Maritime fur trade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The maritime fur trade was a ship-based
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based 
 The most profitable furs were those of
The most profitable furs were those of
 The
The
 As traders sailed farther east, the voyages became longer and more expensive. Smaller enterprises were merged into larger ones. During the 1780s, Grigory Shelikhov began to stand out as one of the most important traders through the
As traders sailed farther east, the voyages became longer and more expensive. Smaller enterprises were merged into larger ones. During the 1780s, Grigory Shelikhov began to stand out as one of the most important traders through the
 The British entry into the maritime fur trade dates to 1778 and the third voyage of Captain James Cook. While sailing north to search for the fabled
The British entry into the maritime fur trade dates to 1778 and the third voyage of Captain James Cook. While sailing north to search for the fabled
, by Bruce Alden Cox. Chapter 13 "Women Traders in the Maritime Fur Trade", by Loraine Littlefield. Pages 173–174, 180–181 George Dixon and
, The Maritime Paintings of Gordon Miller and the first woman to sail around the world without deception. Only two women are known to have sailed around the world before Frances:
ABCBookWorld Barkley chose to sail under the flag of Austria to evade paying for EIC and SSC licences. During their stop in Hawaii, the Barkleys hired a
, Ilya Vinkovetsky; Library of Congress In 1818 the Russian government took control of the RAC from the merchants who held the charter. The explorer and naval officer Ferdinand Petrovich von Wrangel was the first president of the company during the government period. In 1867, the
 Colony Ross, known as
Colony Ross, known as
 As the North West trade developed it became riskier to depend solely upon acquiring sea otter furs through trade with the indigenous people of the coast. Diversification began in the first decade of the 19th century if not earlier, and increased over time. Maritime fur trading voyages were no longer solely about taking sea otter furs from the North West Coast to Canton. Other commodities and markets throughout the Pacific were added to the system.
As the North West trade developed it became riskier to depend solely upon acquiring sea otter furs through trade with the indigenous people of the coast. Diversification began in the first decade of the 19th century if not earlier, and increased over time. Maritime fur trading voyages were no longer solely about taking sea otter furs from the North West Coast to Canton. Other commodities and markets throughout the Pacific were added to the system.
, Northwest Power & Conservation Council The British and American maritime fur traders took their furs to the Chinese port of Guangzhou (Canton), where they worked within the established Canton system. Furs from Russian America were mostly sold to China via the Mongolian trading town of Kyakhta, which had been opened to Russian trade by the 1727 Treaty of Kyakhta (1727), Treaty of Kyakhta.
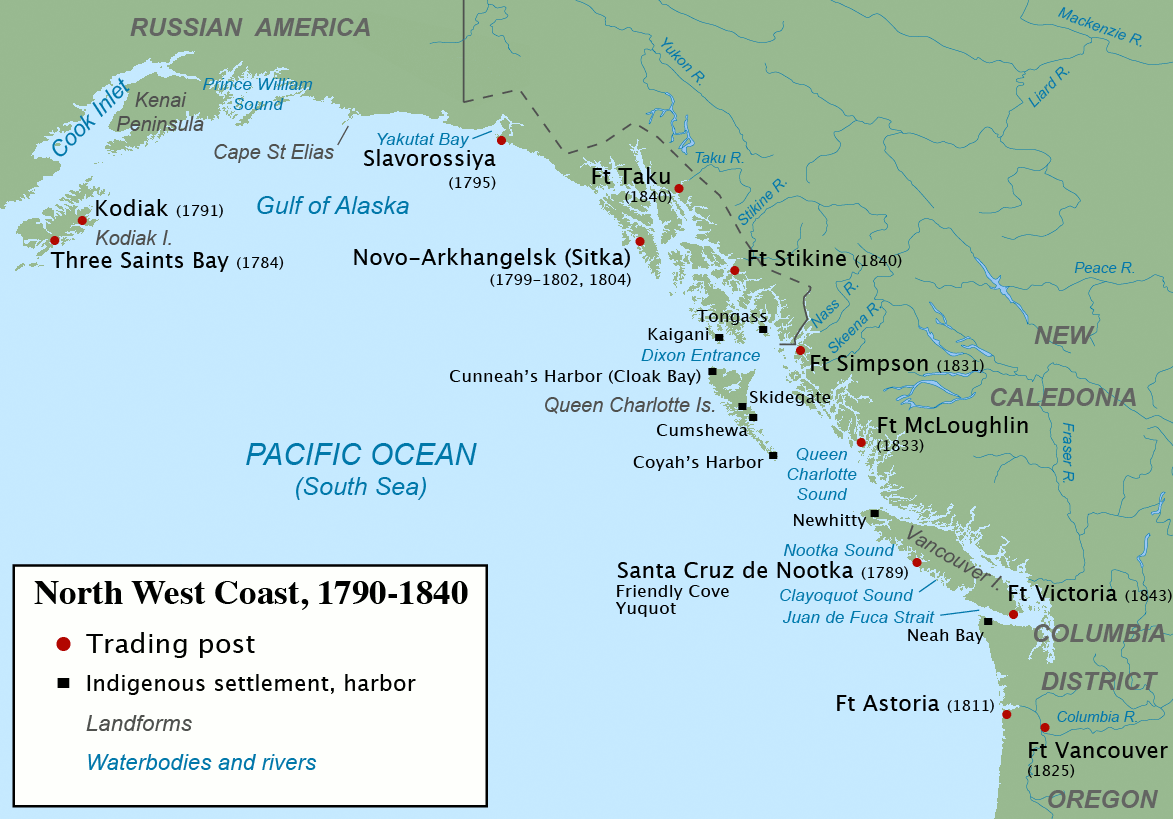
, Fort Vancouver: Cultural Landscape Report, Instrodution, Volume 2. National Park Service The struggle, which eventually reached the point of armed battles such as the 1816 Battle of Seven Oaks (1816), Battle of Seven Oaks, was mostly over control of Rupert's Land, east of the Continental Divide. Around the turn of the 19th century the NWC expanded its operations westward, across the Rocky Mountains into the mostly unexplored Pacific Northwest. By the 1810s the NWC had established new fur trading operations west of the Rockies, in New Caledonia (Canada), New Caledonia and the Columbia District. Starting in 1811 the American Pacific Fur Company (PFC) challenged the NWC in the Pacific Northwest, but during the War of 1812 the PFC, at risk of being captured by the British Navy, sold its entire operation to the NWC. The PFC had built Fort Astoria at the mouth of the Columbia River. Under the NWC it was renamed Fort George, and became the Columbia District's Pacific seaport. The NWC sought to establish a profitable beaver fur trade with China. Due to the East India Company's (EIC) control over British trading in Canton the NWC turned to American shipping companies. Starting in 1792 the NWC had beaver furs shipped to China by American firms. After the acquisition of Fort George (Astoria) in 1815 the NWC began to supply the Columbia District by sea through the Boston-based firm of Perkins and Company. After arriving at Fort George the American ship took a cargo of NWC beaver furs to Canton, exchanged them for China goods and conveyed them to Boston for sale. Even though Perkins and Company took 25% of the proceeds the arrangement was still about 50% more profitable than using British ships and selling furs in Canton through the EIC for Promissory note, bills payable on London and returning from China with no cargo. In 1821, after tensions between the NWC and HBC had erupted into violence the NWC was forced to merge into the HBC. As a result, the HBC acquired the Columbia District and its trade with China. At first the system of shipping furs via the American Perkins and Company was continued, but in 1822 the United States Customs Service imposed a heavy ''Ad valorem tax, ad valorem'' duty on the proceeds. The HBC stopped using American middlemen and instead tried selling furs through the EIC. In 1824 and 1825 the HBC sold 20,000 beaver and 7,000 land-otter skins in China through the EIC, but the arrangement did not prove advantageous for either firm. In the wake of the NWC's forced merger into the HBC, George Simpson reorganized operations in New Caledonia and the Columbia District, Columbia Department. His efforts and keen fiscal sense, combined with a resurgence of American traders on the coast after the To strengthen its coast trade the Hudson's Bay Company built a series of fortified trading posts, the first of which was Fort Langley National Historic Site, Fort Langley, established in 1827 on the Fraser River about from the river's mouth. The next was Fort Simpson (Columbia Department), Fort Simpson, founded in 1831 at the mouth of the Nass River, and moved in 1834 several miles to the present Lax Kw'alaams, British Columbia, Port Simpson. In 1833 Fort McLoughlin was established on an island in Milbanke Sound and Fort Nisqually was built at the southern end of Puget Sound. An overland trail linked Fort Nisqually and Fort Vancouver, so HBC vessels trading along the northern coast could unload furs and take on trade goods without having to navigate the Columbia River and its hazardous bar. Later coastal posts included Fort Stikine (1840), Fort Durham (1840), and Fort Victoria (British Columbia), Fort Victoria (1843).
To strengthen its coast trade the Hudson's Bay Company built a series of fortified trading posts, the first of which was Fort Langley National Historic Site, Fort Langley, established in 1827 on the Fraser River about from the river's mouth. The next was Fort Simpson (Columbia Department), Fort Simpson, founded in 1831 at the mouth of the Nass River, and moved in 1834 several miles to the present Lax Kw'alaams, British Columbia, Port Simpson. In 1833 Fort McLoughlin was established on an island in Milbanke Sound and Fort Nisqually was built at the southern end of Puget Sound. An overland trail linked Fort Nisqually and Fort Vancouver, so HBC vessels trading along the northern coast could unload furs and take on trade goods without having to navigate the Columbia River and its hazardous bar. Later coastal posts included Fort Stikine (1840), Fort Durham (1840), and Fort Victoria (British Columbia), Fort Victoria (1843).
 The maritime fur trade brought the natives of the Northwest Coast material prosperity, wealth, and technology. It enlarged and transformed intertribal relations, trade, and war, including the "coastalization" of inland natives. Many inland natives adopted potlatching and coastal descent systems.Gibson (1992), pp. 269–277 At first the trade caused a rise in the power of a few key chiefs such as
The maritime fur trade brought the natives of the Northwest Coast material prosperity, wealth, and technology. It enlarged and transformed intertribal relations, trade, and war, including the "coastalization" of inland natives. Many inland natives adopted potlatching and coastal descent systems.Gibson (1992), pp. 269–277 At first the trade caused a rise in the power of a few key chiefs such as
Contact and conflict: Indian-European relations in British Columbia, 1774–1890
by Robin Fisher; UBC Press, 1992
Fishing for Ivory Worms: A Review of Ethnographic and Historically Recorded ''Dentalium'' Source Locations
by Andrew John Barton
Russian Routes
Common-place {{Good article Fur trade Guangzhou History of foreign trade in China History of Macau History of the Pacific Northwest Hudson's Bay Company Maritime history of Canada Maritime history of the United Kingdom Maritime history of the United States Native American history of Alaska Oregon Country Pre-statehood history of Alaska Pre-statehood history of California Pre-statehood history of Hawaii Russian America
 The maritime fur trade was a ship-based
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the small ...
s and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese goods, which were then sold in Europe and the United States. The maritime fur trade was pioneered by Russians, working east from Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and wes ...
along the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a cha ...
to the southern coast of Alaska. British and Americans entered during the 1780s, focusing on what is now the coast of British Columbia
, settlement_type = Region of British Columbia
, image_skyline =
, nickname = "The Coast"
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 = British ...
. The trade boomed around the beginning of the 19th century. A long period of decline began in the 1810s. As the sea otter population was depleted, the maritime fur trade diversified and transformed, tapping new markets and commodities, while continuing to focus on the Northwest Coast and China. It lasted until the middle to late 19th century.
Russians controlled most of the coast of present-day Alaska during the entire era. The coast south of Alaska saw fierce competition between, and among, British and American trading vessels. The British were the first to operate in the southern sector, but were unable to compete against the Americans, who dominated from the 1790s to the 1830s. The British Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
entered the coast trade in the 1820s with the intention of driving the Americans away. This was accomplished by about 1840. In its late period, the maritime fur trade was largely conducted by the British Hudson's Bay Company and the Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
.
The term "maritime fur trade" was coined by historians to distinguish the coastal, ship-based fur trade from the continental, land-based fur trade of, for example, the North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
and American Fur Company. Historically, the maritime fur trade was not known by that name, rather it was usually called the "North West Coast trade" or "North West Trade". The term "North West" was rarely spelled as the single word "Northwest", as is common today.
The maritime fur trade brought the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
coast into a vast, new international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significant ...
network, centered on the north Pacific Ocean, global in scope, and based on capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
, but not, for the most part, on colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
. A triangular trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
network emerged linking the Pacific Northwest coast, China, the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
(only recently discovered by the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
), Britain, and the United States (especially New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
). The trade had a major effect on the indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest coast, especially the Aleut
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the U ...
, Sugpiaq
The Alutiiq people (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a sout ...
, Tlingit
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ),
, Haida, Nuu-chah-nulth
The Nuu-chah-nulth (; Nuučaan̓uł: ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifte ...
, and Chinook people
Chinookan peoples include several groups of Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest in the United States who speak the Chinookan languages. Since at least 4000 BCE Chinookan peoples have resided along the Lower and Middle Columbia River (W ...
s. A rapid increase of wealth occurred among the Northwest Coast natives, along with increased warfare, potlatching, slaving, and depopulation due to epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
disease. However, the indigenous culture was not overwhelmed by rapid change, but actually flourished. For instance, the importance of totem
A totem (from oj, ᑑᑌᒼ, italics=no or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system.
While ''the wo ...
s and traditional nobility crests increased, and the Chinook Jargon, which remains a distinctive aspect of Pacific Northwest culture, was developed during this era. Native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawaii ...
society was similarly affected by the sudden influx of Western wealth and technology, as well as epidemic diseases. The trade's effect on China and Europe was minimal, but for New England, the maritime fur trade and the significant profits it made helped revitalize the region, contributing to its transformation from an agrarian to an industrial society. The wealth generated by the maritime fur trade was invested in industrial development, especially textile manufacturing
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
.

 The most profitable furs were those of
The most profitable furs were those of sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the small ...
s, especially the northern sea otter, ''Enhydra lutris kenyoni'', which inhabited the coastal waters between the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
in the south to the Aleutian Islands in the north. Sea otters possess a thicker fur than any other mammal, and the sea otter's habit of grooming their coat prevents molting. The reason for their exploitation was due to this 'dark hickand silver tipped fur'. The popularity and demand in fashion of sea otter pelts in China was one of the reasons why it was hunted to the point of disappearance. These mammals of the Pacific are currently 'listed as Threatened under the Canadian Species at Risk Act'. Sea otter distribution extends from the north of Japan all the way to the vicinity of Cedros Island, Mexico. The species stayed approximately within the arc of the Northern Pacific until the pressure of the maritime trade forced them to move north. The start of their decline with the first Russian expeditions in this region. Aleut hunters were the providers of the skins to the Russians; the former became 'the main purveyor of prime otter skins to Russian traders and American adventurers'. Before the exploitation of these mammals, their population ranged from 150,000 to 300,000. Sea otters are 'slow breeders, only one sometimes two pups rebeing born at a time', which does not help the population when being pursued.
The trade and subsequent killings of beavers were devastating for the local beaver population. The natural ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s that came to rely on the beavers for dams
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
, water and other vital needs were also devastated leading to ecological destruction, environmental change, and drought in certain areas. Following this beaver populations in North America would take centuries to recover in some areas, while others would never recover. The killings would have catastrophic effects for pacific western species including otters
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes wea ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, and bears
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
leading to the water, soil, ecosystems and resources to be devastated by the trade.
Origins
 The
The Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
was one of the last significant nonpolar regions in the world to be explored by Europeans. Centuries of reconnaissance and conquest had brought the rest of North America within the claims of imperial powers. During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, a number of empires and commercial systems converged upon the Northwest Coast, by sea as well as by land across the continent. The Russian and Spanish empires were extended into the region simultaneously, from opposite directions. Russian fur companies expanded into North America along the Aleutian Islands, reaching the Fox Islands and the Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The ...
in the early 1760s. Kodiak Island
Kodiak Island ( Alutiiq: ''Qikertaq''), is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second la ...
was discovered in 1763 by Stepan Glotov. In 1768, an expedition was carried out by the Russian Navy, under Pyotr Krenitsyn
Pyotr Kuzmich Krenitsyn (russian: Пётр Кузьмич Креницын) (1728 – July 4, 1770), spelt "Krenitzin" in the United States, was a Russian explorer and Captain/Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy. Following Vitus Bering's 1741 ...
and Mikhail Levashev
Mikhail Dmitrievich Levashov (russian: Михаи́л Дми́триевич Левашо́в; c. 1738–1774-76) was a Russian explorer and Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy. After Vitus Bering's 1741 tragic venture he was, together with Pe ...
. Two ships sailed from Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and wes ...
to the Alaska Peninsula for the purpose of assessing the existing Russian activity and the possibilities of future development.Haycox, pp. 58–62 Reports about the voyage, meant to be kept secret, spread through Europe and caused alarm in Spain. The Spanish government, already concerned about Russian activity in Alaska, decided to colonize Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
and sent exploratory voyages to Alaska to assess the threat and strengthen Spanish claims of sovereignty on coast north of Mexico.
The province of Alta California was established by José de Gálvez in 1769, just as the Krenitsyn-Levashev expedition was concluding. Five separate expeditions were dispatched to Alta California in 1769. By 1782, presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th century, 16th and 18th century, 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Captaincy Genera ...
s had been established at San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
, Monterey
Monterey (; es, Monterrey; Ohlone: ) is a city located in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, it functioned as the capital of Alta California under bot ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
and Santa Barbara, linked by a series of mission stations along the coast. Spanish exploration voyages to the far north were launched in 1774, 1775, and 1779. In 1784, the center of Russian activity shifted east to Kodiak Island and hunting operations were extended into Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet ( tfn, Tikahtnu; Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its so ...
. The two empires seemed destined to clash, but before direct Russian-Spanish contact was made new powers appeared on the Northwest Coast—Britain and the United States. When the clash came, at Nootka Sound in 1789, it was not between Spain and Russia but between Spain and Britain. The British first reached the region by sea in 1778, during James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
's third voyage, and by land in 1793, when Alexander Mackenzie's transcontinental explorations reached the Pacific. The first British maritime fur trader, James Hanna
James Hanna (born July 14, 1989) is a former American football tight end in the National Football League (NFL) for the Dallas Cowboys. He was drafted in the sixth round (186th overall) of the 2012 NFL Draft. He played college football at the Un ...
, arrived on the Northwest Coast in 1785. The first American traders, John Kendrick and Robert Gray, arrived by sea in 1788. The Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gro ...
arrived overland in 1805.
The early maritime fur traders were explorers, as well as traders. The Northwest Coast is very complex — a "labyrinth of waters", according to George Simpson— with thousands of islands, numerous strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
s and fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Ice ...
s, and a mountainous, rocky, and often very steep shoreline. Navigational hazards included persistent rain, high winds, thick fogs, strong current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
s, and tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s, and hidden rocks. Wind patterns were often contrary, variable, and baffling, especially within the coastal straits and archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
es, which makes sailing dangerous. Early explorations before the maritime fur trade era—by Juan Pérez, Bruno de Heceta
Bruno de Heceta (Hezeta) y Dudagoitia (1743–1807) was a Spanish Basque explorer of the Pacific Northwest. Born in Bilbao of an old Basque family, he was sent by the Viceroy of New Spain, Antonio María Bucareli y Ursúa, to explore the area nort ...
, Bogeda y Quadra, and James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
—produced only rough surveys of the coast's general features. Detailed surveys were undertaken in only a few relatively small areas, such as Nootka Sound
, image = Morning on Nootka Sound.jpg
, image_size = 250px
, alt =
, caption = Clouds over Nootka Sound
, image_bathymetry =
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Map of Nootka So ...
, Bucareli Bay Bucareli Bay is a bay in the Alexander Archipelago, in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located off the western coast of Prince of Wales Island, between Baker Island and Suemez Island. To the east it connects to various wat ...
, and Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet ( tfn, Tikahtnu; Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its so ...
. Russian exploration before 1785 had produced mainly rough surveys, largely restricted to the Aleutian Islands and mainland Alaska west of Cape Saint Elias
Cape Saint Elias is a cape in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located at the southwest end of Kayak Island, 104 km (65 mi) southeast of Cordova, at . It is commonly believed that Mount Saint Elias, the second highest mountain in the Un ...
. British and American maritime fur traders began visiting the Northwest Coast in 1785, at which time it was mostly unexplored. Although noncommercial exploration voyages continued, especially by the Spanish Navy, the maritime fur traders made a number of significant discoveries. Notable examples include the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, Clayoquot Sound
, image = Clayoquot Sound - Near Tofino - Vancouver Island BC - Canada - 08.jpg
, image_size = 260px
, alt =
, caption =
, image_bathymetry = Vancouver clayoquot sound de.png
, alt_bathyme ...
, and Barkley Sound
, image = Fishing boat in the Broken Group Islands.jpg
, image_size = 260px
, alt =
, caption = Barkley Sound
, image_bathymetry =
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, locat ...
, all found by Charles William Barkley
Charles William Barkley (1759 – 16 May 1832) was a ship captain and maritime fur trader. He was born in Hertford, England, son of Charles Barkley.Queen Charlotte Strait
, image = Canadian pilot, near Port Hardy BC.jpg
, alt =
, caption = A pilot boat plies Queen Charlotte Strait near Port Hardy
, image_bathymetry = Locmap-QCS-Hecate-Dixon.png
, alt_bathymetry = ...
by James Strange, Fitz Hugh Sound
Fitz Hugh Sound, sometimes spelled Fitzhugh Sound, is a sound on the British Columbia Coast of Canada, located between Calvert Island and the mainland.
Etymology
Fitz Hugh Sound was given its name in 1785 by James Hanna, the first non-indigenous ...
by James Hanna
James Hanna (born July 14, 1989) is a former American football tight end in the National Football League (NFL) for the Dallas Cowboys. He was drafted in the sixth round (186th overall) of the 2012 NFL Draft. He played college football at the Un ...
, Grays Harbor Grays Harbor is an estuarine bay located north of the mouth of the Columbia River, on the southwest Pacific coast of Washington state, in the United States of America. It is a ria, which formed at the end of the last ice age, when sea levels flood ...
and the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
by Robert Gray. George Dixon explored the Dixon Entrance
The Dixon Entrance (french: Entrée Dixon) is a strait about long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part o ...
and was the first to realize that the Queen Charlotte Islands
Haida Gwaii (; hai, X̱aaydag̱a Gwaay.yaay / , literally "Islands of the Haida people") is an archipelago located between off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Heca ...
were not part of the mainland.
Russia
Russian maritime fur trading in the northern Pacific began after the exploration voyages ofVitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering (baptised 5 August 1681 – 19 December 1741),All dates are here given in the Julian calendar, which was in use throughout Russia at the time. also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in ...
and Aleksei Chirikov
Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov (russian: Алексе́й Ильи́ч Чи́риков; 1703 – November 14, 1748) was a Russian navigator and captain who, along with Vitus Bering, was the first Russian to reach the northwest coast of North America. ...
in 1741 and 1742. Their voyages demonstrated that Asia and North America were not connected but that sea voyages were feasible, and that the region was rich in furs. Private fur traders, mostly ''promyshlenniki
The ''promyshlenniki'' (russian: промышленники, singular form: russian: промышленник, translit=promyshlennik), were Russian and indigenous Siberian artel- or self-employed workers drawn largely from the state serf and ...
'', launched fur trading expeditions from Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and wes ...
, at first focusing on nearby islands such as the Commander Islands
The Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands (russian: Командо́рские острова́, ''Komandorskiye ostrova'') are a series of treeless, sparsely populated Russian islands in the Bering Sea located about ea ...
. Unlike fur trading ventures in Siberia, these maritime expeditions required more capital than most ''promyshlenniki'' could obtain. Merchants from cities such as Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and mn, Эрхүү, ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is ...
, Tobolsk
Tobolsk (russian: Тобо́льск) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1590, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, an ...
, and others in European Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
, became the principal investors.
An early trader, Emilian Basov, traded at Bering Island
Bering Island (russian: о́стров Бе́ринга, ''ostrov Beringa'') is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea.
Description
At long by wide, it is the largest and westernmost of the Commander Islands, with an area of . ...
in 1743, collecting a large number of sea otter, fur seal
Fur seals are any of nine species of pinnipeds belonging to the subfamily Arctocephalinae in the family '' Otariidae''. They are much more closely related to sea lions than true seals, and share with them external ears (pinnae), relatively l ...
, and blue Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in ...
furs. Basov made four trips to Bering Island and nearby Medny Island and made a fortune, inspiring many other traders. From 1743 to the founding of the Russian-American Company in 1799, over 100 private fur-trading and hunting voyages sailed from Kamchatka to North America. In total, these voyages garnered over eight million silver rubles. During the early part of this era, the ships would typically stop at the Commander Islands
The Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands (russian: Командо́рские острова́, ''Komandorskiye ostrova'') are a series of treeless, sparsely populated Russian islands in the Bering Sea located about ea ...
to slaughter and preserve the meat of Steller's sea cows, a defenseless sea mammal whose range was limited to those islands. They were hunted not only for food, but also for their skins, used to make boats, and their subcutaneous fat, used for oil lamp
An oil lamp is a lamp used to produce light continuously for a period of time using an oil-based fuel source. The use of oil lamps began thousands of years ago and continues to this day, although their use is less common in modern times. Th ...
s. By 1768, Steller's sea cow was extinct. As furs were depleted on nearby islands, Russian traders sailed farther east along the Aleutian chain
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large vo ...
. By the 1760s, they were regularly sailing to Kodiak Island. Notable Russian traders in the early years of the trade include Nikifor Trapeznikov (who financed and participated in 10 voyages between 1743 and 1768), Maksimovich Solov'ev, Stepan Glotov, and Grigory Shelikhov
Grigory Ivanovich Shelikhov (Григо́рий Ива́нович Ше́лихов in Russian) (1747, Rylsk, Belgorod Governorate – July 20, 1795 (July 31, 1795 New Style)) was a Russian seafarer, merchant, and fur trader who perpetrated t ...
.
 As traders sailed farther east, the voyages became longer and more expensive. Smaller enterprises were merged into larger ones. During the 1780s, Grigory Shelikhov began to stand out as one of the most important traders through the
As traders sailed farther east, the voyages became longer and more expensive. Smaller enterprises were merged into larger ones. During the 1780s, Grigory Shelikhov began to stand out as one of the most important traders through the Shelikhov-Golikov Company
The Shelikhov-Golikov Company (SGC) was a Russian fur trading venture, founded by Irkutsk entrepreneurs Grigory Shelikhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov in 1783. Formed in Eastern Siberia during the 1780s along with several competing companies, ...
. In 1784, Shelikhov founded the first permanent Russian settlement in North America, at Three Saints Bay
Three Saints Bay (russian: Бухта Трёх Святителей, r ''Bukhta Tryokh Svyatitelyej'') is a 9 Mile (14 Kilometer)-long inlet on the southeast side of Kodiak Island, Alaska, north of Sitkalidak Strait. It is southwest of Ko ...
on Kodiak Island. Shelikhov envisioned a continual extension of the Russian maritime fur trade, with trading posts being set up farther and farther along the coast all the way to California. He sought exclusive control of the trade, and in 1788 Empress Catherine II decided to grant his company a monopoly only over the area it already occupied. Other traders were free to compete elsewhere. Catherine's decision was issued as the imperial ''ukase
In Imperial Russia, a ukase () or ukaz (russian: указ ) was a proclamation of the tsar, government, or a religious leader ( patriarch) that had the force of law. " Edict" and "decree" are adequate translations using the terminology and concep ...
'' (proclamation) of 28 September 1788.
By the time of Catherine's ''ukase'' of 1788, just as other nations were entering the maritime fur trade, the Russians had spent over 40 years establishing and expanding their maritime operations in North America. A number of colonies were being established over a large region stretching from the Aleutian Islands to Cook Inlet and Prince William Sound
Prince William Sound ( Sugpiaq: ''Suungaaciq'') is a sound of the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the T ...
. Many ships sailed from Kamchatka to Alaska each year. The Russians not only had an early start, but they also controlled the habitats of the most valuable sea otters. The Kurilian, Kamchatkan, and Aleutian sea otters' fur was thicker, glossier, and blacker than those on the Northwest Coast and California. The four grades of fur were based on color, texture, and thickness. The most prized furs were those of Kurilian and Kamchatkan sea otters, Aleutian furs were second-grade, those of the Northwest Coast third, and the poorest grade was those of Californian sea otters. Russia also controlled the sources of sable furs, the most valuable fur-bearing land mammal.
The Russian system differed from the British and American systems in its relationship with indigenous peoples. Using the same method they had used in Siberia, the Russians employed or enserfed Aleut and Alutiiq
The Alutiiq people (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a so ...
people, the latter being a subgroup of the Yupik Yupik may refer to:
* Yupik peoples, a group of indigenous peoples of Alaska and the Russian Far East
* Yupik languages, a group of Eskimo-Aleut languages
Yupꞌik (with the apostrophe) may refer to:
* Yup'ik people
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg ...
Eskimo people.Gibson (1976), pp. 32–33 The Aleut and Alutiiq people were expert sea otter hunters, noted for their use of kayaks and baidarka
The baidarka or Aleutian kayak (Aleut: iqyax) is a watercraft consisting of soft skin (artificial or natural) over a rigid space frame. Its initial design was created by the native Aleut (or Unangan) people of the Aleutian Islands. The Aleut pe ...
s. Russian ships were mainly used for transporting and assisting native hunting parties. This differed from the British and American system, where the natives hunted sea otters and prepared the furs on their own, and were essentially independent agents of the fur trade. The Russians did not trade freely with the native Alaskans; rather, they imposed a fur tribute known as ''yasak
''Yasak'' or ''yasaq'', sometimes ''iasak'', (russian: ясак; akin to Yassa) is a Turkic word for "tribute" that was used in Imperial Russia to designate fur tribute exacted from the indigenous peoples of Siberia.
Origin
The origins of yasa ...
''. The ''yasak'' system, which was widely used in Siberia, essentially enslaved the natives. In 1788, it was banned in Russian America, only to be replaced by compulsory labor.
Britain
 The British entry into the maritime fur trade dates to 1778 and the third voyage of Captain James Cook. While sailing north to search for the fabled
The British entry into the maritime fur trade dates to 1778 and the third voyage of Captain James Cook. While sailing north to search for the fabled Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
, Cook discovered the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
. On the Northwest Coast, he spent a month in Nootka Sound
, image = Morning on Nootka Sound.jpg
, image_size = 250px
, alt =
, caption = Clouds over Nootka Sound
, image_bathymetry =
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Map of Nootka So ...
, during which he and his crew traded with the Nuu-chah-nulth from the village of Yuquot
Yuquot , also known as Friendly Cove, is a small settlement of around six people—the Williams family of the Mowachaht band—plus two full-time lighthouse keepers, located on Nootka Island in Nootka Sound, just west of Vancouver Island, British C ...
. They ended up with over 300 furs, mostly sea otter, but thought them of no great value. Later, after Cook had been killed in Hawaii, the expedition visited Canton and were surprised by how much money the Chinese were willing to pay for the furs. A profit of 1,800% was made. James King, one of the commanders after Cook's death, wrote, "the advantages that might be derived from a voyage to that part of the American coast, undertaken with commercial views, appear to me of a degree of importance sufficient to call for the attention of the public." The crews of the two ships were so eager to return to Nootka Sound and acquire more furs, they were "not far short of mutiny". Nevertheless, they sailed for England, arriving there in October 1780.Pethick (1976), pp. 72–76 Accounts of Cook's voyage and the sea otter trade were published in the 1780s, triggering a rush of entrepreneurial voyages to the Northwest Coast.
British interest in the maritime fur trade peaked between 1785 and 1794, then declined as the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
diminished Britain's available manpower and investment capital. The country also concentrated its foreign trade activities in India. British maritime fur traders were hindered by the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
(EIC) and South Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America, and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
(SSC). Although the SSC was moribund by the late 18th century, it had been granted the exclusive right to British trade on the entire western coast of the Americas from Cape Horn to Bering Strait and for 300 leagues (around ) out into the Pacific Ocean. This, coupled with the EIC monopoly on British trade in China, meant sea otter skins were procurable only in the preserve of one monopoly and disposable only in that of the other. To operate legally, British maritime fur traders had to obtain licenses from both companies, which was difficult and expensive. Some traders obtained a license from the EIC only, figuring the SSC was unable to enforce its monopoly. Others obtained only the SSC license and took their furs to England, where they were trans-shipped to China. Some traders tried to evade the licenses by sailing their ships under foreign flags.Gibson (1992), pp. 25–28 The EIC's primary focus in China was the tea trade, with never much interest within the company for the maritime fur trade. The EIC usually allowed British vessels to import furs into Canton, but required the furs to be sold via EIC agents, and the company took a percentage of the returns. Worse, the EIC did not allow the British fur traders to export Chinese goods to Great Britain. Thus, the last and most profitable leg of the maritime fur trade system—carrying Chinese goods to Europe and America—was denied to British traders.
The first trading vessel dispatched solely for the purpose of the fur trade was the British ''Sea Otter'' commanded by James Hanna
James Hanna (born July 14, 1989) is a former American football tight end in the National Football League (NFL) for the Dallas Cowboys. He was drafted in the sixth round (186th overall) of the 2012 NFL Draft. He played college football at the Un ...
in 1785. In his brief visit to the coast, he obtained 560 pelts, which fetched a profit of $20,000 in Canton. The promise of such profits encouraged other traders.''Native People, Native Lands: Canadian Indians, Inuit and Métis'', by Bruce Alden Cox. Chapter 13 "Women Traders in the Maritime Fur Trade", by Loraine Littlefield. Pages 173–174, 180–181 George Dixon and
Nathaniel Portlock
Nathaniel Portlock (c. 1748 – 12 September 1817) was a British ship's captain, maritime fur trader, and author.
He entered the Royal Navy in 1772 as an able seaman, serving in . In 1776 he joined as master's mate and served on the third Pac ...
, former members of Cook's crew, became partners in the King George's Sound Company
The King George's Sound Company, also known as Richard Cadman Etches and Company after its "prime mover and principal investor", was an English company formed in 1785 to engage in the maritime fur trade on the northwest coast of North America. Th ...
, formed in 1785 for the purpose of developing the maritime fur trade. They sailed from England on the '' King George'' and ''Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms ...
'' and spent 1786 and 1787 exploring and trading on the North West Coast. They spent the winters in Hawaii, where they were among the first visitors after Cook. Charles William Barkley
Charles William Barkley (1759 – 16 May 1832) was a ship captain and maritime fur trader. He was born in Hertford, England, son of Charles Barkley.Imperial Eagle
The eagle is used in heraldry as a charge, as a supporter, and as a crest. Heraldic eagles can be found throughout world history like in the Achaemenid Empire or in the present Republic of Indonesia. The European post-classical symbolism of ...
'' from England to the North West Coast via Hawaii, 1786–1788. He was accompanied by his wife, Frances Barkley, who became the first European woman to visit the Hawaiian IslandsCapt. Barkley in IMPERIAL EAGLE in Barkley Sound, The Maritime Paintings of Gordon Miller and the first woman to sail around the world without deception. Only two women are known to have sailed around the world before Frances:
Jeanne Baré
Jeanne Baret (; 27 July 1740 – 5 August 1807) was a member of Louis Antoine de Bougainville's expedition on the ships '' La Boudeuse'' and '' Étoile'' in 1766–1769. Baret is recognized as the first woman to have completed a voyage of c ...
, disguised as a man, and Rose de Freycinet, wife of Louis de Freycinet
Louis Claude de Saulces de Freycinet (7 August 1779 – 18 August 1841) was a French Navy officer. He circumnavigated the earth, and in 1811 published the first map to show a full outline of the coastline of Australia.
Biography
He was born at ...
, as a stowaway.BARKLEY, FrancesABCBookWorld Barkley chose to sail under the flag of Austria to evade paying for EIC and SSC licences. During their stop in Hawaii, the Barkleys hired a
native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawaii ...
named Winée as a maidservant. Winée was the first native Hawaiian to visit the Pacific Northwest—the first of many Kanakas
Kanakas were workers (a mix of voluntary and involuntary) from various Pacific Islands employed in British colonies, such as British Columbia (Canada), Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Queensland (Australia) in the 19t ...
. Barkley explored the coast south of Nootka Sound, discovering the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
in the process. He was the first trader to visit Neah Bay
Neah Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) on the Makah Reservation in Clallam County, Washington, United States. The population was 865 at the 2010 census. It is across the Canada–US border from British Columbia. Originally called "Scarboro ...
, a Makah
The Makah (; Klallam: ''màq̓áʔa'')Renker, Ann M., and Gunther, Erna (1990). "Makah". In "Northwest Coast", ed. Wayne Suttles. Vol. 7 of '' Handbook of North American Indians'', ed. William C. Sturtevant. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Instit ...
settlement that later became an important port of call for maritime fur traders.

John Meares
John Meares (c. 1756 – 1809) was an English navigator, explorer, and maritime fur trader, best known for his role in the Nootka Crisis, which brought Britain and Spain to the brink of war.
Career
Meares' father was Charles Meares, "formerly an ...
, who had also served under Cook, sailed to the North West Coast in 1786. He spent the winter in Prince William Sound
Prince William Sound ( Sugpiaq: ''Suungaaciq'') is a sound of the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the T ...
, his ship trapped by ice and his men dying of scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding ...
. He was rescued by the timely arrival of Dixon and Portlock. Meares organized a second expedition of two ships, the ''Felice Adventurero'' and ''Iphigenia Nubiana''. Meares was captain of the ''Felice'' and William Douglas was captain of the ''Iphigenia''. Meares decided not to license his ships with the EIC, instead trying to conceal the illegal activity by using the flag of Portugal. They arrived at Nootka Sound in May 1788. Meares later claimed that Chief Maquinna
Maquinna (also transliterated Muquinna, Macuina, Maquilla) was the chief of the Nuu-chah-nulth people of Nootka Sound, during the heyday of the maritime fur trade in the 1780s and 1790s on the Pacific Northwest Coast. The name means "possessor of ...
sold him some land and on it Meares had a building erected. These claims later became a point of dispute during the Nootka Crisis
The Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between the Nuu-chah-nulth Nation, the Spanish Empire, the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the fledgling United States of America triggered b ...
. Spain, which sought control of Nootka Sound, rejected both claims; the true facts of the matter have never been fully established. There is no doubt, however, that Meares had the sloop ''North West America
''North West America'' was a British merchant ship that sailed on maritime fur trading ventures in the late 1780s. It was the first non-indigenous vessel built in the Pacific Northwest. In 1789 it was captured at Nootka Sound by Esteban José ...
'' built in Nootka Sound, the first nonindigenous vessel built in the Pacific Northwest.
Meares and others organized another expedition the following year. A number of vessels sailed to Nootka Sound, including ''Argonaut'' under James Colnett
James Colnett (1753 – 1 September 1806) was an officer of the British Royal Navy, an explorer, and a maritime fur trader. He served under James Cook during Cook's second voyage of exploration. Later he led two private trading expeditions that ...
, , under Thomas Hudson, and ''Iphigenia Nubiana'' and ''North West America''. Colnett intended to establish a permanent fur-trading post at Nootka Sound. However, Spain had also decided to permanently occupy Nootka Sound and assert sovereignty on the North West Coast. The decision was mostly due to Russian activity in Alaska and Russia's threat to occupy Nootka Sound themselves. Spanish naval officer Esteban José Martínez Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend t ...
arrived at Nootka in May 1789 and built Fort San Miguel
Fort San Miguel was a Spanish fortification at Yuquot (formerly Friendly Cove) on Nootka Island, just west of north-central Vancouver Island. It protected the Spanish settlement, called Santa Cruz de Nuca, the first colony in British Columbia ...
. When the ''Argonaut'' arrived, a dispute arose between Colnett and Martínez, leading to the seizure of several British ships and the arrest of their crews. This incident led to the Nootka Crisis, an international crisis
The term international crisis is a widespread term without a single common definition. To some, it involves "a sequence of interactions between the governments of two or more sovereign states in severe conflict, short of actual war, but involving ...
between Britain and Spain. War was averted with the first Nootka Convention
The Nootka Sound Conventions were a series of three agreements between the Kingdom of Spain and the Kingdom of Great Britain, signed in the 1790s, which averted a war between the two countries over overlapping claims to portions of the Pacific No ...
of 1790.
United States
American traders were largely influenced by an unauthorized report published byJohn Ledyard
John Ledyard (November 1751 – 10 January 1789) was an American explorer and adventurer.
Early life
Ledyard was born in Groton, Connecticut, in November 1751. He was the first child of Abigail Youngs Ledyard and Capt. John Ledyard Jr, son o ...
in Hartford, Connecticut, in 1783. By the 1790s, American traders were outcompeting the British and soon came to dominate the maritime fur trade south of Russian America. The opening of the trade came at a good time for New England's merchants. It provided a way to escape the depression that had followed the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. It presented new trading opportunities that more than made up for the closure of British home and colonial ports to US imports. First Nations along the coast referred to American traders in the Chinook jargon as Boston or Boston-men – after their main port in New England.Thompson, Laurence C. & M. Dale Kinkade "Languages" in Handbook of the North American Indian: Volume 7 Northwest Coast. p.51
One of the first and most notable American maritime fur traders was Robert Gray. Gray made two trading voyages, the first from 1787 to 1790 and the second from 1790 to 1793. The first voyage was conducted with John Kendrick and the vessels ''Columbia Rediviva
''Columbia Rediviva'' (commonly known as ''Columbia'') was a privately owned American ship under the command, first, of John Kendrick, and later Captain Robert Gray, best known for going to the Pacific Northwest for the maritime fur trade. ...
'' and ''Lady Washington
''Lady Washington'' is a ship name shared by at least four different 80-100 ton-class Sloop-of-war and merchant sailing vessels during two different time periods. The original sailed during the American Revolutionary War and harassed British shi ...
''. After the 1789 fur trading season was over, Gray sailed the ''Columbia'' to China via Hawaii, then to Boston via the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is t ...
. The arrival of the ''Columbia'' at Boston was celebrated for being the first American circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical object, astronomical body (e.g. a planet or natural satellite, moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circ ...
of the world. However, the venture was not a commercial success. The ship's owners financed a second attempt and Gray sailed the ''Columbia'' from Boston only six weeks after arriving. Gray's second voyage was notable in several ways. After spending the summer trading on the Northwest Coast, Gray wintered on the coast. In Clayoquot Sound
, image = Clayoquot Sound - Near Tofino - Vancouver Island BC - Canada - 08.jpg
, image_size = 260px
, alt =
, caption =
, image_bathymetry = Vancouver clayoquot sound de.png
, alt_bathyme ...
, Gray's crew built a house, dubbed Fort Defiance, and had the sloop built, the first American vessel built on the Northwest Coast. It was launched in March 1792 under the command of Robert Haswell
Robert Haswell (November 24, 1768 – 1801?) was an early American maritime fur trader to the Pacific Northwest of North America. His journals of these voyages are the main records of Captain Robert Gray's circumnavigation of the globe. Later du ...
. During the 1792 trading season, Gray concentrated on the southern part of the North West Coast, including the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
. Although the mouth of the river had been spotted by the Spanish explorer Bruno de Heceta
Bruno de Heceta (Hezeta) y Dudagoitia (1743–1807) was a Spanish Basque explorer of the Pacific Northwest. Born in Bilbao of an old Basque family, he was sent by the Viceroy of New Spain, Antonio María Bucareli y Ursúa, to explore the area nort ...
in 1775, no other explorer or fur trader had been able to find it and enter the river. Gray was the first to do so. He named the river after his ship. The event was later used by the United States in support of their claims to the Pacific Northwest.
Other notable American maritime fur traders include William F. Sturgis,Gibson (1992), pp. 291-296 Joseph Ingraham
Joseph Ingraham (1762–1800) was an American sailor and maritime fur trader who discovered several islands of the Marquesas Islands while on his way to trade along the west coast of North America. He was also a prisoner in the American Revolutio ...
, Simon Metcalfe
Simon Metcalfe (also spelled Metcalf) (c. 1741 – 1794) was a British-born American surveyor and one of the first American maritime fur traders to visit the Pacific Northwest coast.
As early visitors to the Hawaiian Islands in 1789, Metcalfe and ...
and his son Thomas Humphrey Metcalfe
Thomas Humphrey Metcalfe (also spelled Metcalf) ( – March 16, 1790) was an American maritime fur trader who worked with his father, Simon Metcalfe. After being separated from his father in a storm, Thomas sailed a small schooner with a crew of ...
, Daniel Cross, John Boit
John Boit Jr (15 October 1774 – 8 March 1829) was one of the first Americans involved in the maritime fur trade. He sailed as fifth mate under Captain Robert Gray on the second voyage of the ''Columbia Rediviva'', 1790–1793. During the voyage ...
, and James Magee, among many others. One of the most successful American firms involved in the Northwest Trade was Perkins and Company.Gibson (1992), pp. 249–250
Boom years
American ascendancy
The maritime fur trade was dominated by American traders from the 1790s to the 1820s. Between 1788 and 1826, American merchant ships made at least 127 voyages between the United States and China, via the Northwest Coast. The returns were lucrative. During the late 1810s, the return on investment ranged from about 300% to 500%. Even higher profits were common in the first decade of the 19th century. Returns of 2,200% or higher were common, although when taking into account the cost of buying and outfitting vessels, the 2,200% return would be closer to 525%. The trade's boom years ended around 1810, after which a long decline was marked by increasing economic diversification. By 1810, the supply of sea otter pelts had fallen due to overhunting. American trade declined during theWar of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
, but after 1815, Americans were able to resume and expand the maritime fur trade, and continued to dominate.
Russian expansion
The Russian entry to the Northwest Coast, beyond Prince William Sound, was slow because of a shortage of ships and sailors.Yakutat Bay
Yakutat Bay ( Lingít: ''Yaakwdáat G̱eeyí'') is a 29-km-wide (18 mi) bay in the U.S. state of Alaska, extending southwest from Disenchantment Bay to the Gulf of Alaska. "Yakutat" is a Tlingit name reported as "Jacootat" and "Yacootat" ...
was reached in 1794 and the settlement of Slavorossiya, originally intended to be the colonial capital, was built there in 1795. Reconnaissance of the coast as far as the Queen Charlotte Islands was carried out by James Shields, a British employee of the Golikov-Shelikhov Company. In 1795, Alexandr Baranov sailed into Sitka Sound
Sitka Sound is a body of water near the city of Sitka, Alaska. It is bordered by Baranof Island to the south and the northeast, by Kruzof Island to the northwest and by the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. During the early 19th century it was a ...
, claiming it for Russia. Hunting parties arrived in the following years. By 1800, three-quarters of the Russian-American Company's sea otter skins came from the Sitka Sound area, amounting to several thousand per year. Sitka Sound was also where serious competition between the Russians, British, and Americans first arose.Gibson (1992), pp. 13–14
In July 1799, Baranov returned to Sitka Sound on the brig ''Oryol'' and established the settlement of Arkhangelsk, also known as Fort Archangel Gabriel. In June 1802, Tlingit warriors attacked the settlement and killed or captured most of the 150 Russians and Aleuts living there. Baranov led an armed expedition to retake Sitka by force in June 1804. The Russian warship ''Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it ...
'' joined Baranov at Sitka. A new Russian fort was established while the Tlingit prepared to defend themselves with a well-armed fort of their own. Tension rapidly escalated into skirmishes and negotiations broke down. In early October, the Russians attacked the Tlingit fort with cannon from the ''Neva'' and from a land party. The Tlingit responded with powerful gun and cannon fire of their own. The Battle of Sitka
The Battle of Sitka (russian: Сражение при Ситке; 1804) was the last major armed conflict between Russians and Alaska Natives, and was initiated in response to the destruction of a Russian trading post two years before. The primary ...
continued for several days until the Tlingit abandoned their fort and left the area. Tlingit accounts of the battle refuse to admit defeat or give the Russians credit for taking the Tlingit fort. The Russians destroyed the abandoned Tlingit fort and named the new Russian fort '' Novo-Arkhangelsk'' (New Archangel), also known as Fort Archangel Michael and Fort Saint Michael. The confrontations at Sitka in 1802 and 1804 played a significant role in subsequent Tlingit-Russian relations for generations.
Novo-Arkhangelsk soon became the primary settlement and colonial capital of Russian America. After the Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
, it was renamed Sitka, and became the first capital of Alaska Territory
The Territory of Alaska or Alaska Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from August 24, 1912, until Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959. The territory was previously Russian America, 1784–1867; the ...
.
The Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
(RAC) was incorporated in 1799, putting an end to the ''promyshlenniki'' period and beginning an era of centralized monopoly. Its charter was laid out in a 1799 ''ukase
In Imperial Russia, a ukase () or ukaz (russian: указ ) was a proclamation of the tsar, government, or a religious leader ( patriarch) that had the force of law. " Edict" and "decree" are adequate translations using the terminology and concep ...
'' by the new Tsar Paul
Paul I (russian: Па́вел I Петро́вич ; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1796 until his assassination. Officially, he was the only son of Peter III and Catherine the Great, although Catherine hinted that he was fathered by her l ...
, which granted the company monopolistic control over trade in the Aleutian Islands and the North America mainland, south to 55° north latitude (approximating the present border on coast between British Columbia and Alaska). The RAC was modeled on Britain's East India Company (EIC) and Hudson's Bay Company (HBC). Russian officials intended the company to operate both as a business enterprise and a state organization for extending imperial influence, similar to the EIC and HBC. It was also hoped that the company would be able to conduct maritime trade with China and Japan, although this goal was not realized.Circumnavigation, Empire, Modernity, Race: The Impact of Round-the-World Voyages on Russia's Imperial Consciousness, Ilya Vinkovetsky; Library of Congress In 1818 the Russian government took control of the RAC from the merchants who held the charter. The explorer and naval officer Ferdinand Petrovich von Wrangel was the first president of the company during the government period. In 1867, the
Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
transferred control of Alaska to the United States and the commercial interests of the Russian American Company were sold to Hutchinson, Kohl & Company of San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
, who then merged with several other groups to form the Alaska Commercial Company.
The Russian population in America never surpassed 1,000—the peak was 823 in 1839. However, the RAC employed and fed thousands of natives. According to official census counts by the Russians, the population of Russian America peaked at 10,313 in 1838. An additional 12,500 people were known local residents not included in the colonial register. An estimated 17,000 more local residents were present but unknown to the Russians. Thus, the total population of Russian America was approximately 40,000.
Diversification and transformation
Russian-American Company
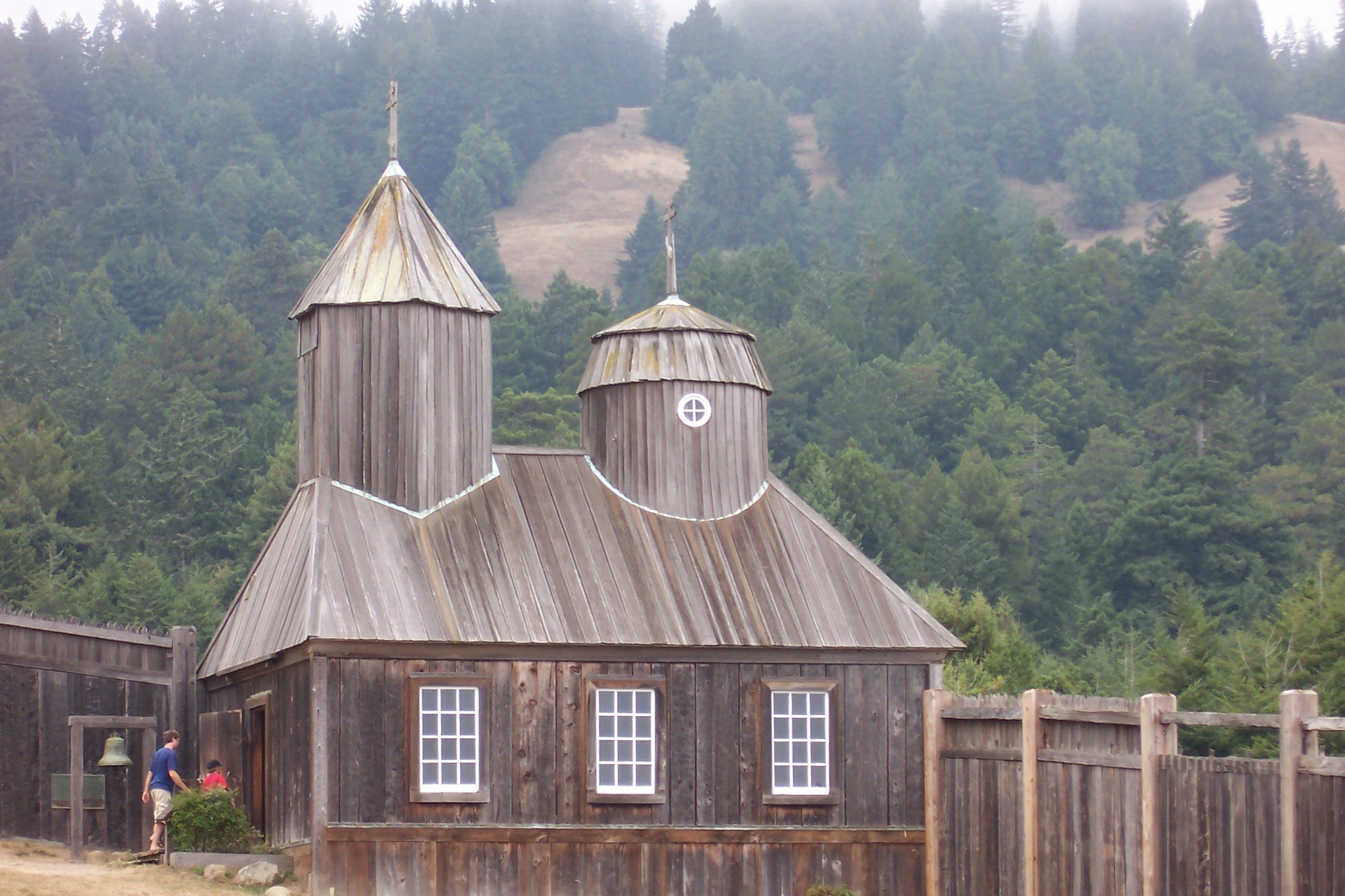
 Colony Ross, known as
Colony Ross, known as Fort Ross
Fort Ross ( Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America i ...
today, was built in California just north of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
. It was the RAC's southernmost outpost and operated from 1812 to 1841, and was established as an agricultural base for supplying the northern settlements with food as well as for conducting trade with Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
. The Ross Colony included a number of settlements spread out over an area stretching from Point Arena
Point Arena, formerly known as Punta Arena (Spanish language, Spanish for "Sandy Point") is a small coastal city in Mendocino County, California, Mendocino County, California, United States. Point Arena is located west of Hopland, California, H ...
to Tomales Bay
Tomales Bay is a long, narrow inlet of the Pacific Ocean in Marin County in northern California in the United States. It is approximately long and averages nearly wide, effectively separating the Point Reyes Peninsula from the mainland of Mar ...
. The administrative center was Port Rumianstev at Bodega Harbor
Bodega Harbor is a small, shallow, natural harbor on the Pacific coast of northern California in the United States, approximately northwest of San Francisco. The harbor is approximately in area.
The harbor is in Sonoma County at , on the eastern ...
, off Bodega Bay
Bodega Bay ( es, Bahía Bodega) is a shallow, rocky inlet of the Pacific Ocean on the coast of northern California in the United States. It is approximately across and is located approximately northwest of San Francisco and west of Santa Ros ...
. An ''artel
An artel (russian: арте́ль) was any of several types of cooperative associations and (later) corporate enterprises in the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the Soviet Union. They began centuries ago but were especially prevalent ...
'' hunting camp was located on the Farallon Islands. Three ranches were established: the Kostromitinov Ranch on the Russian River near the mouth of Willow Creek, the Khlebnikov Ranch in the Salmon Creek valley about a mile (1.6 km) north of the present day Bodega, and the Chernykh Ranch near present-day Graton. Fort Ross employed native Alaskans to hunt seals and sea otters on the California coast. By 1840, California's sea otter population had been severely depleted.
The Russian Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Alexander I issued the Ukase of 1821
The Ukase of 1821 (russian: Указ 1821 года) was a Russian proclamation (a ''ukase'') of territorial sovereignty over northwestern North America, roughly present-day Alaska and most of the Pacific Northwest. The ''ukase'' was declared on Se ...
which announced Russian hegemony over the Northwest Coast from 45°50′ north latitude onwards in a northern direction. The only Russian attempt to enforce the ''ukase'' of 1821 was the seizure of the US brig ''Pearl'' by the Russian sloop ''Apollon'', in 1822. The ''Pearl'', a maritime fur trading vessel, was sailing from Boston to Sitka. On a protest from the US government, the vessel was released and compensation paid. Britain and the United States protested and negotiations ultimately resulted in the Russo-American Treaty of 1824
The Russo-American Treaty of 1824 (also known as the Convention of 1824) was signed in St. Petersburg between representatives of Russia and the United States on April 17, 1824, ratified by both nations on January 11, 1825 and went into effect on J ...
and the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825. These treaties established 54°40′ as the southern boundary of exclusively Russian territory. The Anglo-Russian treaty delineated the boundary of Russian America fully. The border began on the coast at 54°40′, then ran north along the mountains near the coast until it reached 141° west longitude, after which the boundary ran north along that line of longitude to the Arctic Ocean. Aside from boundary adjustments to the Alaska Panhandle, stemming from the Alaska boundary dispute
The Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, which then controlled Canada's foreign relations. It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had existed ...
of the late 19th century, this is the current boundary of the state of Alaska. In 1839 the RAC-HBC Agreement was signed, giving the Hudson's Bay Company a lease of the southeastern sector of what is now the Alaska Panhandle, as far north as 56° 30' north latitude.
American methods and strategies
American traders developed the "Golden Round" trade route around the world. Ships sailed from Boston to the Pacific viaCape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramírez ...
, then to the North West Coast, arriving in the spring or early summer. They would spend the summer and early autumn fur trading on the coast, mainly between Sitka and the Columbia River. In late autumn they sailed to the Hawaiian Islands, where they typically spent the winter, then from Hawaii to Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a pop ...
on the Pearl River Delta
The Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region (PRD; ; pt, Delta do Rio das Pérolas (DRP)) is the low-lying area surrounding the Pearl River estuary, where the Pearl River flows into the South China Sea. Referred to as the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Mac ...
, arriving in autumn. Trading in Canton did not begin until November, when tea shipments were ready. The Americans had to hire pilots to take their ships up the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
to Canton's "out port" of Whampoa. Foreign ships were not allowed in Canton itself. Trading took weeks or months, after which the ships were loaded with Chinese goods such as teas, silks, porcelains, sugar, cassia, and curios. They left in the winter and used the northeasterly monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds of the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
to reach the Sunda Strait, then used the southeasterly trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
s to cross the Indian Ocean to the Cape of Good Hope. From there the ships sailed to Boston, where they traditionally docked at the India Wharf
India Wharf (1804-c. 1962) in Boston, Massachusetts, flourished in the 19th century, when it was one of the largest commercial wharves in the port. The structure began in 1804 to accommodate international trade at a time when several other improve ...
.Gibson (1992), pp. viii, 39–56 Frederic William Howay
Frederic William Howay (November 25, 1867 – October 4, 1943), also spelled Frederick, was a Canadian historian, lawyer, and jurist.
Biography
Born in London, Ontario, London, Ontario, Howay moved to British Columbia as a child. After atten ...
described this as the "golden round", writing: ''The Americans had a perfect golden round of profits: first, the profit on the original cargo of trading goods when exchanged for furs; second, the profit when the furs were transmuted into Chinese goods; and, third, the profit on those goods when they reached America.'' In the later years of the North West Trade the pattern became more complex as additional markets and side voyages were incorporated.
 As the North West trade developed it became riskier to depend solely upon acquiring sea otter furs through trade with the indigenous people of the coast. Diversification began in the first decade of the 19th century if not earlier, and increased over time. Maritime fur trading voyages were no longer solely about taking sea otter furs from the North West Coast to Canton. Other commodities and markets throughout the Pacific were added to the system.
As the North West trade developed it became riskier to depend solely upon acquiring sea otter furs through trade with the indigenous people of the coast. Diversification began in the first decade of the 19th century if not earlier, and increased over time. Maritime fur trading voyages were no longer solely about taking sea otter furs from the North West Coast to Canton. Other commodities and markets throughout the Pacific were added to the system. Sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus ''Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for us ...
, mainly from Hawaii, became an important item of the China trade. Just as the sea otter trade was waning the sandalwood trade boomed, peaking in 1821, then declined. Hawaiian sandalwood was depleted by 1830.Gibson (1992), pp. 251–267 Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
and the Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
were the other principal sources of sandalwood. Most had been cut by 1820. Fiji was also a source of bêche-de-mer, a gourmet delicacy in China. American traders began acquiring Fijian bêche-de-mer in 1804 and trepanging
Trepanging is the act of collection or harvesting of sea cucumbers, known in Indonesian as ''trepang'', Malay těripang, and used as food.
The collector, or fisher, of ''trepang'' is a trepanger.
Trepanging is comparable to clamming, crabbing ...
boomed there. Bêche-de-mer became Fiji's leading export by 1830. Depletion led to a decline and the end of the trade by 1850. Trepanging was also done from 1812 in Hawaii and from 1814 in the Marquesas. Other side trades included Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
an copper from Valparaíso
Valparaíso (; ) is a major city, seaport, naval base, and educational centre in the commune of Valparaíso, Chile. "Greater Valparaíso" is the second largest metropolitan area in the country. Valparaíso is located about northwest of Santiago ...
, scrimshaw
Scrimshaw is scrollwork, engravings, and carvings done in bone or ivory. Typically it refers to the artwork created by whalers, engraved on the byproducts of whales, such as bones or cartilage. It is most commonly made out of the bones and teeth ...
(whale teeth), tortoise
Tortoises () are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin: ''tortoise''). Like other turtles, tortoises have a turtle shell, shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, ...
shells and meat from the Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands (Spanish: , , ) are an archipelago of volcanic islands. They are distributed on each side of the equator in the Pacific Ocean, surrounding the centre of the Western Hemisphere, and are part of the Republic of Ecuador ...
, sugar from Manila, and, from Java, areca nuts (so-called betel nuts) and coffee beans. Seal hunting, Sealing boomed in the Juan Fernández Islands and the Juan Fernández fur seal was rapidly exploited to near-extinction. The northern fur seal Rookery, rookeries were controlled by Russia, so Americans acquired northern fur seal skins through trade rather than sealing.
Another side trade was smuggling along the Pacific coast of the Spanish Empire, where foreign trade was prohibited by Spanish law. This trade peaked in the 1810s, then faded in the 1820s. Traders concentrated on Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
, which produced a surplus of grain, beef, tallow, and hide (skin), hides, but was chronically short of manufactured goods. American ships brought goods to the Spanish missions in California, missions of Alta California in exchange for grain, beef, and Californian sea otter skins. The grain, beef, and other provisions were taken to Sitka, which was perennially short of foods supplies. After Mexico gained independence in 1821 the American trade with Alta California continued in a slightly modified form. American traders brought mostly clothing, cottons, silks, lace, cutlery, alcohol, and sugar, which were traded for hides and tallow at a profit generally between 200% and 300%. The California Hide Trade became a major industry in its own right. By the 1830s, however, the missions of Alta California had been Mexican secularization act of 1833, secularized by Mexican authorities and deserted by Indian labourers. The trade slid into unprofitability. The decline of the American trade with Alta California left just one significant alternative to the ever-dwindling sea otter trade—the provisioning of the settlements of Russian America, which lasted until the Americans abandoned the North West Coast altogether in the early 1840s. From the first decade of the 19th century until 1841 American ships visited Sitka regularly, trading provisions, textiles, and liquor for fur seal skins, timber, and fish. This trade was usually highly profitable for the Americans and the Russian settlements depended on it. Thus when Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, Nicholas I issued the ''ukase'' of 1821, banning foreign trade north of the 51st parallel north, 51st parallel, the Russian colonies in America were forced to ignore the ban and engage in smuggling.
On the Northwest Coast itself the fur trade was supplemented with slave trade, slave trading. The pre-existing Slavery among Native Americans in the United States, indigenous slave trade was enlarged and expanded upon by fur traders, especially the American traders. While working the coast for furs, traders would purchase slaves around the mouth of the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
and in the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, then sell or trade them on the northern coast. Few traders admitted to slaving, although some wrote about it in detail. Further information comes from sources such as reports by HBC officers. Aemelius Simpson of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
wrote in 1828 that American traders on coast trafficked in slaves, "purchasing them at a cheap rate from one tribe and disposing of them to others at a very high profit." He concluded that the American traders made more money from selling slaves, rum, and gunpowder than they did from fur trading.
The Chinese sought this mammal's fur due to its great commercial value and its 'prime coat' all year long. The pelt was used by the wealthy Chinese as clothing decoration (robe trimming) and the Russians used it as an ornamental piece. The other furs that were sent to Europe and America were changed to 'coat collars or hats'.Web- Alaska History and Cultural Studies Due to this great demand and worth of the sea otters pelt, the Russian-America Company (RAC) annual expenses was around 1000,000 rubles each year and profited over 500,000 rubles per year. The fur of the Californian southern sea otter, ''E. l. nereis'', was less highly prized and thus less profitable. After the northern sea otter was hunted to local extinction, maritime fur traders shifted to California until the southern sea otter was likewise nearly extinct.Fur trade, Northwest Power & Conservation Council The British and American maritime fur traders took their furs to the Chinese port of Guangzhou (Canton), where they worked within the established Canton system. Furs from Russian America were mostly sold to China via the Mongolian trading town of Kyakhta, which had been opened to Russian trade by the 1727 Treaty of Kyakhta (1727), Treaty of Kyakhta.
Decline
Large-scale economic issues played a role in the decline of the maritime fur trade and the China trade in general. Before the 19th century, Chinese demand for Western raw materials or manufactured goods was small, but Precious metal#Bullion, bullion (also known as specie) was accepted, resulting in a general drain of precious metals from Western world, the West to China. The situation reversed in the early 19th century for a variety of reasons. Western demand for Chinese goods declined relative to new options (for example, coffee from the West Indies began to replace tea in the United States), while Chinese demand for Western items increased, such as for English manufactures, American cotton goods, and opium which was outlawed but smuggled into China on a large and increasing scale. Before long, China was being drained of specie and saturated with Western goods. At the same time, intense speculation in the China trade by American and British merchant companies began. By the 1820s, too many firms were competing for an overstocked market, resulting in bankruptcies and consolidation. The inevitable commercial crisis struck in 1826–27, after the Panic of 1825. Tea prices plummeted and the China trade's volume collapsed by about a third. By this time, the old maritime fur trade on the Northwest Coast and the Old China Trade itself were dying. The final blow came with the depression of 1841–43, following the Panic of 1837. Over time, the maritime fur traders concentrated on different parts of the North West Coast. In the 1790s, the west coast of Vancouver Island, especially Nootka Sound, was frequently visited. By the 1810s, the locus had shifted to the Queen Charlotte Islands and Alexander Archipelago, and in the 1820s, farther north to areas nearSitka Sound
Sitka Sound is a body of water near the city of Sitka, Alaska. It is bordered by Baranof Island to the south and the northeast, by Kruzof Island to the northwest and by the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. During the early 19th century it was a ...
. After about 1830, it shifted south to the area from Dixon Entrance
The Dixon Entrance (french: Entrée Dixon) is a strait about long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part o ...
to Queen Charlotte Sound (Canada), Queen Charlotte Sound. During the early years, ships tended to cruise the coast, seeking trading opportunities whenever they arose. Later, ships spent more time in specific harbors. As fur resources dwindled and prices rose, ship captains increasingly concentrated on a few key ports of call and stayed longer. Eventually, acquiring enough furs for the China trade in a single year was no longer possible. Some traders wintered in Hawaii, returning to the coast in the spring, but many wintered on the North West Coast, usually in one of the key trading harbors. These harbors included "Clemencitty" on Tongass Island, today called Port Tongass; the several "Kaigani (trading site), Kaigani" harbors on south Dall Island north of Cape Muzon, including American Bay and Datzkoo Harbor (known as Taddiskey or Tattasco); "Nahwitti (trading site), Nahwitti" or "Newhitty" on northern Vancouver Island; and "Tongass" in Clarence Strait, today called Tamgas Harbor, which was said to be the most popular wintering place for American ships in the 1830s. Many significant trading sites were on the Queen Charlotte Islands, including Cloak Bay, Masset, British Columbia, Masset, Skidegate, Cumshewa, British Columbia, Cumshewa, Skedans, and Houston Stewart Channel, known as "Coyah's Harbor", after Chief Koyah.
As marine furs became depleted in the early 19th century, American ship captains began to accept increasing numbers of land furs such as beaver, which were brought from the interior to the coast via indigenous trade networks from New Caledonia—today the Omineca Country, Omineca and Nechako Country, Nechako districts of the British Columbia Interior, Central Interior of British Columbia. During the 1820s, the British Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), which considered the interior fur trade to be its domain, began to experience significant losses as a result of this diversion of furs to the coast. To protect its interests, the HBC entered the coast trade to drive away the American traders. This goal was achieved during the 1830s. By 1841, the American traders had abandoned the North West Coast. For a time, the North West Coast trade was controlled by the HBC and the RAC. Following the 1846 resolution of the Oregon Territory controversy between the United States and England, and the American purchase of Alaska in 1867, American hunters returned to hunting sea otters in the region, both from land and sea. Hunting throughout the Aleutian and Kuril Islands by American commercial outfits also contributed to the near-extinction of the species by the late 1800s.
Hudson's Bay Company
From 1779 to 1821 two British fur trading companies, the Montreal-based North West Company (NWC) and the London-based Hudson's Bay Company, competed for control of the fur trade of what later became Western Canada.The Hudson's Bay Company, Fort Vancouver: Cultural Landscape Report, Instrodution, Volume 2. National Park Service The struggle, which eventually reached the point of armed battles such as the 1816 Battle of Seven Oaks (1816), Battle of Seven Oaks, was mostly over control of Rupert's Land, east of the Continental Divide. Around the turn of the 19th century the NWC expanded its operations westward, across the Rocky Mountains into the mostly unexplored Pacific Northwest. By the 1810s the NWC had established new fur trading operations west of the Rockies, in New Caledonia (Canada), New Caledonia and the Columbia District. Starting in 1811 the American Pacific Fur Company (PFC) challenged the NWC in the Pacific Northwest, but during the War of 1812 the PFC, at risk of being captured by the British Navy, sold its entire operation to the NWC. The PFC had built Fort Astoria at the mouth of the Columbia River. Under the NWC it was renamed Fort George, and became the Columbia District's Pacific seaport. The NWC sought to establish a profitable beaver fur trade with China. Due to the East India Company's (EIC) control over British trading in Canton the NWC turned to American shipping companies. Starting in 1792 the NWC had beaver furs shipped to China by American firms. After the acquisition of Fort George (Astoria) in 1815 the NWC began to supply the Columbia District by sea through the Boston-based firm of Perkins and Company. After arriving at Fort George the American ship took a cargo of NWC beaver furs to Canton, exchanged them for China goods and conveyed them to Boston for sale. Even though Perkins and Company took 25% of the proceeds the arrangement was still about 50% more profitable than using British ships and selling furs in Canton through the EIC for Promissory note, bills payable on London and returning from China with no cargo. In 1821, after tensions between the NWC and HBC had erupted into violence the NWC was forced to merge into the HBC. As a result, the HBC acquired the Columbia District and its trade with China. At first the system of shipping furs via the American Perkins and Company was continued, but in 1822 the United States Customs Service imposed a heavy ''Ad valorem tax, ad valorem'' duty on the proceeds. The HBC stopped using American middlemen and instead tried selling furs through the EIC. In 1824 and 1825 the HBC sold 20,000 beaver and 7,000 land-otter skins in China through the EIC, but the arrangement did not prove advantageous for either firm. In the wake of the NWC's forced merger into the HBC, George Simpson reorganized operations in New Caledonia and the Columbia District, Columbia Department. His efforts and keen fiscal sense, combined with a resurgence of American traders on the coast after the
Russo-American Treaty of 1824
The Russo-American Treaty of 1824 (also known as the Convention of 1824) was signed in St. Petersburg between representatives of Russia and the United States on April 17, 1824, ratified by both nations on January 11, 1825 and went into effect on J ...
, resulted in the HBC's decision to enter the coast maritime fur trade and drive out the Americans. By the early 1820s American traders were taking 3,000 to 5,000 beaver skins, mostly from New Caledonia, to Canton every year. By the early 1830s the number had reached 10,000 annually, which was as many as the HBC itself was acquiring from New Caledonia and half of the total output of the entire Columbia Department. In addition, the Americans were paying higher prices for the furs, which forced the HBC to do the same. The HBC effort to gain control of the coastal fur trade began in the late 1820s. It took some time for the HBC to acquire the necessary ships, skilled seamen, trade goods, and intelligence about the coast trade. Simpson decided that the "London ships", which brought goods to Fort Vancouver and returned to England with furs, should arrive early enough to make a coasting voyage before departing. The first London ship to do this was the schooner ''Cadboro (schooner), Cadboro'', in 1827. However, its voyage did not get beyond the Strait of Georgia and only 2 sea otter and 28 land otter and beaver skins were acquired. In 1828 the HBC decided to deploy three ships for the coast trade, but setbacks caused delays. The ''William and Ann'' was lost in 1829, and the ''Isabella'' in 1830, both at the Columbia Bar. The HBC's shipping was inadequate for the coast trade until the middle 1830s.Gibson (1992), pp. 67–68 In 1835 two ships were added to the HBC's coast fleet. One of them, the ''Beaver (steamship), Beaver'', was a steamship, and it proved extremely useful in the variable winds, strong currents, and long narrow inlets.Gibson (1992), pp. 64–83
 To strengthen its coast trade the Hudson's Bay Company built a series of fortified trading posts, the first of which was Fort Langley National Historic Site, Fort Langley, established in 1827 on the Fraser River about from the river's mouth. The next was Fort Simpson (Columbia Department), Fort Simpson, founded in 1831 at the mouth of the Nass River, and moved in 1834 several miles to the present Lax Kw'alaams, British Columbia, Port Simpson. In 1833 Fort McLoughlin was established on an island in Milbanke Sound and Fort Nisqually was built at the southern end of Puget Sound. An overland trail linked Fort Nisqually and Fort Vancouver, so HBC vessels trading along the northern coast could unload furs and take on trade goods without having to navigate the Columbia River and its hazardous bar. Later coastal posts included Fort Stikine (1840), Fort Durham (1840), and Fort Victoria (British Columbia), Fort Victoria (1843).
To strengthen its coast trade the Hudson's Bay Company built a series of fortified trading posts, the first of which was Fort Langley National Historic Site, Fort Langley, established in 1827 on the Fraser River about from the river's mouth. The next was Fort Simpson (Columbia Department), Fort Simpson, founded in 1831 at the mouth of the Nass River, and moved in 1834 several miles to the present Lax Kw'alaams, British Columbia, Port Simpson. In 1833 Fort McLoughlin was established on an island in Milbanke Sound and Fort Nisqually was built at the southern end of Puget Sound. An overland trail linked Fort Nisqually and Fort Vancouver, so HBC vessels trading along the northern coast could unload furs and take on trade goods without having to navigate the Columbia River and its hazardous bar. Later coastal posts included Fort Stikine (1840), Fort Durham (1840), and Fort Victoria (British Columbia), Fort Victoria (1843).
American disadvantage
It was not easy for the HBC to drive the Americans away from the North West Coast. The Americans had decades of experience and knew the coast's complex physical and human geography. It took until 1835 for the HBC to gain this level of experience, but the Americans still had several advantages. For a number of reasons they were willing and able to pay high prices for furs—much higher than the HBC could match without taking large financial losses. The American ventures were global in scope. They tapped multiple markets of which the North West Coast was but one. By the 1820s American ships routinely spent years in the Pacific, making several voyages between various places such as California, Hawaii, the Philippines, and Canton. American ships were usually stocked with a surplus of trade goods intended for trade on the North West Coast. It was always best to get rid of any extra trade goods on the North West Coast, "dumping" them at any price, before leaving. They would use up stowage space that could be used more profitably elsewhere. The HBC therefore faced a major challenge even after they became experienced with the coast's geography and indigenous peoples. The American system not only raised the price of furs but also lowered the value of trade goods. Furthermore, the indigenous people knew that increased competition served their interests and gave them bargaining power. They had no desire to see the Americans abandon the coast trade. Therefore, the HBC had to not just match but exceed the prices paid by Americans if they hoped to drive the Americans away. Beaver fur prices on the coast could be many times what the HBC was paying in the interior. There was no hope of making a profit. In order to compete on the coast the HBC had to take large, long-term financial losses. The main advantage the HBC had over the Americans was that it could take such losses. As a vast corporation with a large amount of capital, the company was able to undersell the Americans, taking a loss, for years on end. By the middle to late 1830s the HBC policy on the coast was to pay whatever price necessary to ensure that furs fell into their hands and not the Americans. American traders soon found the coast fur trade unprofitable—the HBC had captured the trade. But Americans still traded with the Russians at Sitka and, once on the coast were wont to seek a few furs. As long as this continued, the HBC continued to have to pay high prices for furs and take losses. Eventually the Sitka trade became financially risky. The American-Russian agreement of 1824, which allowed Americans to trade in the Alaska Panhandle, expired in 1834 and was not renewed. In 1839 the HBC made an agreement with the Russian American Company (RAC), under which the HBC would supply the RAC with provisions and manufactures in exchange for a ten-year lease for portions of the Alaska Panhandle. This proved to be the final blow for the American traders, who were finally driven out of the North West Coast maritime fur trade altogether. The HBC drastically reduced the price paid for furs, by 50% in many cases. By this time, however, the fur trade was in decline, both on the coast and the continent, due to a general depletion of fur-bearing animals, along with a reduction in the demand for beaver pelts. A financial panic in 1837 resulted in a general slump in the fur and China trade, bringing an end to a half-century boom. During the 1840s, the HBC closed most of their coastal trading posts, leaving the coast trade to just Fort Simpson and the ''Beaver'', with the new depot at Fort Victoria anchoring the southern coast.Significance
The half century or so of the maritime fur trade and the North West Coast trade enriched Boston shipowners, creating capital that helped New England's transformation from an agrarian to an industrial society. The trade stimulated the culture of North West Coast natives, made Hawaii famous and nearly overwhelmed the native Hawaiians with foreign influences. It played a role in increased commercial pressure on China at Canton. Fur bearing animals were devastated, especially sea otters. By 1850, sea otters were virtually extinct throughout the North West Coast and found only in the Aleutian Islands and California.Northwest Coast
 The maritime fur trade brought the natives of the Northwest Coast material prosperity, wealth, and technology. It enlarged and transformed intertribal relations, trade, and war, including the "coastalization" of inland natives. Many inland natives adopted potlatching and coastal descent systems.Gibson (1992), pp. 269–277 At first the trade caused a rise in the power of a few key chiefs such as
The maritime fur trade brought the natives of the Northwest Coast material prosperity, wealth, and technology. It enlarged and transformed intertribal relations, trade, and war, including the "coastalization" of inland natives. Many inland natives adopted potlatching and coastal descent systems.Gibson (1992), pp. 269–277 At first the trade caused a rise in the power of a few key chiefs such as Maquinna
Maquinna (also transliterated Muquinna, Macuina, Maquilla) was the chief of the Nuu-chah-nulth people of Nootka Sound, during the heyday of the maritime fur trade in the 1780s and 1790s on the Pacific Northwest Coast. The name means "possessor of ...
, Wickaninish, Tatoosh, Concomly (Madsaw), Kotlean (Sitka Tlingit), Kow (Kaigani Haidas), Cuneah (Coyac; Kiusta Haida), Legaic (Tsimshian), Woyala (Heiltsuk), and Cumshewa (Haida). This was followed by a proliferation of chiefs and a general debasement of chieftainship, in part due to widespread wealth, giving individual hunters the means to challenge the traditional chiefs. There was an increase in the frequency of potlatching, which was used by the ''nouveau riche'' in challenging the traditional chiefs. In response the hereditary clan chiefs defended their traditional powers through an increased use of noble ancestry names, totems, and crests, all validated by potlatches.
The increase in trade, and new items had a significant impact on First Nations material cultures, seeing the rise of such traditions as fabric appliqué (Button Blankets), metalwork (Northwest Coast engraved silver jewelry originated around this time as native craftsmen learned to make jewelry from coins), and contributed to a cultural fluorescence with the advent of improved (iron) tools that saw the creative of more and larger carvings (a.k.a. 'totem poles'). New pigments available included vermilion, from China, that rapidly replaced earlier red pigments and can be seen on many artifacts from this era.
Negative effects of the coast trade on the native peoples of the Northwest included waves of epidemic disease, smallpox worst of all. Other health problems included the spread of alcoholism, tuberculosis, venereal diseases including syphilis, and sterility. The coast trade also promoted and enhanced the pre-existing system of native slavery and native slave trading. The overall number of slaves increased, as did their distribution and exploitation. Despite these negative effects, the North West Coast natives were largely spared the additional effects that would have come had there been more permanent posts, political administration, missionizing, and colonization. The early traders were mostly seasonal visitors and the later HBC posts were few and small. Missionization and direct colonial rule over the coastal natives did not begin in earnest until the late 19th century. During the early 19th century, native culture not only survived but flourished.
The maritime trade also brought changes to the natives' traditional seasonal migration patterns and settlement locations. The coastal people were "cosmopolitanized", that is, they were incorporated into a global market economy. At first their main export was furs, later supplemented and replaced by salmon, lumber, and artwork. By the late 19th century the North West Coast was famous for its arts and crafts, especially large works like totem poles, causing a flourishing of indigenous art. The natives imported many western goods and soon became dependent on many, such as firearms and metal tools. Textiles became a vital trade item during the early maritime fur trade era. The value of furs caused a shift in native dress from furs to textiles, which was reinforced by the general depletion of fur animals. Firearms had both positive and negative effects. They made hunting much more efficient but also made warfare much more deadly.
Russian America
The Russians, unlike the British and Americans, endeavoured to convert the natives to Christianity. Many Aleuts joined the Russian Orthodox Church. Russian Missionary, missionaries founded a number of churches for the natives, such as the Church of the Holy Ascension in Unalaska. A notable Russian missionary was Innocent of Alaska, Saint Innocent of Alaska. For his work as a missionary, bishop, and later archbishop in Alaska and the Russian Far East he was Canonization, canonized. One of the earliest Christian martyrs in North America was Saint Peter the Aleut. Other important Russian missionaries include Herman of Alaska and Joasaph Bolotov.Haycox, pp. 94–96, 144–146Hawaii
The effect of the maritime fur trade on native Hawaiians was similar to that of the North West Coast natives, but more powerfully transformative. The Hawaiians were generally receptive to Western incursion and settlement. The rise of King Kamehameha I and the unification of the islands under his rule were made possible in part by the effects of the maritime fur trade and its larger Pacific scope. The influx of wealth and technology helped make the new Kingdom of Hawaii relatively strong, in political and economic terms.Gibson (1992), pp. 278–291 Many non-native foodstuffs were introduced to the Hawaiian Islands during the early trading era, including plants such as beans, cabbage, onions, squash, pumpkins, melons, and oranges, as well as cash crops like tobacco, cotton, and sugar. Animals introduced included Hawaiian wild cattle, cattle, horses, sheep, and goats. Due to its high fertility Oahu became the most important of the islands. By the 1820s the population of Honolulu was over 10,000. The native Hawaiian population suffered waves of epidemic disease, including cholera. The availability of alcohol, especially grog and gin, led to widespread boozing and an increased use of traditional kava intoxication. These health issues, plus warfare related to the unification of the islands, droughts, and sandalwooding taking precedence over farming all contributed to an increase in famines and a general population decline. By 1850 the native population had dropped by perhaps 50%.South China
The effect of the maritime fur trade in Southern China by itself was probably not great. The Canton trade as a whole had limited effect on China, mostly limited to the tea growers of Fujian, the silk producers of Nanjing, the craftsmen of Canton, and various middlemen, and merchants. The ruling Manchus kept foreign trade by ship at bay. It was restricted to Canton, and even there was allowed only outside the city walls. China was generally self-sufficient. The main effect of the Old China Trade was an increased import of opium and related outflow of specie, which resulted in China being incorporated into the capitalist world system after 1830. However, the maritime fur trade played a minor role in this process.New England
The maritime fur trade was, for the United States, a branch of the "East India" (Asian) trade based in Salem, Massachusetts, Salem, Boston, Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, New York City (Fanning & Coles), Philadelphia, and Baltimore. The trade focused on Asian ports such as Canton, Kolkata (Calcutta), Chennai (Madras), Manila, Jakarta (Batavia), and the islands of Mauritius and Sumatra. Goods exported included furs, rum, ammunition, ginseng, lumber, ice, salt, Spanish dollar, Spanish silver dollars, iron, tobacco, opium, and tar. Goods brought back from Asia included muslins, silks, nankeens, spices, cassia, chinaware (porcelain), tea, sugar, and drugs. The maritime fur trade was just one part of the overall system. As a whole the Asian trade had a significant effect on the early United States, especiallyNew England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. The accumulation of large amounts of capital in short time contributed to American industrial and manufacturing development, which was compounded by rapid population growth and technological advancements. In New England the textile industry rose to dominance in early to middle 19th century. In light of the decline of the fur trade and a post-Napoleonic depression in commerce, capital shifted "from wharf to waterfall", that is, from shipping ventures to textile mills (which were originally located where water power was available). The textile industry in turn had large effect on slavery in the United States, increasing the demand for cotton and helping make possible the rapid expansion of the cotton plantation system across the Deep South.
See also
* California Fur Rush * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, First Nations * Fort McLoughlin * History of the west coast of North America * Maritime history of California * North American fur trade * Thirteen Factories * Awa'uq Massacre * ''Il’mena'' * ''Margaret (1791 ship)'' * ''North West America'' * ''Atahualpa (ship)'' * ''Union (sloop)''References
Books cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * Dick A. Wilson, ''King George's Men: British Ships and Sailors in the Pacific Northwest-China Trade, 1785–1821,'' Ann Arbor, Mich., University Microfilms International,2004. *External links
Contact and conflict: Indian-European relations in British Columbia, 1774–1890
by Robin Fisher; UBC Press, 1992
Fishing for Ivory Worms: A Review of Ethnographic and Historically Recorded ''Dentalium'' Source Locations
by Andrew John Barton
Russian Routes
Common-place {{Good article Fur trade Guangzhou History of foreign trade in China History of Macau History of the Pacific Northwest Hudson's Bay Company Maritime history of Canada Maritime history of the United Kingdom Maritime history of the United States Native American history of Alaska Oregon Country Pre-statehood history of Alaska Pre-statehood history of California Pre-statehood history of Hawaii Russian America