—English and French are both official languages—and multicultural
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for "Pluralism (political theory), ethnic pluralism", with the tw ...
. In 2006, the House of Commons of Canada
The House of Commons of Canada (french: Chambre des communes du Canada) is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada.
The House of Common ...
voted in favor of ''Government Business No. 11'', which states that the Québécois "form a nation within a united Canada". According to Canadian political philosopher Charles Blattberg, Canada should be seen as a multinational country. All Canadians are members of Canada as a civic or political community, a community of citizens, and this is a community that contains many other kinds within it. These include not only communities of ethnic, regional, religious, and civic (the provincial and municipal governments) sorts, but also national communities, which often include or overlap with many of the other kinds. He thus recognizes the following nations within Canada: those formed by the various First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
, that of francophone Quebecers, that of the anglophones who identify with English Canadian culture
The culture of Canada embodies the artistic, culinary, literary, humour, musical, political and social elements that are representative of Canadians. Throughout Canada's history, its culture has been influenced by European culture and traditi ...
, and perhaps that of the Acadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the des ...
.
Asia
China
ThePeople's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(PRC) is a multinational state consisting of 56 ethnic groups with the Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
people the largest ethnic group in mainland China. As of 2010, 91.51% of the population were classified as Han (~1.2 billion). Besides the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
majority, 55 other ethnic (minority) groups are categorized in present China, numbering approximately 105 million people (8%), mostly concentrated in the bordering northwest, north, northeast, south and southwest but with some in central interior areas.
The major minority ethnic groups in China are Zhuang (16.9 million), Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
(10.5 million), Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
(10.3 million), Uyghur (10 million), Miao Miao may refer to:
* Miao people, linguistically and culturally related group of people, recognized as such by the government of the People's Republic of China
* Miao script or Pollard script, writing system used for Miao languages
* Miao (Unicode ...
(9.4 million), Yi (8.7 million), Tujia (8.3 million), Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
(6.2 million), Mongolian (5.9 million), Dong (2.8 million), Buyei
The Bouyei (also spelled ''Puyi'', ''Buyei'' and ''Buyi''; self called: Buxqyaix, or "Puzhong", "Burao", "Puman"; ; vi, người Bố Y), otherwise known as the Zhongjia, are an ethnic group living in Southern Mainland China. Numbering 2.5 mil ...
(2.8 million), Yao (2.7 million), Bai (1.9 million), Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
(1.8 million), Hani (1.6 million), Li (1.4 million), Kazakh (1.4 million) and Dai (1.2 million). At least 126,000 people from Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the US and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
are living in Mainland China. In addition, there are also unrecognized ethnic groups, for example: Chuanqing people
The Chuanqing people () are an East Asian ethnic group. According to popular ethnogenesis, they are descended from Han Chinese soldiers who were sent to Guizhou area in the eighth and ninth centuries to quell Miao rebellions. The Chuanqings, how ...
(穿青人), and others, who comprise over 730,000 people.
However, the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
(ROC), which ruled mainland China from 1912 to 1949 and currently governs the island of Taiwan since 1945, had recognized five main ethnic groups under Five Races Under One Union
Five Races Under One Union was one of the major principles upon which the Republic of China was founded in 1911 at the time of the Xinhai Revolution. Its central tenet was the harmonious existence under one nation of what were considered the f ...
: Han, Hui, Manchu, Mongol and Tibetan. Since retreating to Taiwan, the ROC government recognizes 16 groups of Taiwanese aborigines, which constitutes a number 569,000 or 2.38% of the island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
's population. The PRC classifies them as ''Gaoshan''.
India
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
has more than 2,000 ethnic groups and over 80,000 subcultures, and every major religion is represented, as are four major language families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hi ...
( Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The te ...
, and Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
) and a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The num ...
( Nihali).
Each state and union territory of India has one or more official languages, and the Constitution of India
The Constitution of India (IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental ri ...
recognizes in particular 22 " scheduled languages". It also recognizes 212 scheduled tribal groups, which together constitute about 7.5% of the country's population.
Most of its states are based on a linguistic
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
ethnicity, including Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
, and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prade ...
( Hindustani), Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
(Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
), Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
and Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India b ...
(Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
), Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
(Kannadigas
The Kannada people or Kannadigaru IAST">nowiki/>IAST:_Kannadadavaru_or_Kannadigas_(English_term).html" ;"title="IAST.html" ;"title="nowiki/>IAST">nowiki/>IAST: Kannadadavaru or Kannadigas (English term)">IAST.html" ;"title="nowiki/>IAST">nowik ...
), Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of ...
(Odia
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
), Jammu and Kashmir (Dogra
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himachal ...
s and Kashmiris
Kashmiris are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group speaking the Kashmiri language, living mostly, but not exclusively, in the Kashmir Valley of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir, India.(a) (subscriptio ...
), Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
( Konkanis), Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
(Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub ...
), West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
(Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
), Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
(Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
), Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
( Punjabi), Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
(Haryanvi
Haryanvi ( ' or '), also known as Bangru, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the state of Haryana in India, and to a lesser extent in Delhi. Haryanvi is considered to be part of the dialect group of Western Hindi, which also includes Kharibo ...
), Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
(Rajasthani
Rajasthani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Rajasthan, a state of India
* Rajasthani languages, a group of languages spoken there
* Rajasthani people, the native inhabitants of the region
* Rajasthani architecture
* Rajasthani art ...
), Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
(Malayali
The Malayali people () (also spelt Malayalee and also known by the demonym Keralite) are a Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. ...
), Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of Myanm ...
(Manipuris
The Meitei people, also known as the Manipuri people,P.20: "historically, academically and conventionally Manipuri prominently refers to the Meetei people."P.24: "For the Meeteis, Manipuris comprise Meeteis, Lois, Kukis, Nagas and Pangal." is ...
), Mizoram
Mizoram () is a state in Northeast India, with Aizawl as its seat of government and capital city. The name of the state is derived from "Mizo people, Mizo", the endonym, self-described name of the native inhabitants, and "Ram", which in the Mizo ...
(Mizos
The Mizo people ( Mizo: ''Mizo hnam'') are an ethnic group native to the Indian state of Mizoram and neighbouring regions of Northeast India. The term covers several related ethnic groups or clans inside the Mizo group.
All Mizo tribes and cla ...
) and Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
( Nagas).
Furthermore, several Indian states are themselves ethnically, religiously, and linguistically diverse. Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
and Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . It ...
are home to the Maithils
Maithils (Tirhuta: মৈথিল, Devanagari: मैथिल), also known as Maithili people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group from the Indian subcontinent, who speak the Maithili language as their native language. They inhabit the M ...
, Santalis and the Hindustani language
Hindustani (; Devanagari: ,
*
*
*
* ; Perso-Arabic: , , ) is the '' lingua franca'' of Northern and Central India and Pakistan. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu. Thus, the lan ...
speaking people. Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
is home to the Tulu and Kannada people
The Kannada people or Kannadigaru IAST">nowiki/>IAST:_Kannadadavaru_or_Kannadigas_(English_term).html" ;"title="IAST.html" ;"title="nowiki/>IAST">nowiki/>IAST: Kannadadavaru or Kannadigas (English term)">IAST.html" ;"title="nowiki/>IAST">nowik ...
; Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
includes the Assamese, Bodo Bodo may refer to:
Ethnicity
* Boro people, an ethno-linguistic group mainly from Northwest Assam, India
* Bodo-Kachari people, an umbrella group from Nepal, India and Bangladesh that includes the Bodo people
Culture and language
* Boro cu ...
, and Karbi people and Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares int ...
having various tribes like Nyishis, Apatanis, Monpas and others.
Indonesia
Indonesia is a very diverse country with over 1,300 ethnic groups. The predominant ethnic group of in Indonesia is Javanese which makes up 40% of the population. Most of Javanese people reside in Java island, the most populous island in the country, however, there are other numerous ethnic groups from the island such as Sundanese, Betawi (Jakartans), Banten people and many more. Generally, people who live outside of Jakarta still retain the ethnic language and utilize it in daily conversations. As a result, formation of distinct dialects each unique to the regions, is prominently used among the population.Malaysia
When it was formed on 16 September 1963,Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
comprised four independent, self-governing nations: Malaya, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, Sabah
Sabah () is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indone ...
, and Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the M ...
. In 1965, Singapore seceded from the federation. Today, Malaya, Sabah, and Sarawak each have their own ethnic majority. Generally, however, Malaysia is considered to have three major ethnic groups: Malays, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, and Indians. The Iban people
The Ibans or Sea Dayaks are a branch of the Dayak peoples on the island of Borneo in South East Asia. Dayak is a title given by the westerners to the local people of Borneo island. It is believed that the term "Iban" was originally an exonym ...
are the majority in Sarawak, while Sabah is dominated by the Kadazan-Dusun
Kadazan-Dusun (also written as Kadazandusun or Mamasok Kadazan-Dusun) also less-known as "Mamasok Sabah" are two indigenous peoples of Sabah, Malaysia—the ethnic groups Kadazan and Dusun. The Kadazandusun is the largest native group of Bumip ...
, Murut Murut may refer to:
* Murut people
The Murut are an indigenous ethnic group, comprising 29 sub-ethnic groups inhabiting the northern inland regions of Borneo. The Murutic languages are a family of half a dozen closely related Austronesian lan ...
, and Bajau peoples. Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
is the primary national language, followed by English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
. In Sabah and Sarawak, English is the official language, although many locals speak a dialect of Malay.
Pakistan
Present-dayPakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
arose out of the Pakistan Movement
The Pakistan Movement ( ur, , translit=Teḥrīk-e-Pākistān) was a political movement in the first half of the 20th century that aimed for the creation of Pakistan from the Muslim-majority areas of British India. It was connected to the pe ...
, which demanded a separate state for the Muslims of the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
. The movement was based on the two-nation theory
The two-nation theory is an ideology of religious nationalism that influenced the decolonisation of the British Raj in South Asia. According to this ideology, Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus are two separate nations, with their own customs, ...
put forward by Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the ...
: the idea that Hindus and Muslims in British India represented not only different religious communities but also distinct nations, and hence that, in the event of Indian independence, they should be divided into two nation states. Jinnah (known in Pakistan as "Quaid-e-Azam", meaning "the great leader") outlined the theory as follows:
This movement culminated in the creation of Pakistan in 1947 through the partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
. Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''
''
South Asian Muslims. However, Pakistan remains ethnically diverse.
, 2002 census, ''Demoscope Weekly''. Retrieved 5 February 2009. while rest of the 19% of the population were minorities; while around 84.93% of the Russia's population was of
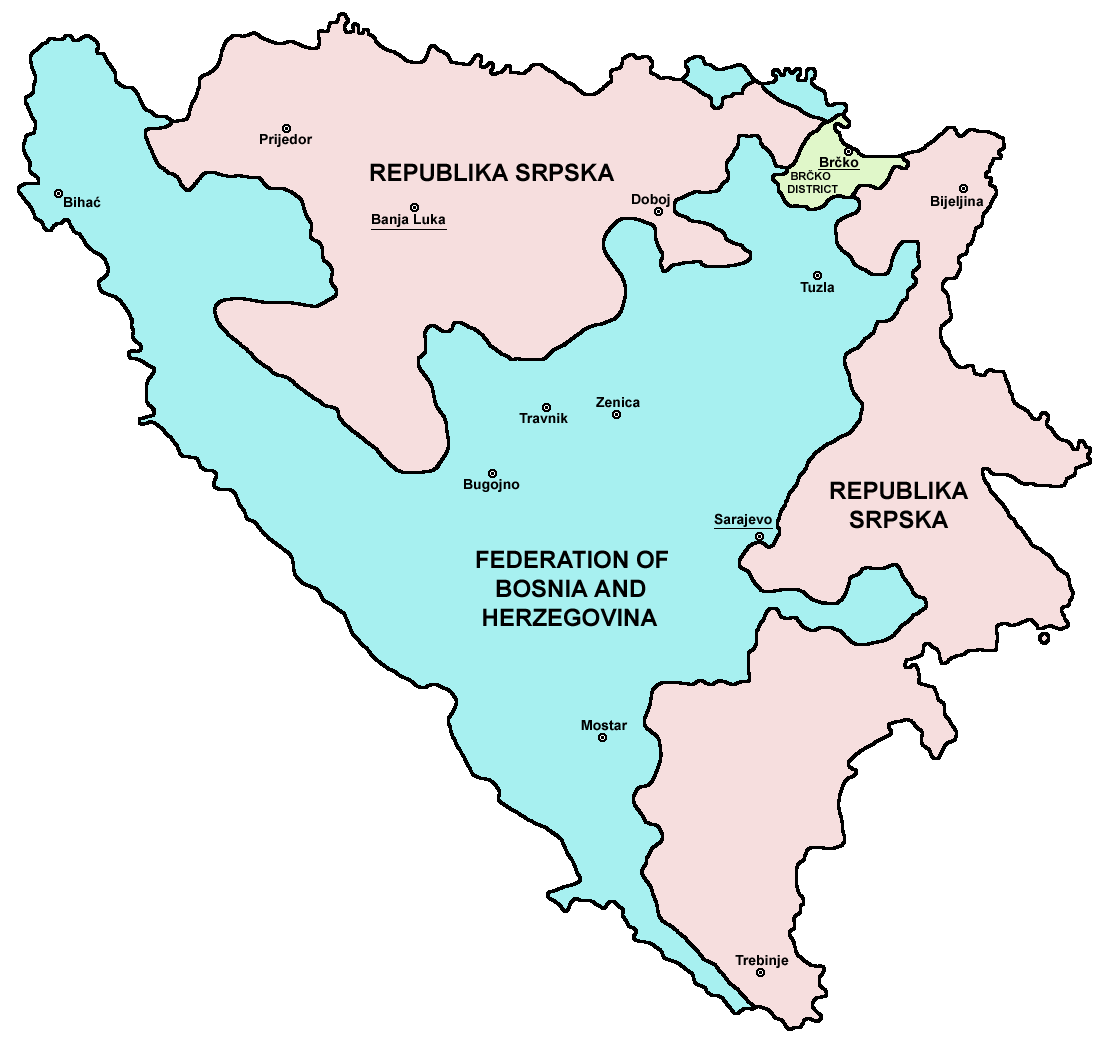 Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples": Bosniaks (50.11%), Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs (30.78%), and Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croats (15.43%). The country's political divisions were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government comprising two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (mostly Bosniaks and Croats) and the Republika Srpska (mostly Serbs), with each governing roughly half of the state's territory. A third region, the Brčko District, was governed locally. Today, all three ethnic groups have an equal constitutional status over the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The country has a bicameral, bicameral legislature and a Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, three-member presidency composed of one member of each major ethnic group.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples": Bosniaks (50.11%), Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs (30.78%), and Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croats (15.43%). The country's political divisions were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government comprising two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (mostly Bosniaks and Croats) and the Republika Srpska (mostly Serbs), with each governing roughly half of the state's territory. A third region, the Brčko District, was governed locally. Today, all three ethnic groups have an equal constitutional status over the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The country has a bicameral, bicameral legislature and a Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, three-member presidency composed of one member of each major ethnic group.

 The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, known until 3 October 1929 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia (to which the Kingdom of Montenegro had been annexed on 13 November 1918), and the Conference of Ambassadors gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 and abolished as a result of World War II. It was succeeded by Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement. When a communist government was established in 1946, the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1963, it was renamed again, becoming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, with Istria and Rijeka having been added after World War II.
The country consisted of six constituent "socialist republics" (SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia, and SR Serbia) and two "socialist autonomous provinces" (SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo, which became largely equal to other members of the federation after 1974).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars, which followed the secession of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, this last vestige separated into Serbia and Montenegro, but only to go further in 2008 after Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence but with limited recognition.
The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, known until 3 October 1929 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia (to which the Kingdom of Montenegro had been annexed on 13 November 1918), and the Conference of Ambassadors gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 and abolished as a result of World War II. It was succeeded by Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement. When a communist government was established in 1946, the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1963, it was renamed again, becoming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, with Istria and Rijeka having been added after World War II.
The country consisted of six constituent "socialist republics" (SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia, and SR Serbia) and two "socialist autonomous provinces" (SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo, which became largely equal to other members of the federation after 1974).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars, which followed the secession of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, this last vestige separated into Serbia and Montenegro, but only to go further in 2008 after Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence but with limited recognition.
Punjabis
The Punjabis ( Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. The ...
are the largest language group, but at 45 percent of the population, they do not make up an absolute majority. Furthermore, only 8 percent of Pakistanis speak the national language, Urdu, as their mother tongue
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
. As a result, many nationalist movements that oppose the two-nation theory have emerged, arguing that Pakistan is not only a linguistically diverse state but also a multinational one, and that, therefore, each ethnolinguistic group of Pakistan is a distinct nation. Common grievances of these movements include the idea that Punjabis dominate Pakistan politically and economically, thus marginalizing other groups, and that the establishment of Urdu as the country's sole official language is a form of cultural imperialism
Cultural imperialism (sometimes referred to as cultural colonialism) comprises the cultural dimensions of imperialism. The word "imperialism" often describes practices in which a social entity engages culture (including language, traditions, ...
that ignores the heritage of Pakistan's diverse peoples.
The most successful of these movements was Bengali nationalism
Bengalism or Bengali nationalism () was a form of nationalism that focused on Bengalis as a singular nation. The people of Bengali ethnicity speak Bengali language. Bengalis mostly live across Bangladesh and the Indian states of Tripura an ...
, which led to the creation of the Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
-speaking nation-state of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. The movement asserted that Urdu's official status gave an unfair advantage to Muhajirs (most of whom speak Urdu as their mother tongue) and Punjabis (whose mother tongue, Punjabi, is similar to Urdu, and many of whom were educated in Urdu under British rule). Bengalis feared they would be marginalized despite their demographic strength as, at the time, the largest ethnic group of Pakistan. These grievances culminated in the secession of East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = East ...
(which had been part of the administrative unit of East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
) and the creation of Bangladesh.
Today, nationalist movements within Pakistan include those of the Sindhis
Sindhis ( sd, سنڌي Perso-Arabic: सिन्धी Devanagari; ) are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group who speak the Sindhi language and are native to the province of Sindh in Pakistan. After the partition of British Indian empire in 1947, man ...
, Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
, Balochs
The Baloch or Baluch ( bal, بلۏچ, Balòc) are an Iranian people who live mainly in the Balochistan region, located at the southeasternmost edge of the Iranian plateau, encompassing the countries of Pakistan, Iran, and Afghanistan. There ar ...
, Mohajirs, and Kashmiris
Kashmiris are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group speaking the Kashmiri language, living mostly, but not exclusively, in the Kashmir Valley of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir, India.(a) (subscriptio ...
. The members of these movements assert that Islam cannot be considered the sole basis for nationhood, and that Pakistan is therefore a multinational state. Their demands range from increased autonomy or the transformation of Pakistan into a federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
, to the recognition of language rights
Linguistic rights are the human and civil rights concerning the individual and collective right to choose the language or languages for communication in a private or public atmosphere. Other parameters for analyzing linguistic rights include the ...
for non-Urdu-speaking populations, to outright secession.
Despite the fact that Punjabis are widely seen as the dominant ethnic group in Pakistan, both economically and politically, there is also a small Punjabi movement that asserts that the Punjabi language has been unfairly subordinated to Urdu and supports the reestablishment of cultural and economic links with East Punjab
East Punjab (known simply as Punjab from 1950) was a province and later a state of India from 1947 until 1966, consisting of the parts of the Punjab Province of British India that went to India following the partition of the province between ...
in India.
Philippines
The Philippines has 175 distinct ethnic groups, with theVisayans
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, ...
, Tagalogs
The Tagalog people ( tl, Mga Tagalog; Baybayin: ᜋᜅ ᜆᜄᜎᜓᜄ᜔) are the largest ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines, numbering at around 30 million. An Austronesian people, the Tagalog have a well developed society due to their ...
, Ilocanos
The Ilocanos ( ilo, Tattao nga Iloko/), Ilokanos, or Iloko people are the third largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group and mostly reside within the Ilocos Region in the northwestern seaboard of Luzon, Philippines. The native language of the Ilo ...
, Bicolanos, Kapampangans
The Kapampangan people ( pam, Taung Kapampangan), Pampangueños or Pampangos, are the sixth largest ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines, numbering about 2,784,526 in 2010. They live mainly in the provinces of Pampanga, Bataan and Tarlac, as ...
, Pangasinans, Moro and Igorots
The indigenous peoples of the Cordillera Mountain Range of northern Luzon, Philippines are often referred to using the exonym Igorot people, or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples. There are nine main ethnolinguistic groups whose domains ar ...
being the most prevalent.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
is inhabited by Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
, Sri Lankan Tamils
Sri Lankan Tamils ( or ), also known as Ceylon Tamils or Eelam Tamils, are Tamils native to the South Asian island state of Sri Lanka. Today, they constitute a majority in the Northern Province, live in significant numbers in the Eastern Pro ...
, Indian Tamils, Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
, Veddas
The Vedda ( si, වැද්දා , ta, வேடர் (''Vēḍar'')), or Wanniyalaeto, are a minority indigenous group of people in Sri Lanka who, among other sub-communities such as Coast Veddas, Anuradhapura Veddas and Bintenne Vedd ...
, Burghers, and other small ethnic groups.
Europe
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
is the only European state with no ethnic majority, but many others have ethnic minorities that form a majority within a province or region (see multilingual countries and regions of Europe).
Russia
Russia is anation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
, but it is home to over 193 ethnic groups. In the 2010 Census, roughly 81% of the population were ethnic Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
,Ethnic groups in Russia, 2002 census, ''Demoscope Weekly''. Retrieved 5 February 2009. while rest of the 19% of the population were minorities; while around 84.93% of the Russia's population was of
European descent
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as " ...
, of which the vast majority were Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
, with minorities of Germanic, Baltic-Finns and other peoples. There are 22 republics in Russia, designated to have their own ethnicities, cultures, and languages. In 13 of them, ethnic Russians consist a minority. According to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, Russia's immigrant population is the third-largest in the world, numbering over 11.6 million; most of which are from post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that wer ...
, mainly Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
.
The Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
, and the Chechens are three predominantly Muslims, Muslim minorities in the country. Russia is also home to small Buddhism, Buddhist populations, such as the nomadic Buryats in Buryatia, and the Kalmyks; native to Kalmykia, the only Buddhist region in Europe. There are also the Shamanism, Shamanistic peoples of Siberia and the Far North (Russia), Far North; the Finnic peoples of Northwest Russia and the Volga region; the Sakhalin Koreans, Korean inhabitants of Sakhalin; and the diverse peoples of the North Caucasus.
Russia's official language is Russian language, Russian. However, Russia's 193 minority ethnic groups speak over 100 languages. According to the 2002 Census, 142.6 million people speak Russian, followed by Tatar language, Tatar with 5.3 million, and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian with 1.8 million speakers. The constitution gives the individual republics of the country the right to Languages of Russia#Official languages, establish their own state languages in addition to Russian.
Belgium
The territory of Belgium is almost equally divided between the two linguistic groups of Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Flanders and Francophone, French-speaking Wallonia and Brussels. This led to political unrest throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, and in the aftermath of the difficult 2007–08 Belgian government formation, the Belgian media envisaged a partition of Belgium as a potential solution. There is also a German-speaking Community of Belgium, German-speaking minority in the east.Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples": Bosniaks (50.11%), Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs (30.78%), and Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croats (15.43%). The country's political divisions were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government comprising two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (mostly Bosniaks and Croats) and the Republika Srpska (mostly Serbs), with each governing roughly half of the state's territory. A third region, the Brčko District, was governed locally. Today, all three ethnic groups have an equal constitutional status over the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The country has a bicameral, bicameral legislature and a Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, three-member presidency composed of one member of each major ethnic group.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples": Bosniaks (50.11%), Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs (30.78%), and Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croats (15.43%). The country's political divisions were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government comprising two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (mostly Bosniaks and Croats) and the Republika Srpska (mostly Serbs), with each governing roughly half of the state's territory. A third region, the Brčko District, was governed locally. Today, all three ethnic groups have an equal constitutional status over the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The country has a bicameral, bicameral legislature and a Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, three-member presidency composed of one member of each major ethnic group.
France
In order to maintain a nation state, France does not recognize any French people, national identity or French language, language other than French in its territory. However, many of its current and former territories—Alsace, Brittany, Corsica, Flanders, Moselle (department), Moselle, Northern Catalonia, Occitania, Savoy, and the French Basque Country, Basque Country—were not fully French in cultural terms until they underwent Francization in the late 19th century. According to WikiLeaks, former Prime Minister Michel Rocard told the American ambassador to France, Craig Roberts Stapleton, in 2005, "France created itself by destroying five [ethnic] cultures: Breton, Occitan, Alsatian, Corsican, and Flemish."Montenegro
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
is a multiethnic state in which no ethnic group forms a majority. The preamble of the Constitution of Montenegro identifies numerous nationalities—Montenegrins, Serbs of Montenegro, Serbs, Bosniaks of Montenegro, Bosniaks, Albanians in Montenegro, Albanians, Islam in Montenegro, Muslims, Croats of Montenegro, Croats, and others—as citizens of a civic and democratic state. The largest ethnic groups are Montenegrins (45%), Serbs (28.7%), Bosniaks (8.6%), Albanians (4.9%), and Muslims (3.3%).
The official language is Montenegrin language, Montenegrin, but Serbian language, Serbian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, Albanian language, Albanian, and Croatian language, Croatian are also in official use. In the 2011 census, Serbian was the most common mother tongue (42.88%), Montenegrin the second (36.97%), and Bosnian the third (5.33%).
Norway
Official policy states that Norway was founded on the territory of two peoples, Norwegians and Sami people, Samis. In addition, Forest Finns, Kven people, Kvens, Jews in Norway, Jews, Romani people, Romani, and the Norwegian and Swedish Travellers are recognised as national minorities.Serbia
Nineteen ethnic groups are officially recognised as national minorities in Serbia. Serbs are the largest ethnic group in the country, constituting 83.3 percent of the population (excluding Kosovo). The largest national minorities are Hungarians in Serbia, Hungarians, Romani people in Serbia, Roma, and Bosniaks of Serbia, Bosniaks, and there are also significant populations of Croats of Serbia, Croats, Montenegrins of Serbia, Montenegrins, Albanians in Serbia, Albanians, Slovaks in Serbia, Slovaks, Romanians of Serbia, Romanians, Vlachs of Serbia, Vlachs, Pannonian Rusyns, Rusyns, Gorani people, Gorani, Macedonians in Serbia, Macedonians, and Bulgarians in Serbia, Bulgarians. Since 2002, minorities have been entitled to organize their own national councils. Through those councils, members of national minorities can exercise their rights in the spheres of culture, education, information, and the official use of their own languages and scripts. Vojvodina is a multiethnic Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province in northern Serbia, with Ethnic groups in Vojvodina, more than 26 ethnic groups and six official languages.Spain
Definitions of ethnicity and nationality in Spain are politically fraught, particularly since the transition from Francoist Spain to the (restored) Kingdom of Spain in the 1970s, when local regionalisms and peripheral nationalisms became a major part of national politics. The term Spanish people (Spanish: ''pueblo español'') is defined in the Spanish Constitution of 1978 as the political sovereign, i.e., the citizens of the Kingdom of Spain. The same constitution, in its preamble, speaks of "peoples and nationalities of Spain" (''pueblos y nacionalidades de España'') and their respective cultures, traditions, languages, and institutions. The ''CIA World Factbook'' (2011) describes Spain's ethnic makeup as a "composite of Mediterranean and Nordic types", instead of the usual breakdown of ethnic composition. This reflects the formation of the modern Kingdom of Spain by the accretion of numerous independent Iberian Peninsula, Iberian realms: Andalusia, Aragon, Asturias, Castile (historical region), Castile, Catalonia, Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Kingdom of León, León, Majorca, Navarre, and Valencian Community, Valencia. Thus, today's Spaniards include Andalusians, Aragonese people, Aragonese, Asturians, Basques, Cantabrian people, Cantabrians, Castilians, Catalan people, Catalans, Galicians, Leonese people, Leonese, and Valencian people, Valencians, and individual members of these groups may or may not consider them distinct nations.United Kingdom
While the Office for National Statistics describes the United Kingdom as a nation state, other people, including former Prime Minister Gordon Brown, describe it as a multinational state. The term "Home Nations" is used to describe the national teams that represent the four nations of the United Kingdom: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales in various sports. The Kingdom of Great Britain was created on 1 May 1707 by the political union of the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland. This unification was the result of the Treaty of Union, which was agreed on 22 July 1706 and then ratified by the parliaments of Parliament of England, England and Parliament of Scotland, Scotland in the 1707 Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union. The two kingdoms, along with the Kingdom of Ireland, had already been in a personal union as a result of the 1603 Union of the Crowns, in which James I of England, James VI, King of Scots, inherited the Kingdoms of England and Ireland and moved his court (royal), court from Edinburgh to London. However, until 1707, all three had remained separate political entities with separate political institutions. Prior to the Acts of Union, the Kingdoms of England and Scotland both had minority populations of their own that could themselves be called nations. Wales and Cornwall were part of the Kingdom of England (Wales had been officially incorporated into England by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, although it had been a ''de facto'' English territory Conquest of Wales by Edward I, since the 13th century; Cornwall had been conquered during the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period). The Northern Isles, with their Norsemen, Norse-derived culture, were part of Scotland, having been pledged by Norway as security against the payment of a dowry for Margaret of Denmark, Queen of Scotland, Margaret of Denmark and then integrated in 1471. When the Kingdom of Great Britain was created, many of its inhabitants retained a sense of English, Scottish, or Welsh identity. Many of them also spoke languages other than English: principally Scottish Gaelic, Scots language, Scots, Welsh language, Welsh, Cornish language, Cornish, and Norn language, Norn. Almost a century later, the Kingdom of Ireland merged with the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland under the 1800 Act of Union (1800), Acts of Union. The United Kingdom thus became the union of the kingdoms of England, Ireland, and Scotland.D. Ross, ''Chronology of Scottish History'' (Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset, 2002), , p. 56.J. Hearn, ''Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture'' (Edinburgh; Edinburgh University Press, 2002), , p. 104. Eventually, disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule movement, Irish home rule led to the Partition of Ireland, partition of the island: The Irish Free State received Dominion, dominion status in 1922, while Northern Ireland remained part of the UK. As a result, in 1927, the formal title of the UK Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927, was changed to its current form, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Political, ethnic, and religious tensions between Irish people, Irish and British people, British groups in Northern Ireland culminated in The Troubles. This period of armed conflict erupted in 1966 between Ulster loyalism, loyalist paramilitaries, seeking to maintain the country's position in the UK, and Irish republicanism, republican paramilitaries, seeking to United Ireland, unify Ireland as a 32-county independent republic. The British Army also played a key role. Following the deaths of over 3,500 people, a Good Friday Agreement, peace treaty was reached in 1998, although divisions remain high in some areas and sporadic violence still occurs. The end of the 20th century brought major governing changes, with the establishment of devolution, devolved national administrations for Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales following pre-legislative Referendums in the United Kingdom, referendums. The Scottish National Party, the largest political party in Scotland, is committed to the goal of an Scottish independence, independent Scotland within theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, but this is opposed by the leadership of the next three largest parties in the Scottish Parliament. A referendum on Scottish independence was held in September 2014, and 55% of the electorate rejected independence in favour of retaining the union. Plaid Cymru, a Welsh nationalist party, has a similar ambition for Wales. Plaid Cymru is currently the second- or third-largest party in Wales depending on how it is measured. Several parties in Northern Ireland, including the second- and third-largest, seek to establish an independent United Ireland, and have repeatedly called for border polls. The D'Hondt method, d'Hondt system used in Northern Ireland means that either the First Minister or Deputy First Minister will be from one of these parties.
Former multinational states
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, which succeeded the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867), Kingdom of Hungary, was a historical monarchy composed by two multinational states. The centrifugal forces within it, coupled with its loss in World War I, led to its breakup in 1918. Its successor states de jure included the First Austrian Republic, the Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Kingdom of Hungary, while part from her former territories entirely new states were created such as Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, or other parts incorporated into the Yugoslavia, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, Second Polish Republic, Poland, Kingdom of Romania, Kingdom of Italy and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
.
The principal languages of Austria-Hungary were German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Polish language, Polish, Czech language, Czech, and Croatian language, Croatian, but there were also many minor languages, including Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, Romanian language, Romanian, Slovak language, Slovak, Serbian language, Serbian, Slovene language, Slovene, Rusyn language, Rusyn, Italian language, Italian, and Yiddish language, Yiddish.
Ottoman Empire
TheOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
was the dynastic state of the Turkish House of Osman. At its peak in the 16th and 17th centuries, it controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, the Caucasus, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.
In addition to Turkish people, Turks, the ethnic groups of the Ottoman Empire included Albanians, Amazighs, Arabs, Armenians, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Bosnians, Bulgarians, Circassians, Georgians, Greeks, Jews, Kurds, Laz people, Laz, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Romanians, Serbs, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, and Zazas.
Through Millet (Ottoman Empire), millet courts, confessional community, confessional communities were allowed to rule themselves under their own legal systems: for example, Sharia, sharia law for Muslims, Canon law for Christians, and Halakha, halakha law for Jews. After the Tanzimat reforms from 1839–76, the term "millet" was used to refer to legally protected religious minority groups, similar to the way other countries use the word "nation". (The word "millet" comes from the Arabic language, Arabic word "millah" (ملة), which literally means "nation".) The millet system has been called an example of pre-modern religious pluralism.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Soviet Union
TheSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
was a state composed of the Republics of the Soviet Union, Soviet republics (of which there were 15 after 1956), with the capital in Moscow. It was founded in December 1922, when the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR—which formed during the Russian Revolution of 1917 and emerged victorious in the ensuing Russian Civil War—unified with the Transcaucasian SSR, Transcaucasian, Ukrainian SSR, Ukrainian, and Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Belarusian SSRs. Addressing the Extraordinary Eighth Congress of Soviets of the Soviet Union on 25 November 1936, Joseph Stalin stated that "within the Soviet Union there are about sixty nations, national groups, and nationalities. The Soviet state is a multinational state." Among the 15 republics were the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, which they were illegally annexed into the Soviet Union in 1940 and the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states was not recognized by a number of Western governments including the United States.
In the late 1980s, some of the republics sought sovereignty over their territories, citing Article 72 of the Constitution of the Soviet Union, USSR Constitution, which stated that any constituent republic was free to secede. On 7 April 1990, a law was passed allowing a republic to secede if more than two-thirds of its residents voted for secession in a referendum. Many held free elections, and the resulting legislatures soon passed bills that contradicted Soviet laws, in what became known as the War of Laws.
In 1989, the Russian SFSR—the largest constituent republic, with about half of the USSR's population—convened a new Congress of People's Deputies of Russia, Congress of People's Deputies and elected Boris Yeltsin its chairman. On 12 June 1990, the Congress Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, declared Russia's sovereignty over its territory and proceeded to pass legislation that attempted to supersede Soviet laws. Legal uncertainty continued through 1991 as constituent republics slowly gained ''de facto'' independence.
In 1991 Soviet Union referendum, a referendum on 17 March 1991, majorities in nine of the 15 republics voted to preserve the Union. The referendum gave Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev a minor boost, and in the summer of 1991, the New Union Treaty was designed and agreed upon by eight republics. The treaty would have turned the Soviet Union into a much looser federation, but its signing was interrupted by the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, August Coup—an attempted coup d'état against Gorbachev by hardline Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Communist Party members of the government and the KGB, who sought to reverse Gorbachev's reforms and reassert the central government's control over the republics. When the coup collapsed, Yeltsin—who had publicly opposed it—came out as a hero, while Gorbachev's power was effectively ended.
As a result, the balance of power tipped significantly toward the republics. In August 1991, Latvia and Estonia had regained their independence (following Lithuania's 1990 example), while the other twelve republics continued to discuss new, increasingly loose models for the Union.
On 8 December 1991, the presidents of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus signed the Belavezha Accords, which declared the Soviet Union dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in its place. Doubts remained about the authority of the Belavezha Accords to dissolve the Union, but on 21 December 1991, representatives of every Soviet republic except Georgian SSR, Georgia—including those that had signed the Belavezha Accords—signed the Alma-Ata Protocol, which confirmed the dissolution of the USSR and reiterated the establishment of the CIS. On 25 December 1991, Gorbachev yielded, resigning as the president of the USSR and declaring the office extinct. He turned the powers vested in the Soviet presidency over to Yeltsin, the president of Russia.
The following day, the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, Supreme Soviet, the highest governmental body of the Soviet Union, dissolved itself. Many organizations, such as the Soviet Army and Militsiya, police forces, remained in place in the early months of 1992, but were slowly phased out and either withdrawn from or absorbed by the newly independent states.
Yugoslavia
 The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, known until 3 October 1929 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia (to which the Kingdom of Montenegro had been annexed on 13 November 1918), and the Conference of Ambassadors gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 and abolished as a result of World War II. It was succeeded by Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement. When a communist government was established in 1946, the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1963, it was renamed again, becoming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, with Istria and Rijeka having been added after World War II.
The country consisted of six constituent "socialist republics" (SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia, and SR Serbia) and two "socialist autonomous provinces" (SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo, which became largely equal to other members of the federation after 1974).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars, which followed the secession of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, this last vestige separated into Serbia and Montenegro, but only to go further in 2008 after Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence but with limited recognition.
The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, known until 3 October 1929 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia (to which the Kingdom of Montenegro had been annexed on 13 November 1918), and the Conference of Ambassadors gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 and abolished as a result of World War II. It was succeeded by Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement. When a communist government was established in 1946, the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1963, it was renamed again, becoming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, with Istria and Rijeka having been added after World War II.
The country consisted of six constituent "socialist republics" (SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia, and SR Serbia) and two "socialist autonomous provinces" (SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo, which became largely equal to other members of the federation after 1974).
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars, which followed the secession of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, this last vestige separated into Serbia and Montenegro, but only to go further in 2008 after Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence but with limited recognition.
See also
* Multiculturalism * Multiracial * Nation state * Stateless nation * PolyethnicityReferences
{{Authority control Cultural politics Ethnicity in politics Multiculturalism Nation Supraorganizations Transnationalism World government it:Multicomunitarismo he:חברה רב-אתנית